BIO 111 Exam 1 flash cards
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
160 Terms
Which of the following class of biomolecules is NOT considered as a true polymer?
nucleic acids
lipids
protiens
carbs
lipids
Why can humans digest starch but not cellulose?
humans lack the enzyme which recognizes β-1,4-glycosidic linkages
What are the 4 major elements that make up macromolecules?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen
What do we call a reaction where water is removed ?
Dehydration
The complexity and variety of organic molecules is due to the properties of what element?
Carbon
How do you calculate hydrogen ion concentration?
[H+]=10-pH
How do calculate pH from pOH?
pH=14 - pOH
How do you calculate molar concentration aka molarity?
Moles of solute / volume of suction (L)
How much KCl would you need to make a 250 ml of a 1.0 molar solution? KCl has a molecular mass of 74.55 daltons.
18.64
If the H+ ion concentration of a household item is 10-3, what is the concentration (M) of OH-ions?
10^-11
Ph above 7 means basic or acidic?
basic
pH below 7 means basic or acidic?
acidic
Which polysaccharide contains nitrogen and is produced by fungi and most arthropods?
Chitin
You are examining the sequence of a polypeptide (protein) and notice that there is a region of the sequence that contains mostly nonpolar amino acids. As this polypeptide adopts its tertiary structure, where are these amino acids likely to be found?
these residues are hydrophobic and thus should be on the interior away from water
Is non-polar hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
hydrophobic
Is polar hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
hydrophilic
Is water polar or non-polar?
polar
If something has “ose” at the end of word what does that mean ?
It is a sugar
What are the 4 major classes of macromolecules?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
What does dehydration do?
removes a water molecule, forming a new bond
What does hydrolysis do?
adds a water molecule, breaking a bond
What are the individual subunits is macromolecules?
monomers
What is a polymer?
a bunch of monomers bonded together by covalent bonds
What are the 3 subtypes of carbs ?
Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, and Polysaccharides
What type of carb is also known as simple sugars?
monosaccharides
How many carbons are in Trioses sugars?
3-carbons
How many carbons are in Pentoses sugars?
5-carbons
How many carbons are in Hexoses sugars?
6-carbons
Glucose, Galactose, and Fructose all have the same formula, what makes them different?
their structure
What chemical shape are monosaccharides found in?
rings
What are disaccharides?
two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic linkage
What are polysaccharides?
a long chain of monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages
What is the function of polysaccharides?
energy storage and provides structure to cellulose and chitin
What is Amylose?
unbranched glucose monomers in a 1-4 glycosidic bonds
What is Amylopectin?
branched glucose monomers in a 1-4 and a 1-6 glycosidic bonds
How can polysaccharides be distinguished?
their linkages
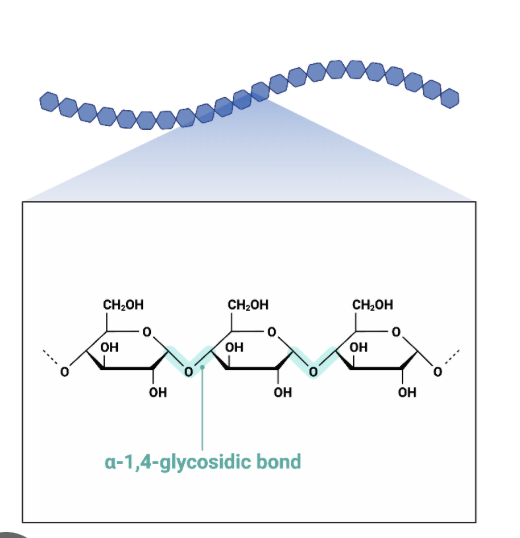
What type of polysaccharide is this ?
Amylose
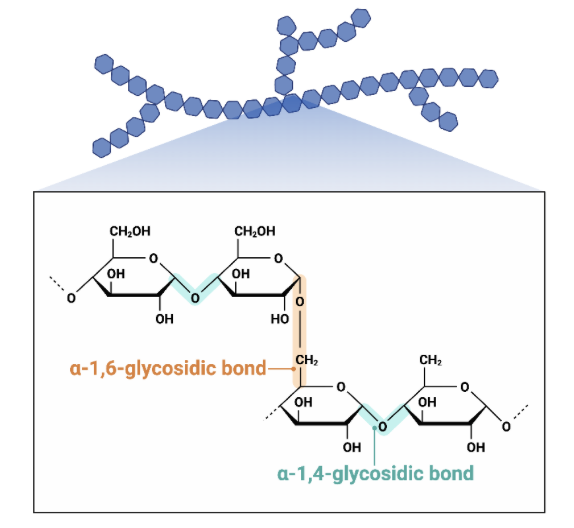
What type of polysaccharide is this?
Amylopectin
Most organisms cannot digest?
cellulose
Can glycogen be digested by humans ?
yes
What polysaccharide is found in the exoskeleton of arthropods and in fungal cell walls?
Chitin
On the molecular level what makes Chitin different than the other polysaccharides?
it contains nitrogen
What happens when CO2 dissolves in the ocean?
from carbonic acid causes ocean to be more acidic
What happens to pH when H+ increases?
pH decreases (more acidic)
What type of covalent bonds are in Methane and Ethane ?
single non-polar covalent bonds
What type of covalent bonds are in Ethene?
non polar sigma and pi bonds
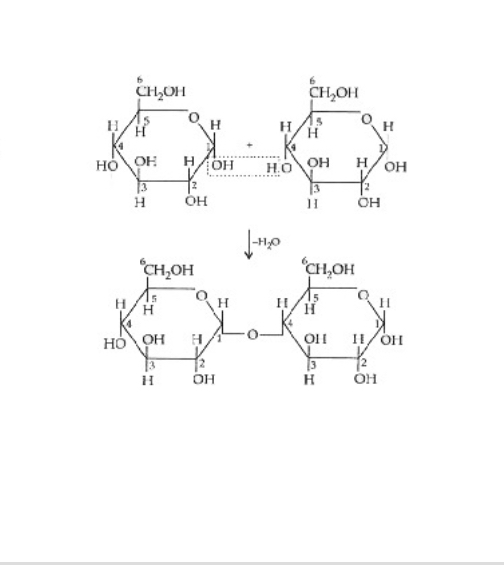
What kind of reaction is this?
dehydration
What is a glycosidic bond?
covalent bonds that link carbs (sugars) to another molecule
What property of water is a direct result of hydrogen bonding?
surface tension
What is formula of pH?
-log[H+]
What is one mole?
6.02×1023
What makes a symmetrical molecule?
when there are 4 different things attached to a carbon
What does a catholic enzyme do?
break down substrates
What does an anabolic enzyme do?
build more complex molecules
What are amino acids ?
monomers that make up proteins
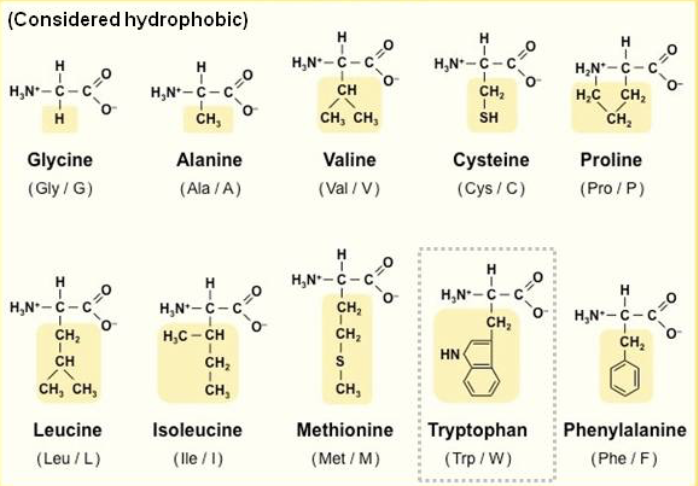
is this a polar or non polar amino acid?
non-polar amino acid
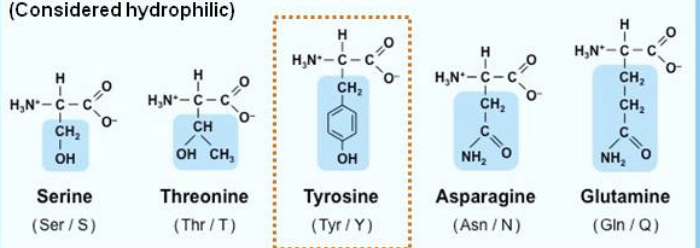
is this a polar or non polar amino acid?
polar amino acid
What level of protein structure is this ?
primary
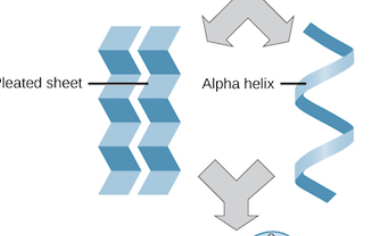
What level of protein structure is this ?
secondary
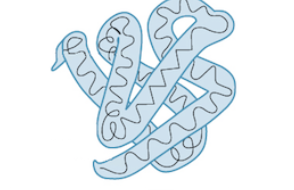
What level of protein structure is this ?
tertiary

What level of protein structure is this ?
quaternary
In sickle cell disease what level of protein structure is affected?
primary level
Why are unsaturated fats liquid?
Because the double bonds between carbons make it flexible and there are less hydrogens present
Why are saturated fats usually solid?
Because it doesn’t contain any double bonds and has a lot of hydrogens.
what is hydrogenation?
adds hydrogens to a compound, usually converts unsaturated fats to saturated fats.
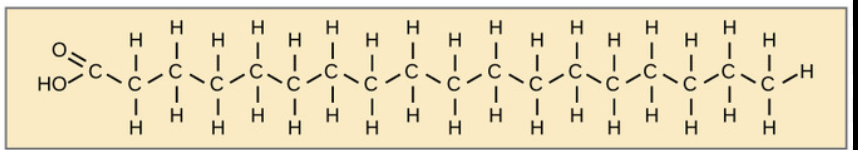
what is this?
saturated fat
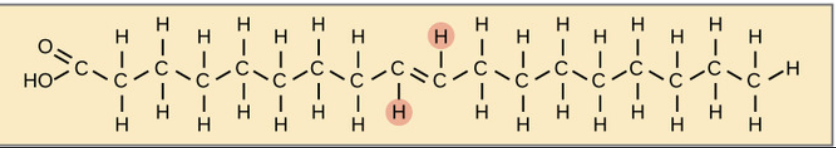
What is this?
unsaturated fat (cis)
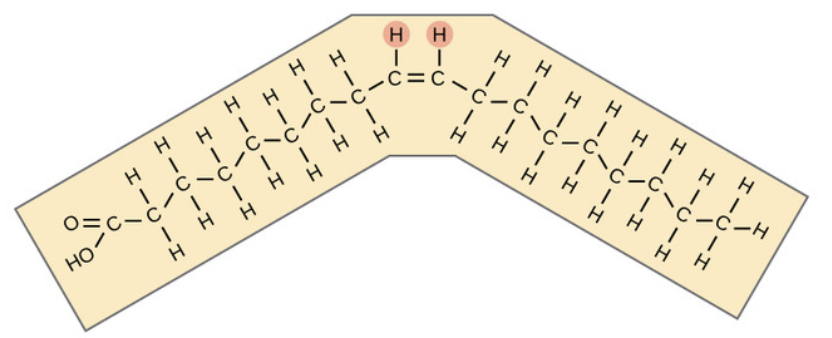
What is this ?
Trans fat
What is one type of stereo that we covered, it is found in cell membranes ?
cholesterol
What are the nitrogenous bases for purines?
Adenine and Guanine (two pure AGgies)*****
What are the nitrogenous bases for pyramines?
Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil
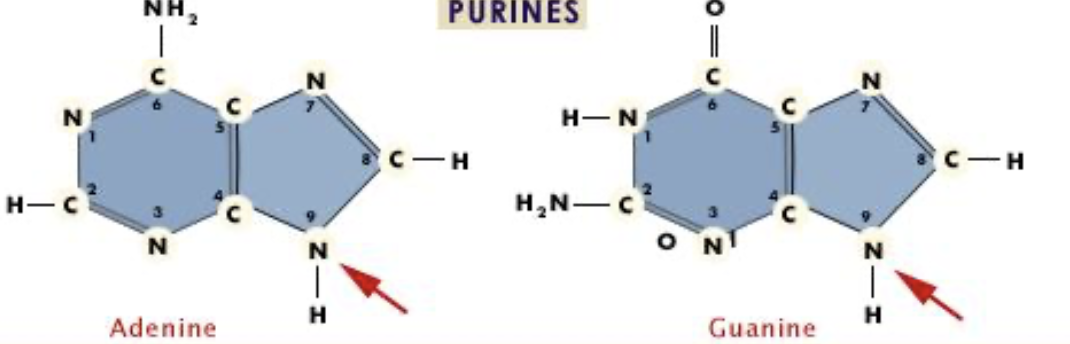
are these purines or pyrimidines?
purines
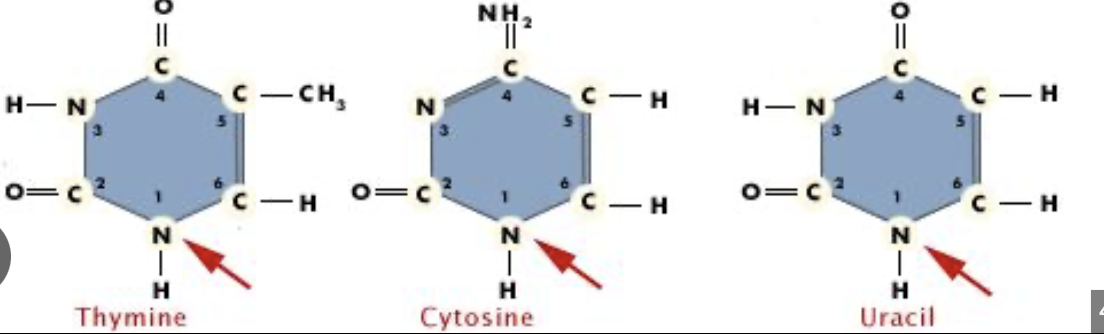
are these purines or pyrimidines?
pyrimidines
are hydrogen binds weak or strong?
weak
What is the function of DNA?
Carries and stores genetic information
What is the function of RNA?
involved in protein synthesis
What is natural science?
The study of the physical world, its phenomena, and processes
What are the two main types of scientific reasoning?
Inductive reasoning (specific → general) and deductive reasoning (general → specific)
What is the difference between discovery science and hypothesis-driven science?
Discovery science is based on observations; hypothesis-driven science tests predictions with experiments.
How is a scientific theory different from a hypothesis?
A theory is broad, well-supported, repeatedly tested, and widely accepted, but still open to revision.
What are the tenets of the cell theory?
All organisms are made of cells.
Life’s chemical reactions occur in cells.
Cells come from pre-existing cells.
Cells contain hereditary info (DNA).
What is the theory of evolution?
Organisms change over time; Darwin and Wallace proposed natural selection as the mechanism.
What is the biological hierarchy of life?
Atoms → molecules → organelles → cells → tissues → organs → organ systems → organisms → populations → communities → ecosystems → biosphere.
Describe a prokaryote.
circular DNA, no organelles, small
Describe a Eukaryote.
linear DNA, organelles present, larger
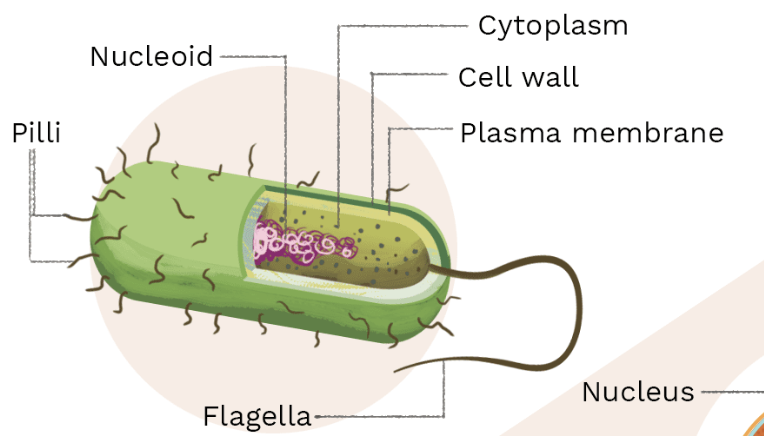
What type of cell is this?
prokaryote
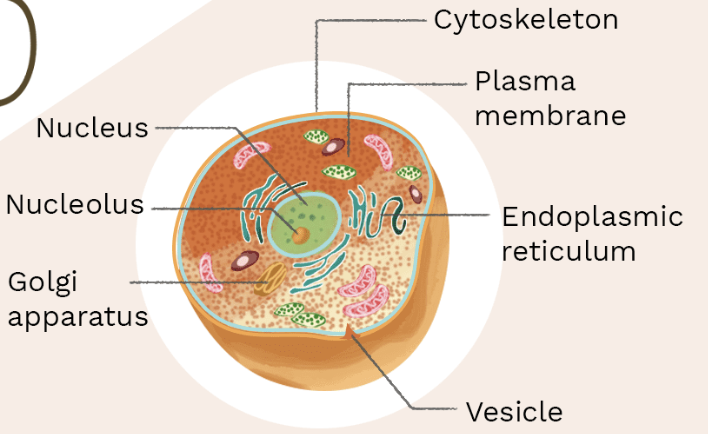
What type of cell is this ?
eukaryote
What is the order of taxonomic ranks?
Domain → Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species.
What the Mnemonic to help remember taxonomic ranks?
King Philip Cried Out For Goodness Sake
What do all forms of life share?
DNA, genetic code, transcription & translation, 20 amino acids in proteins, and ribosomes.
What are subatomic particles and their charges?
Proton (+), neutron (0), electron (–).
What are isotopes?
variants of the same element with different numbers of neutrons.
What determines an atom’s chemical behavior?
The number and arrangement of valence electrons
Difference between polar and nonpolar covalent bonds?
Polar: unequal sharing (H2O). Nonpolar: equal sharing (O2, CH4)
What is an ionic bond?
Attraction between oppositely charged ions formed by electron transfer.
What are weak bonds, and why are they important?
Hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals interactions; they allow flexibility, reversibility, and stabilize large molecules.
What are the 4 emergent properties of water?
Cohesion/adhesion, moderation of temperature, expansion upon freezing, solvent versatility.
Why does ice float?
Hydrogen bonds form a crystalline lattice making ice less dense than liquid water.
Do acids decrease or increase H+ concentration?
increase
Do bases decrease or increase H+ concentration?
decreases