The types of unemployment
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is structural unemployment?
When the pattern of demand and production changes leaving workers unemployed in labour markets where demand has shrunk.
Examples include regional, sectoral or technological unemployment which result from labour immobility. Structural unemployment is a long-term type of unemployment which can have major problems socially and economically as it can lead to a loss of human capital and reduction in economic growth.
What is geographical unemployment?
Refers to the inability of workers to move from one area to another.
What is occupational immobility?
refers to the inability of workers to move between jobs due to lack of appropriate skills.
What is long term unemployment?
The number of people out of work for at least one year.
What is deindustrialization?
a fall in the proportion of national output accounted for by the manufacturing sector of the economy.
Structural unemployment examples in the UK: automation.
The increase in the use of artificial intelligence in industries across the UK has contributed to a growing lack in demand for jobs that involve certain skills, for example, administrative roles.
Structural unemployment examples in the UK: deindustrialization.
Manufacturing industry in the UK has been declining as our economy moves towards services, however, this has led to a decrease in the demand for workers in sectors like steel and coal mining. In addition to this, the specialisation of workers in these sectors has made it harder for those people to transition to other sectors.
Structural unemployment examples in the UK: geographic mismatch.
This occurs when the places where job opportunities are available do not line up with where the job seekers live. If jobs more local to the job seeker require high qualifications, this can create structural unemployment.
Structural unemployment examples in the UK: skills gap.
Skills required for many jobs now available are constantly changing as a result of new technologies being introduced. This leads to a skills gap between the worker’s skills and the skills employers are looking for.
What is Frictional unemployment?
When people move between jobs.
What is frictional unemployment due to?
New workers entering the labour market or people who have chosen to leave their previous job- These people may take a while to locate and gain a job that they are willing to accept.
What will increase the amount of frictional unemployment?
Imperfect information about job opportunities will increase the amount of frictional unemployment. It will therefore always be present in the economy.
What is frictional unemployment sometimes called?
search unemployment and can be voluntary.
Why is frictional unemployment not a major problem?
it is only short term.
What is an example of frictional unemployment?
Emergence from the COVID-19 pandemic saw frictional unemployment, for example, when employers asked employees to return to work in person after they’d worked remotely for many months. Many employees who preferred to work from home voluntarily left their jobs in search of roles that better fit their needs.
How will frictional unemployment be affected by; the level of redundancies?
If there is a high amount of redundancies then many people will be looking for a job at the same time and in the same sector so it will take longer for people to find an alternative job.
How will frictional unemployment be affected by; the level of unemployment related benefits?
people who are made redundant are given a payout so have saving making them unable to claim benefits
high benefits means people can spend more time looking for work
What is seasonal unemployment?
sometimes considered to be a type of frictional unemployment
Seasonal unemployment is unemployment caused when an industry only operates during certain times of the year
Certain industries/ occupations are seasonal in nature
It is also often regional in nature e.g. Cornwall has seasonal unemployment in winter. Spain has a problem with seasonal unemployment due to its large tourism sector.
What is cyclical employmet caused by?
a lack of Aggregate Demand- when there is a severe slowdown in economic growth or a recession.
Why does a lack of AD cause cyclical unemployment?
by factory and office closures and an increase in redundancies. The fall in aggregate demand causes a fall in output in the economy. Firms may reduce their workforce in order to cut costs and maintain their profitability.
What us an example of cyclical unemployment?
During the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, for example, people were confined to their homes, leading many businesses to shut down. During this economic downturn, many employees of those businesses weren’t needed and were left unemployed.
Keynes identified this as the major cause of unemployment in the 1920s and 1930s so it is also sometimes called Keynesian unemployment.
Why is Keynesian unemployment also called ‘demand-deficient’ unemployment?
arises due to a lack of AD
What policies might be appropriate to reduce cyclical unemployment?
can be reduced by increasing AD
fiscal policy- increase government spending but cut taxes
momentary policy- lower the BOE interest rate to incentivise consumption over saving by consumers and encourage investment from firms
Why might there be a time lag between a fall in GDP and a rise in unemployment?
firms are reluctant to make experienced workers redundant as it is covers.difficult to replace them when the economy recovers.
What is real wage inflexibility?
unemployment as a result of real wages (wages after having been adjusted for inflation) being set above the equilibrium wage rate.
This causes an excess supply of labour. Despite the fact that some workers may be prepared to work for less than the minimum wage and companies may employ more workers if they would work for less than the minimum wage, this is illegal so unemployed workers cannot get a job.
What is classical unemployment?
When workers are unemployed because real wages are too high and inflexible downwards, leading to insufficient demand for workers from employers.
This might be caused by a minimum wage above equilibrium wage rates, strong trade union pressure or a high level of benefits deterring some from taking lower paid jobs
What are the best and worse employments to talk about during an essay?

How can real wage inflexibility be shown a graph
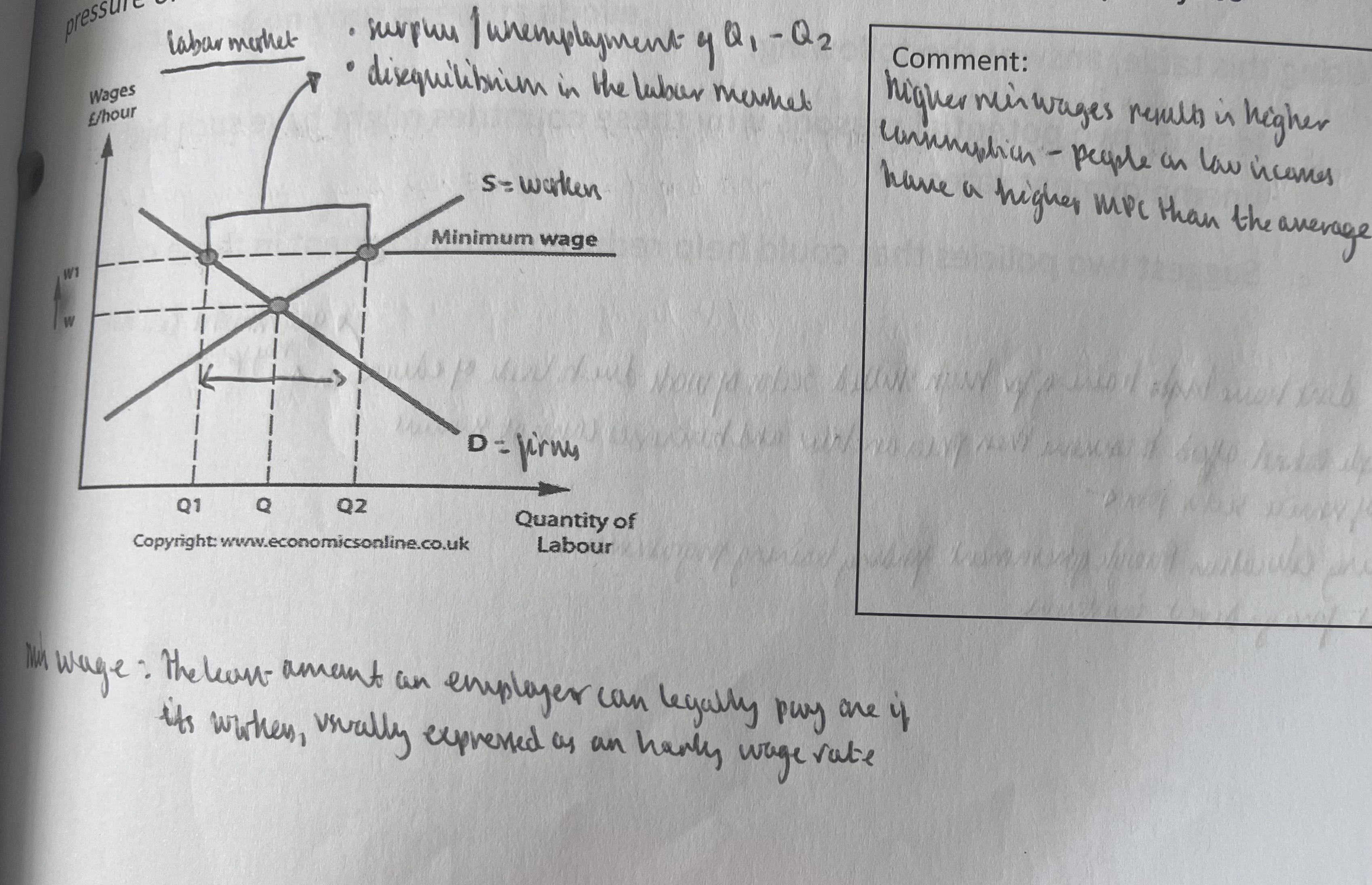
What may low unemployment not reflect a strong economy?
low wages= many people who do not have night training/ education so will be put in jobs that anyone can be trained to do causing them to have a low standard of living or workers will be employed in jobs below their skill level
Insecure job= if their industry is ok longer in demand then workers will not be needed and the skills they have learnt will be the useless ( the gig economy- 0 hour contacts which has insecure pay hours)
Stopped looking for jobs= may not have enough jobs, may claim disability benefits
What are indicators that might provide a fuller picture of economic performance?
GNI per capita
Claimant count
Economic growth
Real wage growth
Why are trade until now less available to push wages above their skill level equilibrium level in most occupation?
tougher laws restricting travel ubtiond
Deindustrialisation- there has to be a decline in the number of workers in traditional industries such as coal, mining, car making and ship building where trade unions were very strong