Mitochondrial Genetics
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Mitochondrial Genetics
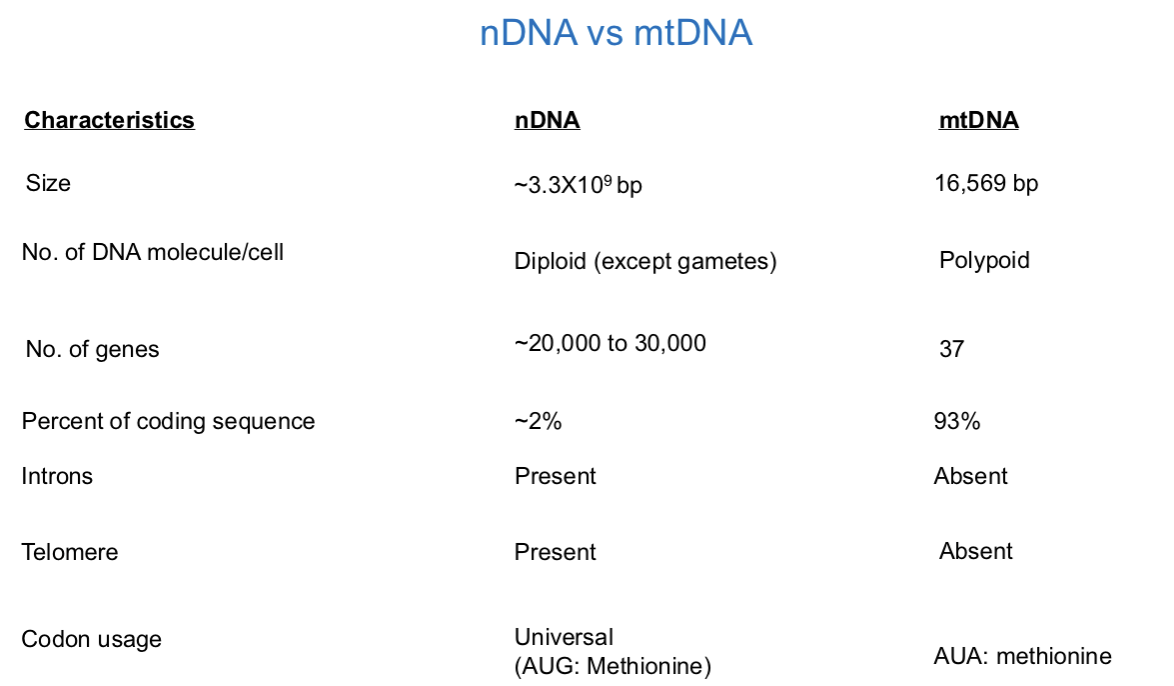
several copies of ______ DNA molecule
mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) encodes ____% of the mitochondrial proteins
all mitochondrial proteins are involved either in ______ or ______ ______
nuclear DNA (nDNA) encodes ____% of mitochondrial proteins
circular
5
ETC, oxidative phosphorylation
95
Mitochondrial Genome
circular DNA: ______ bp
two strands: ______ & ______ strand
the genome encodes ____ genes —> ____ tRNA, ____ rRNA, & ____ protein-coding genes
16,500
heavy, light
37, 22, 2, 13
Which strand is guanine/purine rich?
H-strand
H-strand D-loop region has replication origin site
______ loop (D-loop) region contains:
2 ______ ______ sites/heavy strand promoters —> ______
light strand promoter —> ______
replication origin of heavy strand —> ______
displacement
transcription initiation, HSP 1 & 2
LSP
OH
L-strand has its own replication origin site (OL)
OL is located approximately ______ kb away from OH
synthesized in the ______ direction of H-strand synthesis
11
opposite
Mitochondrial Genome Replication is ______
initiated at ____ different times from ____ different origins of replication
______ replication is initiated first
______ replication is initiated only after completion of ______ of the ______ replication
the H-strand remains ______-stranded until L-strand replication is initiated
asymmetric
2, 2
H-strand
L-strand, 2/3, H-strand
single
Mitochondria are the major source of ______
ROS are produced from the leakage of ____ to form superoxide ____ at complex I and complex III.
produced as ______ during mitochondrial electron transport
causes ______ & ______ damage
reactive oxygen species (ROS)
e-, O2-
byproducts
DNA, mitochondrial
mutation rate: ______ DNA > ______ DNA
______ proximity to ETC —> ______ chance of ROS-induced mitochondrial DNA damage
no ______ proteins
lack of DNA ______ ______
mitochondrial, nuclear
close, higher
structural
repair machinery
T or F:
Mitochondrial disorder can affect every organ in our body.
True
Mitochondrial disorder always follows ______ (maternal/paternal) inheritance.
maternal
Causes of Maternal Inheritance
______ model —> sperms have very ______ (high/low) # of mtDNA
sperm —> 100 copies. egg —> 100,000 copies.
______ ______ model —> sperm’s mtDNA is ______, either before or after fertilization
dilution, low
active degradation, degraded
Types Based of mtDNA:
______ ______ —> identical and wild-type
______ ______ —> identical but mutant
______ —> existence of wild-type and mutant mtDNA —> variability in drug response may occur due to differing levels of functional mitochondria
homoplasmic wild-type
homoplasmic mutants
heteroplasmic
Mitochondrial Threshold Effects
______ and ______ mtDNA coexist in the same cell
______ mtDNA will only cause symptoms when the # of copies exceeds a critical threshold
vary from mutation to mutation, organ to organ, and between different family members
mutated, normal
mutated
heteroplasmic mother may give birth to a normal child
mutation > threshold —> ______ ______
mutation = threshold —> ______ ______
mutation < threshold —> ______ or ______
highly symptomatic
moderately symptomatic
asymptomatic, normal
Drug-Induced Mitochondrial Toxicity
certain drugs can impair mitochondrial function (3) —>
tissues with ______ (high/low) energy demand are particularly vulnerable —> brain & muscle
antiretrovirals, statins, chemotherapy agents
high
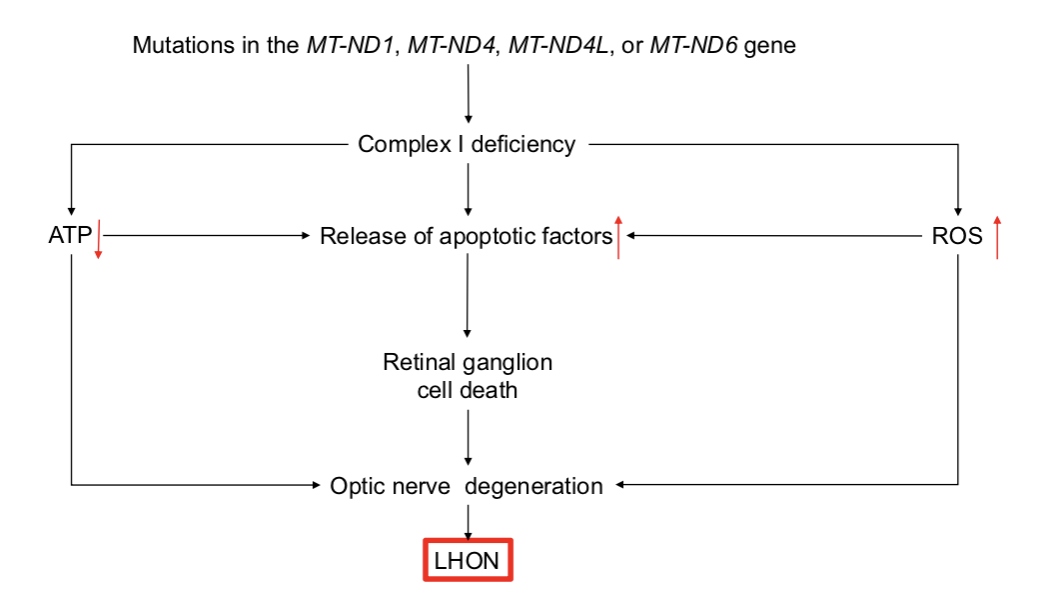
Leber Optic Hereditary Neuropathy (LOHN)
______ form of vision loss
results from the death of cells in the ______ ______ —> which transfers visual information from the ______ to the brain
______ ______ _____ (RGCs) process visual information
treatment: ______, administration of the ______ analog, ______ and _______ supplementation
inherited
optic nerve, retina
retinal ganglion cells
Raxone, quinone, vitamin B12, C
Mitochondrial genome is transcribed as long polycistronic transcripts
______ mRNA —> mRNA that encodes only one protein —> eukaryotes
______ mRNA —> mRNA that encodes several proteins —> bacteria, mitochondria
monocistronic
polycistronic