Biology 1500 test 2
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Hypothesis on why dragon flies were so big according to Clapman and Karr
Amount of oxygen in the air
Lack of evolved predators
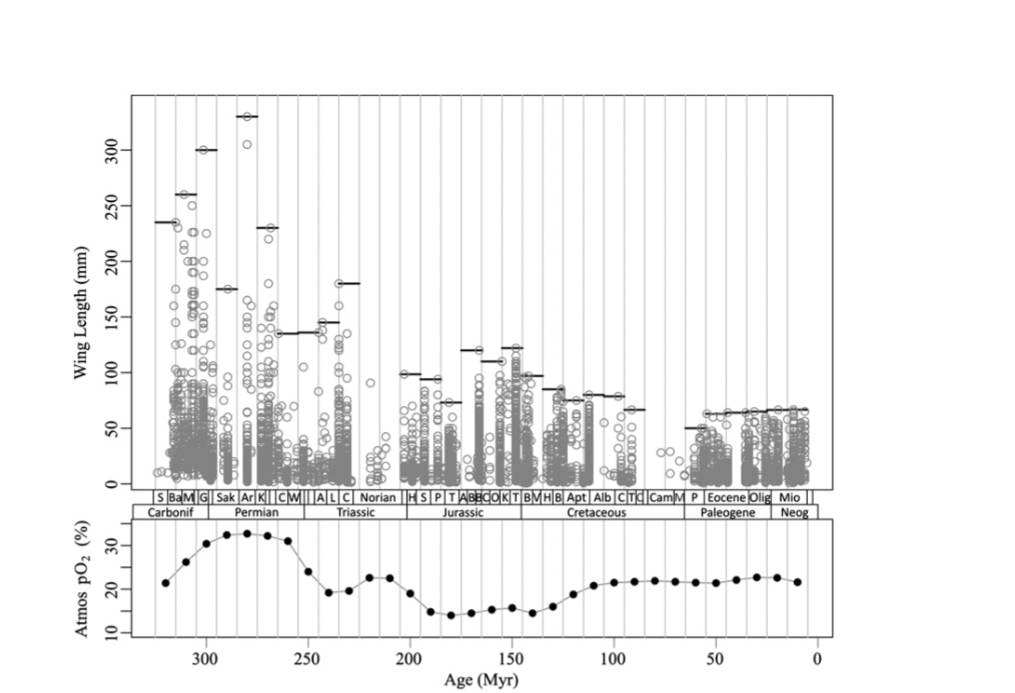
Describe and interpret Figure one of Clapham and Karr
graph relates po2, wing length, and time period. It demonstrates how during the Carboniferous period, wing length was increased as well as po2. This relationship does not always persist, but was true during the Carboniferous period specifically.
Birds evolved which is why dragonflies got smaller
Describe the evidence that supports Clapham and Karr’s conclusions
15,000 Fossils used to determine wing size and age
Partial O2 pressure
Identify the wavelengths (i.e. colors) of light absorbed by chlorophyll
Green light is reflected
wave lengths a plant absorbs are blue, red and violet
What is the product of Photosynthesis
GA3P
Light dependent reactions of Photosynthesis
Sunlight and water make bi product of o2 and product ATP and NADPH
Light independent reactions of Photosynthesis
ATP and NADPH produce glucose from CO2 and water
Takes place in the stoma
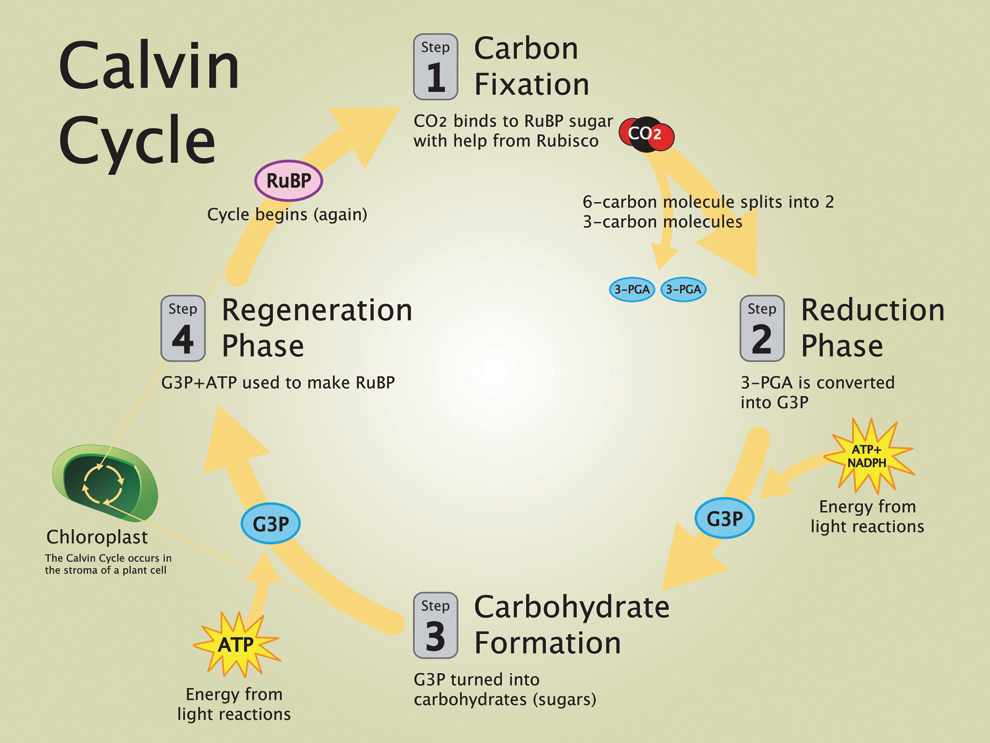
Calvin Cycle
a series of chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and hydrogen-carrier compounds into glucose.
Why is o2 a bi product of Photosynthesis
goes through water photooxydation
water is split apart, releases oxygen
ATP
Adenosine Tri Phosphate
Main transport
Immediate source of energy in cells
Describe chemical and energetic changes that occur as ADP cycles with ATP and back again
ADP gets phosphate to make ATP
ATP is broken Down during calvin cycle resorting back to ADP, then dependent light reaction
ATP has more potential energy then ADP cause of an extra phosphate
How long ago did the Great Oxygenation event take place
2.3-3 BYA
What happened before the great oxygenation event?
All organisms were heterotrophicProkaryotes
What caused the great oxygenation event
Cyanobacteria became prominent and started breathing.
oxygen started escaping into the atmosphere, where it reacted with methane
What happened after the great oxygenation event
Ozone layer was formed
minerals were formed
Snowball iceage
global mass extinction
prokaryotes evolved to be able to use o2; lead to evolution of cellular respiration
DNA
Chromosomes are made up of ____in nucleus
Instructions for genes
Genes
Sections of DNA that code for specific proteins
Allelle
different forms of the same gene
Describe the difference between the various alleles of a gene.
Alleles are more descriptive and determine phenotypic ratio
Explain why one person can have a maximum of two different alleles of a gene.
You inherit one from each parent equaling two
Natural selection
Most fundamental process and characteristic of life
1st Postulate of NS
Phenotypes are variable amongst population, there are a variety of different species and types
2nd Postulate of NS
Off spring have similar phenotypes as parents aka inheritable
3rd postulate of NS
Survival and reproduction depend on Phenotype
4th postulate of NS
Survival and reproduction is not random, those that survive reproduce.
evolution
Change in allele frequencies in a population
population
group of individuals that interbreed
adaptation
trait that increases fitness of individual
fitness
Ability to survive and reproduce in an environment
Kinetic energy
energy that includes movement, heat, light, electricity
Heat
Movement of molecules
light
movement of photons
electricity
movement of electrons
first law of thermodynamics
no energy is created or destroyed, just changes forms
Compare visible light energy with the rest of the electromagnetic spectrum: how is it similar, what makes it special to us?
visible light is something we can see, we cannot visualize radio/ magnetic waves
Describe the potential outcomes of light striking an object
reflected
absorbed
transmitted
Facilitative Diffusion
Passive movement of molecules along concentration gradient
Facilitative diffusion vs diffusion
In simple diffusion, the substance passes between the phospholipids; in facilitated diffusion there are a specialized membrane channels.
Gated proteins
Only allow specific substances and specific amounts through protien channels
when is big body sizes needed
Sexual selection
Temperature
female fecundity
when is smaller body sizes needed
Locomotion
early reproduction
temp in ectotherms
Factors that influence rate of diffusion
Surface area and volume ratio
good for small but not bigger distances
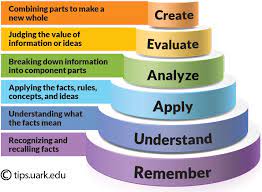
Blooms taxonomy bottom to top
remember
understand
apply
analyze
evaluate
create
Describe the insect respiratory system
Instead of lungs, insects breathe with a network of tiny tubes called tracheae.
Air enters the tubes through a row of holes along an insect's abdomen.
Identify the traits shared by most respiratory systems
moist surface area
thin cells lining respiratory surface
large surface area in contact with outside environment.
What are the two primary functions of all respiratory system
provide oxygen to cells of the body
remove carbon dioxide from body
When Dr. Bush was a young child, she callously tried to kill a grasshopper by holding its head under water. It didn’t work. Why not?
Insects do not inhale through mouths
What is a respiratory surface is and how do gases move across it
Gas exchange occurs across this membrane and is diffusion of oxygen into and carbon dioxide out of the blood
What molecule is the source of the electrons in the electron transport chain?
What molecule is the source of the oxygen that is released as a byproduct of photosynthesis?
What molecule is the source of the protons that are used to establish the proton gradient?
water
What is the proton gradient used for?
Making ATP
What does the term ‘carbon fixation’ refer to?
Making organic compounds