OPP Final
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
_________ is the only bony attachment between the axial skeleton and the upper extremities
sternoclavicular joint
What is located anterior to the head of the ribs?
Sympathetic chain ganglia
sharp stabbing pains in the chest in children and younger adults
precordial catch syndrome
True ribs
1-7
attach directly to the sternum via costochondral cartilage
False Ribs
8-10
Attach via a synchondrosis to the costochondral cartilage of rib 7
Floating Ribs
11-12
Do not attach to sternum
typical ribs
3-9, sometimes 10
demifacets (10 has full facet)
atypical ribs
1, 2, 11, 12
The 2 facets on the head of the rib articulate with the ___________ on the body of ____________________________ and with the __________________ on the body of the vertebra above.
superior facet, its own vertebra, inferior facet
What’s the sympathetic innervation of the ribs?
T1-L2
What’s the parasympathetic innervation of the ribs?
OA, C1, C2
What nerve exits through the jugular foramen and contributes to the parasympathetic innervation to the ribs?
Vagus N.
Naming: Intercostal spaces are numbered according to the rib forming their
superior boundary
Ex) ICS 3 is between ribs 3 and 4
What is the order of the vessels within the costal groove?
VAN
vein
artery
nerve
Intercostal Neuralgia
Intercostal Neuralgia - pain along the distribution of an intercostal nerve
Can be caused by somatic dysfunction
Intercostal neuralgia symptoms in the absence of structural rib dysfunctions should alert you to search for other causes of pain
Herpes zoster (Shingles)
Cord tumor
Inflammatory or neoplastic disease of thoracic viscera
Somatovisceral Reflex vs. Viscerosomatic Reflex
•Rib Cage somatic dysfunction can also cause visceral dysfunction by impinging on these sympathetic chain ganglia
-Somato - visceral reflex
•Visceral upset can also lead to musculoskeletal somatic dysfunction in the ribs or thoracic spine due to irritation of the sympathetic ganglia
-Viscero - somatic reflex
What are the attachments for the left and right crus?
Left crus- attaches to L1, L2
Right Crus- attaches to L1, L2, L3
When does lymph and blood flow more easily upwards?
During inspiration
Describe the diaphragmatic motion in regards to lymph.
As Diaphragm contracts and relaxes it milks the lymphatic channels enabling the lymph to move more freely into the thoracic duct
During inspiration, while there is negative intrathoracic pressure in the lungs, lymph and blood flows more easily upward into chest
Describe diaphragmatic motion in regards to inspiration and expiration.
Inspiration:
Diaphragm contracts, flattening out
Ribcage expands in 3 planes
Vertical
Anterior-Posterior
Transverse Diameter
Creates negative intrathoracic pressure
Increases intra-abdominal pressure (organs pushed inferiorly)
Air more freely flows into lungs
Lymphatic and venous fluids flow from the body to the upper thoracic area
Expiration:
Diaphragm relaxes, becoming a dome (forms a zone of apposition)
Increases intrathoracic pressure
Air forced out of lungs
At what points can diaphragmatic somatic dysfunction occur?
ribs 6-12
Thoracolumbar junction (T12-L1)
Crura of Diaphragm
What nerve controls the diaphragm?
Phrenic
What muscles moves the rib superiorly producing rib cage expansion?
External intercostals
What are the accessory muscles involved in inspiration?
SCM & Scalenes
Attachments for Scalenes
Anterior and Middle → 1st rib
Posterior → 2nd rib
Pec Minor Attachment
coracoid process
ribs 3-5
Pectoralis Major Attachments
ribs 2-6
Serratus Anterior
Attaches to ribs 1-8/9
Latissmus Dorsi
With arm above head, activation of this muscle pulls ribs 11 & 12 superiorly and laterally
Serratus Posterior Superior
Originates on the spinous process of C7-T3 and inserts on ribs 2-5
Elevates ribs 2-5
What results from passive recoil of the lungs?
Quiet breathing
During active breathing what muscles depress and retracts the ribs?
Internal Intercostals
During active breathing what muscles forces the abdominal contents superiorly?
Rectus Abdominis
During active breathing what aids in forced expiration?
Internal and External Oblique abdominals
Quadratus Lumborum Attachments
•Pulls ribs 11 & 12 inferiorly
•Will also stabilize during inspiration
Latissimuss Dorsi aids in
expiration
Serratus Posterior Inferior Action
Depresses ribs 9-12
What ribs perform the pump handle action?
1-5
What ribs perform the bucket handle?
Ribs 6-10
What ribs perform the caliper function?
11-12
Ribs 11 and 12 assist by pulling the back of the diaphragm down so they go out and down in inspiration
Describe the anterior and posterior effects of the pump handle motion.
-Inhalation
•Anterior aspect of rib moves superiorly (cephalad)
•Posterior aspect of rib moves inferiorly (caudad).
-Exhalation
•Anterior aspect of rib moves inferiorly (caudad)
•Posterior aspect of ribs moves superiorly (cephalad)
What plane of motion does the pump handle exist in?
predominantly saggital plane
Describe the motion of bucket handle ribs.
-Inhalation
•Ribs elevate and increase transverse diameter
-Exhalation
•Ribs depress and decrease transverse diameter
What plane of motion does the bucket handle exist in?
coronal plane
Describe the caliper motion of ribs.
-Inhalation
•Moves outward (laterally) and increases transverse diameter
-Exhalation
•Moves inward (medially) and decreases transverse diameter
What plane does caliper motion exist in?
Transverse plane
Somatic dysfunction usually characterized by a rib being held in a position of _______
when
Motion toward inhalation is more free
Motion toward exhalation is restricted
inhalation
Somatic dysfunction usually characterized by a rib being held in a position of ___________.
when
Motion toward exhalation is more free
Motion toward inhalation is restricted
Exhalation
Inhalation Rib Dysfunction
“Key Rib” is bottom rib in group
Associated with extension in thoracic spine
Its motion will stop early in expiration.
Pain with full expiration & may cause rapid shallow breathing
Prominently Anteriorly
Exhalation Rib Dysfunction
“Key Rib” is top rib in group
Associated with flexion in thoracic spine
Its motion will stop early in inspiration.
Difficulty taking a full breath in inspiration
Prominently posteriorly.
What diseases might cause an inhaled rib?
Obstructive Lung Disease; COPD, Emphysema, Chronic Bronchitis, Asthma
Pneumonia
What diseases might cause an exhaled rib?
Restrictive lung disease: Pulmonary fibrosis, Pneumonitis
Neuromuscular disorders
Pneumonia (coughing)
If pain increases when patient inhales indicates
exhalation rib somatic dysfunction
If pain increases when patient exhales indicates
inhalation rib somatic dysfunction
If right ribs have an increased 6th intercostal space (ICS), then at this point either rib 6 is ______ or rib 7 is ______.
inhaled, exhaled
If right ribs have a decreased 6th intercostal space (ICS), then at this point either rib 6 is ______ or rib 7 is ______.
exhalation, inhalation
Muscles used to treat ribs 1-12.
Rib 1: Anterior and middle scalene
Rib 2: Posterior Scalene
Ribs 3 – 5: Pectoralis Minor
Ribs 6 – 8: Serratus anterior
Ribs 9 – 10: Latissimus Dorsi
Rib 11 and 12: Quadratus Lumborum
What bones make up the thoracic inlet?
Consists of the manubrium of the sternum, the proximal clavicles anteriorly, the first ribs laterally and the body of T1-T4 posteriorly
What are the three osteopathic goals in regards to treating ribs and thoracic outlet?
Improve Ventilation Mechanics
Normalize Autonomics
Improve Lymphatics
What must be done first before any lymphatic treatment?
Thoracic Inlet
Majority of patients with TOS are between ________________ years of age.
20 and 50
____________ present with vascular TOS more often than adults.
Adolescents
What are risk factors that lead to TOS.
Anatomic abnormalities (cervical ribs, prominent C7 transverse process, anomalous ligaments or bands)
Acute trauma, especially automobile accidents
Repetitive motion/stress injury, including occupational factors such as poor posture/prolonged computer use, and overhead athletic activities.
Thoracic Cavity Contents
Trachea, Esophagus
Boundaries of the Anatomic Thoracic Inlet
T1 vertebra – posterior
1st ribs and costal cartilages – laterally
Superoposterior border manubrium- anterior
What covers the thoracic Inlet?
Cervicothoracic (diaphragm) fascia
Sibson’s Fascia
What are the boundaries of the thoracic outlet?
Scapula, 1st rib, clavicle
What can be compressed through the scalene triangle as it travels through the neck?
Subclavian Artery
Subclavian Vein
Brachial Plexus
What are the three distinct locations that things may be compressed in the thoracic outlet?
Interscalene space: between the first rib and the anterior and middle scalenes
Costoclavicular space: between the first rib and the clavicle
Subcoracoid space: between the pectoralis minor muscle and the 3rd-5th ribs
_________ TOS involves compression of brachial plexus nerve roots (C5-T1)
Neurogenic
Lower plexus (C8-T1) is most often affected
_________ TOS involves compression of the subclavian artery
Arterial
Almost always associated with trauma or osseous abnormality (typically presence of a cervical rib)
Partial occlusion results in intimal injury, thrombosis, distal embolism, or post-stenotic dilatation, and aneurism
Complete occlusion rare
_______ TOS involves compression of the subclavian vein
Venous
Typically occurs in the costoclavicular space (between the first rib, costoclavicular ligament, and the subclavius tendon)
Commonly occurs in persons participating in physical activities involving repetitive arm and shoulder movements
Persistent trauma of repetitive arm movements injures the vein (inflammation, focal intimal fibrosis, stenosis, blood flow stasis)
Osseous Abnormalities associated with TOS.
Cervical rib
Prominent C7 transverse process
Exostoses (benign bony growth extending outward from surface
Trauma-related abnormalities (displaced first rib, callus from fracture, malunion of fracture, AC or SC joint injury or dislocation)
Soft Tissue Abnormalities associated with TOS.
Hypertrophy of scalene muscles
Fibrosis from trauma
Atypical scalene anatomy
Anomalous ligaments or bands
Tumors and Lymphadenopathy can also be associated with
TOS
Symptoms such as dermatomal pain, Neck Pain, Headaches, paresthesia, weakness, hand coldness, finger swelling, and/or color changes (due to overactive sympathetic nervous system, not ischemia) could point to a differential diagnosis of
Neurologic TOS
Symptoms such as Unilateral symptoms in extremity (typically), Pain in hand or arm (does not follow a dermatomal pattern), Coolness/pallor (arterial), Arm swelling and cyanosis (venous), Arm pain and heaviness could point to a differential diagnosis of
Vascular TOS
What provocative tests are used to diagnose TOS?
Adson, Wright, Halstead (Reverse Adson), Roo
What tests are used to confirm or rule out Neurogenic TOS?
Electrodiagnostic studies
Nonpharmacological interventions for TOS generally consist of ___________________
Nonpharmacological interventions generally consist of patient education, activity modification, and physical therapy
Pharmacological interventions for TOS generally consist of ___________________
Oral agents: NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, TCAs, SSRIs, anticonvulsants
Injections of anesthetic botulinum toxin type A, or steroids may be considered, but are reported to have varying levels of success
What are indications for operative management of TOS?
Neurogenic TOS recalcitrant to 5-6 months of nonoperative management
Symptomatic arterial TOS with evidence of arterial pathology
Acute, chronic, or intermittent venous TOS.
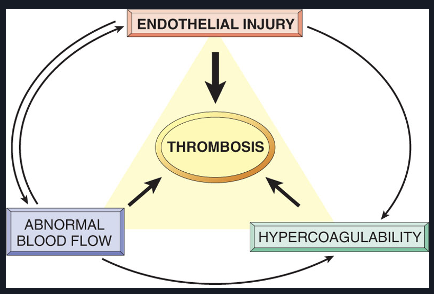
What is Virchow’s Triad?
Virchow's triad refers to a set of three factors that are believed to contribute to the formation of blood clots (thrombus).
Adson’s Test
Radial pulse of the affected extremity is palpated and the patient’s arm is externally rotated and extended
The patient is then instructed to extend, rotate and side bend their head towards the affected side
The maneuver is held for 15-30 seconds while the clinician observes for onset of symptoms and obliteration of the pulse.
Halstead Maneuver (Reverse Adson)
Radial pulse of the affected extremity is palpated and the patient’s arm is externally rotated and extended
The patient is then instructed to extend, rotate and side bend their head away from the affected side
The maneuver is held for 15-30 seconds while the clinician observes for onset of symptoms and obliteration of the pulse.
Wright’s Test
Radial pulse of the affected extremity is palpated and the patient’s arm is abducted and extended (or arm is abducted and elbow is flexed)
The maneuver is held for 15-30 seconds while the clinician observes for onset of symptoms and obliteration of the pulse.
Roo’s Test
The upper extremity is held in the "stick-'em-up" position with the arms abducted and elbows flexed (both at 90°) for 3 minutes
Patient simultaneously and vigorously flexes and extends the fingers
Considered positive if the patient cannot complete the full 3 minutes.