Anatomy Exam 2
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
axial skeletal system includes
skull, auditory ossicles, hyoid bone, vertebral column, and thoracic cage
appendicular skeleton includes
arms, hands, hips, legs, and feet
how many bones is the adult skeleton made up of
206
what is the purpose of the braincase
enclose and protect brain
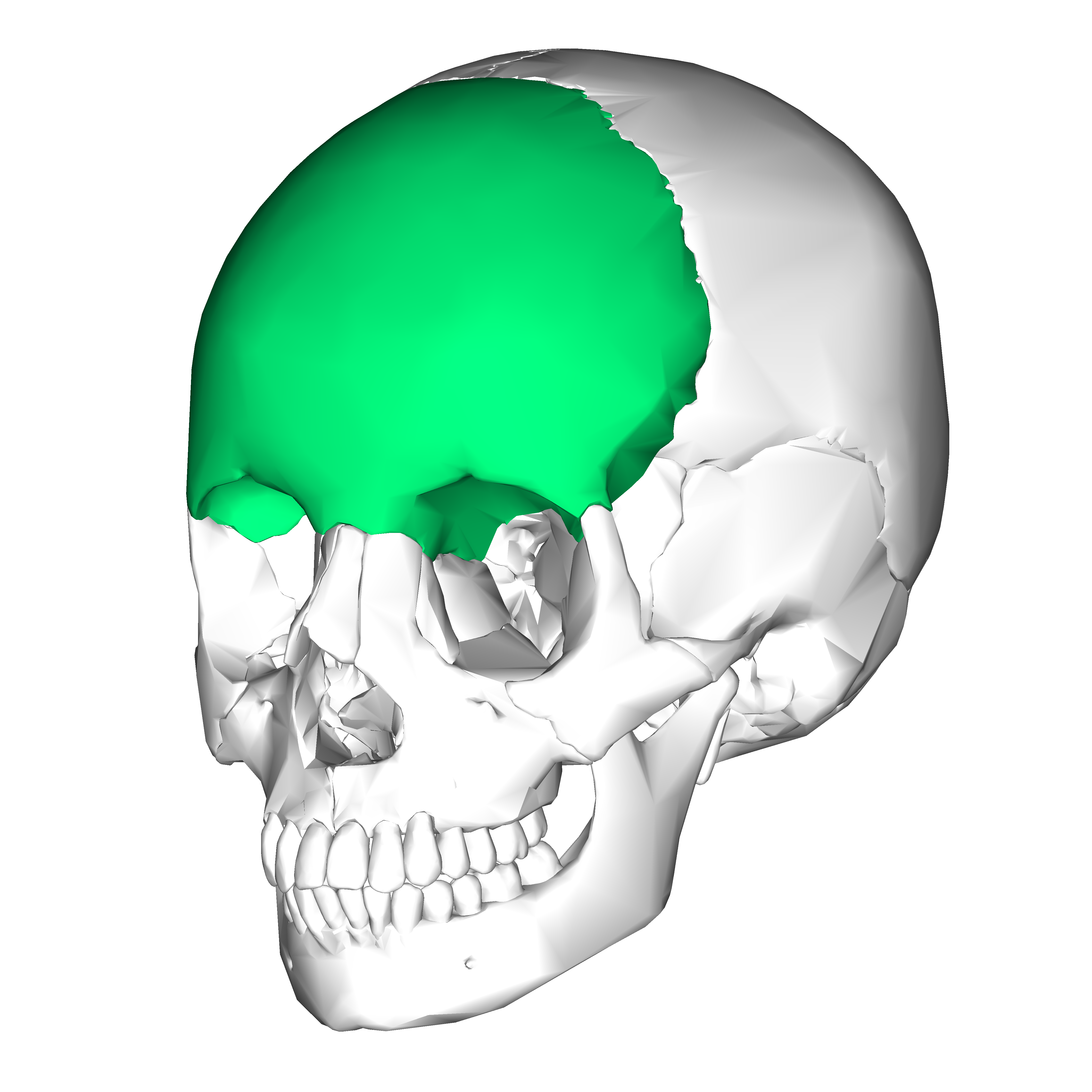
what bone is this
frontal
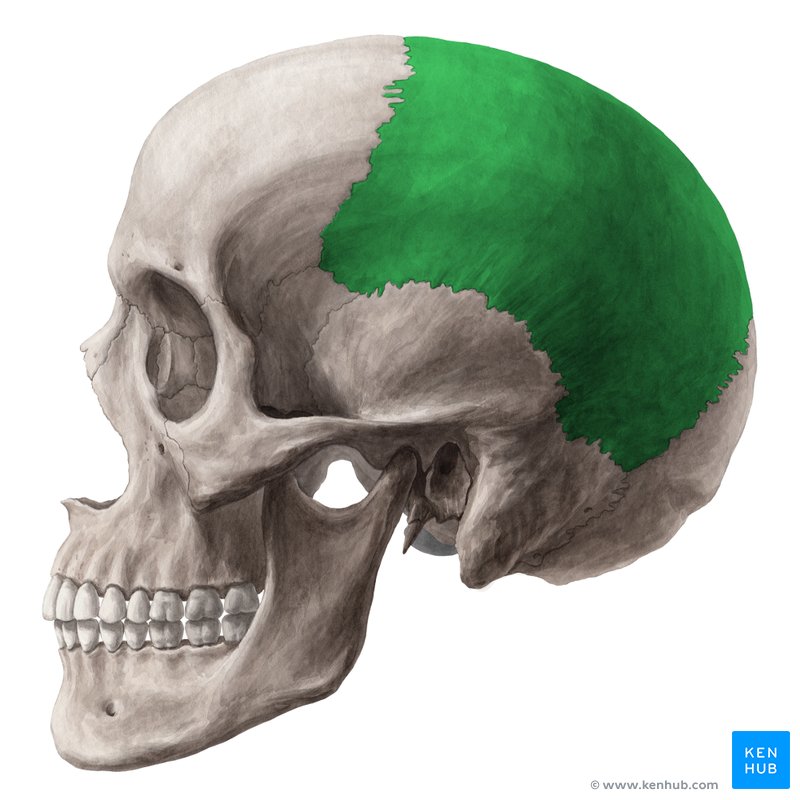
what bone is this
parietal
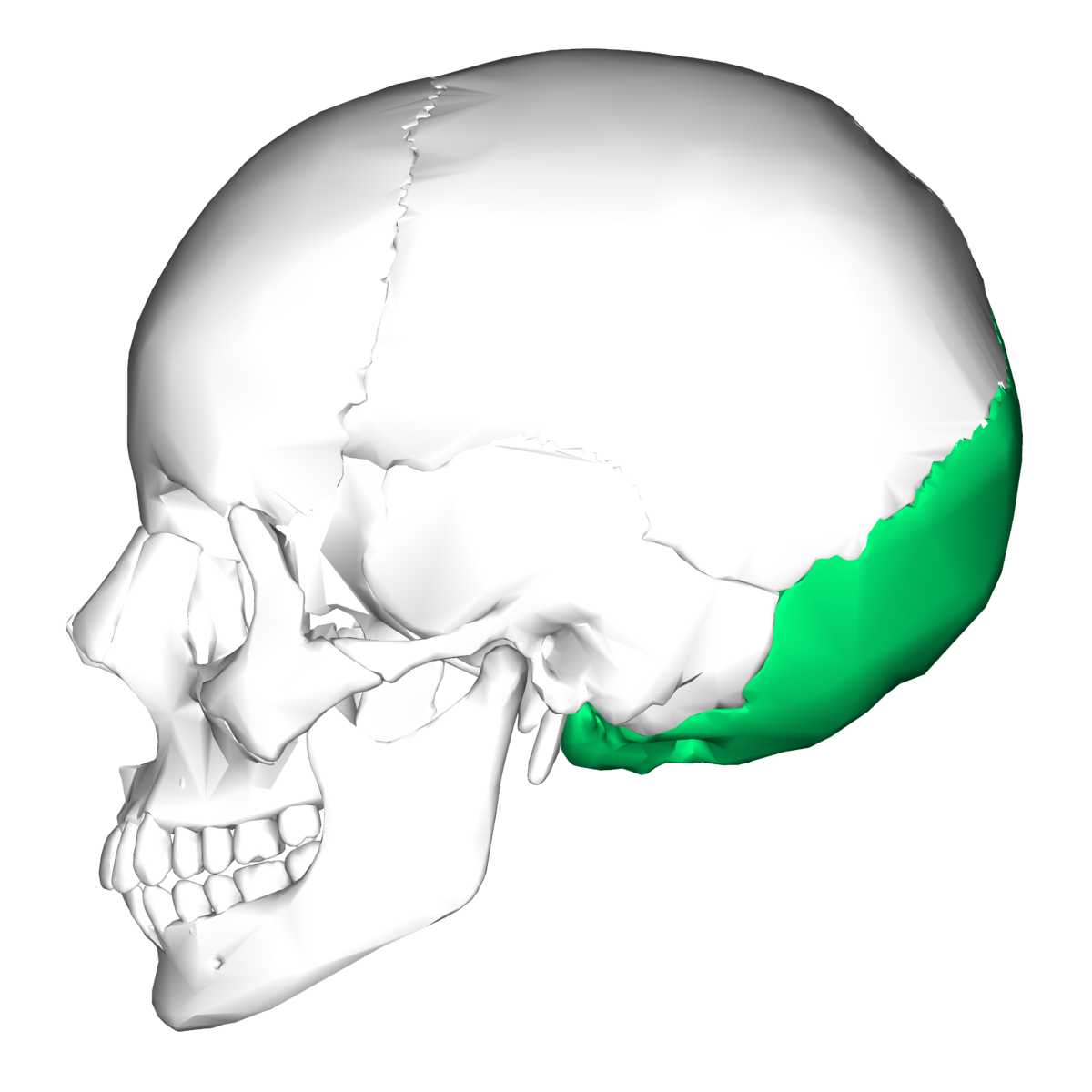
what bone is this
occipital
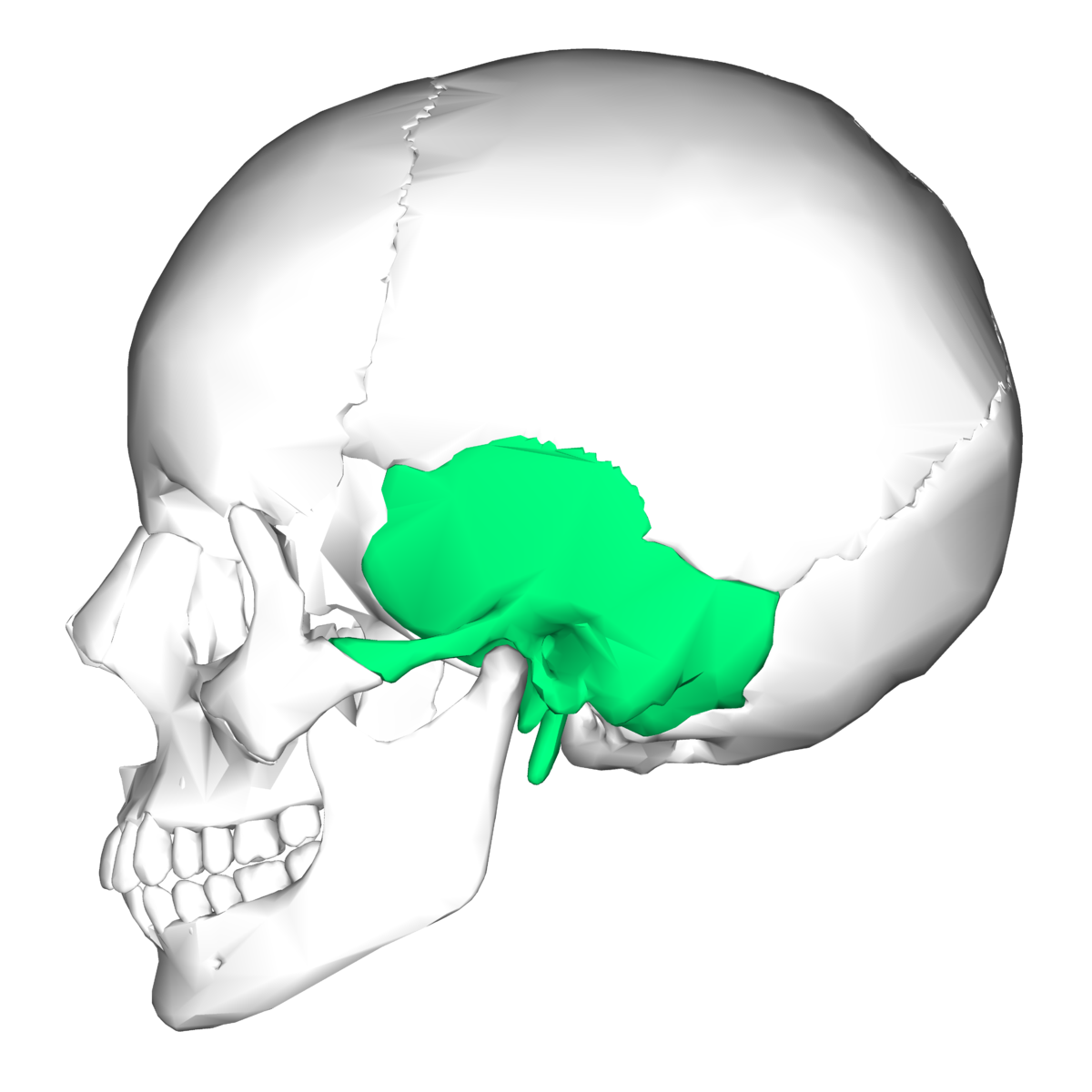
what bone is this
temporal
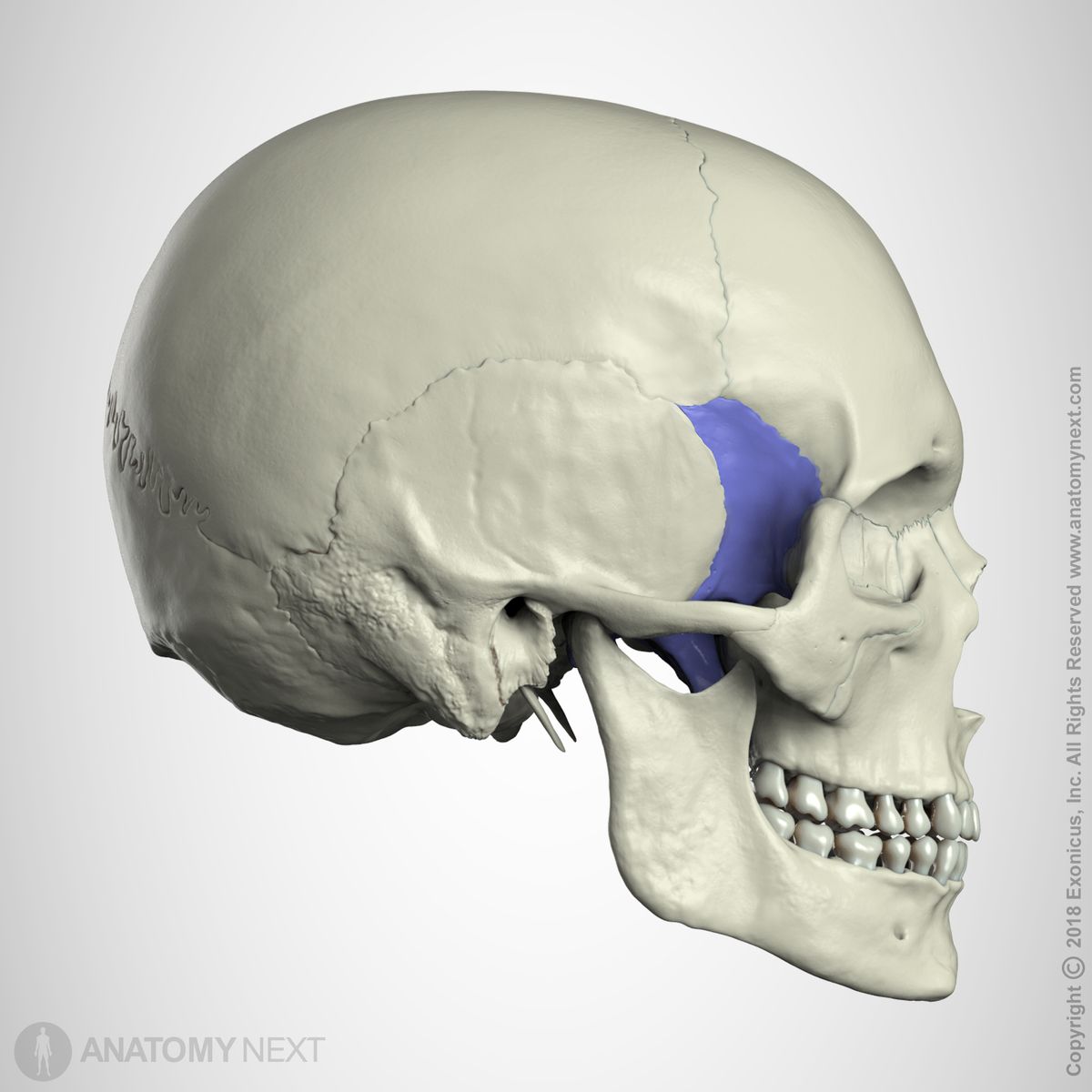
what bone is this
sphenoid
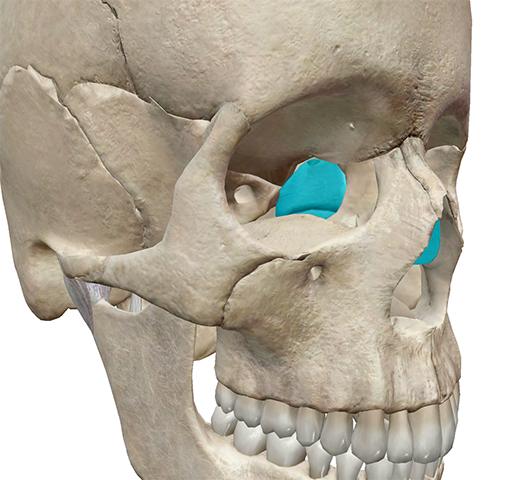
what bone is this
ethmoid
sutures are
immovable joints of interdigitated bone
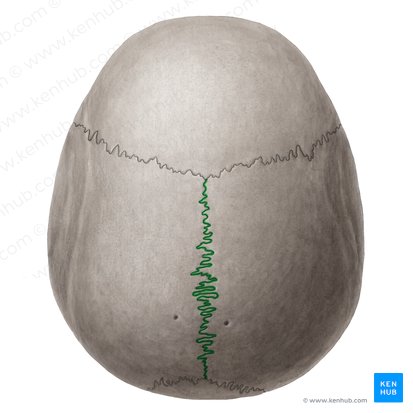
what suture is this and what bones does it connect
saggital suture; connects parietal to parietal
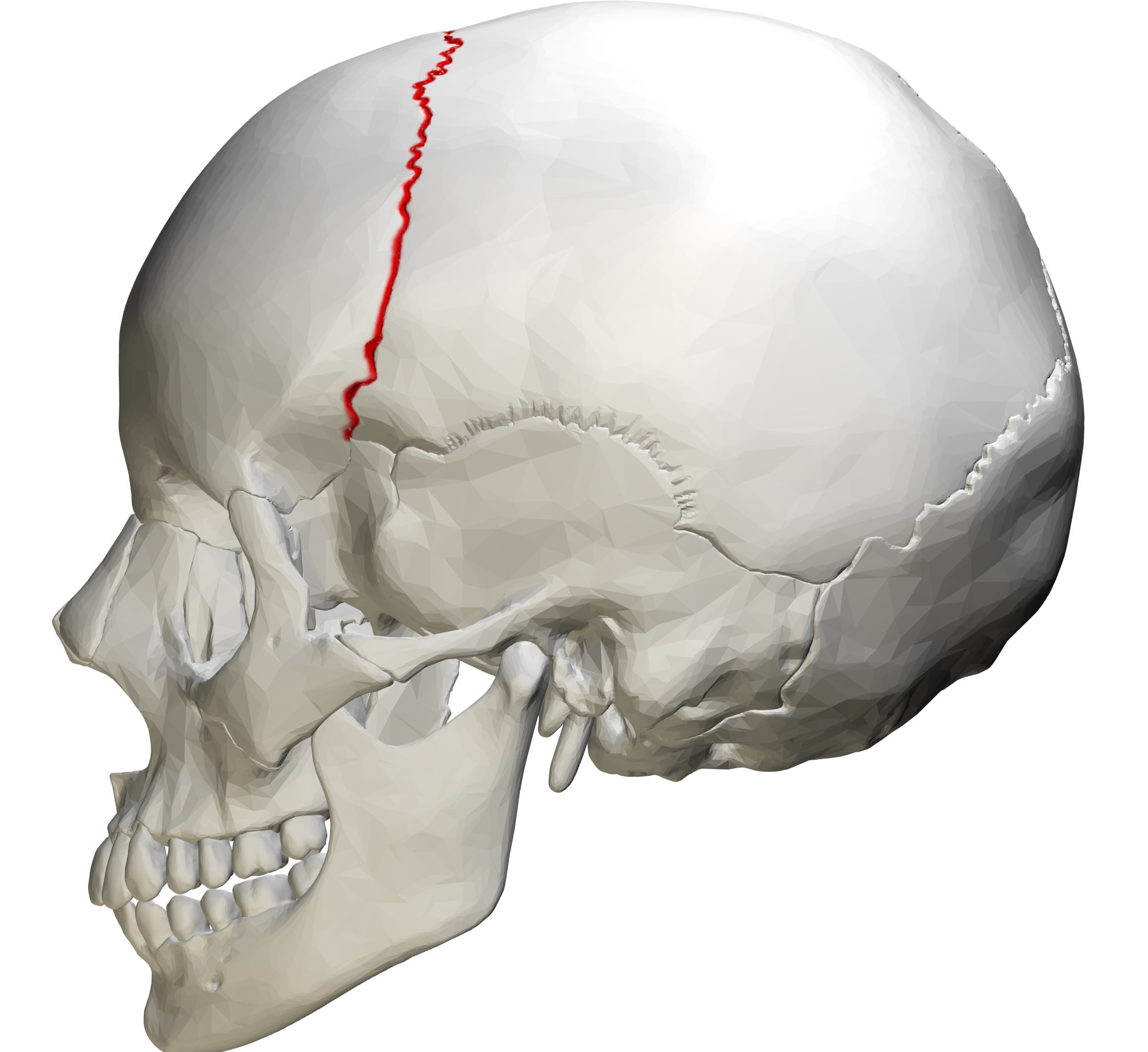
what suture is this and what bones does it connect
coronal suture; connects parietal to frontal
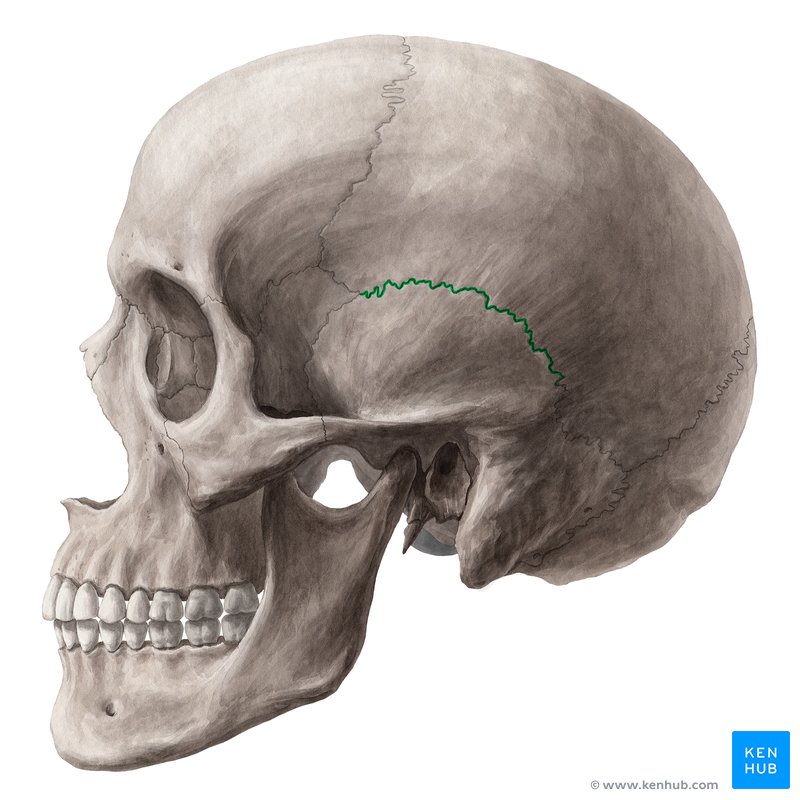
what suture is this and what bones does it connect
squamous suture; connects parietal to temporal
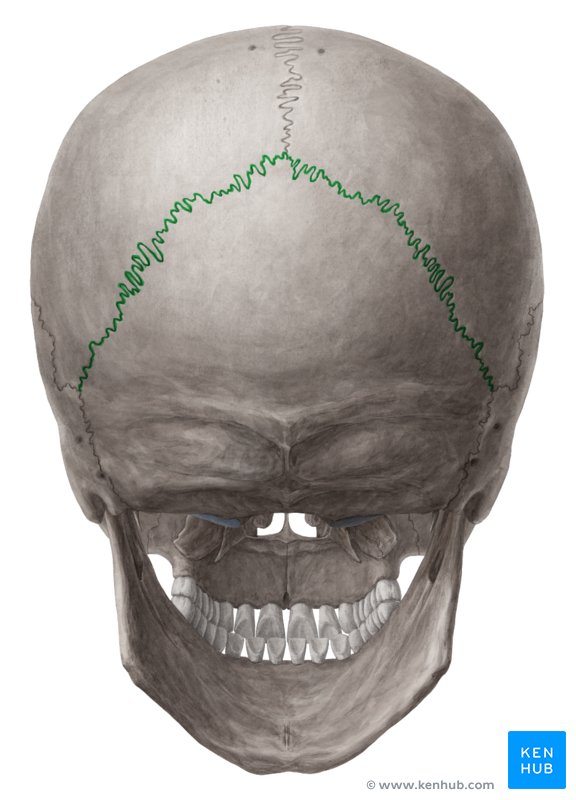
what suture is this and what bones does it connect
lambdoid suture; connects parietal to occipital

what cranial fossa is this and what lobe of the brain does it support
anterior cranial fossa; supports frontal lobe

what cranial fossa is this and what lobe of the brain does it support
middle cranial fossa; supports temporal lobe

what cranial fossa is this and what lobe of the brain does it support
posterior cranial fossa; supports cerebellum
how many facial bones are there
14
what are the function of facial bones
give shape to face and provide support for teeth
what do the facial bones form
part of orbitals and nasal cavities
muscles attach to facial bones for what actions
chewing and expressions
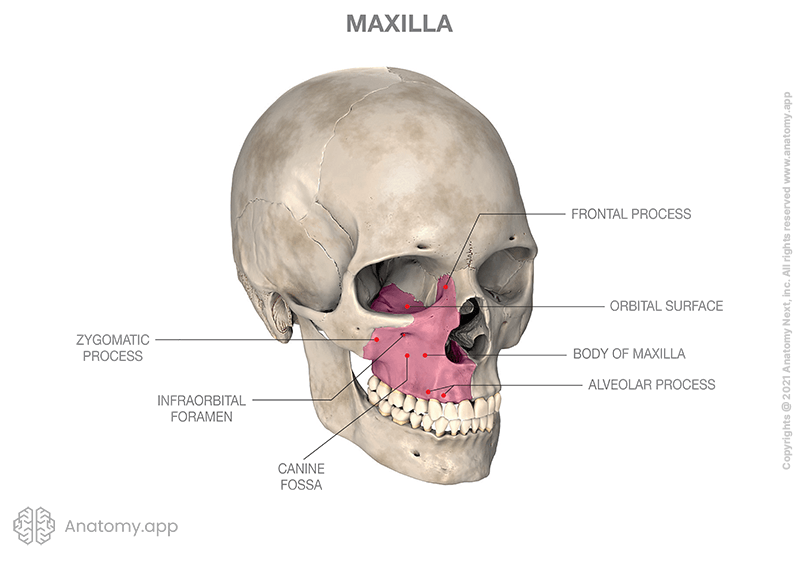
maxillae form
upper jaw and most of hard palate
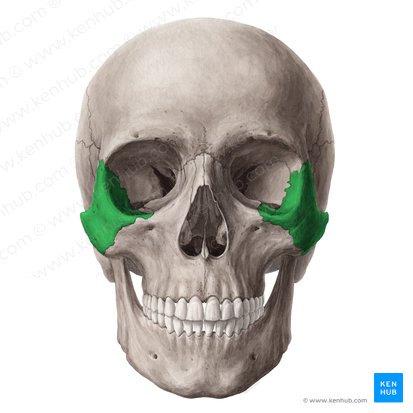
zygomatic bones form
part of cheek bone
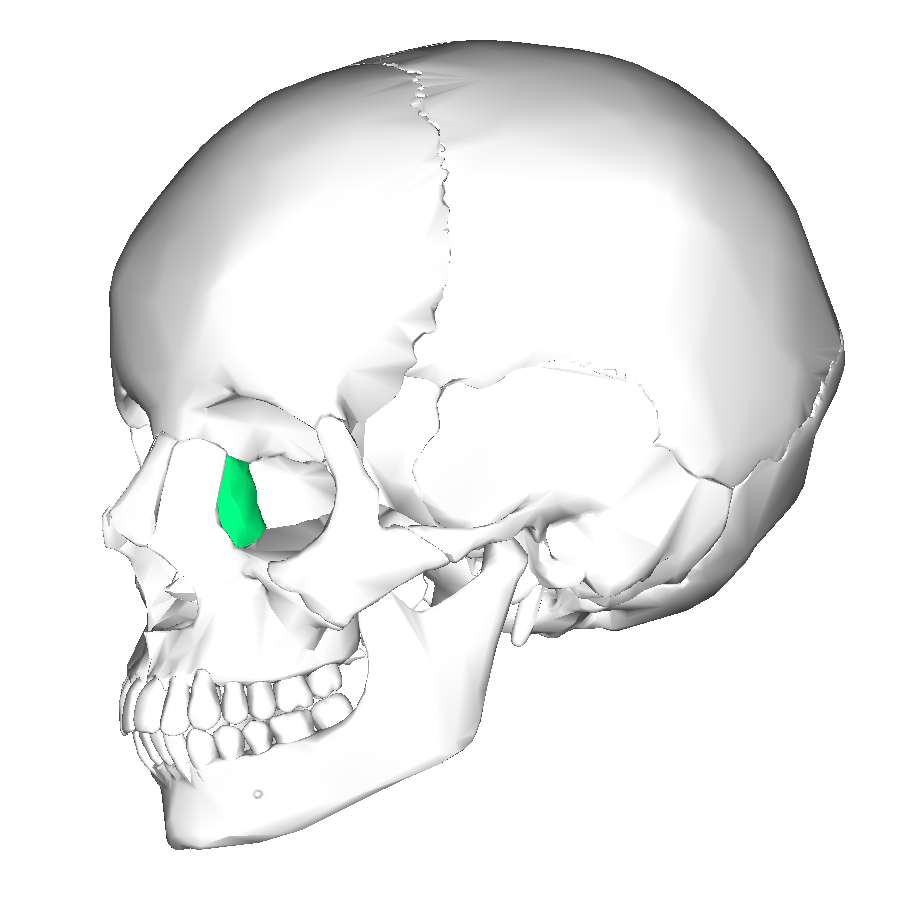
lacrimal forms
part of medial wall of orbit
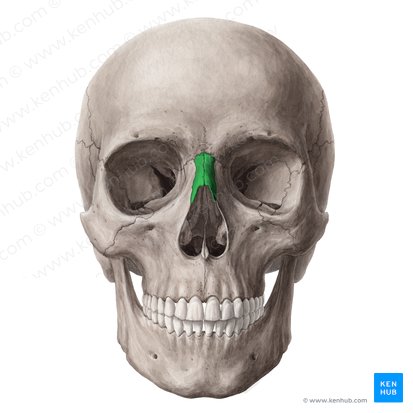
nasal bone forms
bridge of nose
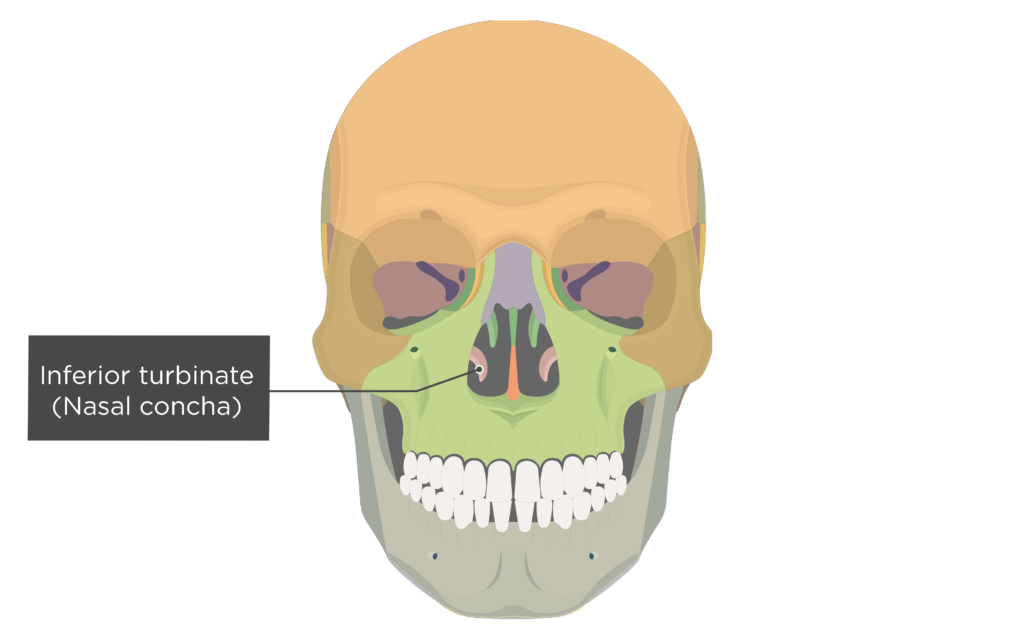
where do inferior nasal conchae project into
medially into nasal cavity
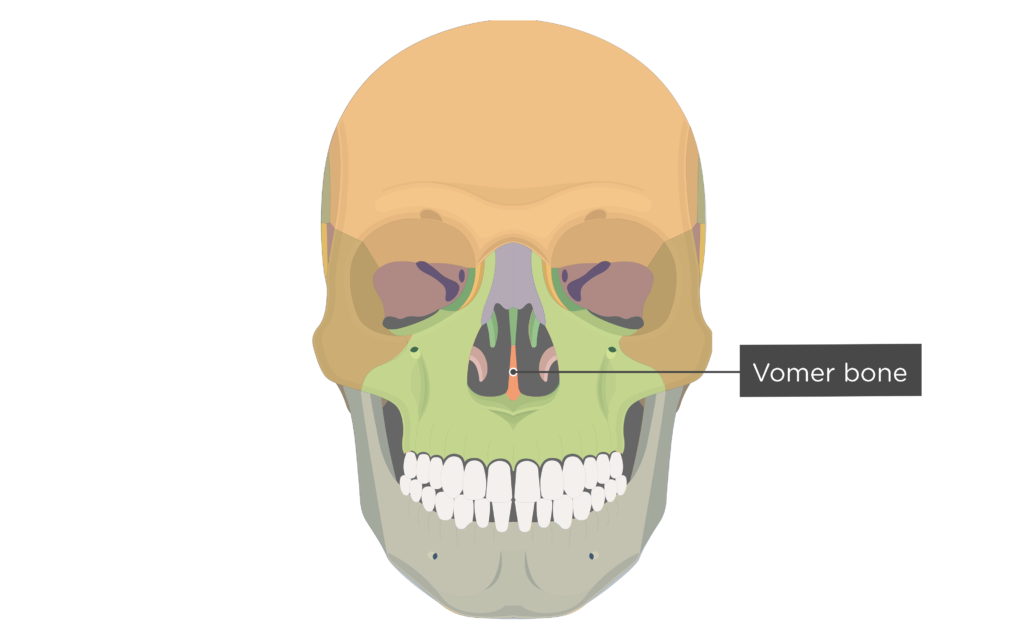
vomer forms
inferior part of nasal system
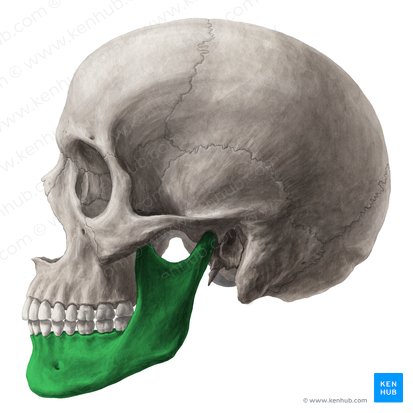
mandible forms
lower jaw bone
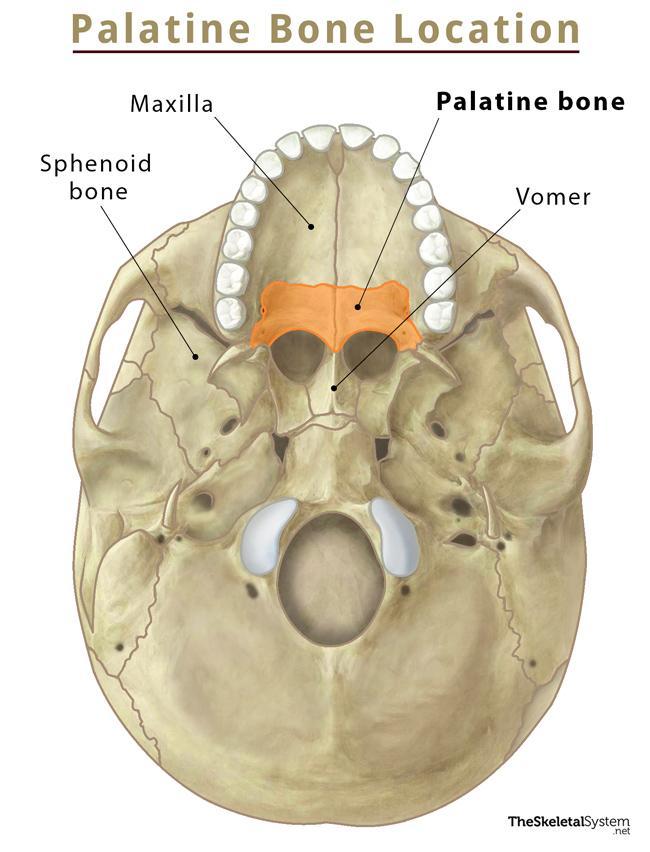
palatine forms
remainder of hard palate, part of nasal cavity wall, and part of orbital floor
how many auditory ossicles are there
3 per ear
hyoid bone is located
between chin and larynx
what is unique about the hyoid bone
only bone not attached to another bone
fontanels
fibrous membranes that join bone together; later on will continue intramembranous ossification (in infants)
paranasal sinuses description
airfilled cavities in facial bones
paranasal sinuses are lined w
mucus membrane
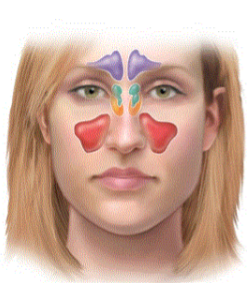
what paranasal sinus is in purple
frontal sinus
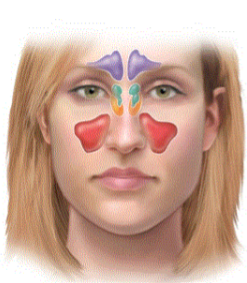
what paranasal sinus is in green
ethmoid sinus
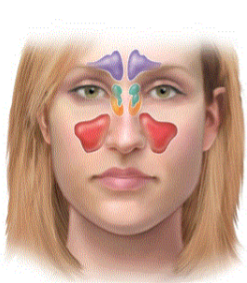
what paranasal sinus is in orange
sphenoid sinus
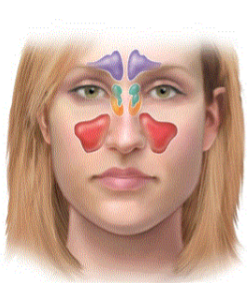
what paranasal sinus is in red
maxillary sinus
what is the purpose of the vertebral column
support skull and trunk, protect spinal column, and attachment site for limbs, thoracic cage, and postural muscles
how many cervical vertebrae are there
7
how many thoracic vertebrae are there
12
how many lumbar vertebrae are there
5
how many bones are fused to make the sacrum
5
how many bones are fused to make the coccyx
4
cervical vertebrae curvature
convex anteriorly
thoracic vertebrae curvature
convex posteriorly
lumbar vertebrae curvature
convex anteriorly
pelvic vertebrae curvature
convex posteriorly
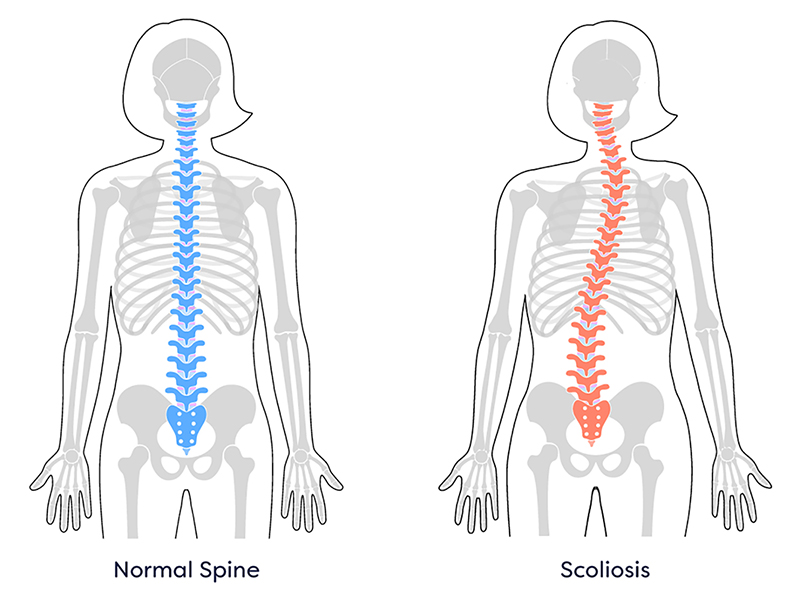
scoliosis
lateral deviation; shoulder and hip affected
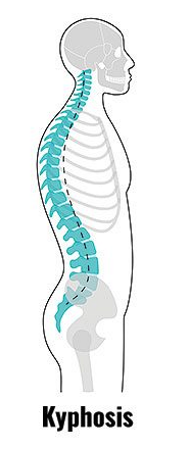
kyphosis
exaggerated thoracic deviation/ curvature
lordosis
exaggerated lumbar deviation/ curvature; normal during pregnancy
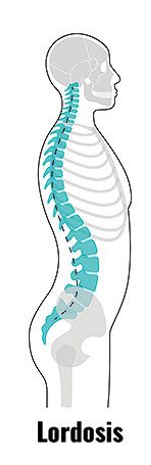
what determines that specific shape of a vertebrae
spinal region
body of vertebrae made up of
compact bony around spongy bone middle which contains red bone marrow
vertebral foramen allows the passage of
spinal cord
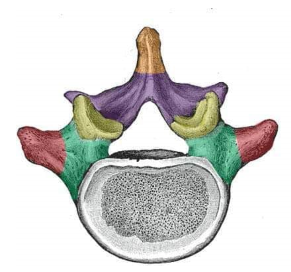
what feature of the vertebrae is in orange
spinous process
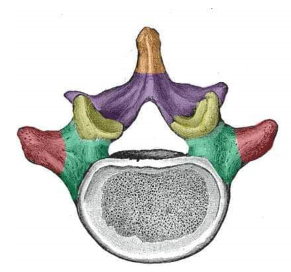
what feature of the vertebrae is in red
transverse process
intervertebral disc serves as
shock-absorbing padding
nucleus pulposis of intervertebral disc
jelly-like interior
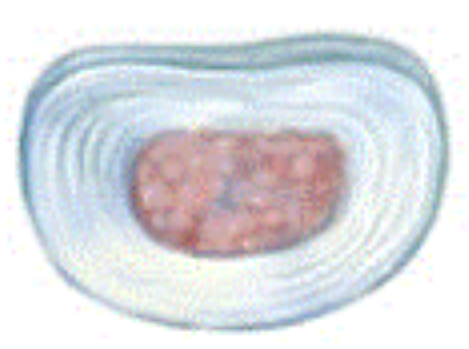
annulus fibrosis of intervertebral disc
ring of fibrocartilage around nucleus pulposis
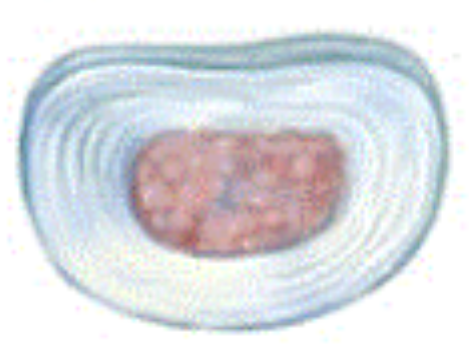
intervertebral disc under load means
nucleus pulposis squeezes out fluid into annulus fibrosis
intervertebral disc unloading means
spine not compressed anymore, fluid back into nucleus pulposis
herniated disc occurs when there is
weakness/ rupture of annulus fibrosis so nucleus pulposis bulges out and presses against spinal nerve
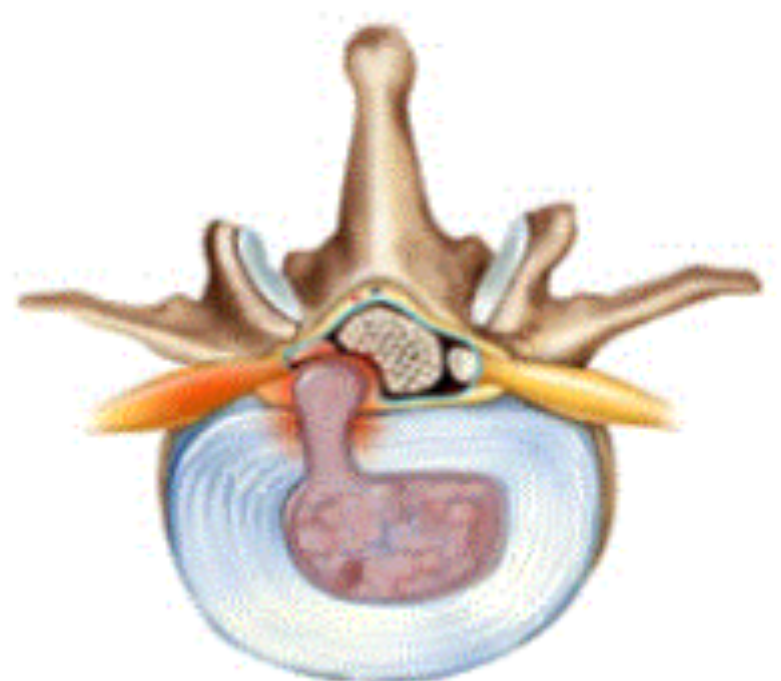
intervertebral foramen allows passage of
spinal nerves
what unique feature does the axis have the allows the “no'“ motion
dens
what feature does the atlas have to allow the “yes” motion
superior articular facets
where in the spinal cord are there no intervertebral discs
between atlas and axis
what are the 3 parts of the sternum
manubrium, body, and xiphoid process
what does the manubrium articulate with
clavicle and costal cartilage of ribs 1 and 2
what are the “true ribs” and where to they connect
ribs 1-7; connect directly to sternum via costal cartilage
what are the “false ribs”
ribs 8-12
where do ribs 8-10 connect
costal cartilage at rib 7
what are the “floating ribs”
11,12
where do ribs 1-9 articulate with spinal vertebrae
transverse process and body
where do ribs 10-12 articulate with spinal vertebrae
body only
which ribs only connect with one vertebrae
1, 10, 11, and 12
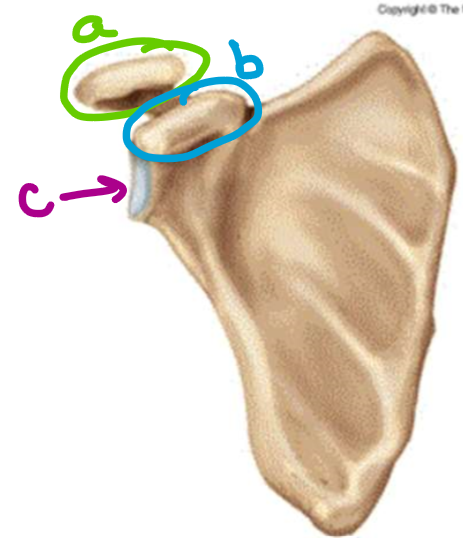
what feature of the scapula is labeled a
acromion
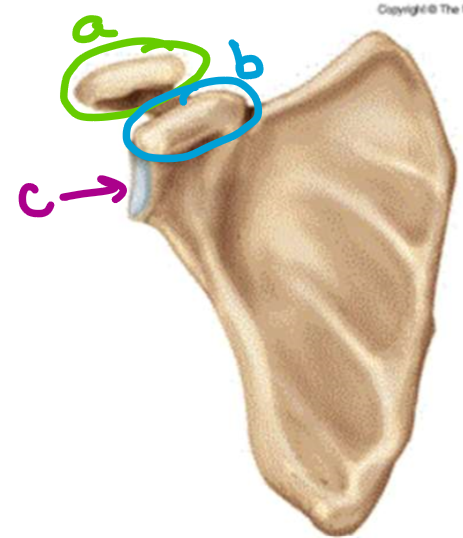
what feature of the scapula is labeled b
coracoid process
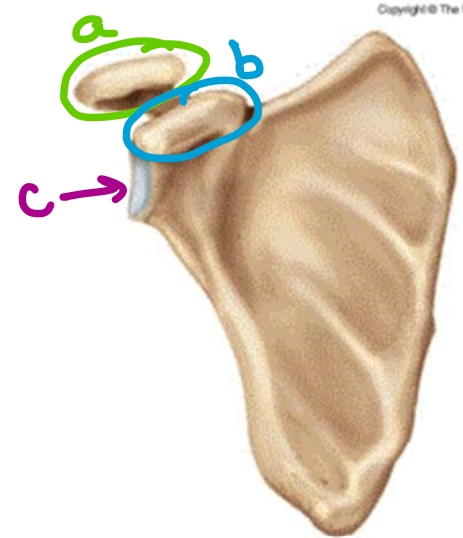
what feature of the scapula is labeled c
glenoid fossa
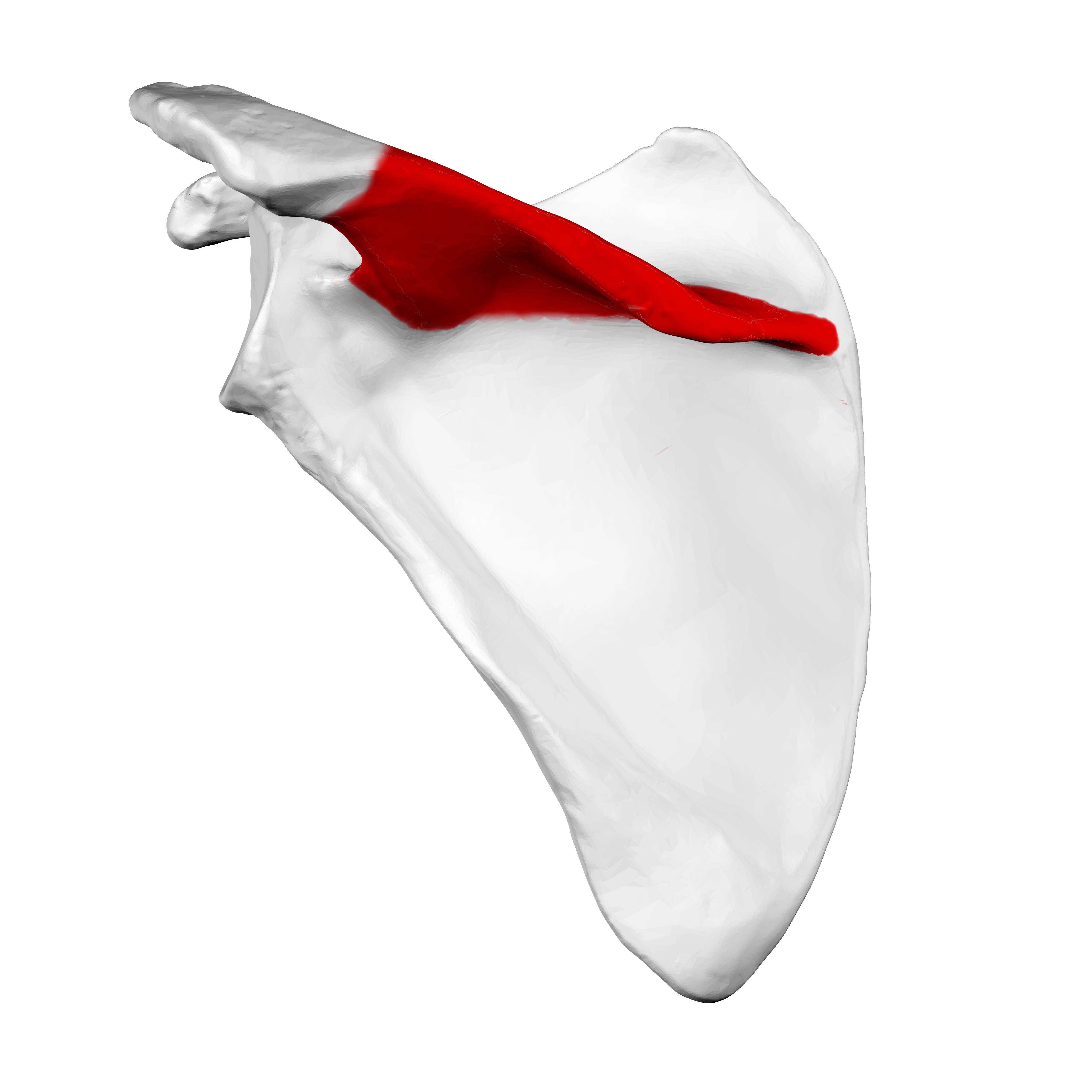
what feature of the scapula is highlighted
spine
acromion articulates with
clavicle
coracoid process attachment site for
bicep brachii
glenoid cavity articulates with
head of humerus
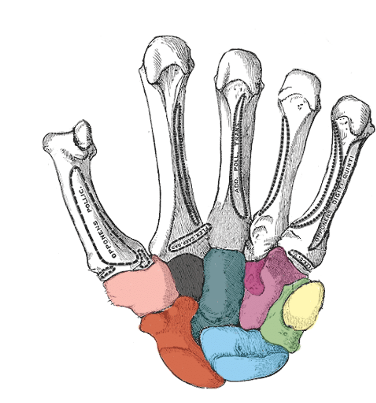
what carpal is light pink
trapezium
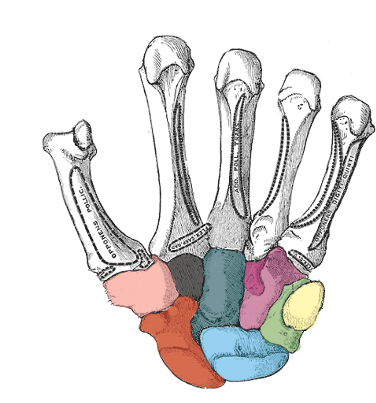
what carpal is black
trapezoid
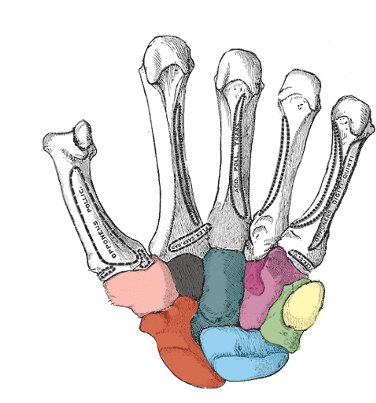
what carpal is dark green
capitate
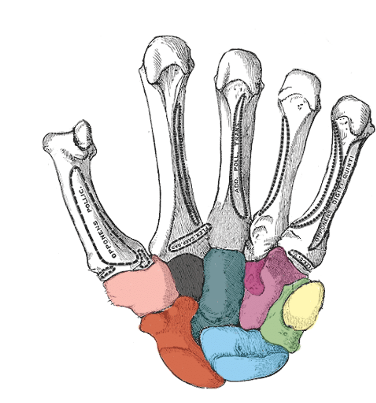
what carpal is purple
hamate
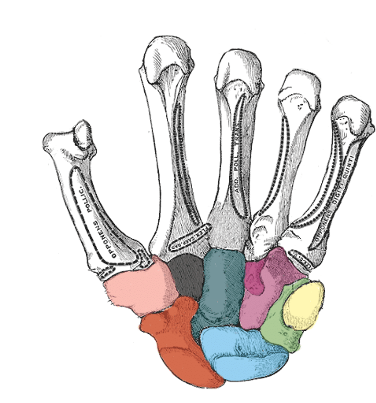
what carpal is red
scaphoid
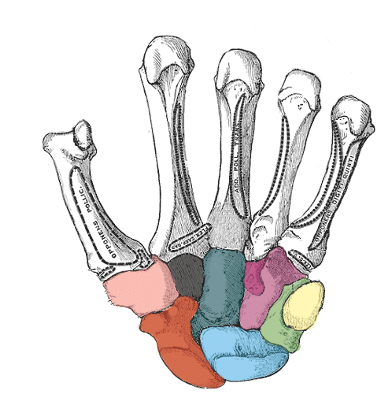
what carpal is blue
lunate
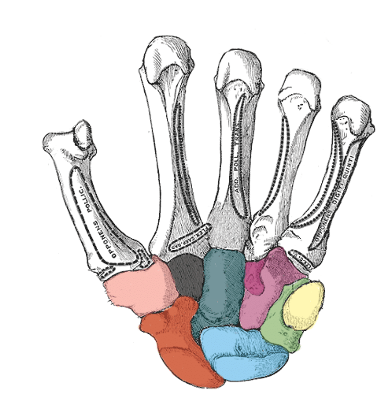
what carpal is light green
triquetrum
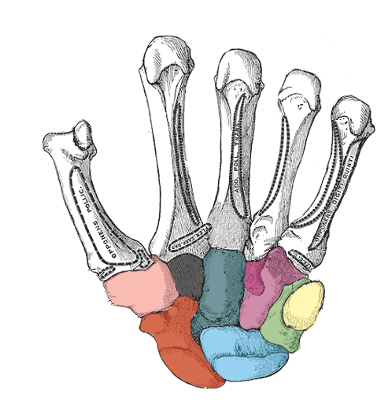
what carpal is yellow
pisiform
capitula articulates with
radial bone
trochlea articles with
ulna
radius is associated with movement of what (body part)
wrist
how many bones are in each upper limb
30
carpal tunnel syndrome
transverse ligament presses on nerve of wrist
pelvis made up of
os coxae and sacrum
acetabulum is where what 2 structures meet
head of femur and os coxae
which is the longest and strongest bone
femur