ATOMIC PHYSICS
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
s, p, d,f stands for
“sharp,” “principal,” “diffuse,” and “fundamental,”
parts of periodic table
periods(rows), blocks(columns) and groups(columns)
difference between blocks and groups
groups are linked ot valence electrons
state the quantum numbers
principal (n), angular (l), magnetic (ml) and spin (ms)
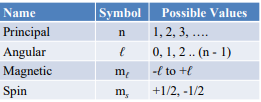
state the possible values of all 4 quantum numbers
recite/write the electron configuration
recite mo <3
what is the purpose of quantum numbers?
solving S.E. gives rise to qunatum numbers, which describe the behavior of quantum systems
when S.E. is solved using radial coordinates, it gives rise to two qunatum numbers, which are _____ and _____
principal and azimuthal/angular
when S.E. is solved using azimuthal coordinates, it gives rise tothe qunatum number
magnetic quantum number
the Pauli exclusion principle created by _________ states that _______
Wolfgang Pauli, no two electrons in the same atom can have identical values for all four of their quantum numbers
explain the zeeman effect
when an electron has a non-zero angular momentum (l), they have a magnetic dipole moment due to the electron motion. Hence these states are affected if the atom is placed in a magnetic field
who confirmed the existence of an electron spin?
(Quantum Numbers) total energy of an atom depends on?
principal qunatum number (n)
(Quantum Numbers) related to magnitude of angular momentum
orbital quantum number (l)
(Quantum Numbers) direction of elctron’s angular momentum
magnetic quantum number (ml)
(Quantum Numbers) only has tow values +1/2 or -1/2, its presence is a relativistic effect
magnetic spin (ms)
who modified schrodinger’s orig theory to contain magnetic spin?
Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac