MECHANICS
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Module 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Calculate 2.897 × 20 giving the result to 3 significant figures
57.9
The Scientific Method derived from an astronomer, philosophist and physicist by the name of ________
Galileo Galilei
The Scientific Method follows the order of
Observation
__________
Experiment
__________
Hypothesis
Conclusion
What are random errors?
Errors that occur due to unpredictable fluctuations in measurements, leading to differing results when repeated under the same conditions.
State 2 factors that may affect the period of a simple pendulum
Length of the string
Angle of release
How does the length of the string affect the period of a pendulum?
The length of the string directly influences the period; longer strings result in a longer period, while shorter strings lead to a shorter period.
What is the ‘period (T)’ of a simple pendulum?
The time taken for one complete oscillation of the pendulum, defined as the interval between two successive points of maximum displacement in the same direction.
All non 0 integers are ______
significant
Trailing zeros are significant only if______
there is a decimal point present
Captive zeros are?
zeros between non-zero digits and are always significant.
How many significant figures are in the number 506.709
6
There are _ significant figures in 8.70
3
State the 2 types of errors that can occur amongst measurements
random and systematic errors
What type of error is a parallax error
random error
List 3 ways to correct/prevent a parallax error
If using a vertical measuring instrument, e.g a measuring cylinder, the measurement should be taken at eye level
Use tools with clear measurement indicators
Observations should be made with the line of sight perpendicular to the scale
What are systematic errors?
Systematic errors are those which make the result always too small or always too large by the same amount. They are usually caused by some problem within the measuring instrument
State 2 ways systematic errors can be reduced
The value of the error must be discovered and then added or subtracted from each reading.
The instrument must be adjusted.
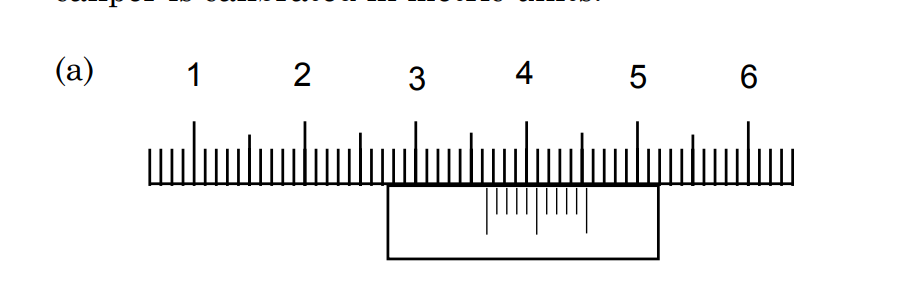
State the reading on the vernier caliper
3.55
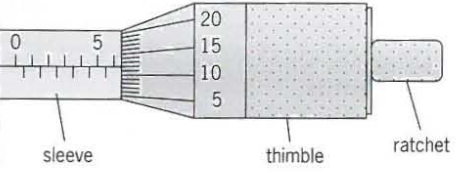
State the reading on the micrometer screw gauge
6.12
State 3 things a micrometer screw gauge can measure
the diameter of wires, the thickness of sheets, the width of a hair strand
Why might a metre rule be chosen over a 30cm rule to measure an object?
The metre rule can measure larger objects or distances compared to a 30cm rule, making it more versatile for various applications. Additionally, it provides greater accuracy and readability for longer measurements.
What is the formula for the density of an object?
Density = mass/volume
Define the term ‘density’
Density is the mass of an object per unit volume.
How can the density of an irregular shaped object be determined?
The density of an irregularly shaped object can be determined by measuring its mass and calculating its volume using water displacement, where the volume is equal to the amount of water displaced when the object is submerged.
The unit for density is ___
kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³)
or
grams per cubic centimetre (g/cm³)
What are vector quantities?
Vector quantities are quantities that have magnitude and direction
What are scalar quantities?
Scalar quantities are quantities that only have magnitude
List 3 examples of vector quantities
displacement, force, acceleration, velocity and momentum.
Mass, Distance/Length and temperature are _____ quantities
scalar
If vectors are parallel to each other then you can ___ or ______ to find the resultant
add or subtract
When vectors are at right angles to each other, _______ _____ can be used to find the resultant
Pythagoras’ theorem
Briefly explain the parallelogram rule which is used to find the resultant of non parallel vectors
The parallelogram rule requires a scale diagram. Two adjacent sides of the parallelogram represent the two vectors to be combined. Those 2 sides are then copied to scale to complete the parallelogram. The resultant is identified by the diagonal formed starting at the point of intersection of the 2 original vectors and is drawn from this intersection point to the opposite corner of the parallelogram.
A force can cause a change in the ____,____ or _____ of a body
size, shape or motion
What is a magnetic force?
A magnetic force is an attractive or repulsive force existing between bodies due to their magnetic properties
What is an electrostatic force?
An electrostatic force is a force existing between bodies due to their electric charge
The nucleus of an atom is held together by strong _______ ____
nuclear forces
The mechanical force that opposes the relative motion of the surfaces of bodies in contact is called ______
frictional force/friction
On earth, the generally accepted value of gravitational field strength is
10 N/kg
Weight = ___ x _____________
mass x gravitational field strength
Determine the mass of a football which has a weight of 0.80N on a planted where the acceleration due to gravity is 2.0ms^-²
To find the mass, use the formula: mass = weight / gravitational field strength. Thus, the mass is 0.80N / 2.0m/s² = 0.40 kg.
The unit kgms^-2 is used to measure ____
Force
4500 is written as ___ x ____ in standard form
4.5 x 10³
Identify 3 real life examples of situations in which the application of a force will result in a turning effect
Opening a door,
Using a wrench to turn a bolt
Pushing a merry-go-round
Sitting on a seesaw
What is meant by the ‘moment (T) of a force’?
The ‘moment’ of a force is the turning effect created when a force acts upon an object at a distance from a pivot point
The unit for moments is ___
Newton-meter (Nm)
T = F x __
d (distance from pivot)
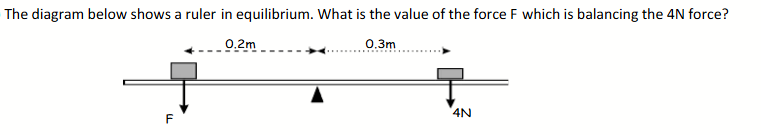
Calculate the force
6N
When describing the action of moments the terms _____ and _______ are used to describe the direction of action
clockwise and counterclockwise/anticlockwise
State the two conditions required for an object to be in ‘equilibrium’
There is no resultant force acting on the object
The clockwise moment equals the counterclockwise moment.
What is the PRINCIPLE OF MOMENTS?
The principle that for an object in equilibrium, the sum of the clockwise moments about a pivot equals the sum of the counterclockwise moments.
A seesaw, scissors and a nail claw hammer are ___ ____ levers
first-class
First class levers have the _____ in between the effort and the load
fulcrum
Second class levers such as wheelbarrows and a diving board have the ____ between the fulcrum and the ______
load; effort
A bottle opener is a ____ ____ lever
second-class
A second-class lever is used to _____ force
amplify or increase
A fishing rod is a ____ ____ lever
third-class
The aim of a third class lever is to…
Increase the distance over which force is applied, allowing for greater speed or range of motion.
A third class lever has the _____ between the _____ and the fulcrum
effort between the load
The _____ __ _____ is the point from which the weight appears to act.
center of gravity
How can the centre of gravity of an irregular shaped lamina be determined?
By balancing it on a point or using plumb lines to locate the central point
What is stable equilibrium?
Stable equilibrium is a state where a body returns to its original position after being displaced slightly. It occurs when any disturbance raises the objects center of gravity
What is unstable equilibrium?
Unstable equilibrium is a state where a body does not return to its original position after being displaced slightly or in other words it falls over. It occurs when any disturbance lowers the object's center of gravity.
What is neutral equilibrium?
Neutral equilibrium is a state where a body remains in the same position after being displaced, with no tendency to return or topple over. This occurs when the center of gravity remains unchanged.
State 3 factors that affect the stability of an object
The width of its base
Its weight
The height of its center of gravity.
Why do cargo buses have their baggage compartments under the floor instead of on the top?
Cargo buses have their baggage compartments under the floor to lower the center of gravity, enhancing stability and reducing the risk of tipping during operation.