Neuro 11 | Motor Cortex and Pathways
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
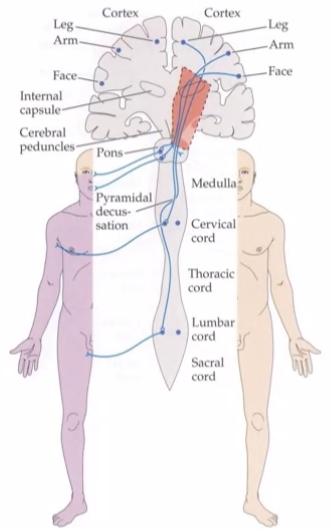
What is the lateral cortico-spinal tract?
A pathway in the spinal cord that carries motor signals from the brain to control voluntary movements on the opposite side of the body.
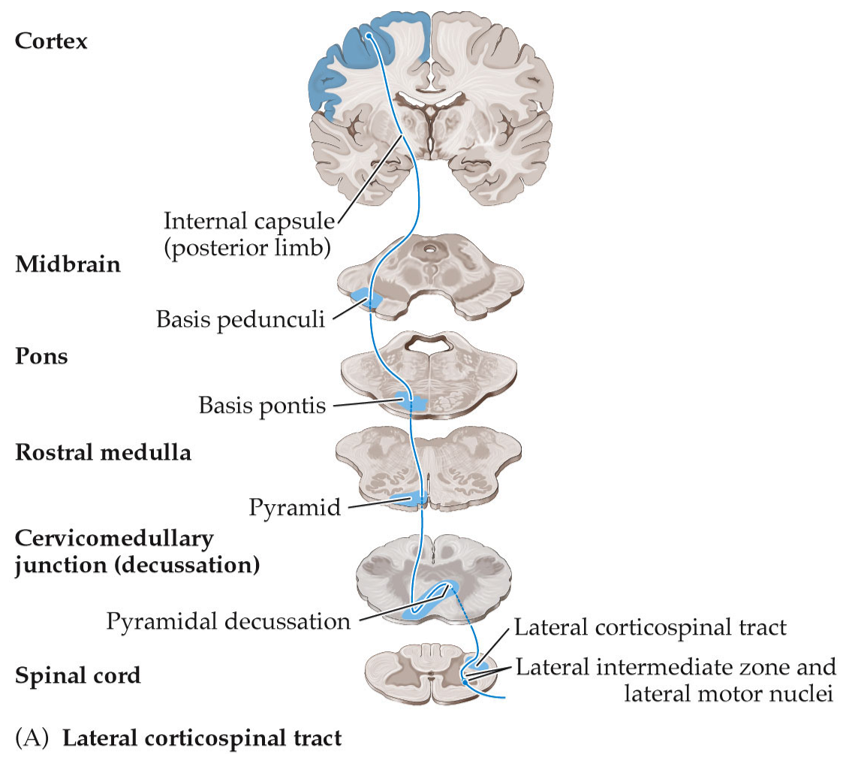
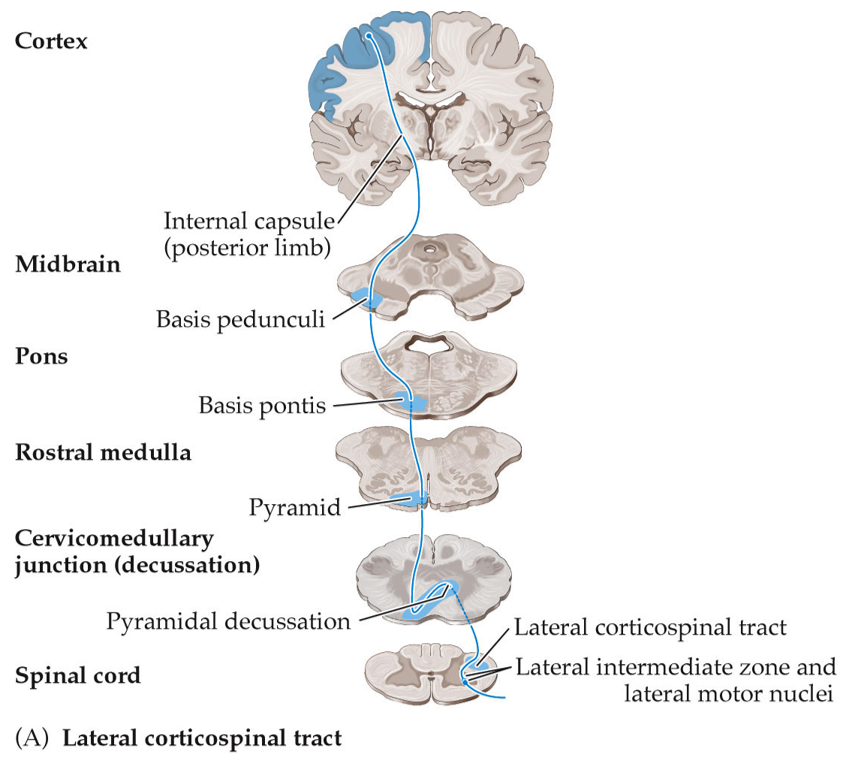
What does the lateral cortico-spinal tract control?
The lateral corticospinal tract controls movements of the arms and legs, allowing for fast, precise movements of individual fingers or joints.

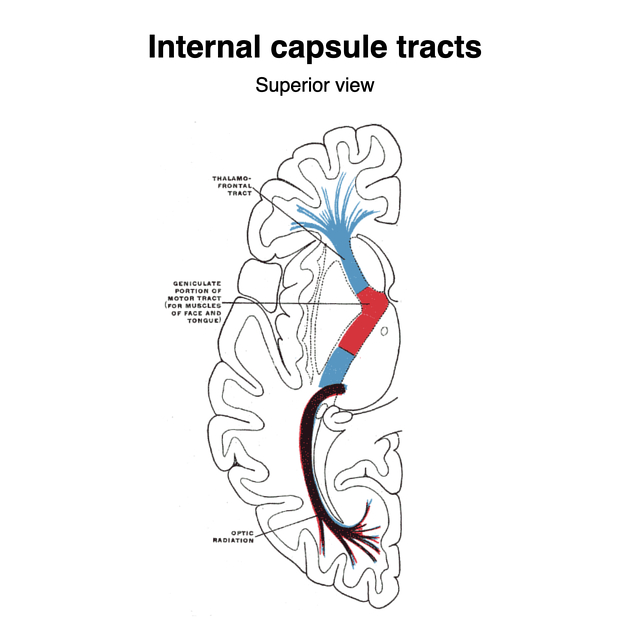
What is the internal capsule?
The internal capsule is a narrow, compact bundle of fibers that passes between the thalamus and the basal ganglia. An area where all the motor and sensory fibers come together in one place
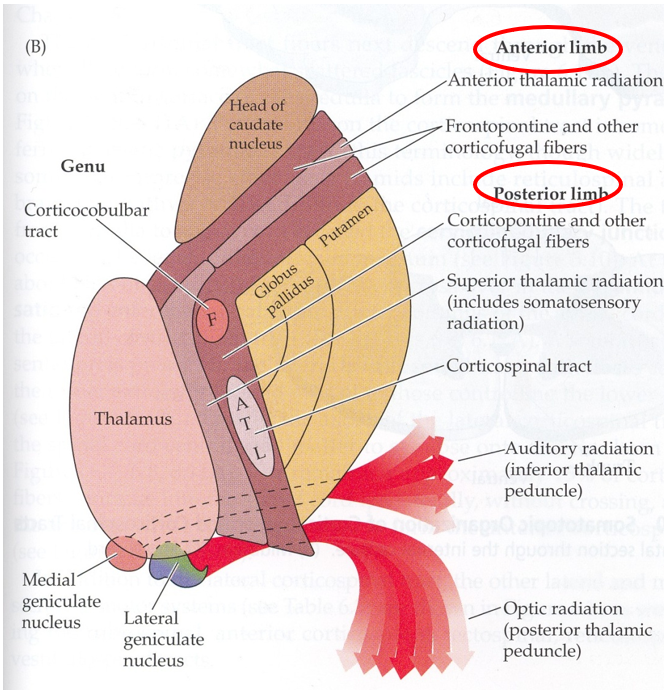
What will occur if the internal capsule is injured?
Only motor pathways affected (no sensory) on the opposite side
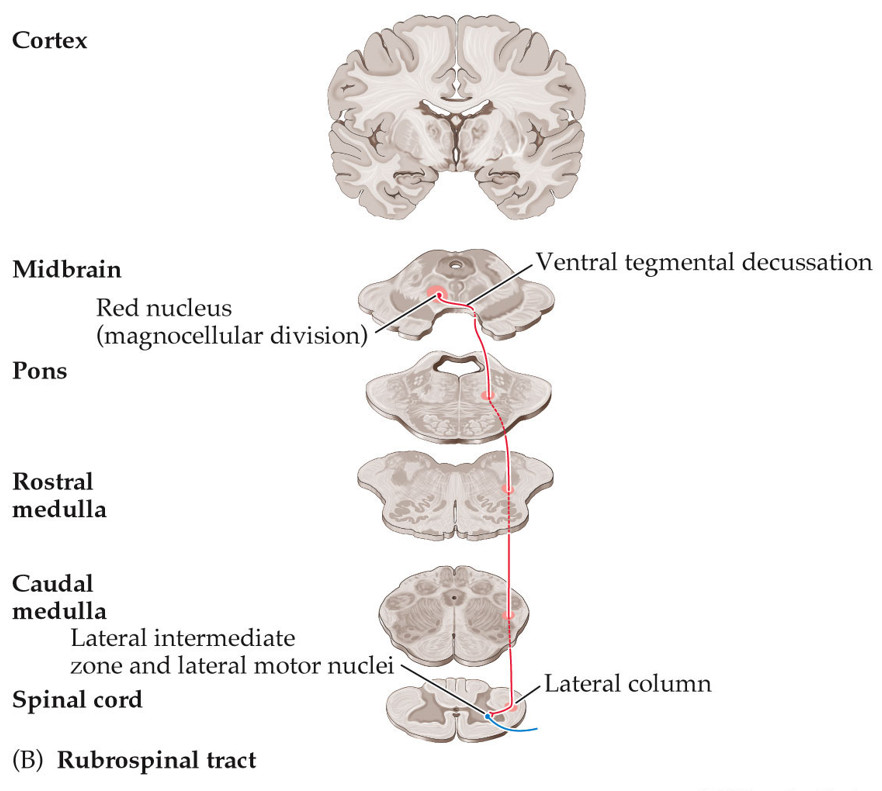
What is the rubrospinal tract?
The rubrospinal tract is a pathway from the red nucleus in the midbrain to the spinal cord, mainly involved in controlling opposite-side limb movements
What reflex tests the integrity of the corticospinal tract?
Babinski reflex
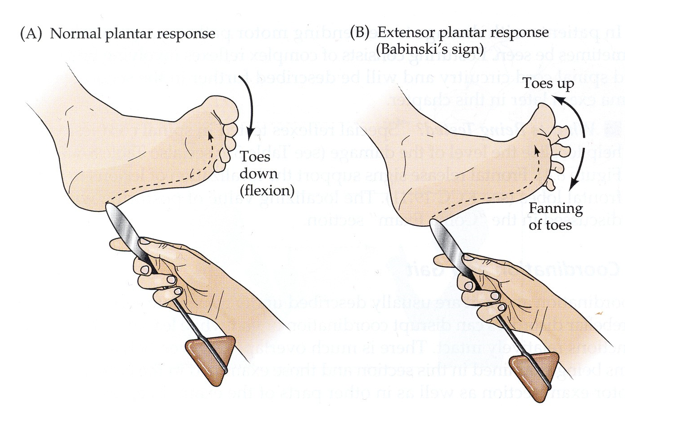
What happens during a positive Babinski reflex?
Upper motor neuron injury (positive): Toes curl up
What happens during a negative Babinski reflex?
No upper motor neuron Injury (negative): Toes curl down
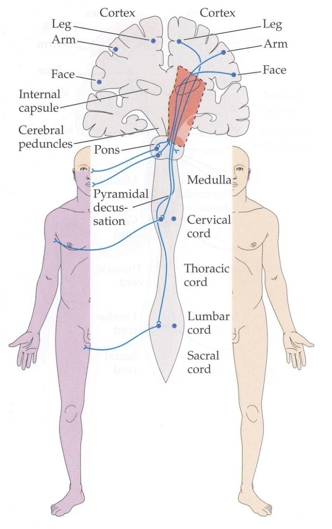
What causes weakness or paralysis on one side of the face, arm, and leg with no loss of sensation?
An injury to the internal capsule. This area of the brain acts like a highway for motor signals. When damaged, it can disrupt movement on one side of the body (face, arm, and leg) while leaving sensation intact.
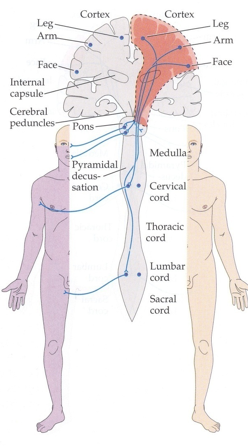
What causes weakness or paralysis on one side of the face, arm, and leg, and sensory loss, vision problems, or difficulty with complex tasks.
Damage to the entire primary motor cortex is likely.
That is the area of the brain controls movement for the face, arm, and leg on the opposite side of the body. If this region is affected, it can cause weakness or paralysis in all three areas at once. (Stroke patients)
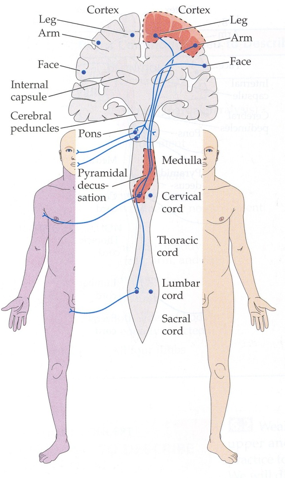
What causes weakness or paralysis in the arm and leg on one side, but the face is not affected. Only body affected.
Damage in either the arm and leg area of the motor cortex or the corticospinal tract between the lower medulla and C5 level.
Cannot be a spinal cord injury as those injuries affect sensory and motor information
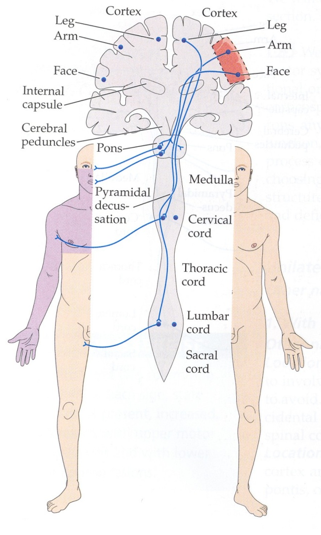
What causes weakness or paralysis on one side of the face and arm, but not the leg?
Likely involves damage to the face and arm areas of the primary motor cortex on the opposite side of the brain.
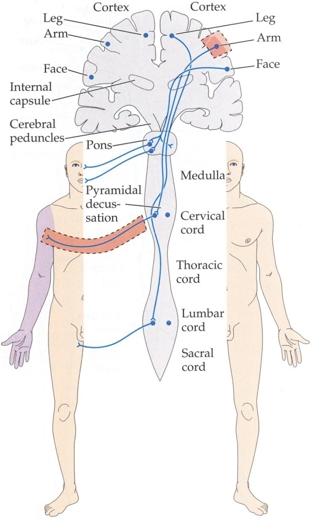
What causes weakness or paralysis in just one arm (brachial monoparesis)?
Likely due to a problem in the arm area of the primary motor cortex on the opposite side of the brain, possibly from a small stroke in the middle cerebral artery (MCA).
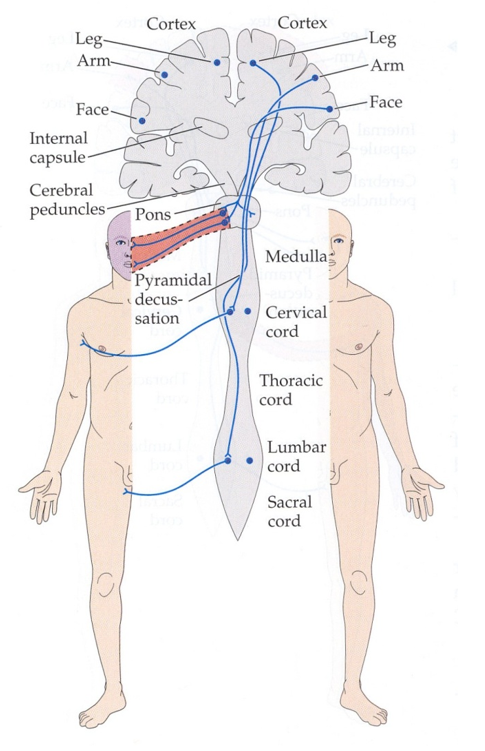
What causes weakness or paralysis on one side of the face, commonly seen in Bell's palsy?
Likely due to an issue with the facial nerve (CN VII), which controls facial muscles.
If the pons is affected, it may also impact other cranial nerves, such as CN VI (eye movement) and CN V (facial sensation).
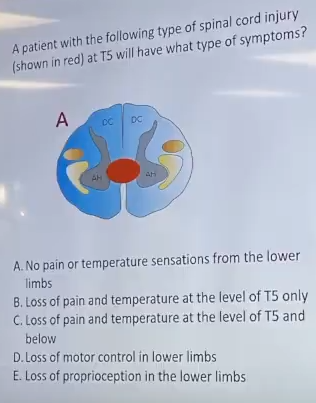
A patient with the following type of spinal cord injury (shown in red) at T5 will have what type of symptoms?
Loss of pain and temperature at the level of T5 and below
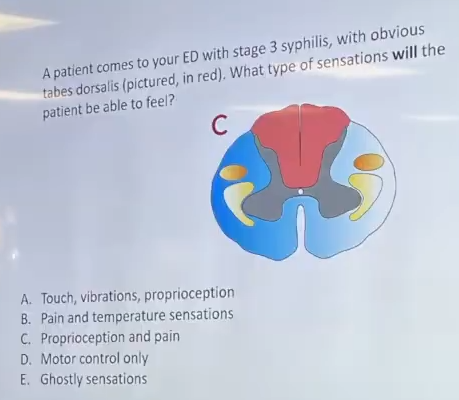
A patient comes to your ED with stage 3 syphilis, with obvious tabes dorsalis (pictured, in red). What type of sensations will the patient be able to feel?
Pain and temperature sensations. They lost touch, vibrations and proprioception