Protists: Part 1
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
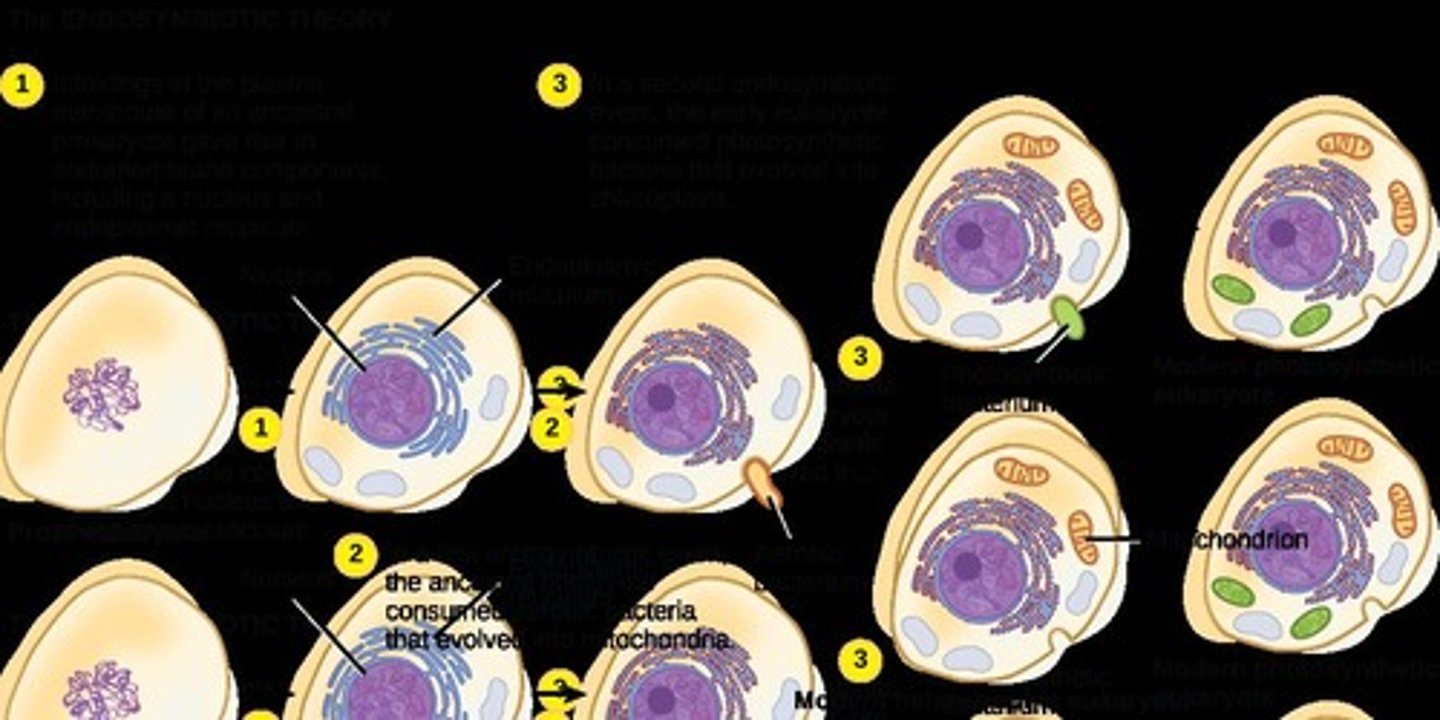
What is the theory of endosymbiosis?
The theory that eukaryotic cells originated through a process where one cell engulfs another, leading to a symbiotic relationship.
Who devised the theory of endosymbiosis?
Lynn Margulis in 1960 at Boston University.
What evidence supports primary endosymbiosis?
DNA in mitochondria and chloroplasts, double membranes, highly folded inner membranes, electron transport chains, and ATP synthases.
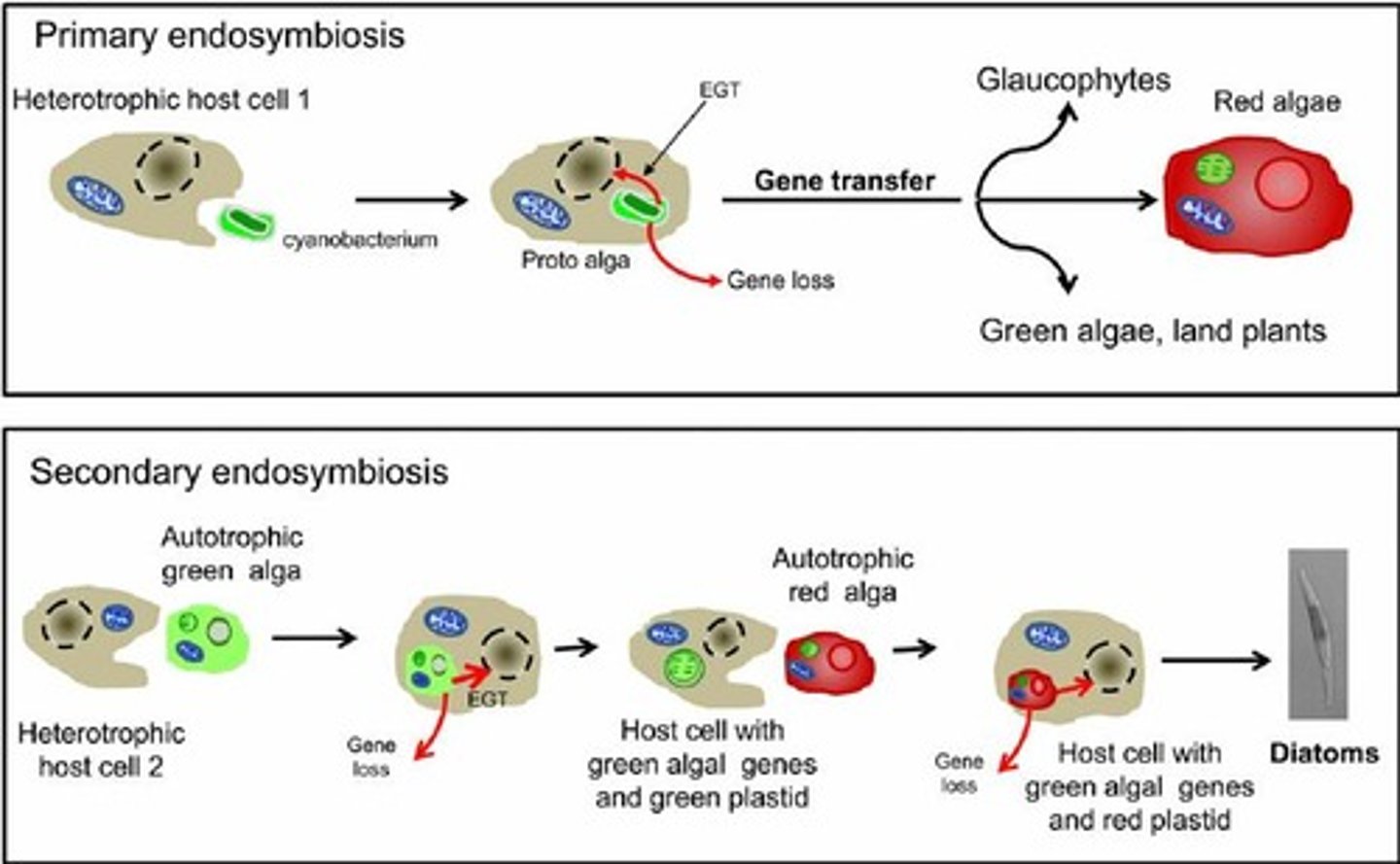
What is secondary endosymbiosis?
A process where some protists have three membranes around plastids instead of four, indicating a more complex evolutionary history.
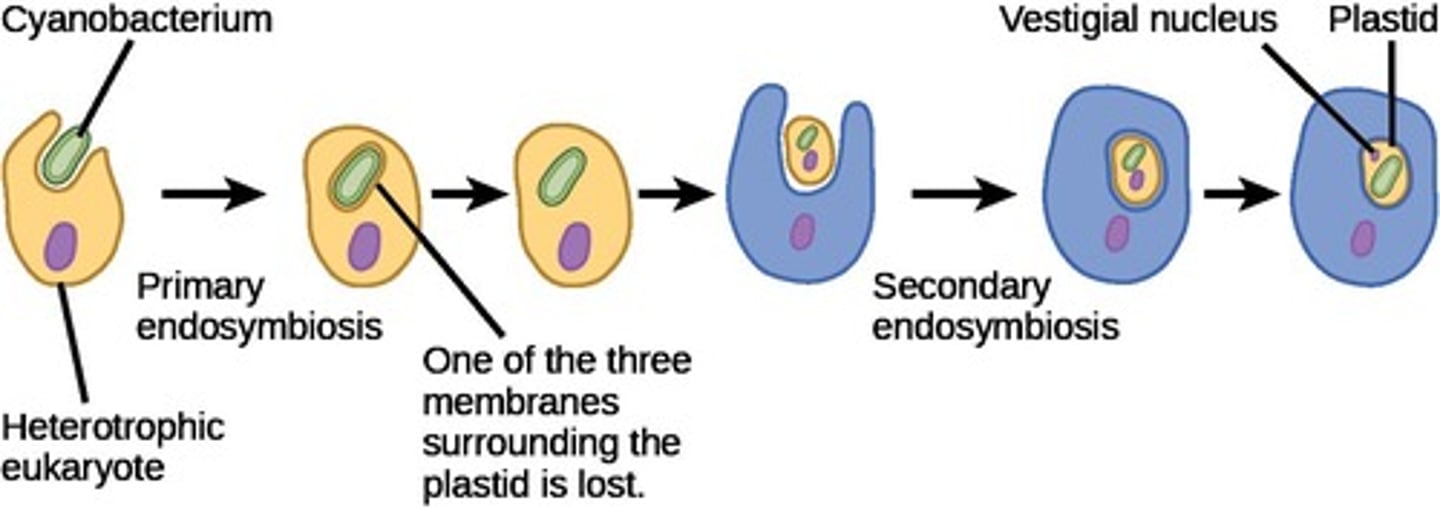
Name three examples of protists that underwent secondary endosymbiosis.
Brown algae, diatoms, and dinoflagellates.
What are the main habitats of protists?
Mostly aquatic environments, including freshwater, marine, and damp soil.
What are the evolutionary trends observed in protists?
Diverse habitats, transition from unicellular to multicellular forms, and varied modes of nutrition.
What types of nutritional strategies do protists exhibit?
Photosynthetic, heterotrophic via ingestion, and heterotrophic via absorption.
What is a characteristic of photosynthetic protists?
All have chlorophyll, many also have carotenoids and other accessory pigments.
What is the feeding strategy of predators among protists?
They surround and engulf prey items.
How do decomposers and parasites obtain nutrients?
They absorb nutrients from their environment.
What is the significance of the eukaryote fossils?
They are approximately 2 billion years old and indicate the early existence of complex life forms.
What role did oxygen play in the evolution of eukaryotes?
The increase of oxygen in the atmosphere facilitated the rapid evolution of eukaryotes.
What type of motion is characteristic of amoeboid protists?
Amoeboid motion, which involves cytoplasmic streaming.
What are examples of protists that move using flagella?
Chlamydomonas, Euglena, and Volvox.
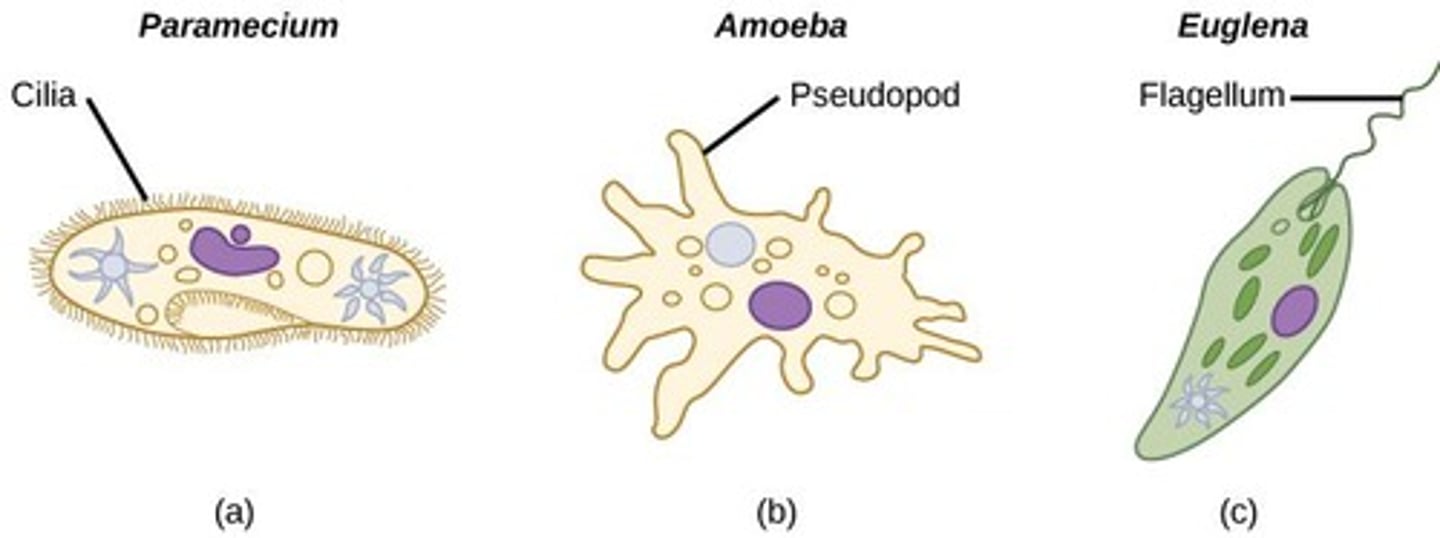
What is a common feature of diatoms?
They secrete mucilage.
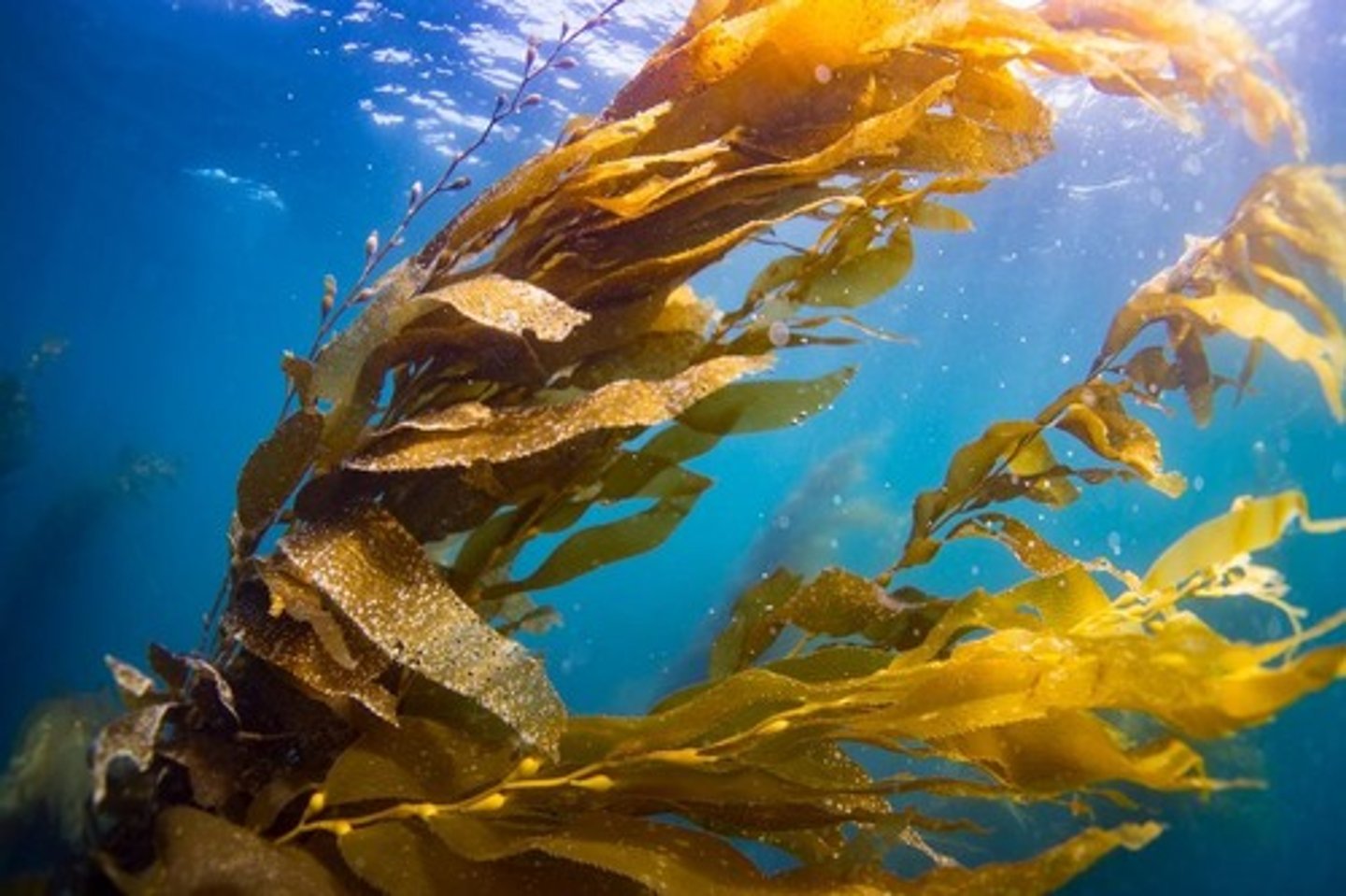
What is the structure of brown algae?
Brown algae like Sargassum can be sessile or float in water.

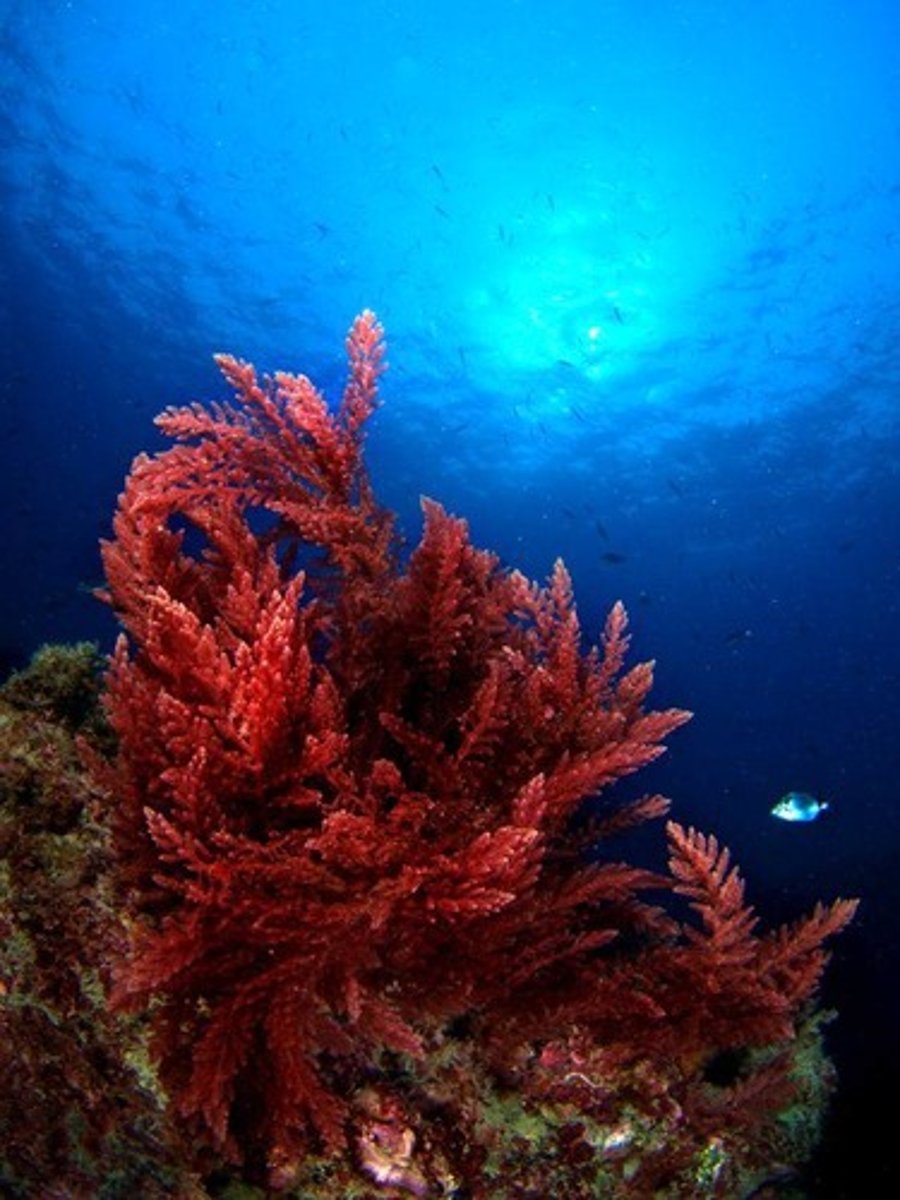
What pigments are found in red algae?
Phycoerythrin, along with chlorophyll.

What is a unique feature of green algae?
They are often referred to as 'green algae' due to their chlorophyll content.
What is the significance of the diversity in protist life cycles?
It reflects the adaptability and evolutionary strategies of protists in various environments.
What is the role of carotenoids in photosynthetic protists?
They serve as accessory pigments that assist in photosynthesis.
What are oomycetes commonly known as?
Water molds.
What is an example of a disease caused by a protist?
Downy mildew on grapes, caused by an oomycete.