Honor Economic Unit 1 Test; The Basics of Economics
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is a commercial Bank?
accepts deposits, offers, checking account services, various loans, offers basic financial products, like certificates of deposits (CD’s)/ mutual funds
What kind of services do commercial banks offer?
Certificates of deposit (CD’s)/ mutual funds
What is a credit union?
type of financial cooperative that provides traditional banking services, ranging in size from small, volunteer-only operations to large entities.
what are three examples of commercial banks?
Bank of America
Citibank
Chase Bank
List 3 examples of credit unions?
Edward’s Federal Credit Union
Welcomed Credit Union
Northrop Grumman Federal Union
Logic Federal Credit Union
What are deposit accounts?
accounts that let you add money to the account
what is the difference between a checking and a savings account?
checking- regular expenses
saving- saving for emergencies/ something you really want
what is the lowest credit points you can have?
400
what should you maintain your credit score at?
750-800
What does a debit card let you do?
Deposit cash into and withdraw it from your checking account
what does credit allow you to do?
loans, student loans, (best way to bring up your credit score), consumer installment
why do you need to watch gimmicks on credit?
some banks have “mini games” to keep you using your credit card
Economics is the study of…
how people make choices to satisfy their wants and mainly their needs best.
define opportunity cost
can be simply defined as what we give up to get something else
Resources might be described as…
potential opportunity costs, things we might give up to get something else
define trade-offs
all alternatives given up when choosing one action over another
define relationship between individuals and trade-offs
decide what is important to personal needs
define relationship between business and trade-offs
companies having to give up something
define relationship between society and trade-offs
decisions here can avoid wars or cause riots in the streets
what does it mean when you are thinking at the margin?
when you decide how much more or less to do
(goods and services) define goods
physical objects such as shoes, shirts, or i-pods
(goods and services) define services
Actions or activities that one person performs for one another (haircuts or dental checkup)
Define factor of production (land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship)
once we decide to use a resource to make something else
define Land
all natural resources used to produce good/ services (farms, coal, water, forest)
Define Labor
efforts a person devotes to a task→ person is paid
define Capital
any human =-made resource that is used to create other goods and services
Define Entrepreneurship
ambitious leaders decide to combine land, labor, and capital resources to create good/ services (Bill Gates of Microsoft, Henry Ford)
What goods and services should be produced?
Societies need to decide what to produce to satisfy needs and wants. How many resources need to be used on defense, education, public health, consumer goods.
How should these goods and services be produced?
This question can be the most important. The countries of the world need to balance their resources carefully so they are not all used up on a few needs and wants
Who consumes these goods and services?
Once the items are produced a society must determine who receives these items. Example might be during times of war the army may get more goods than the regular population
economic efficiency
making most of resources
economic freedom
freedom from government interaction in production/ distribution of goods/ services
economic growth
societies pursue additional goods, such as environmental protection
economic equity
fair distribution of wealth
traditional economies
rely on habit, custom or ritual to decode what to produce, how to produce it, whom to distribute to
Mixed economies
systems combine tradition and free market w/ limited gov intervention
authoritarian economy
questions left to leaders, people make things they’re told
market economy
difficult to understand or authority to answer economic questions, how do we decide what to make
what does a production possibilities graph show?
alternative ways that an economy can use its resources
Production possibilities frontier is what?
the line that shows the max possible output of that economy.
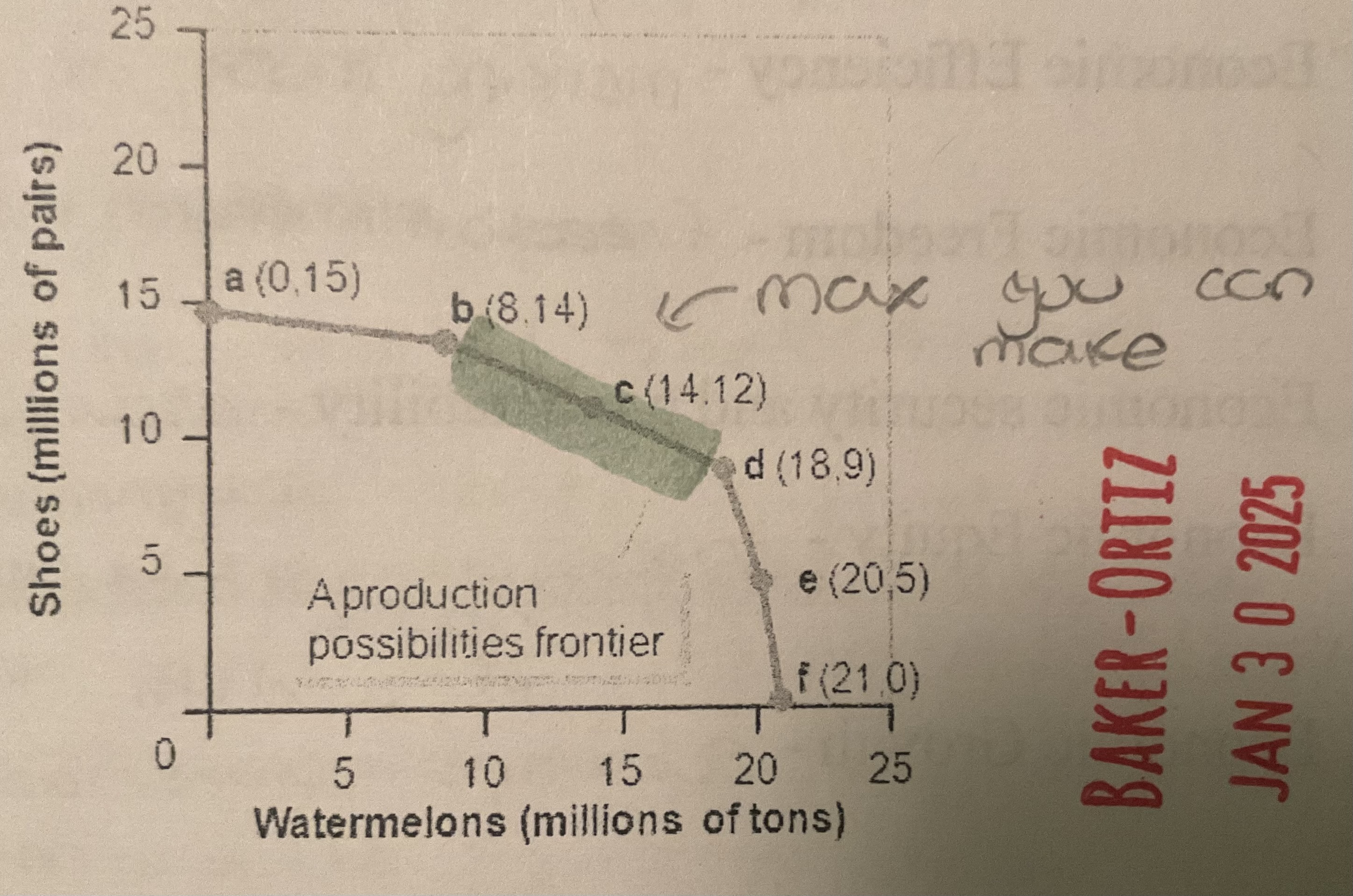
Moving to point C, with all our specialized watermelon resources already being used, we must give up lots of shoes to get watermelons like at point D. In other words,
the more watermelons we produce, the greater the opportunity cost. This is because our resources are specialized
Label all terms. Important!!
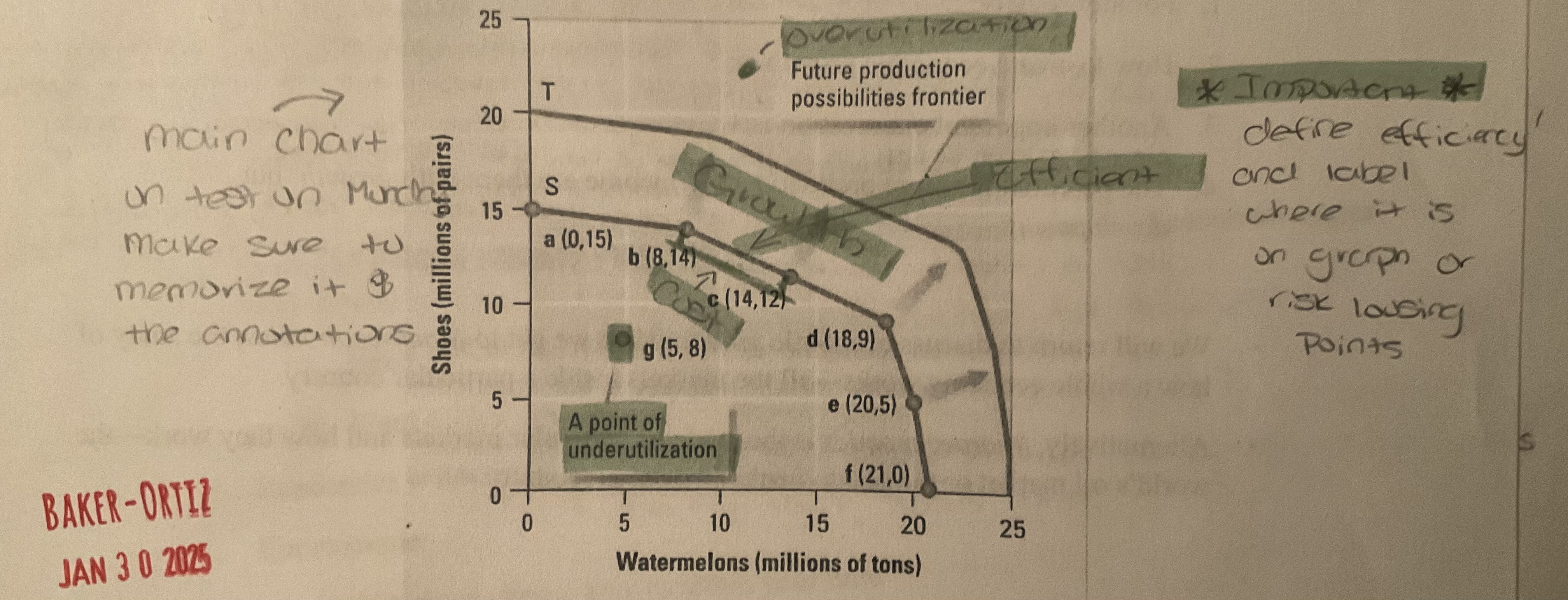
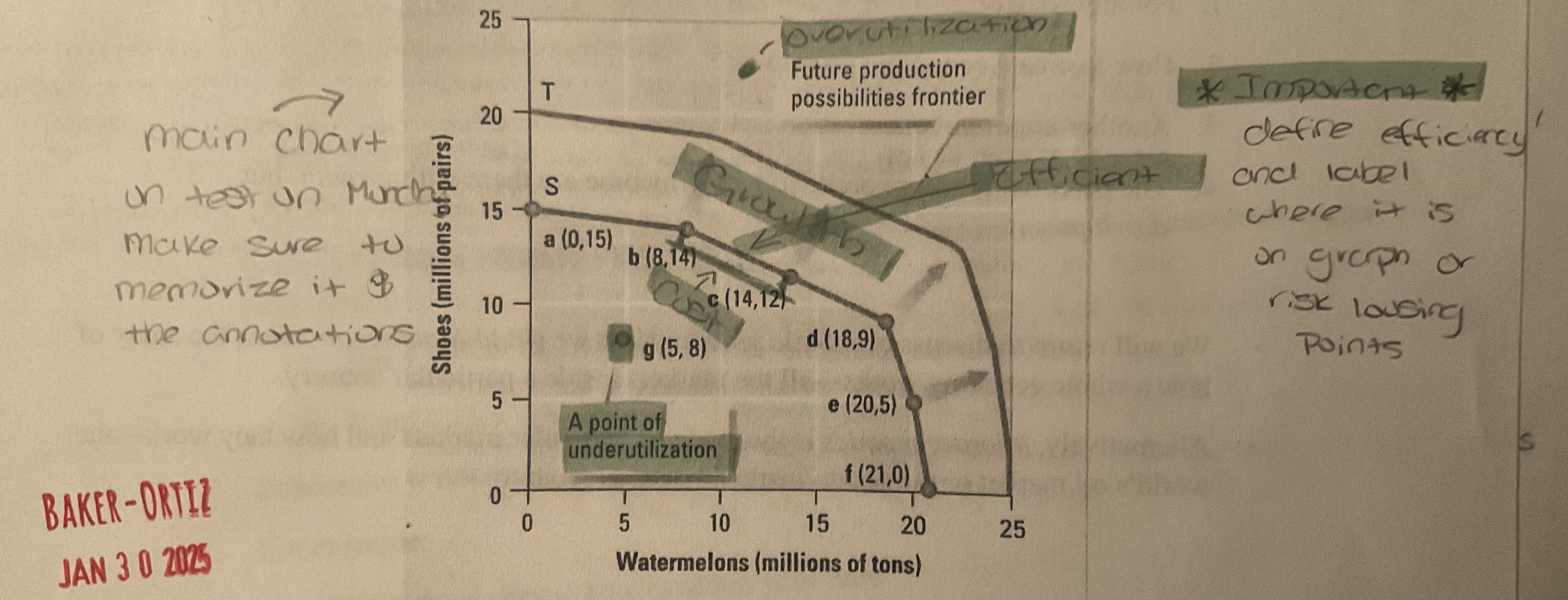
Growth (see above)
as shown above, if more resources became available, or if technology improves, an economy can increase its level of output and grow. When this happens the entire production possibilities curve “shifts to the right”
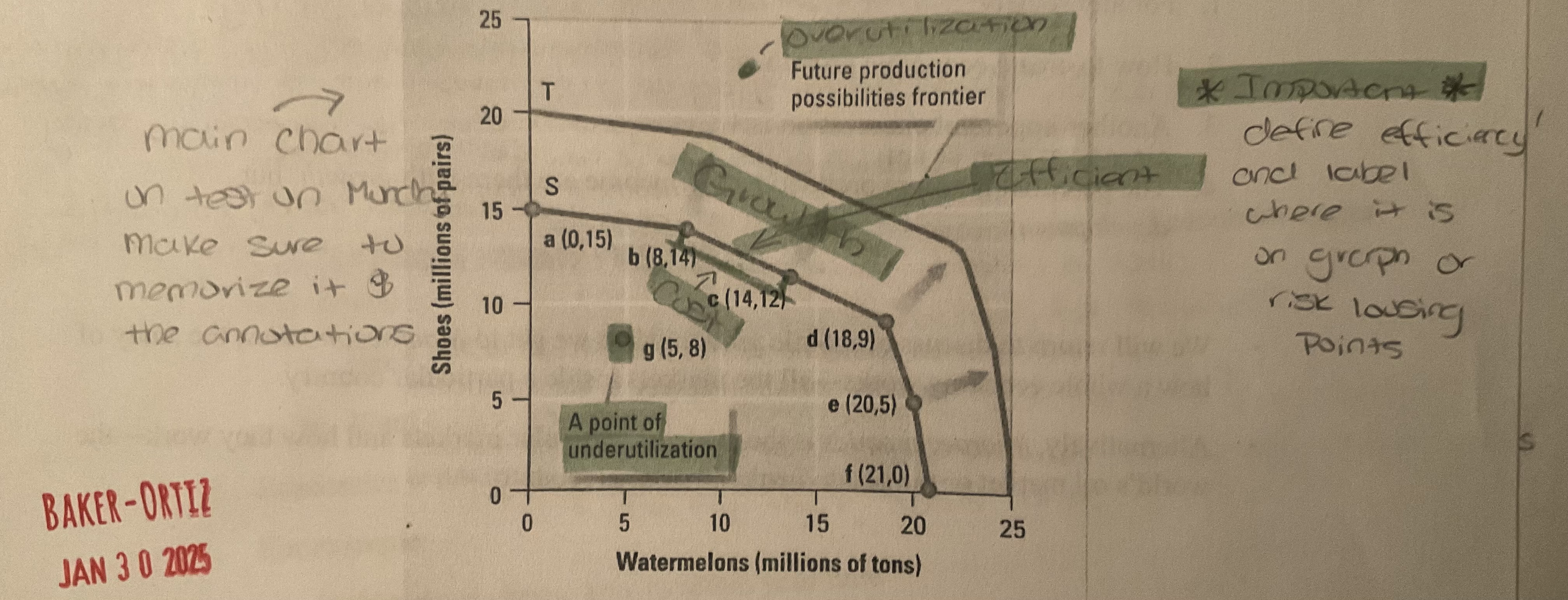
Cost (see labeled on image)
a production possibilities graph shows the cost of producing more of one item. To move from point C to Point D on this graph has a cost of 3 million paires of shoes.
define over utilization
no more product (you’ve used it all up)