retina revision week 3
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from year 1 content
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
layers of eye till retina
sclera(outer white coating) →choroid(middle layer) - retina(inner layer responsible for vision).
retina extend to ?
the ora errata which is most anterior point of retina - and where ciliary body begins
what is the retina in direct contact with
the vitreous
what is the vitreous
substance in anterior chamber ( appears dark on OCT scan)
what is function of retina
detects light and tells brain about aspects of light in relation to objects
where do we receive signals from in retina
Photoreceptors
what does retina do with signals
doesn’t allow it to be processed individually- packages information and sorts it- without overloading brain with repetitive or redundant facts
what is a spatial temporal change
associated with movement- due to variations in light intensity
how are colours detected
wavelength of light reflected off object and into eye
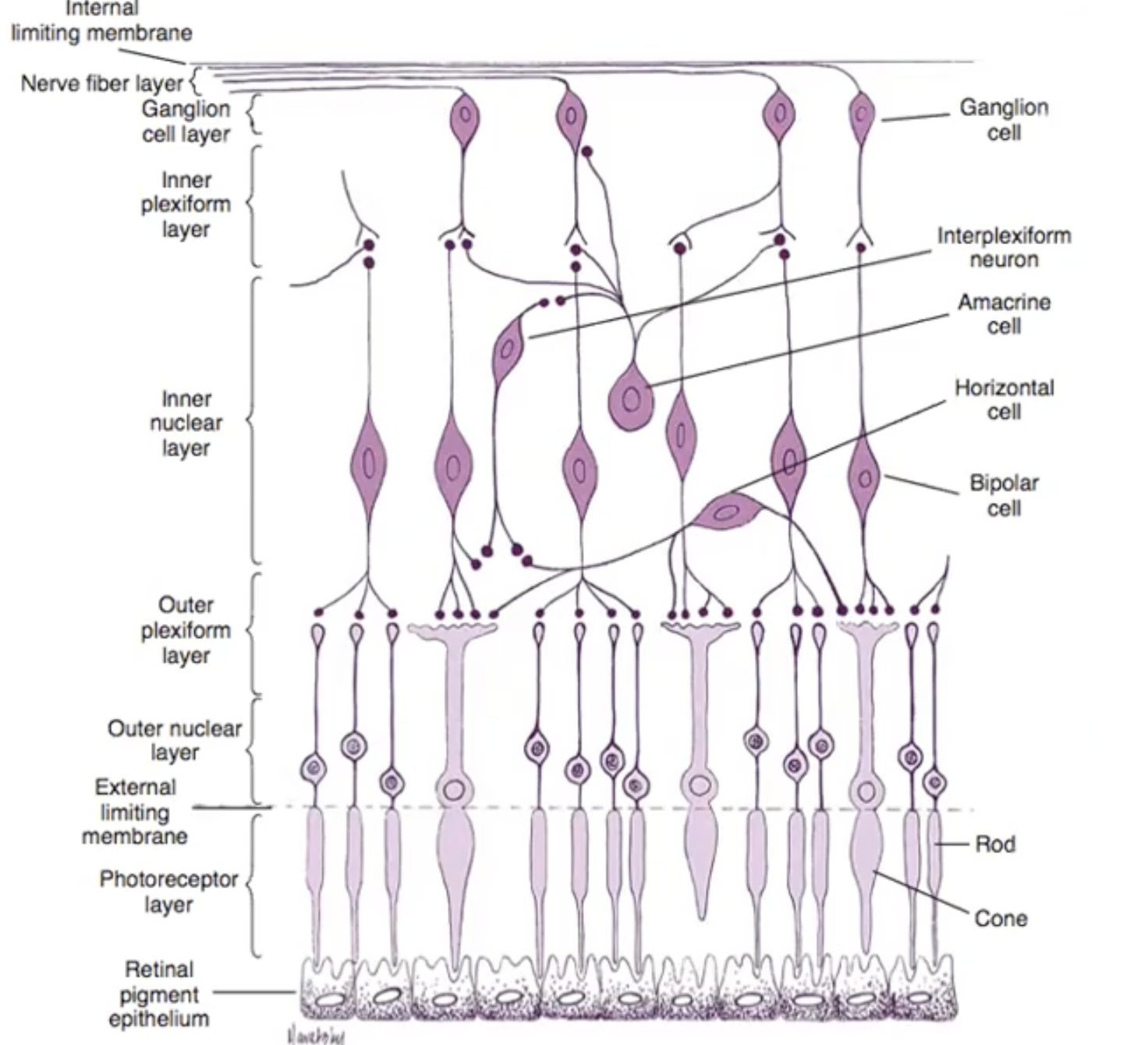
layers of retina in order
-internal limiting membrane
-nerve fibre layer
-ganglion cell layer
inner plexiform layer
-inner nuclear layer
-outer plexiform layer
-outer nuclear layer
-external limiting membrane
-photoreceptor layer
-retinal pigment layer
image of layers
Photoreceptor
rods- 95%
cones-5%
distribution of photoreceptors
centre of fovea aren’t any rods only cones (but smaller cones than in the rest of retina- so more densely packed)
no rods or cones in blind spot- where optic nerve located
away from fovea there is high number of rods - peak is just water fovea and slowly decreases as it moves away
where are they placed
at the back of the retina- placed side by side- light reaches other structures of retina first
how is fovea adapted
all cones at fovea-densely packed for highest acuity
outer layers of retina above photoreceptors not present so more light can be directly supplied to photoreceptors
cones
at centre they are long and thin- more into periphery become shorter and wider diameter
all photoreceptors have
pigment, which absorb energy from the photons oflight-
pigment lies in outer segment next to epithelium
inner segment is filled with mitochondria and merges with nucleus of cell
what happens to photopigment
when it absorbs light they decrease the rate of neuro transmitter and this is how vision occurs
channels close
when in the dark
photoreceptors are most polarised and release glutamate as ion channels are open
photo pigments
4 types
rhodopsin- rods
Erytholabe (long), Chlorolabe(medium) , Cyanolabe(short) wavelength sensitive - cones
what pigment made of
retinal and opsin ( large portion) make up all pigments - there are four
a small protein (retinal )Is the first to be affected by light absorption- this is the active part
outer segemts of photo receptors contain
series of discs - which contain pigment
how does it work
if only one pigment was used different wavelengths would get confused- but brain uses multiple pigments to understand which wavelengths used- so can detect change in intensity of light or wavelength
what happens in dark (scotopic)
rods are more sensitive can detect single photons
cones are weaker- so can’t distinguish colour as much
in photopic conditions
cones work much better
rods work too but not as well as cones
rhodopsin light activation
(11-cis-retinal + opsin) opsin protein loops in and out of membrane forms cage that encloses retinal protein
photon absorption raises energy and breaks bonds so retinal changes shape
into its activated form (all-trans-retinal + opsin)
formula of activated rhodopsin
R to R*
retinal becomes retinol (bleaching of rhodopsin) -removal of opsin from retinal
to regenerate enzymes required for to retinol to become retinal
cycle of photopigment
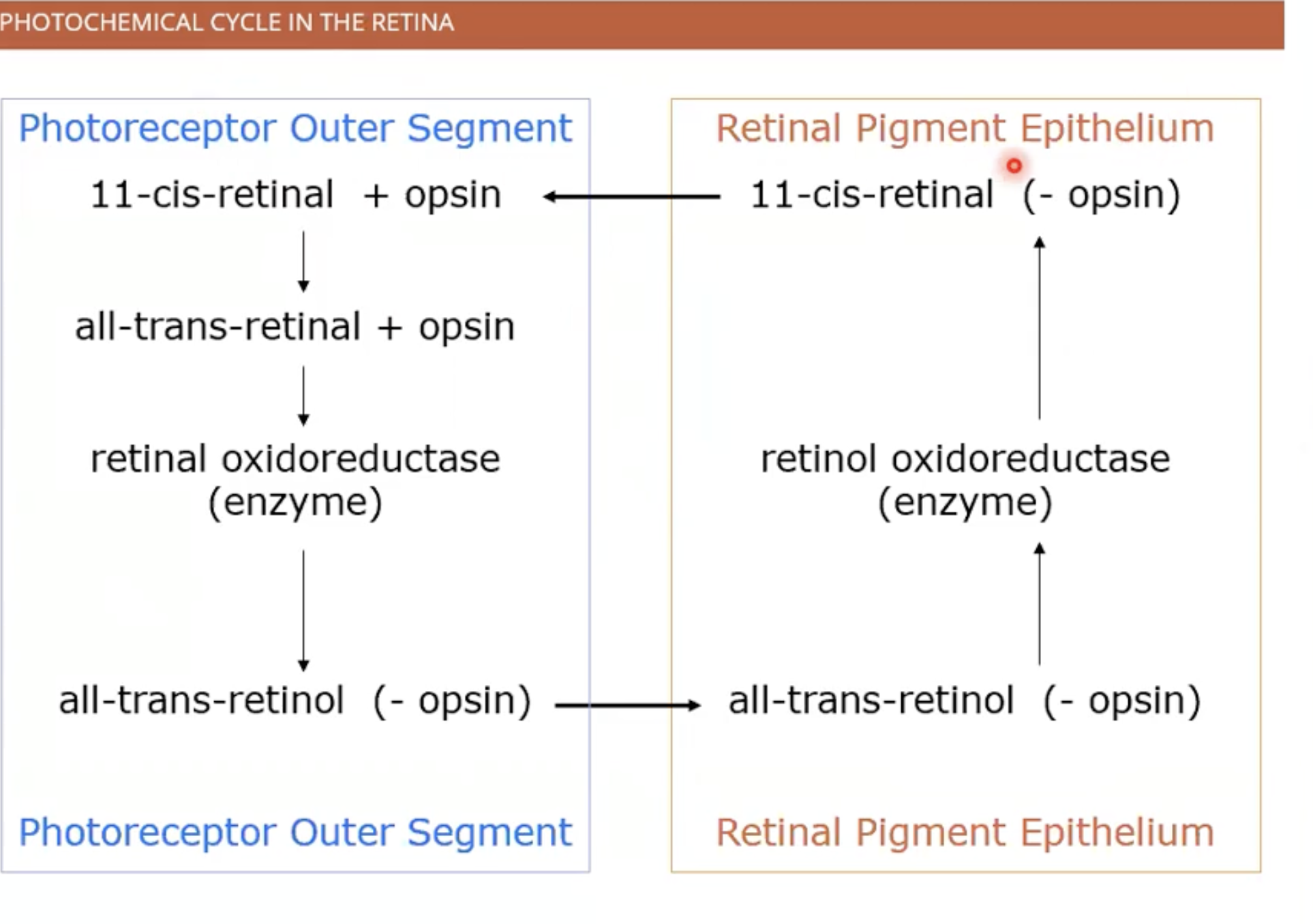
renewal of photoreceptors
regeneration continuous cycle ( most neurons don’t degenerate ) - 2 week process
-amino acids from outside cell make new proteins
diffuse through cell inner segments and photopigments
join as a band
band moves up to outer segment
leaves photo receptor for the pigment epithelial cells (engulfed)
new discs formed and old discs got ride of
retina vertical communication pathway
dendritic end- receives from synaptic connection with photoreceptors
cell body
then axons and terminal end - which communicates with retinal ganglion cell
dendrites of retinal ganglion cell communicate with bipolar cells
essentially (photoreceptors - bipolar cells- retinal ganglion cells)
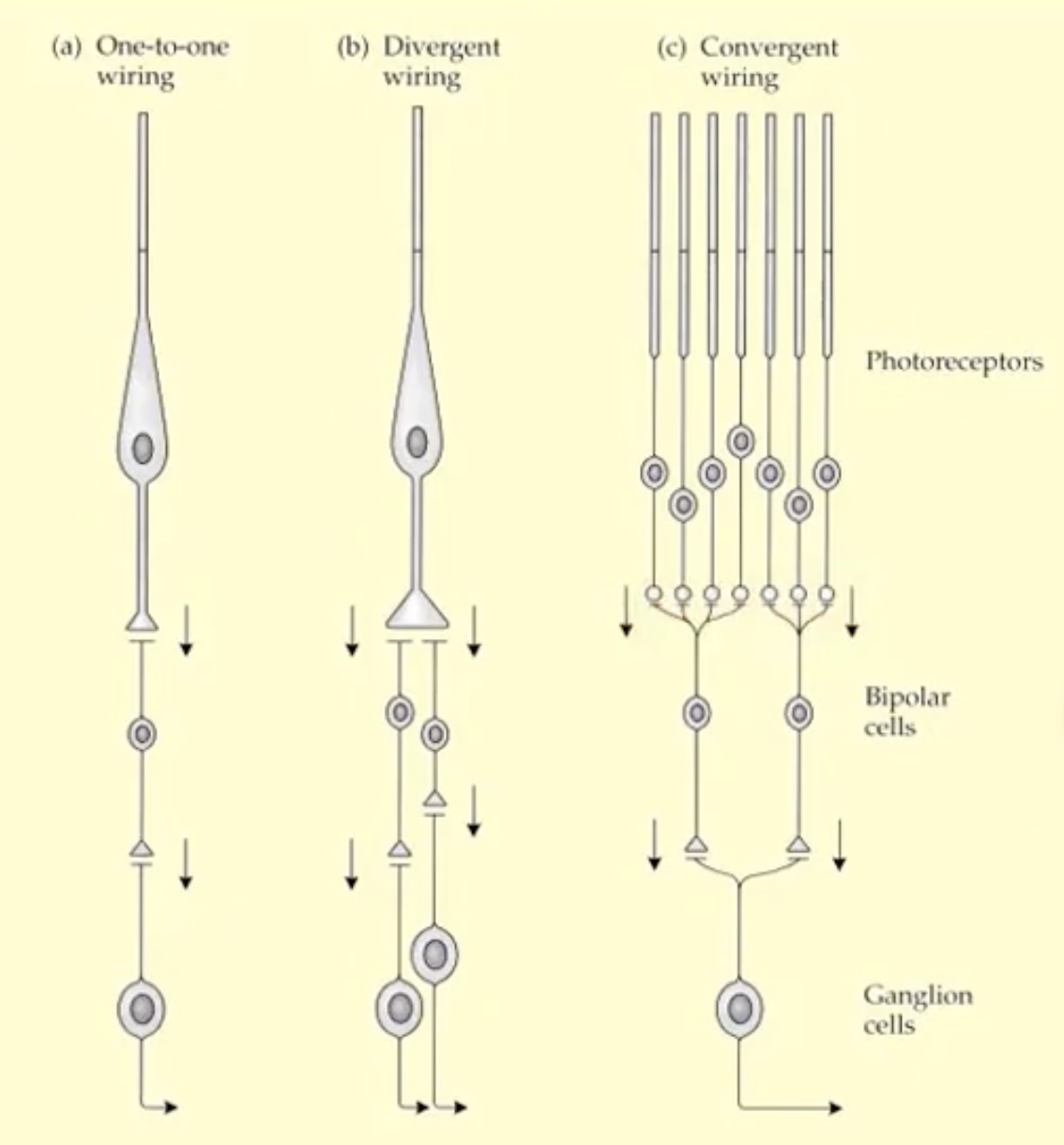
how does the communication work
can be individual so one photoreceptor to one bipolar to one ganglion ( provides finest spatial detail- mainly at fovea)
can be one photoreceptor to more than one bipolar cell and more than one ganglion (divergent wiring)
can be multiple photoreceptors to less bipolar to one ganglion (convergent wiring ) - good for small amounts of light , poor in good light conditions)
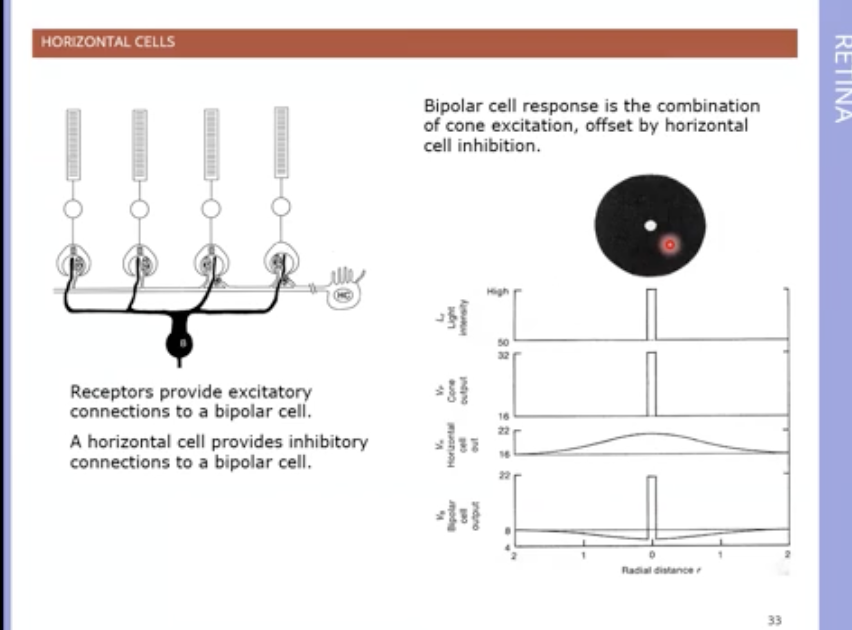
horizontal cells
neurons that receive inputs from photoreceptors and pass onto neighbouring photoreceptors
effect depends on sign / polarity
so if positive it makes resolution less sharp as its same sign as direct photoreceptor input
if negative its opposite so transforms vertical pathway to signalling contrast in illumination instead of amount of light - helps spatial resolution
more on lateral pathway (horizontal)
amacrine cells- they receive input from other amacrine or bipolar cells
and output to amacrine or bipolar or ganglion cells
amacrine cells responses
if burst of activity when :
light intensity increases= On response
light intensity decreases= Off response
some cells have both responses= ON/OFF
interplexiform neurons
receive inputs from bipolar and amacrine from inner retina
output to bipolar cells and horizontal cells in outer retina
opposite direction of flow
involved in adjustment of retinal sensitivity