FINA 320 Module 4
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Investment criteria
Does the decision adjust for the TVM?
Does the decision rule adjust for risk?
Does the decision rule provide info on whether we are creating value for the firm (value for shareholders?)
Net Present Value (NPV)
difference between the intrinsic value of a project and its cost
Intrinsic value > cost = NPV is positive
Intrinsic value < cost = NPV is negative
reason larger intrinsic value = positive NPV is bc it generates more value for shareholders
intrinsic value
the sum of the present values of all its future cash flows
How to estimate intrinsic value
Estimate future expected cash flows
Estimate the required rate of return
Find PV of cash flows & subtract initial investment
Project net PV
intrinsic value - cost
r also stands for
opportunity cost of capitala
What the variables stand for in the NPV equation
Co = initial CF (often negative)
C1 = CF at time 1
C2 = CF at time 2
Ct = CF at time t
t = time period of investment
r = opportunity cost of capital
Always make sure Co is
negative
NPV positive
NPV is negative
accept project
reject project
positive NPV features
project expected to add value to the firm & will increase the wealth of the owners
mutually exclusive
if you take one, can’t take the other, gotta pick between 2 projects
NPV measures
ADDITIONAL value added to project not just values (its not price, that’s why its low
NPV = 0 means
project has rate of return that exactly matches discount rate/ opportunity cost of capital. required rate of return
still profitable (like breakeven)
Relative attractiveness of mutually exclusive projects
are not fixed, they are effected by discount rate
NPV decreases when discount rate increases
Cross over point
when 2 NPVs profiles are the same
Payback method
how long does it take to get the initial cost back in nominal sense?
How to calculate payback method
estimate CFs
subtract cost - future CF’s until initial investment recovered
decision rule for payback method
accept if payback period is less than some present limit
payback period
# of years it takes to recover the initial investment
For calculating payback
subtract cash flow from Co until at last amt then divide remaining amt by CF and add the number of periods completed
discounted payback period
compute the PV of each cash flow then determine how long it takes to payback on a discounted basis
compare to a specific required period
decision rule for adjusted payback period
accept the project if it pays back on discounted basis within the specified time
discount payback always longer than
regular payback period
Internal rate of return (IRR)
most important alternative to NPV - it is the return that makes NPV = 0
based entirely on estimated cash flows + independent of int rates found elsewhere
and not affected by discount rate
decision rule for IRR
accept project if IRR is greater than the require return
IRR equation
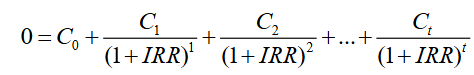
2 times when IRR is unreliable (when NPV is preferred)
non conventional cash flows - cash flow signs change more than once
Mutually exclusive projects
initial investments substantially different
timing of cash flows is substantially different
normal project
project where signs of the cash flow only change once
decision rules for IRR + mutually exclusive projects
NPV - choose the project with the higher NPV
IRR - choose the project with the higher IRR
NPV always trumps IRR in decision making
so if project a has high NPV and low IRR
and project b has low NPV and high IRR
choose project A
NPV directly measures
the increase in value to the firm
whenever there’s a conflict between NPV + another decision rule
always choose NPV
Profitability Index
NPV/ initial investment
Advantages and disadvantages of Payback
Advantages
easy to understand
adjusts for uncertainty of later cash flows
biased towards liquidity
Disadvantages
ignores TVM
may reject positive NPV investments
requires an arbitrary cut off point
biased against long term projects, such as R&D and new products
Advantages and disadvantages of discounted payback
Advantages
includes time value of money
easy to understand
adjusts for uncertainty of later cash flows
biased towards liquidity
Disadvantages
may reject positive NPV investments
requires an arbitrary cutoff point
ignores cash flows beyond the cutoff point
Biased against long term projects such as R&D and new products
IRR is the discounted rate that produces a 0 NPV or the specific discount rate at which the present value of the cost equals ___
a. the future value of the present cash flows
b. the present value of the future benefits or cash inflows
c. the present value of the cash outflow
d. the investment
b. the present value of the future benefits or cash inflows
The IRR is defined as the discount rate that produces a 0 NPV or the specific discount rate at which the present value of the cost (the investment or cash outflows) equals to present value of the future benefits (or cash inflows)
IRR and nonconventional cash flows
when the cash flows change signs more than once, there is more than 1 IRR
when you solve for IRR, you are solving for the root of an equation and when you cross the x axis more than once, there will be more than one return that solves the equation
if you have more than 1 IRR which one do you use to make your decision
Which of the statements below is false?
a. to account for the time value of money with the payback period model, you need to restate the future cash flow in current dollars
b. the discounted payback period method is the time it takes to recover the initial investment in future dollars
c. when we discount a future cash flow with our standard time value of money concepts, we inherently assume that the company received the entire cash flow at the end of the year
d. the discounted payback period method does not correct for the cash flow after the recovery of the initial outlflow
d. the discounted payback period method does not correct for the cash flow after the recovery of the initial outlflow
Normal projects C and D are mutually exclusive. Project C has a higher (positive) NPV if the cost of capital is less than 12%, whereas project D has a higher (positive) npv if the cost of capital exceeds 12% which of the following statements is most correct?
a. project D has a higher internal rate of return
b. project d and project c have a crossover rate of 12%
c. we should be indifferent between the two projects if the cost of capital is 12%
d. statements b and c are correct
e. all of the statements are correct
e. all of the statements are correct
Which of the following statements about the IRR and NPV is least accurate?
a. IRR is the discount rate that equates the pv of the cash inflows with the pv of the outflows
b. for mutually exclusive projects, if the npv rankings and the irr rankings give
incomplete
The discounted payback rule can be best stated as:
a. An investment is acceptable if its discounted payback period is greater than some
prespecified number of years.
b. An investment should be accepted if the discounted payback is positive and rejected
if it is negative.
c. An investment should be rejected if the discounted payback is positive and accepted
if it is negative.
d. An investment is acceptable if its discounted payback period is less than some
prespecified number of years
d. An investment is acceptable if its discounted payback period is less than some
prespecified number of years
Which of the following calculations ignores the impact of the time value of money?
I. Payback
II. IRR
III. Profitability index
a. I only
b. II only
c. III only
d. I and III only
a. I only
Project selection ambiguity can arise if one relies on IRR instead of NPV when:
a. The first cash flow is negative and the remaining cash flows are positive.
b. A project has more than one NPV.
c. The profitability index is greater than one.
d. Project cash flows are not conventional.
d. Project cash flows are not conventional.
A project whose NPV equals zero ____
a. does not make profits for its shareholder
b. has IRR less than its required rate of return
c. has a profitability index that is greater than one
d. has a discounted payback period that exactly matches the life of the project
d. has a discounted payback period that exactly matches the life of the project
Which of the following statements is true?
a. If a project has a profitability index less than one the project should be accepted.
b. If the cost of capital is greater than the IRR, the project should be accepted.
c. If a project has a payback which is longer than the company requires, the project
should be accepted.
d. If the NPV of a project is positive, it should be accepted
d. If the NPV of a project is positive, it should be accepted
___________ is at the heart of corporate finance because it is concerned with making the
best choices about project selection.
a. Capital budgeting
b. Capital structure
c. Payback period
d. Short-term budgeting
a. Capital budgeting
Which of the statements below is false?
a. To account for the time value of money with the payback period model, you need to
restate the future cash flow in current dollars.
b. The discounted payback period method is the time it takes to recover the initial
investment in future dollars.
c. When we discount a future cash flow with our standard time value of money
concepts, we inherently assume that the company received the entire cash flow at the
end of the year.
d. The discounted payback period method does not correct for the cash flow after the
recovery of the initial outflow
b. The discounted payback period method is the time it takes to recover the initial
investment in future dollars.
Initial after tax outlay or after tax cost also means
CF0
Annual depreciation equation
(Beginning Value - Ending Book Value) / (# of yrs)
Operating Cash Flow Equation
Revenue
- operating cost
- depreciation
= EBIT (rev-OC-dep)
*tax rate
= tax
Solve for OCF (EBIT + dep - tax)
Tax rate (for calculating operating cash flows)
Tax rate * EBIT
Operating cash flow individual mini equation
EBIT + Dep - tax
Net income equation
Sales
-variable costs
-fixed costs
-depreciation
=EBT
-taxes (tax rate *EBT)
= Net income
After tax salvage value
= salvage value - tax rate * capital gain
Capital gain = salvage - book value
EBIT other equation
Gross Profit - Depreciation
*Gross profit also called annual pretax cost savings)
changes in Net working capital are due to
increases in inventories
Beginning inventory balance
Ending inventory balance
current months sales projections * % of monthly projected sales
next months sales projection * % of monthly projected sales
increase in net working capital equation
ending inventory - beginning inventory * cost per unit