COMD 3800 chapter 6/7/8 Articulation, Resonance, and Ingestion
1/181
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
182 Terms
articulation
Speech Definition:
Process of bringing mobile and immobile
articulators into contact to shape the sounds of speech.
anatomy Definition:
to connect or join together
resonation
the sound quality given to voiced sounds by the vocal tract
deglutition
swallowing
mastication
chewing
vocal tract
consist of the
1. pharynx
2. nasal cavity
3 oral cavity
mobile articulators
1. lips
2. tongue
3. mandible
4. soft palate (velumn)
5. pharynx
6. cheeks
7. fauces (faucial
pillars)
immobile articulators
1. alveolar ridge of maxillae
2. hard palate (palatine processes of the maxilla & horizontal plates of the palatine bones)
3. teeth
bones of the face
- mandible
- maxillae
- palatine bone
- nasal bone
- inferior nasal conchae
- vomer
- zygomatic bone
- lacrimal bone
- hyoid bone
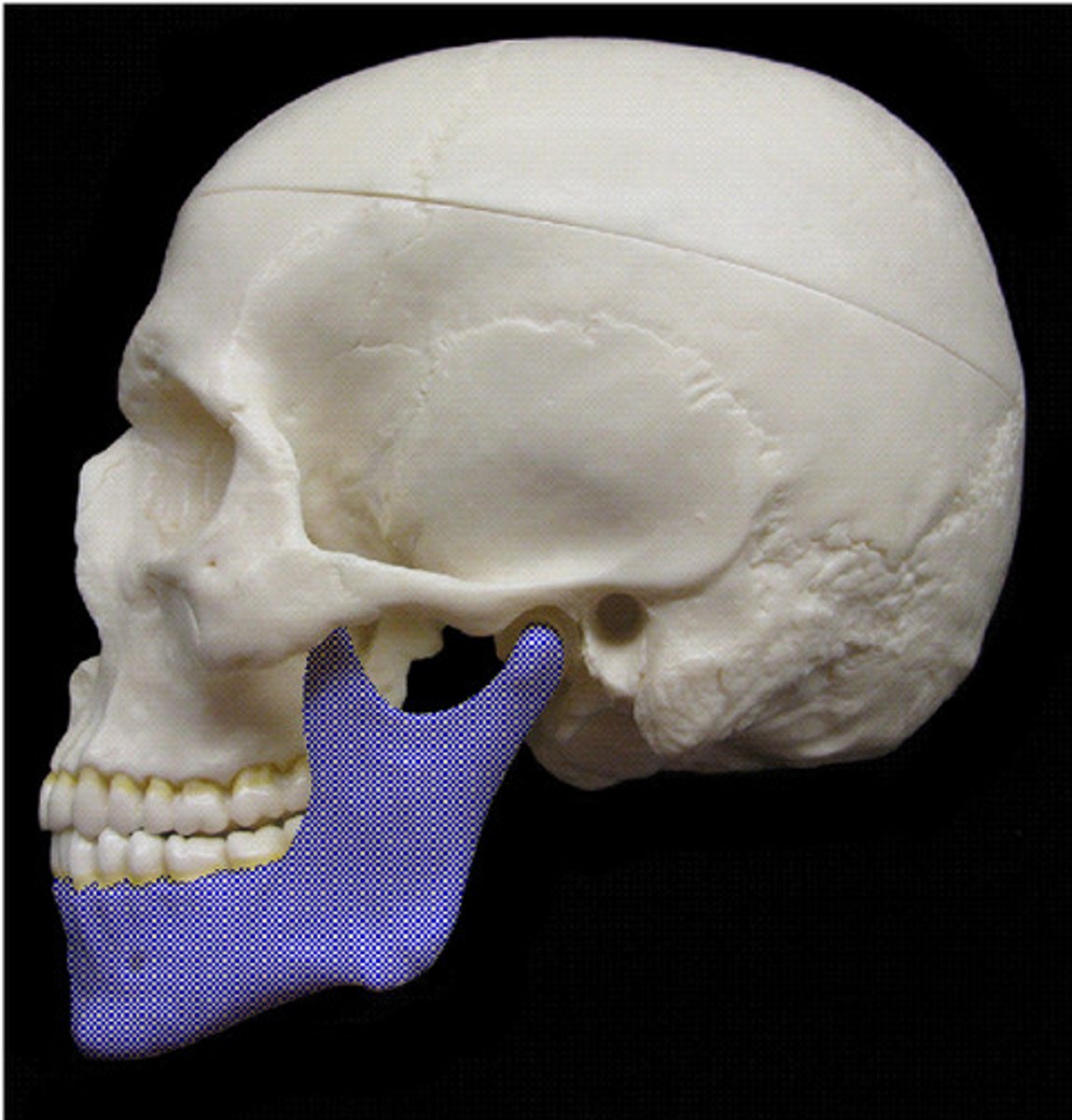
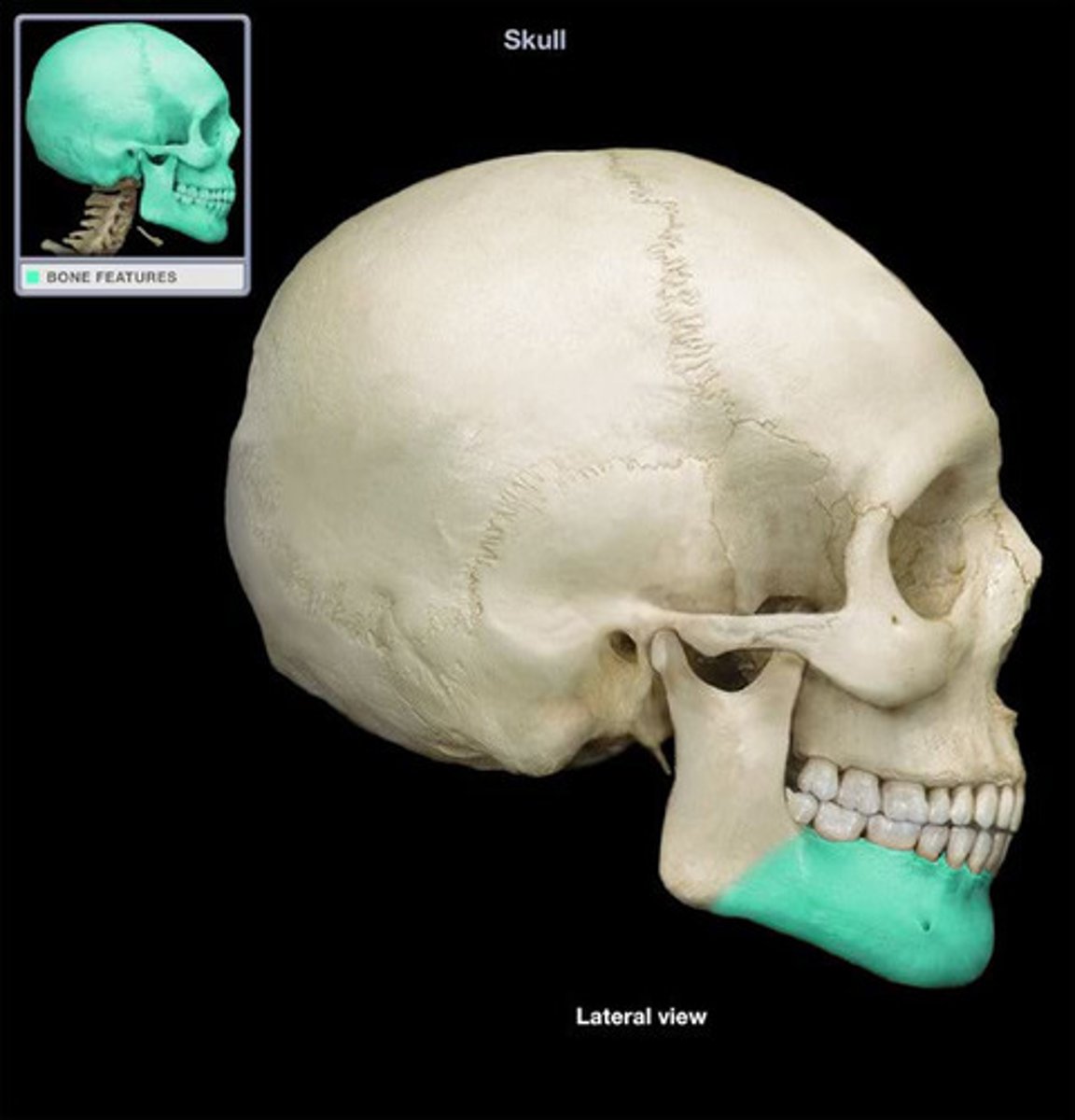
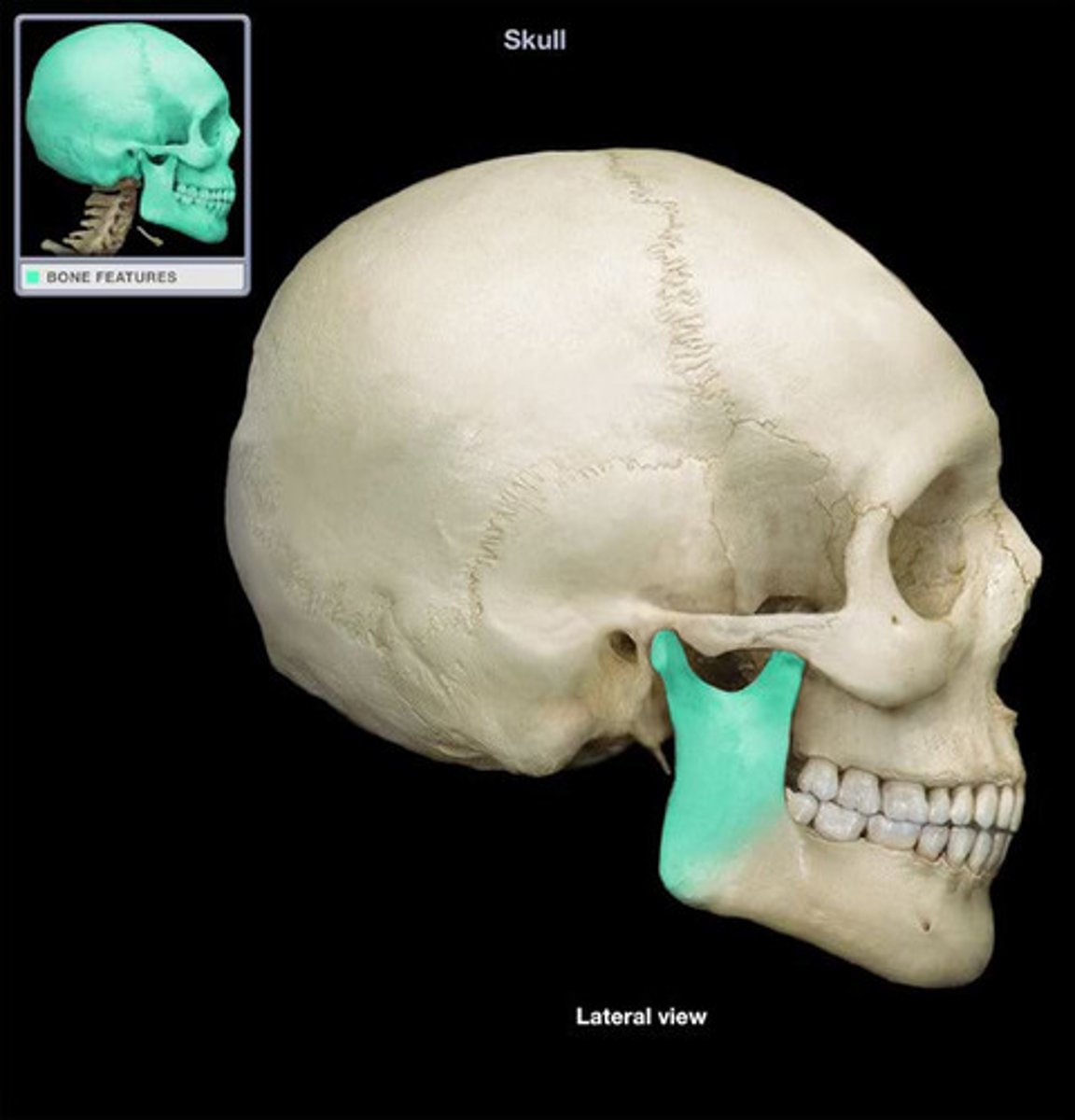
mandible
-lower jaw
-bone of the face
condylar process, coronoid process, mandibular foramen, mental foramen, corpus, angle, ramus, alveolar ridge
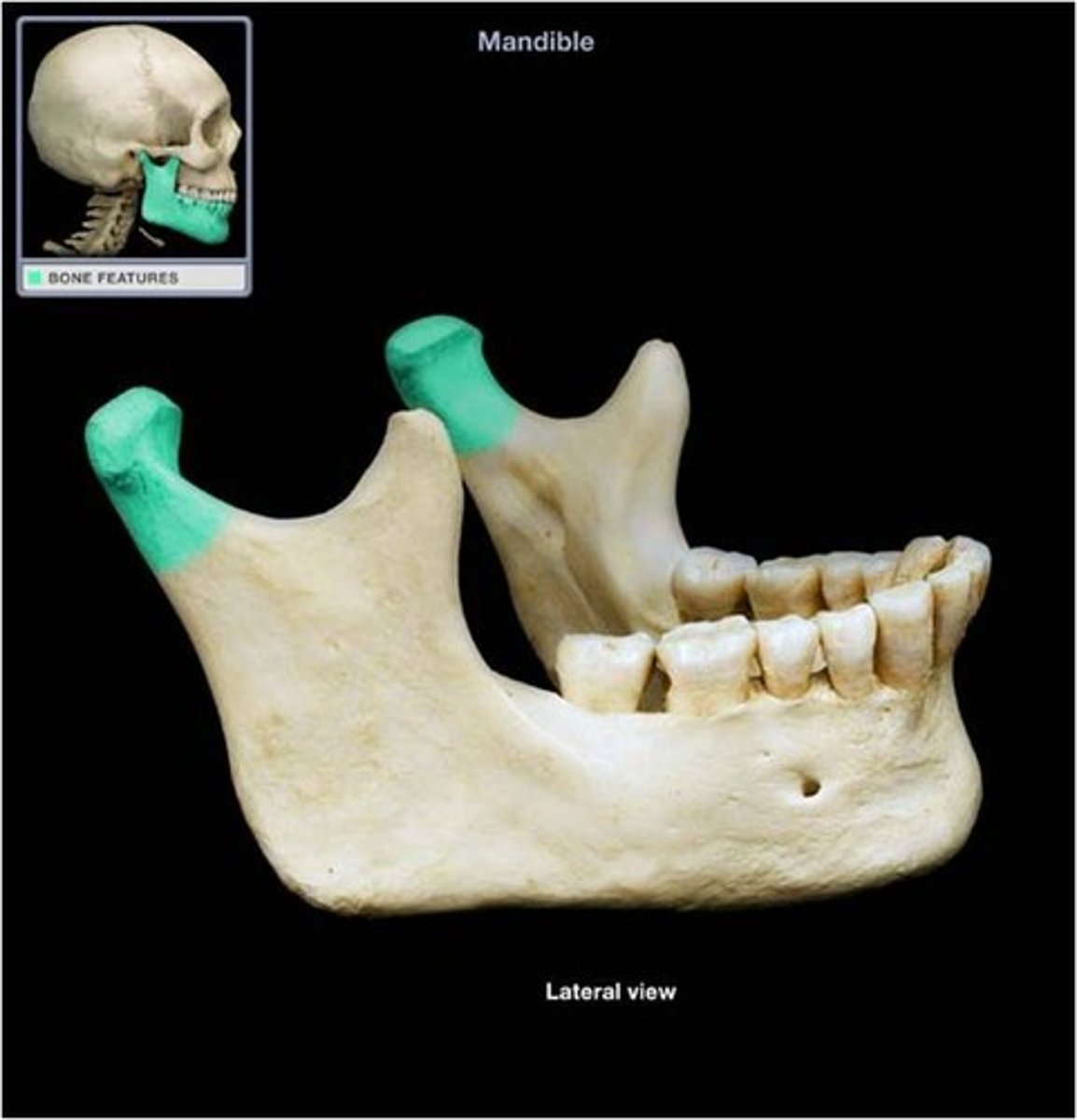
condylar process
articulates with the temporal bone forming the temporomandibular joint
- TMJ: chronic inflammation of the temporomandibular joint
(mandible)
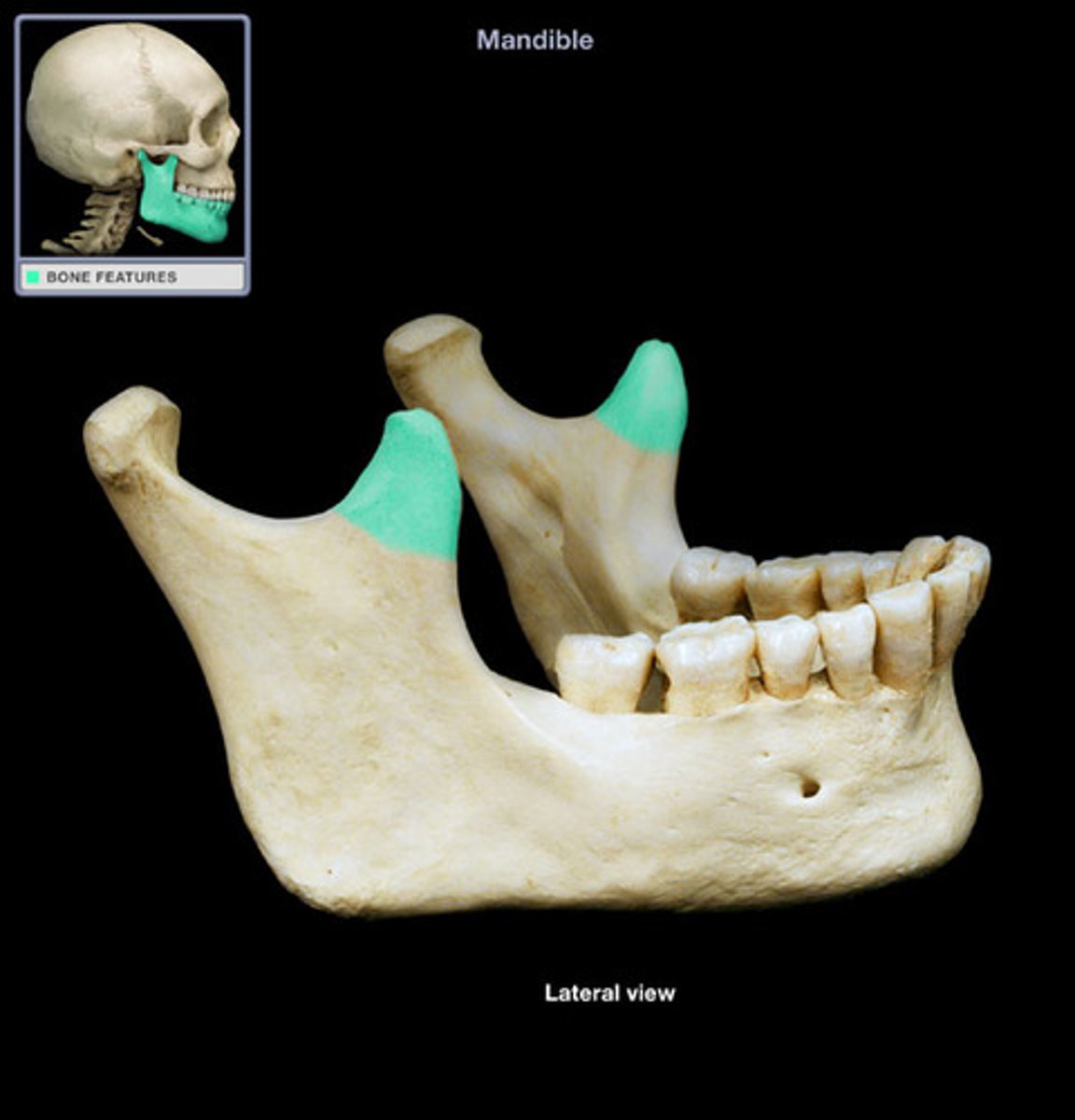
coronoid process
point of attachment for temporalis muscle
(mandible)
mandibular foramen
allows passage of inferior alveolar nerve
(mandible)
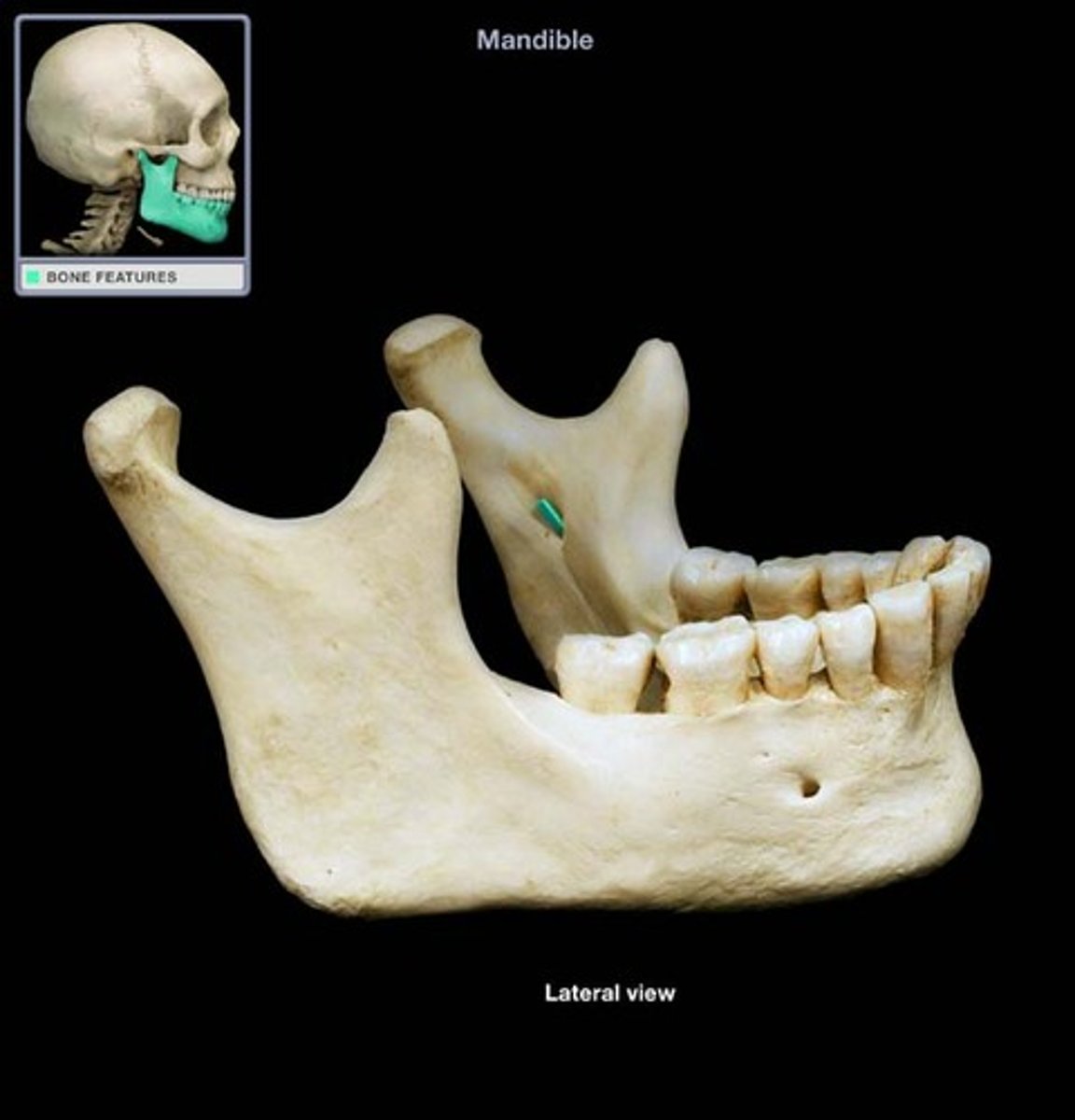
mental foramen
allows passage of the mental nerve which supplies sensation to the chin and lower lip
(mandible)
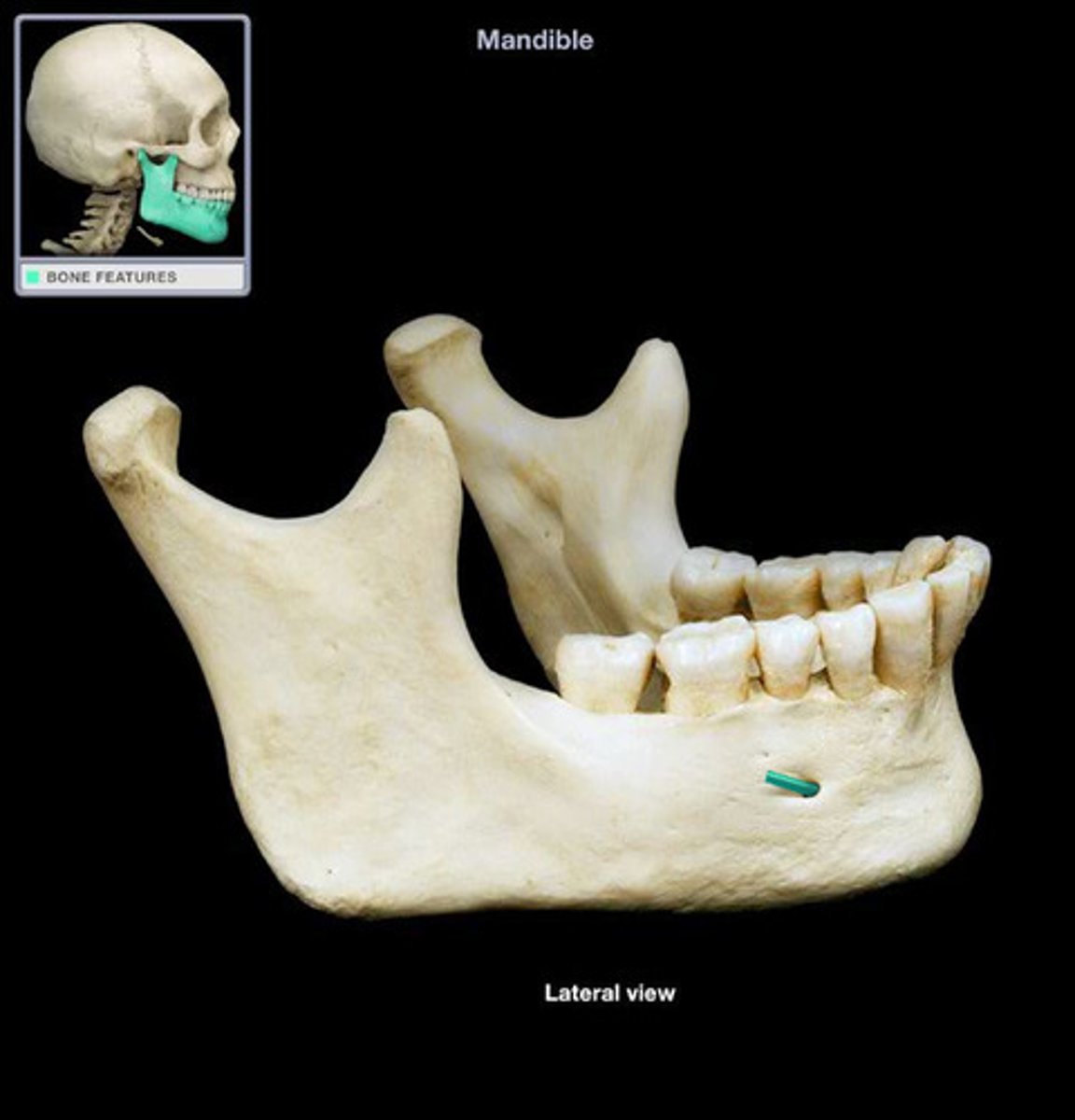
corpus (mandible)
body
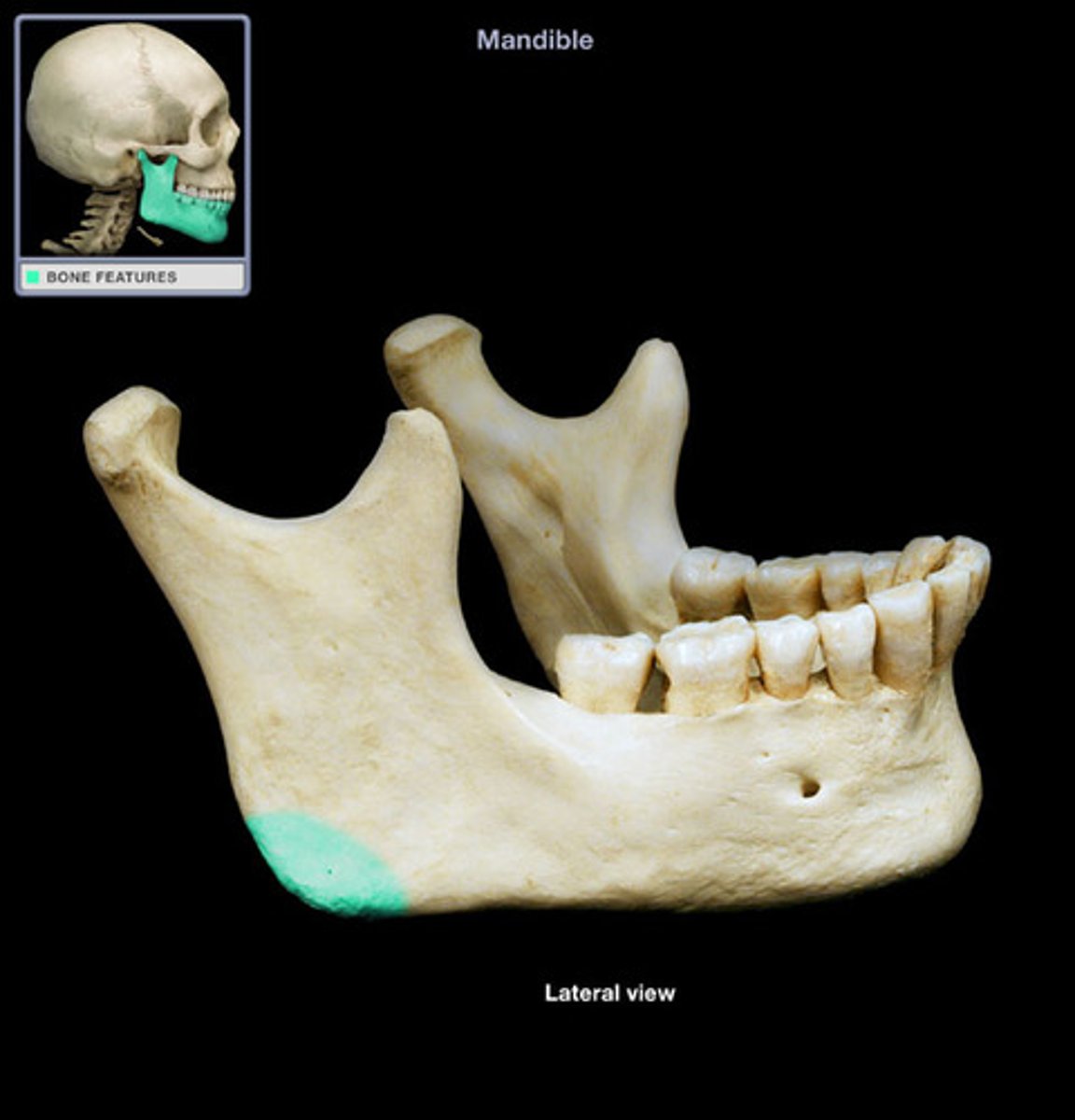
angle (mandible)
point between the vertical ramus and horizontal corpus
ramus
the vertical branch of the mandible
(mandible)
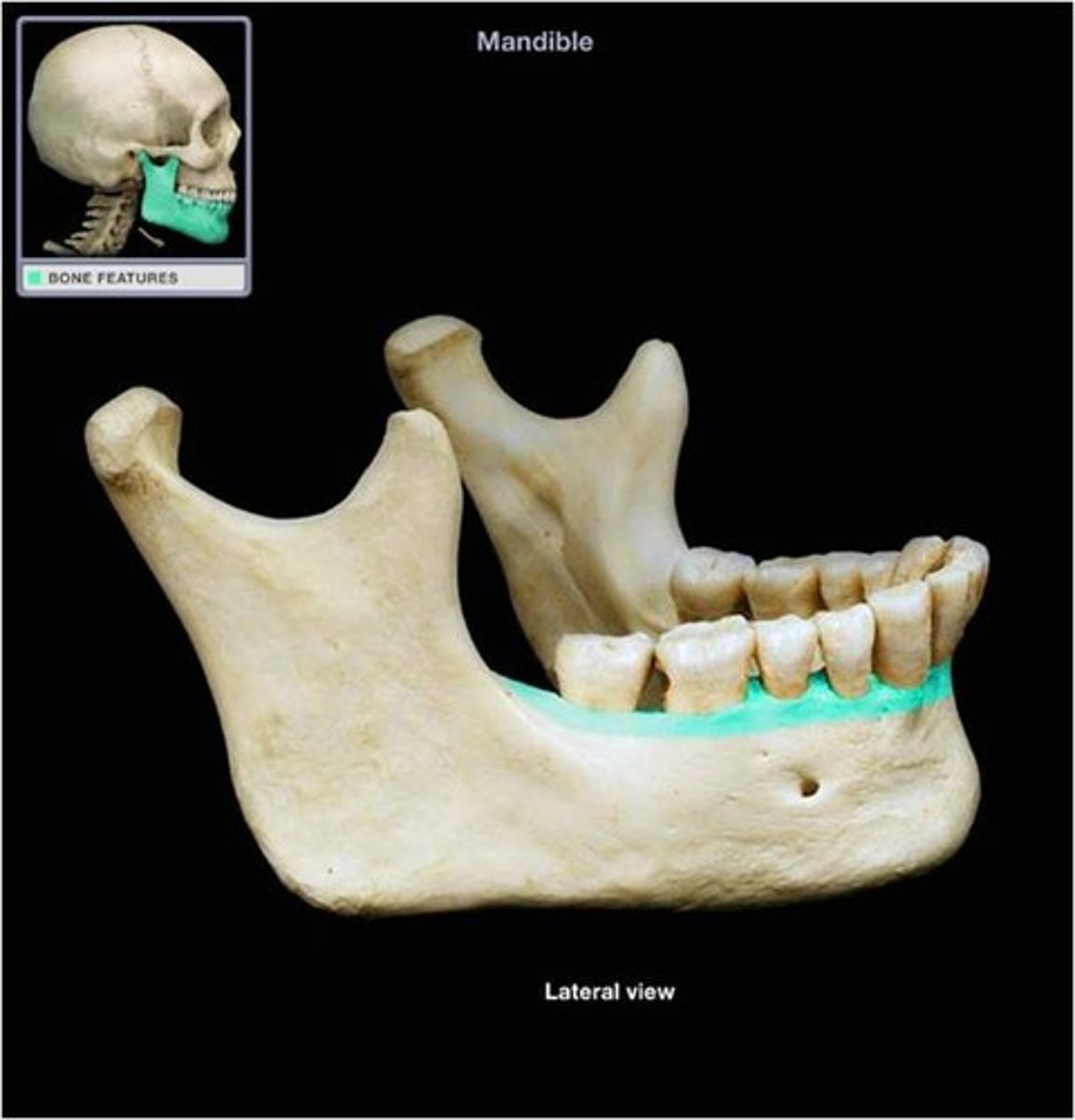
alveolar part (or ridge or process)
houses the teeth in dental alveoli (sacs)
(mandible)
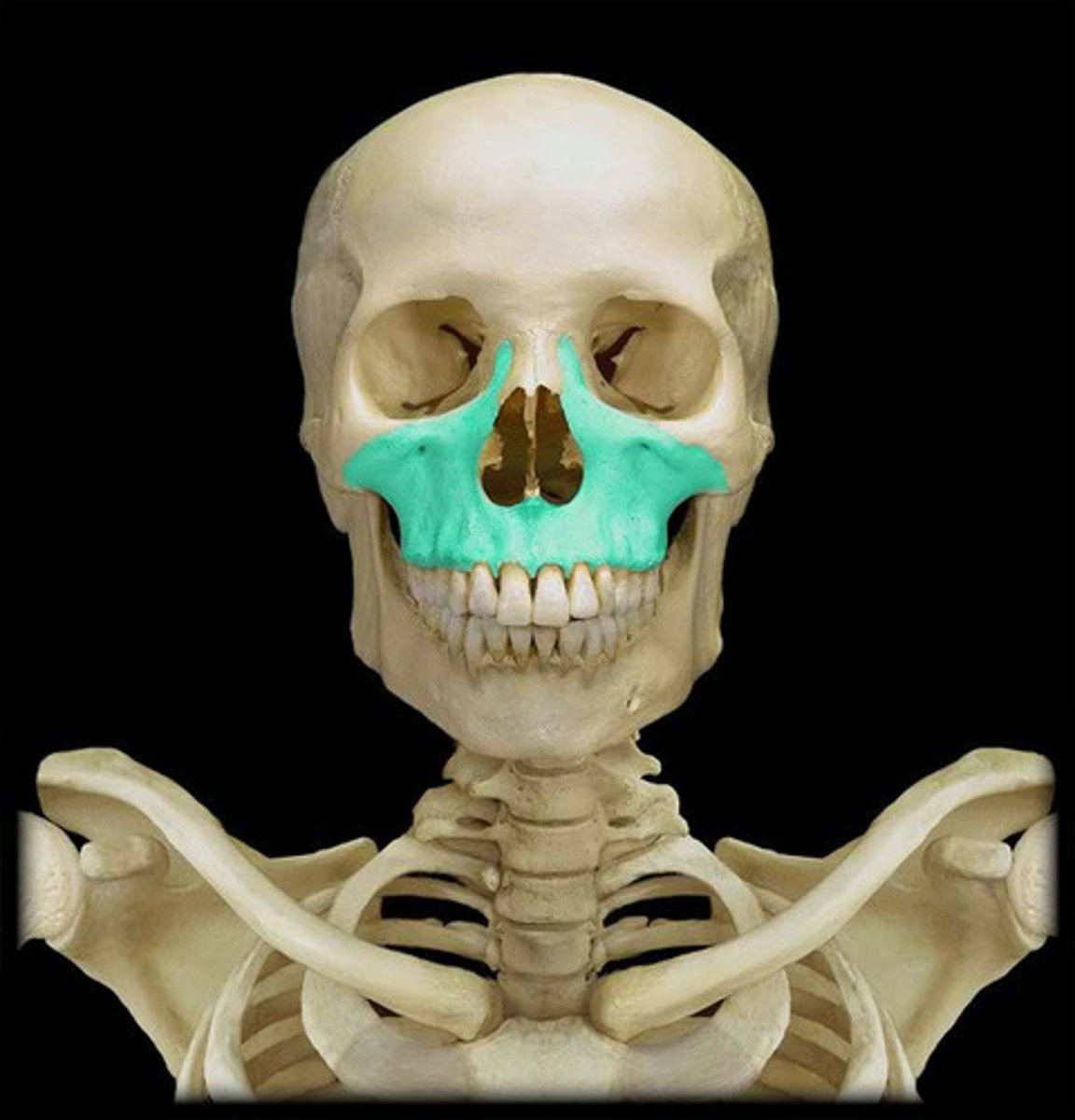
maxillae
upper jaw
frontal process, zygomatic process. palatine process, alveolar process,
premaxilla, incisive foramen,
transverse palatine suture, intermaxillary suture, premaxillary suture
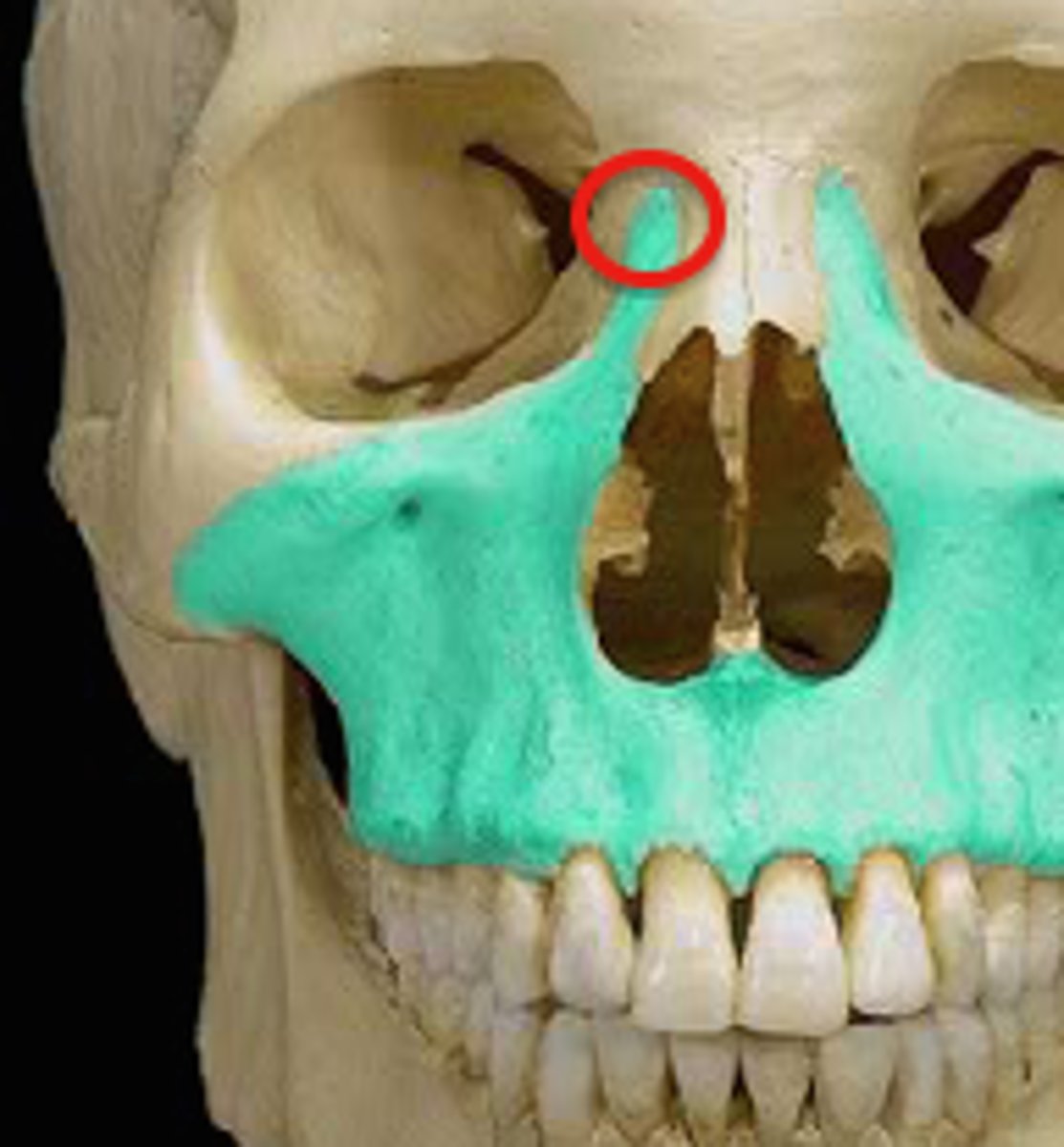
frontal process (maxillae)
articulates with the frontal bone
(maxillae)
zygomatic process (maxillae)
articulates with the zygomatic bone
(maxillae)
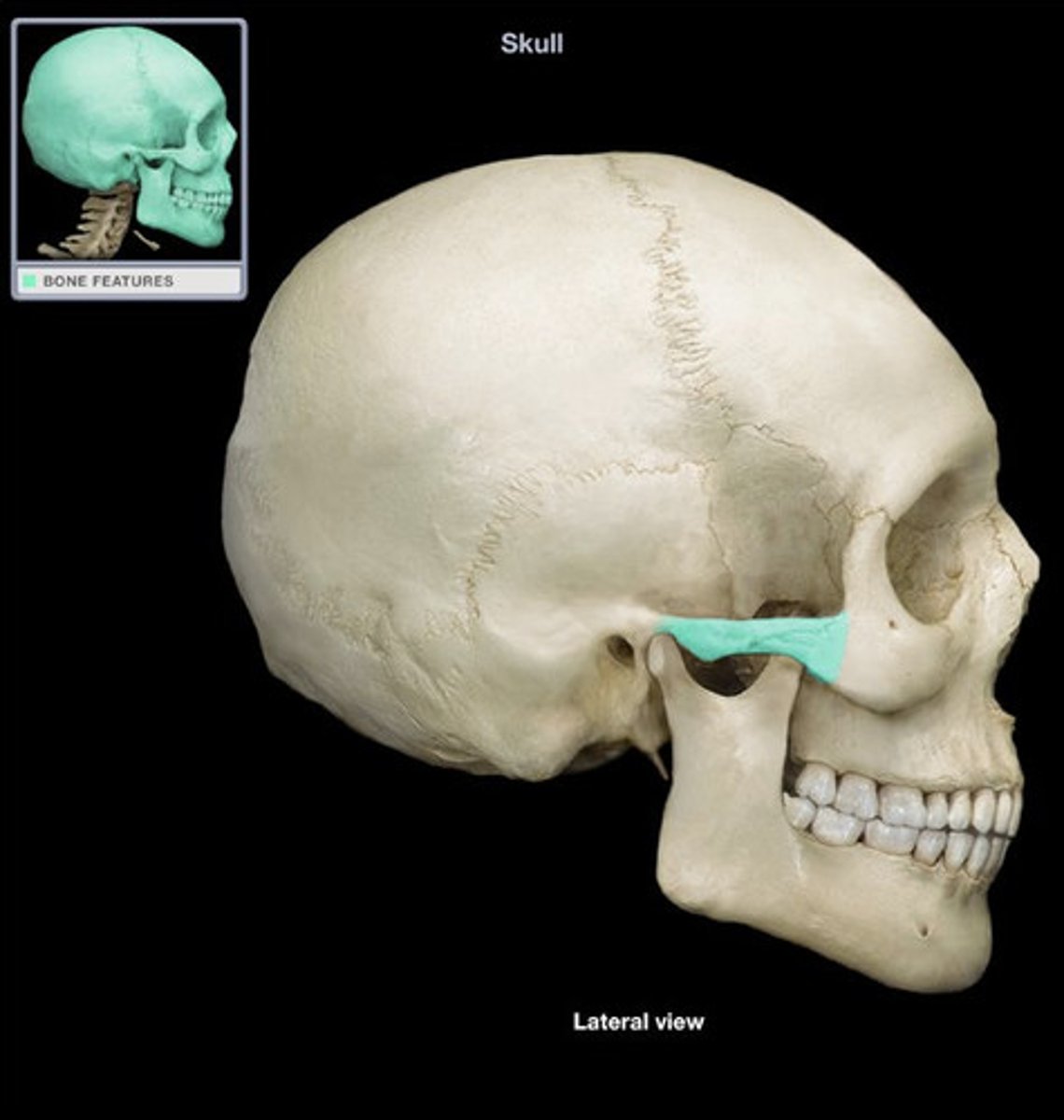
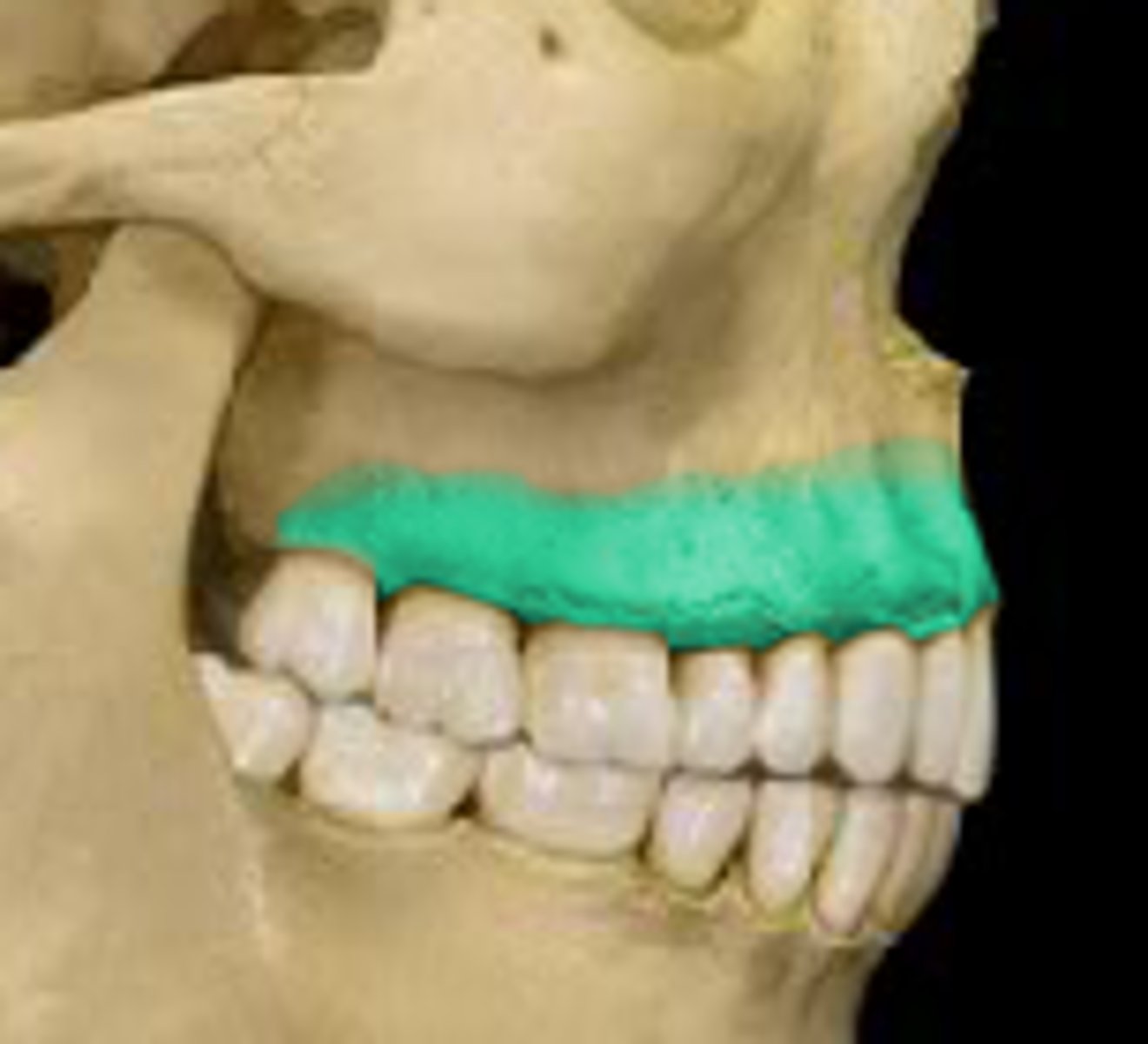
palatine process
forms the floor of the nasal cavity and the anterior 3/4 of the hard palate (roof of the mouth)
(maxillae)
alveolar process
houses teeth
(maxillae)
premaxilla
anterior section of the maxillae
(maxillae)
incisive foramen
marks the connection of the premaxilla and both palatine process
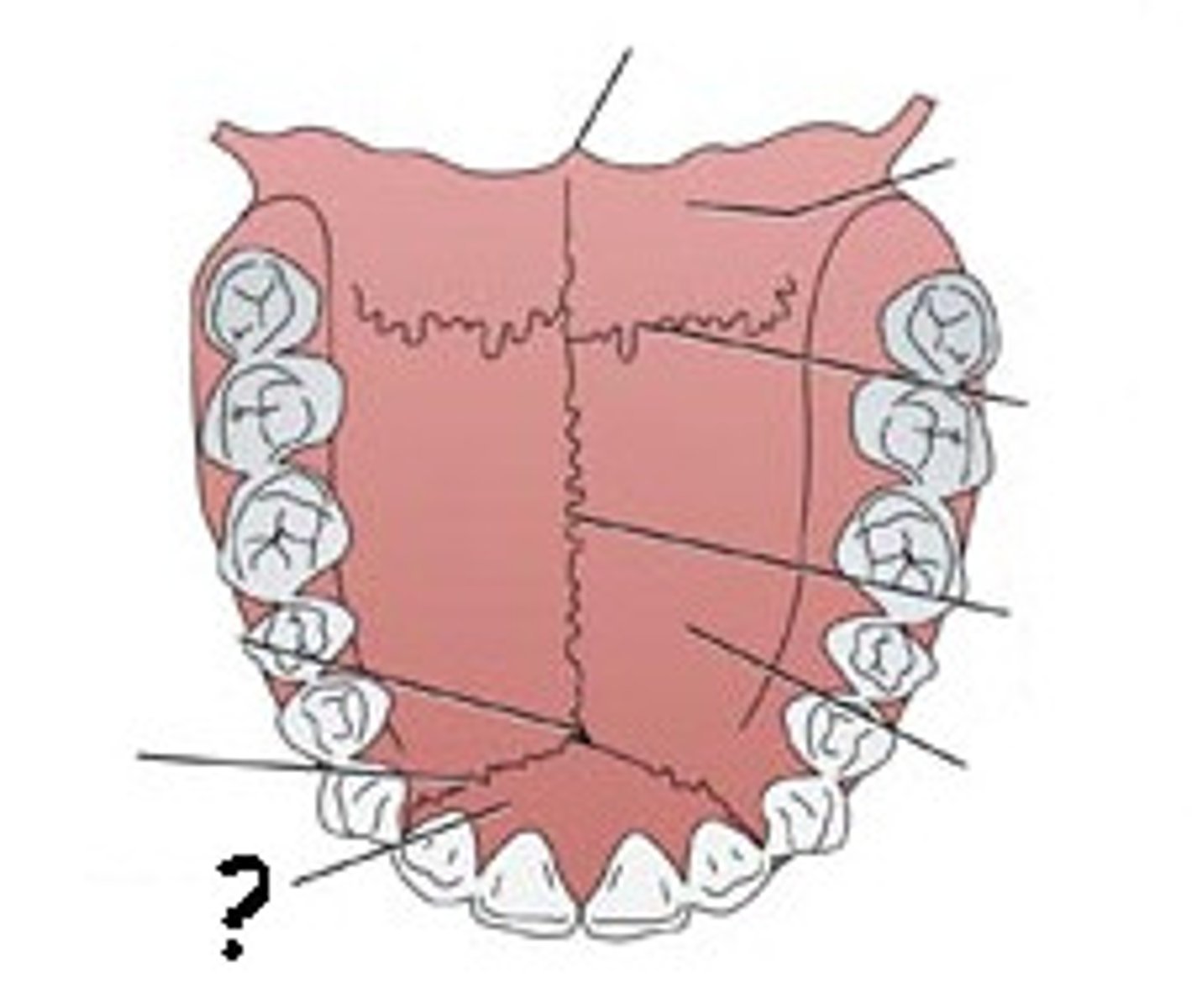
transverse palatine suture
between palatine processes of maxillae and horizontal plates of palatine bones
(maxillae)
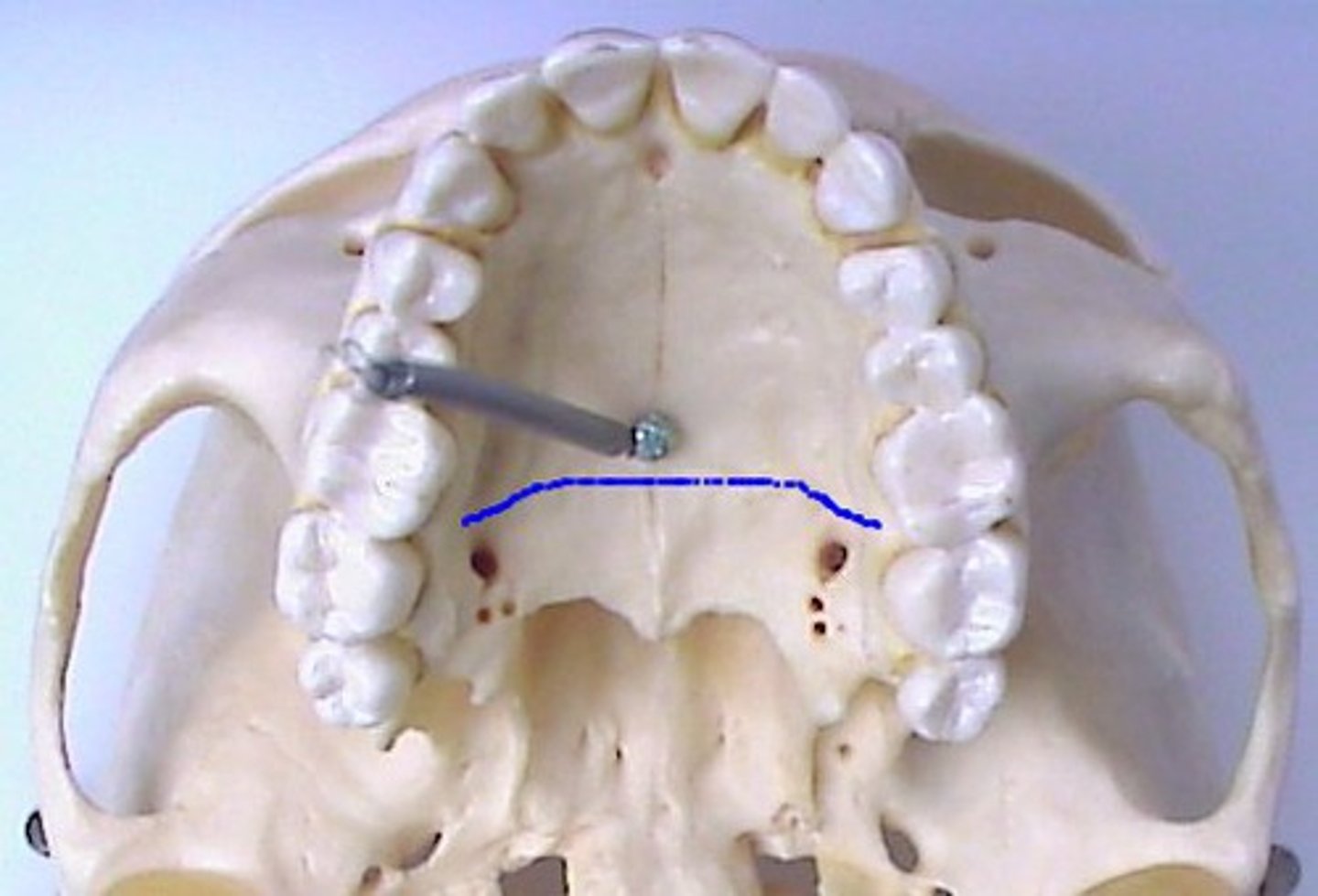
intermaxillary suture
between palatine processes
(maxillae)
premaxillary suture
between palatine processes and premaxilla
(maxillae)
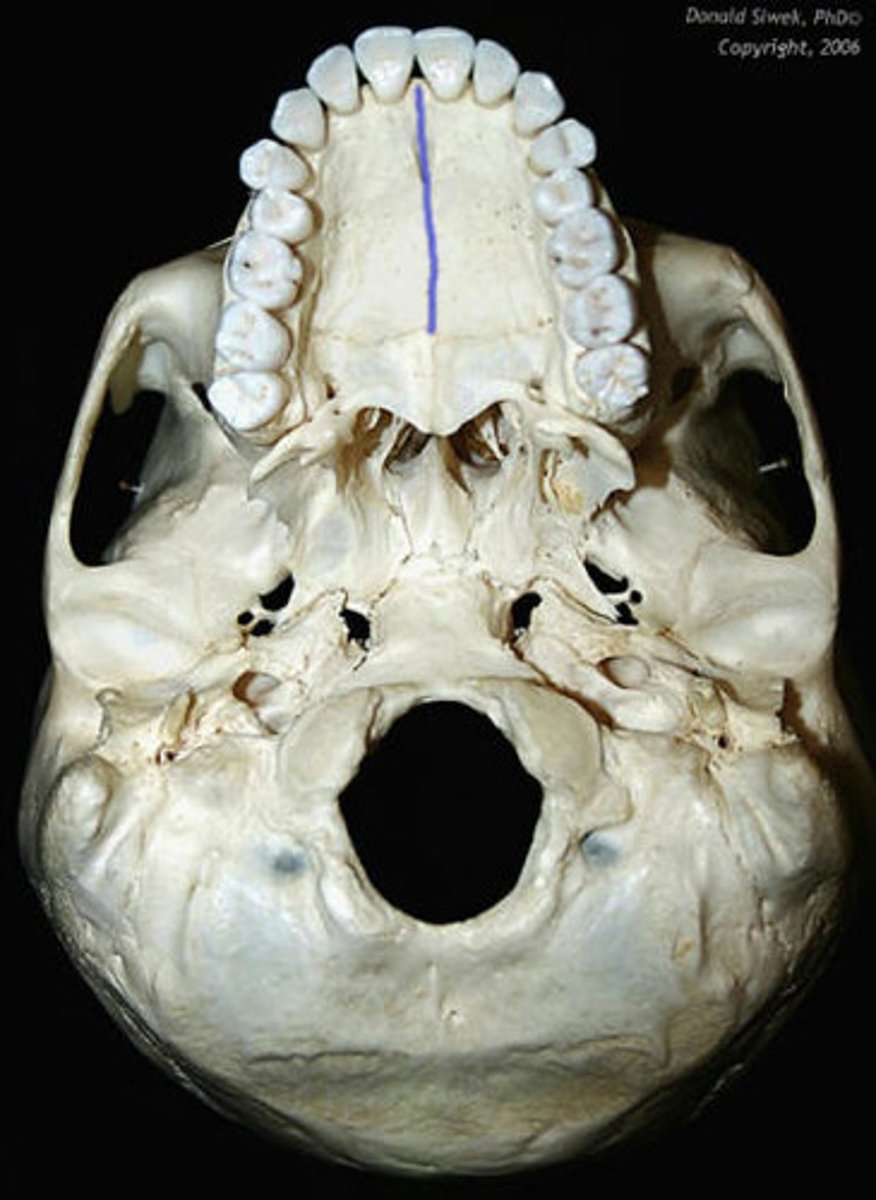
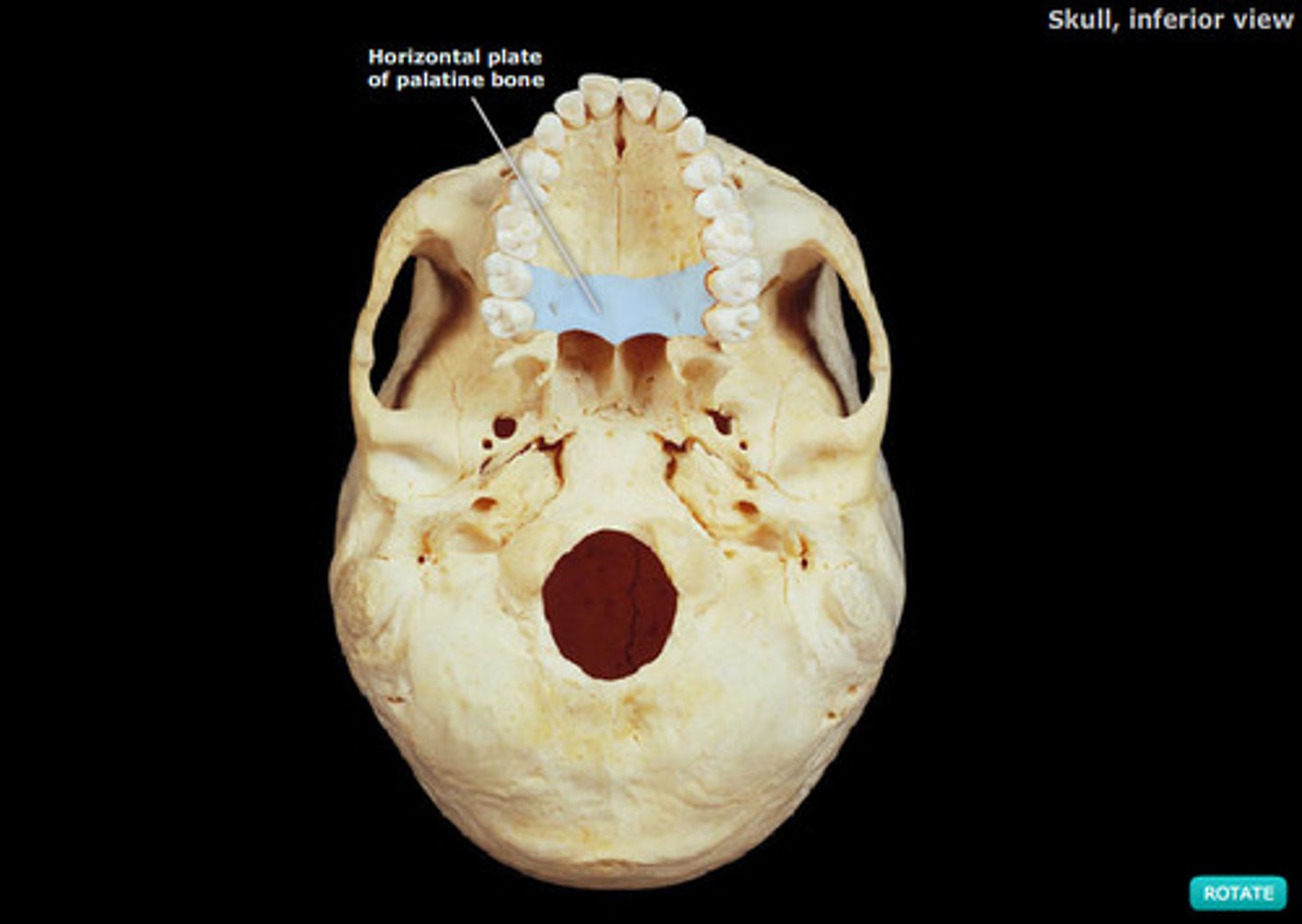
palatine bones
connected to the maxillae
- horizontal plates
- located posterior to the maxillae
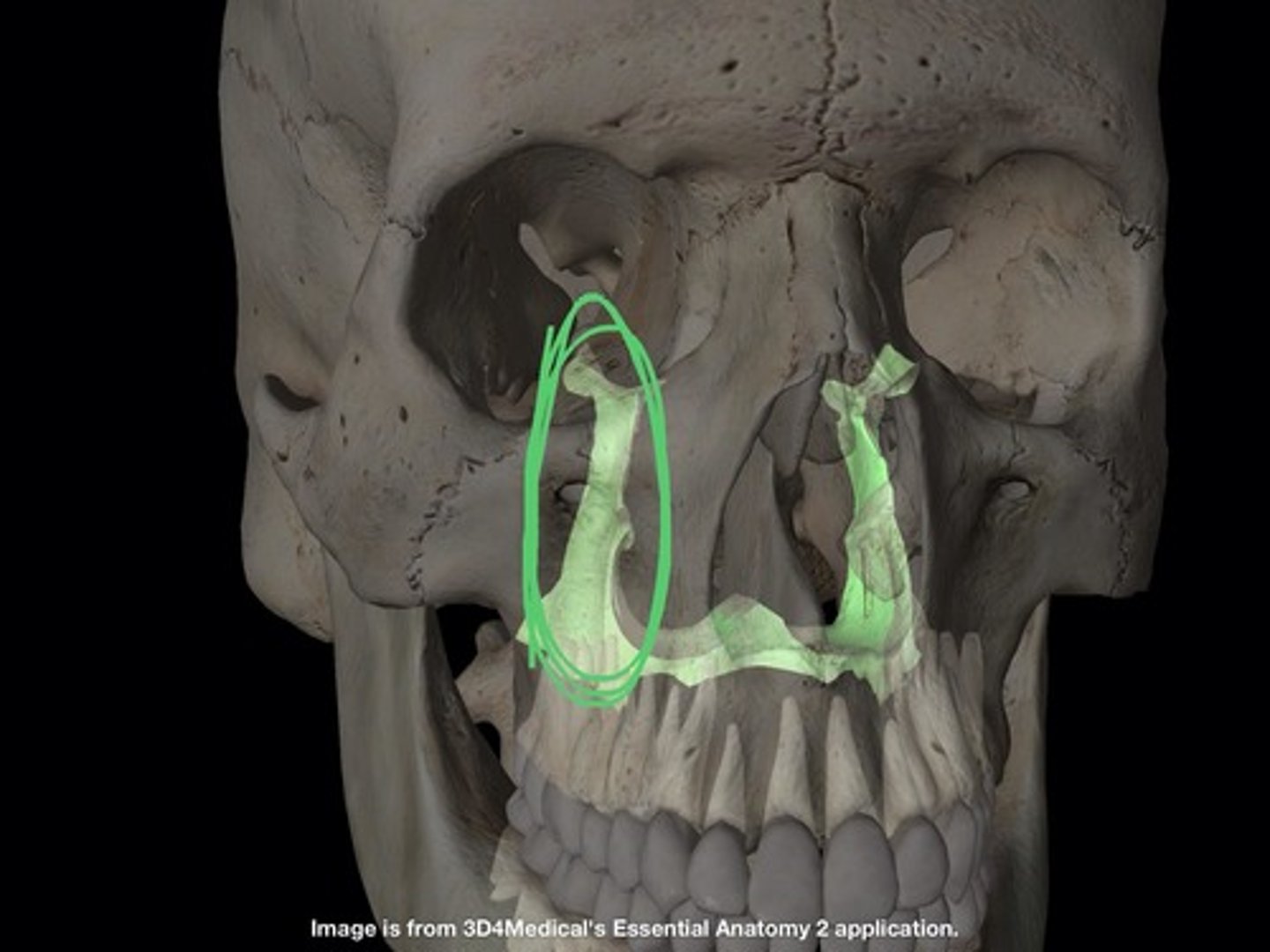
horizontal plates
makes up posterior 1/4 of hard palate
(palatine bones)
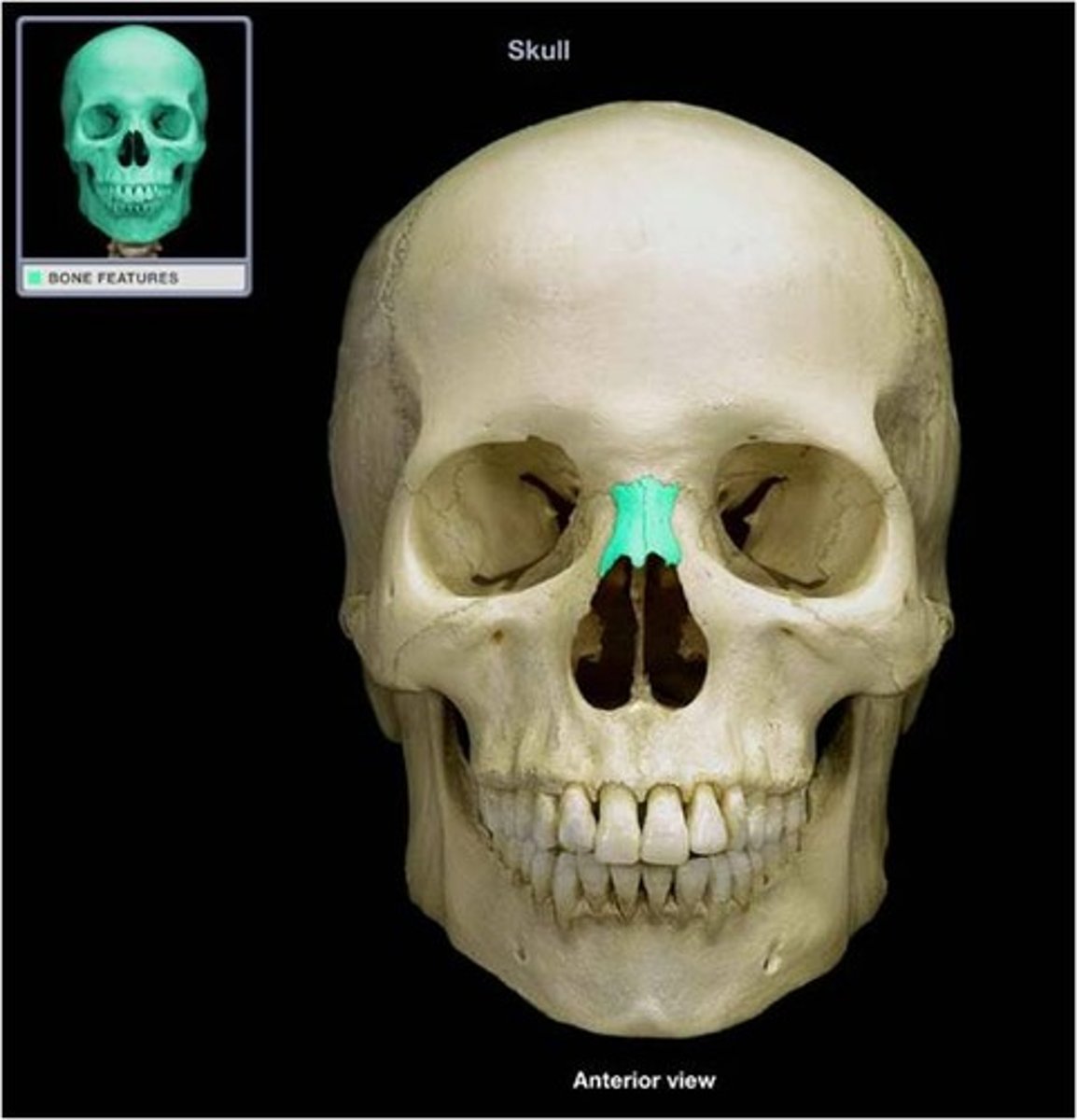
nasal bones
small bones that form the bridge of the nose
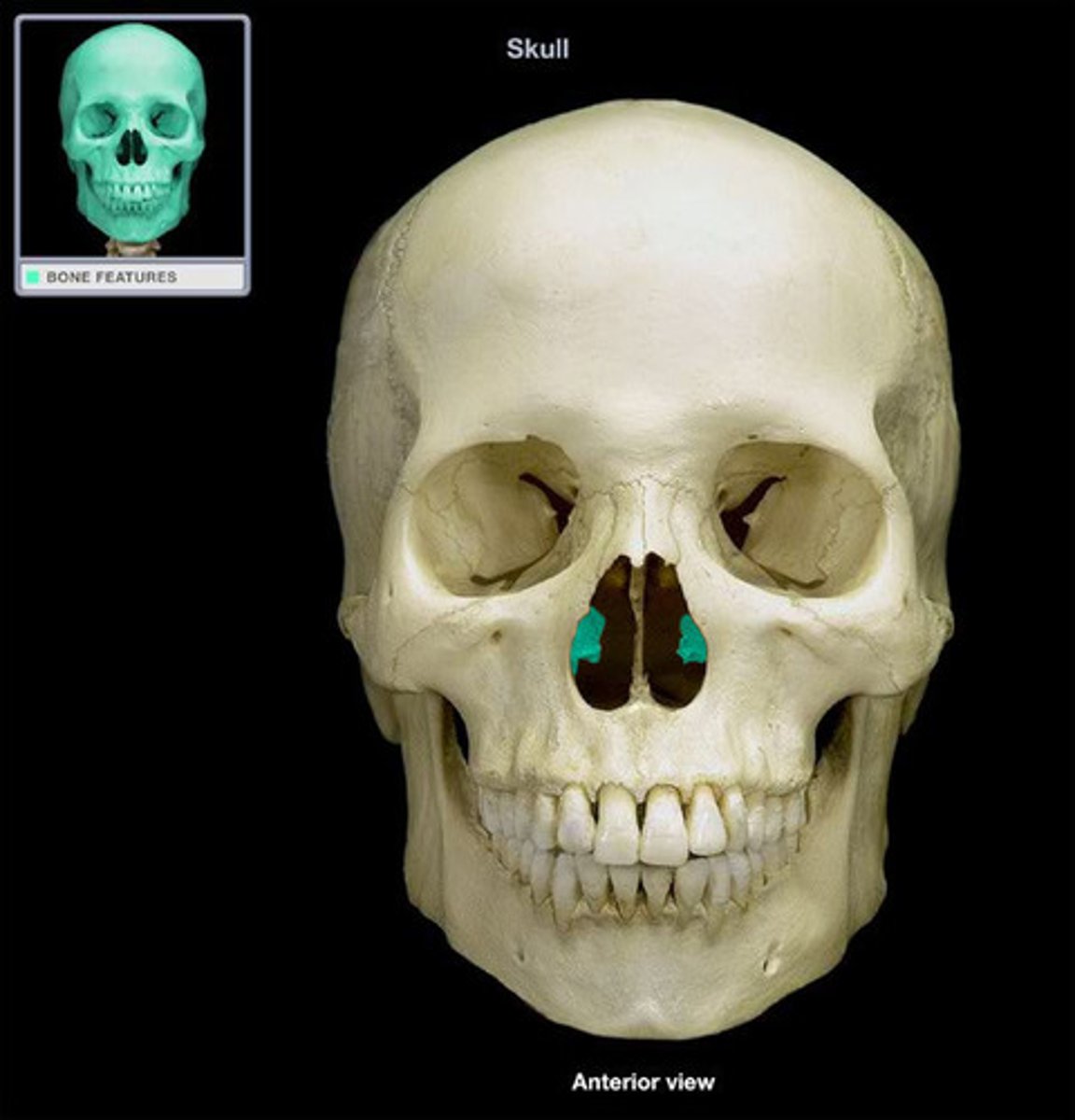
inferior nasal conchae
small scroll like bones @ lateral walls of the nasal cavity
- increases surface area for warming and humidifying air
nasal septum
- vomer
- perpendicular plate of ethmoid
- septal cartilage
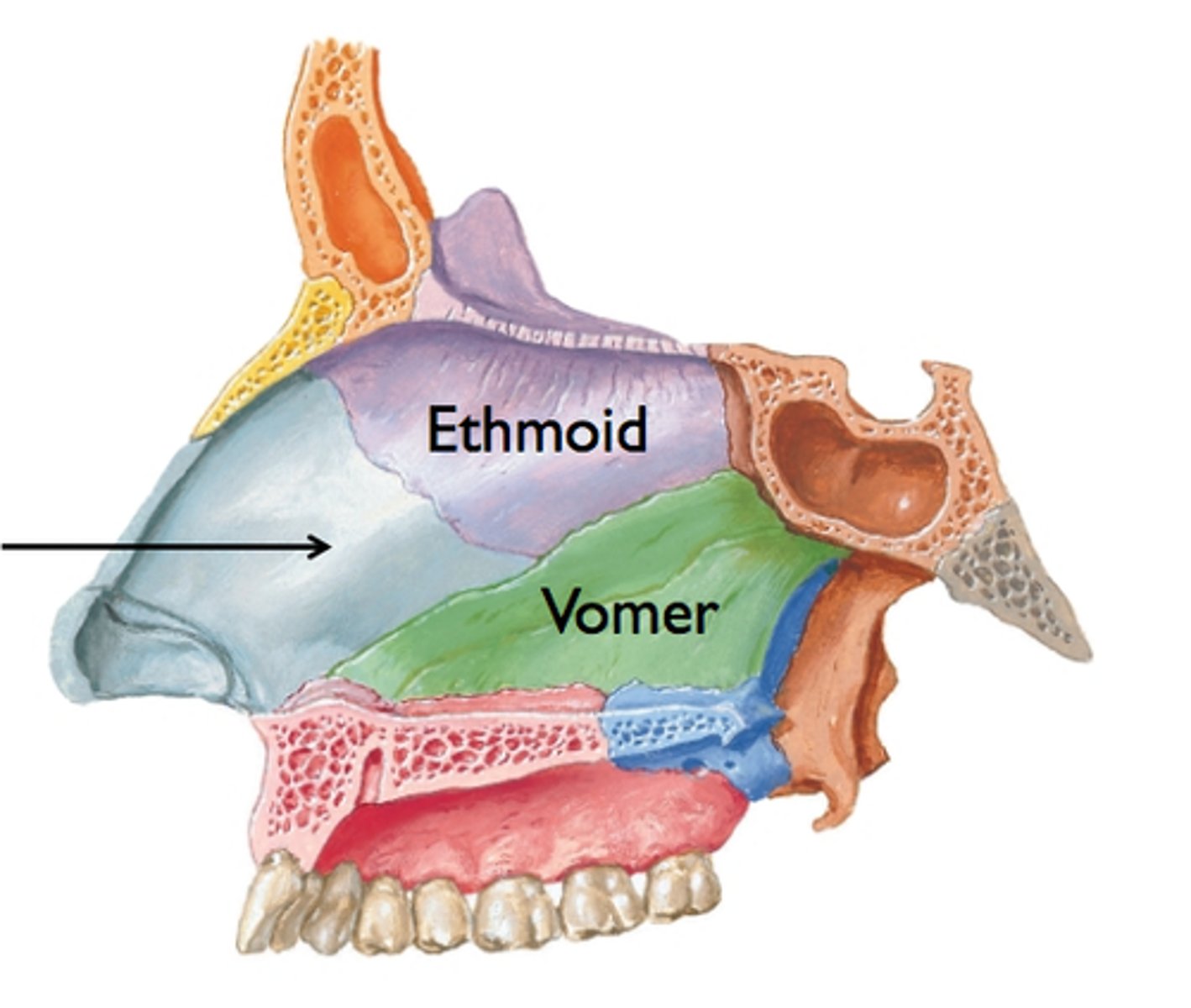
vomer
part of nasal septum
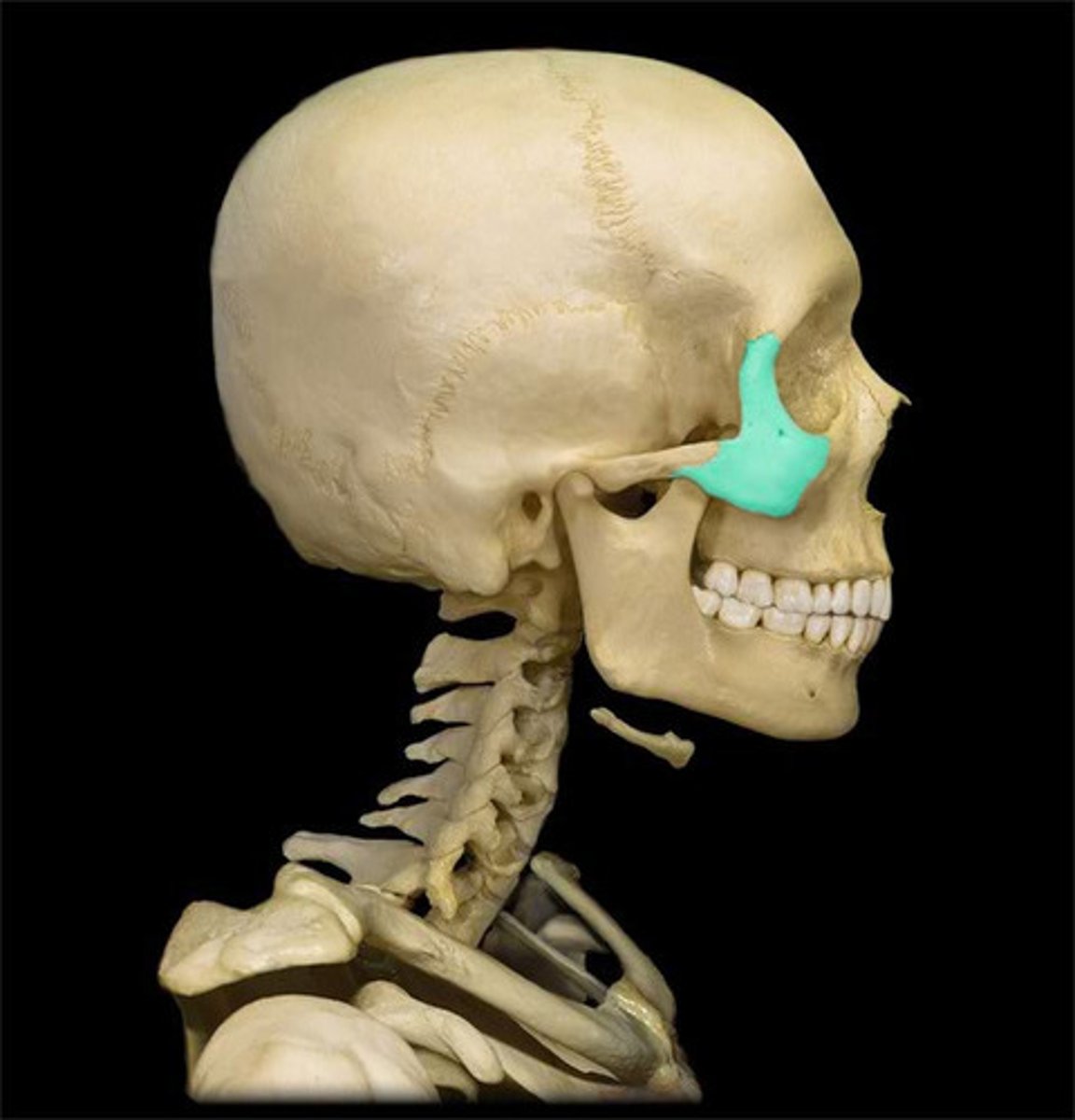
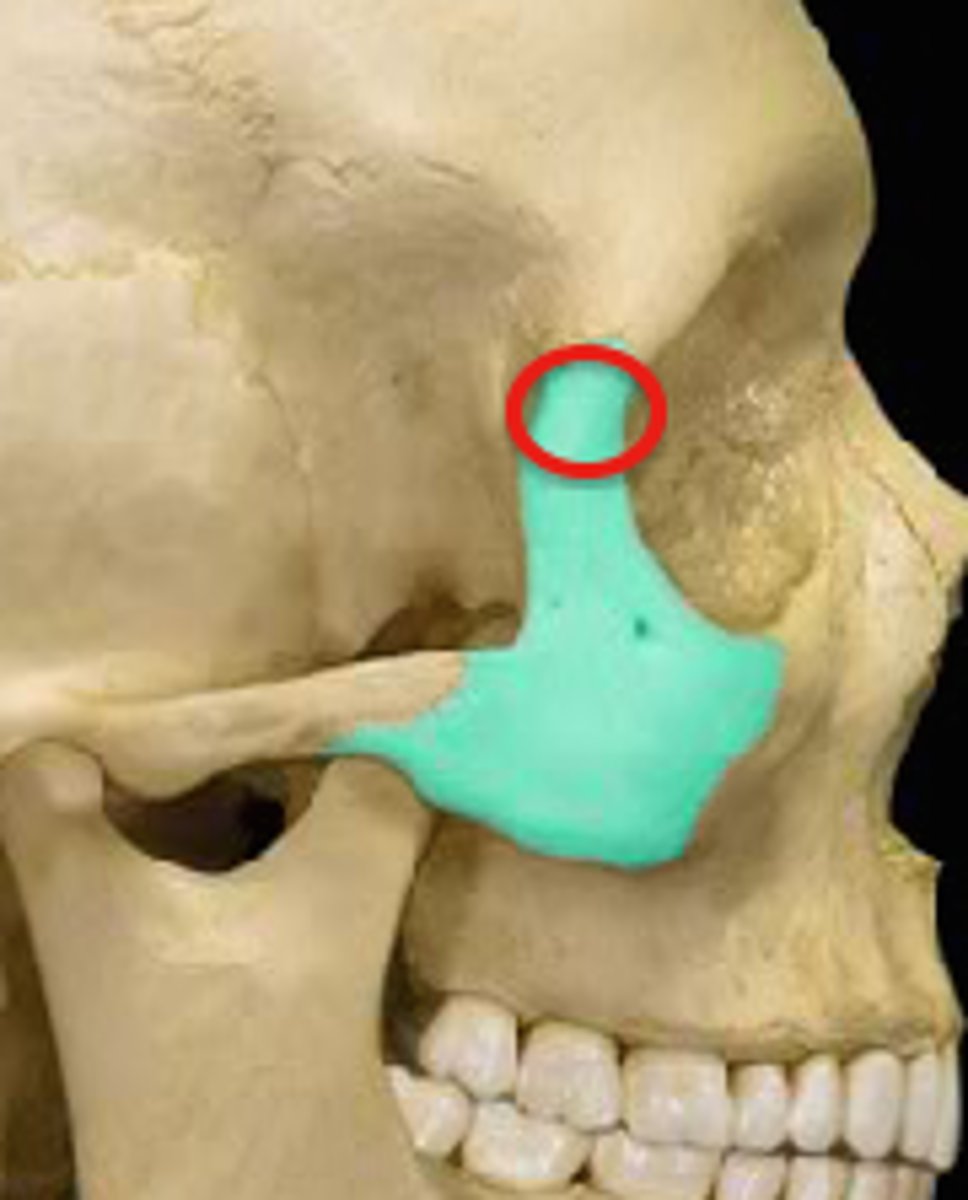
zygomatic bone
1. frontal process
2. temporal process
3. maxillary process
frontal process (zygomatic)
articulates with the frontal bone
temporal process (on zygomatic)
articulates with the temporal bone forming the zygomatic arch
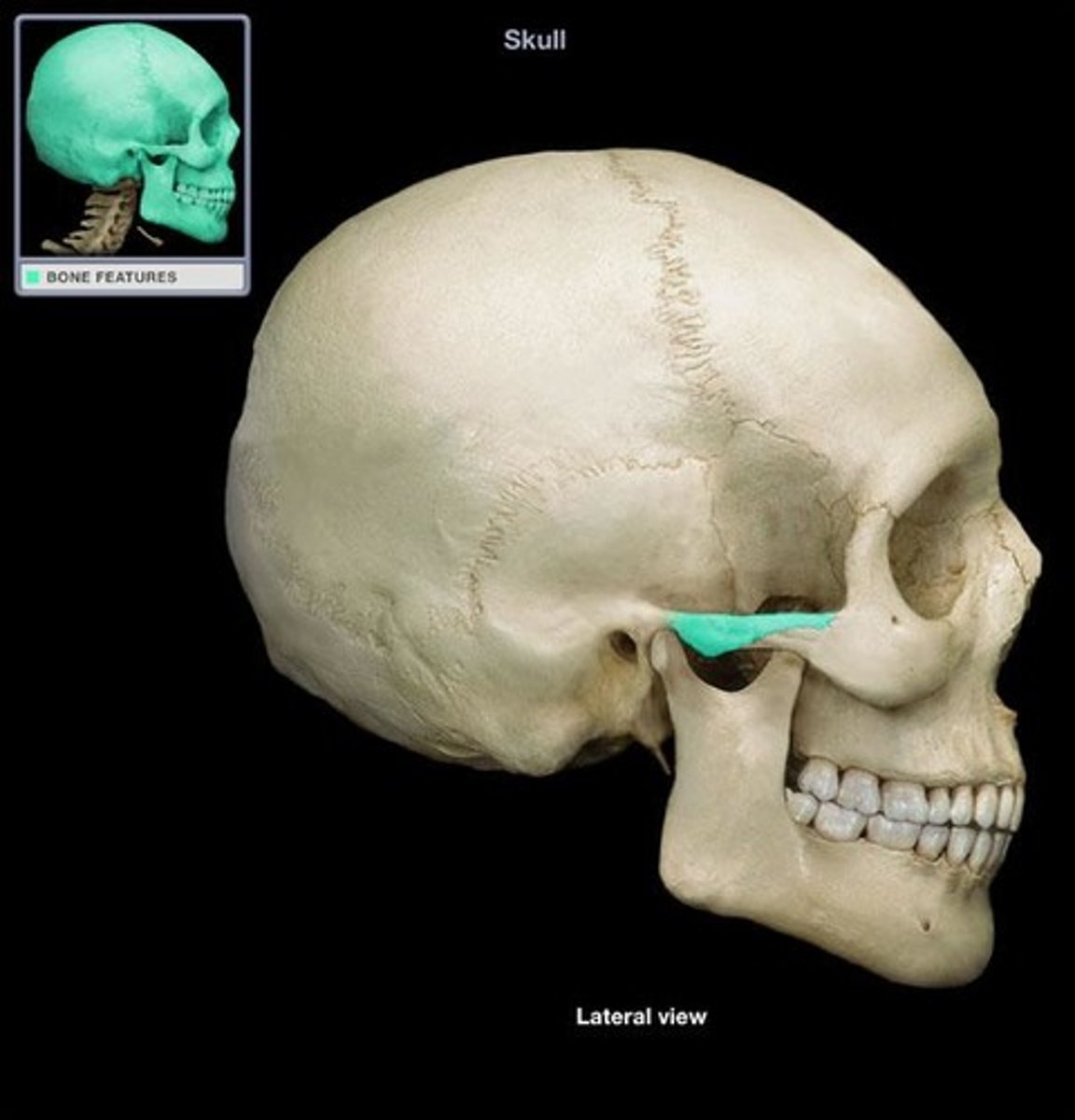
maxillary process (on zygomatic)
articulates with the maxilla
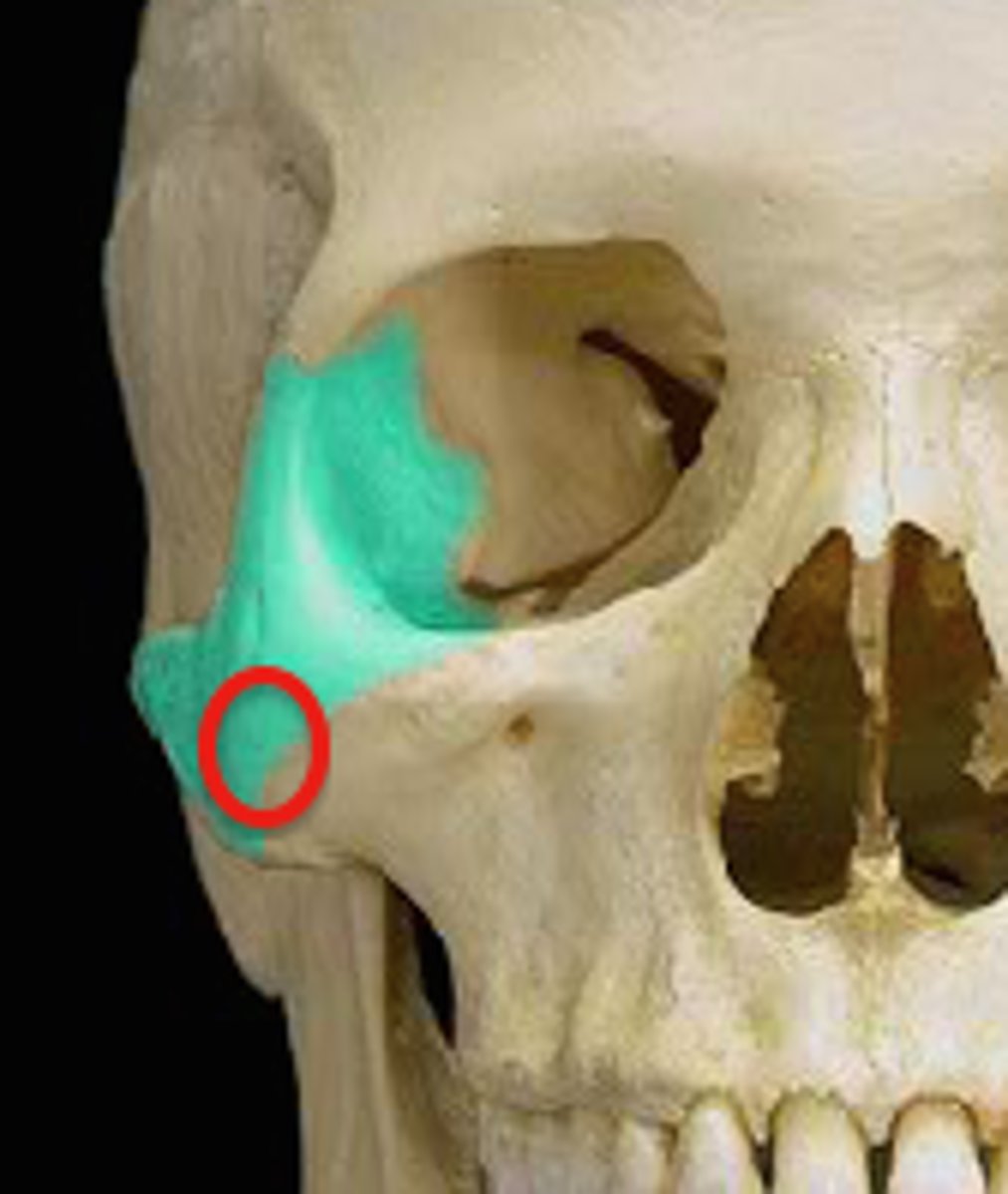
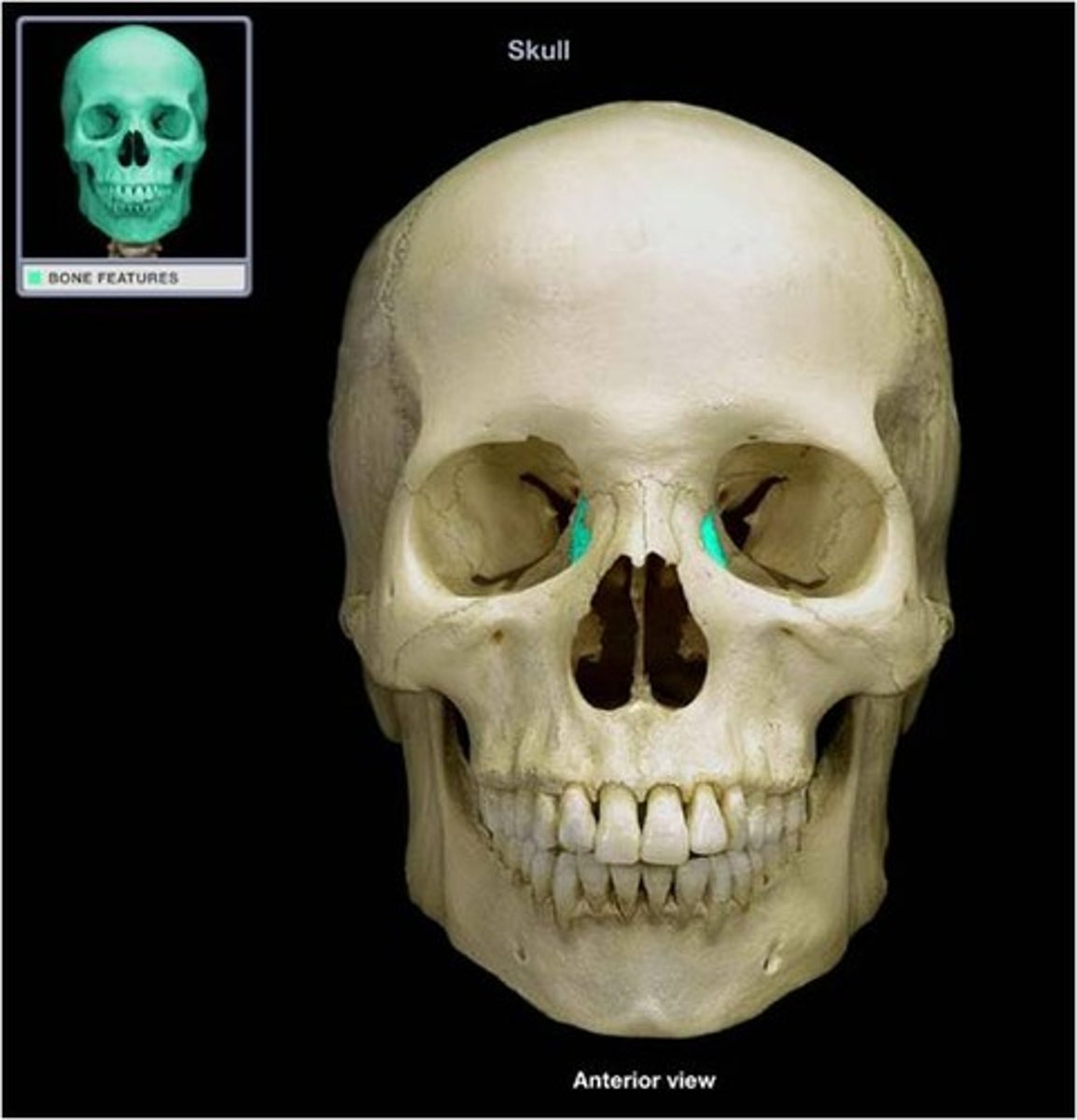
lacrimal bones
small facial bones
contribute to formation of the medial wall of the orbital cavity
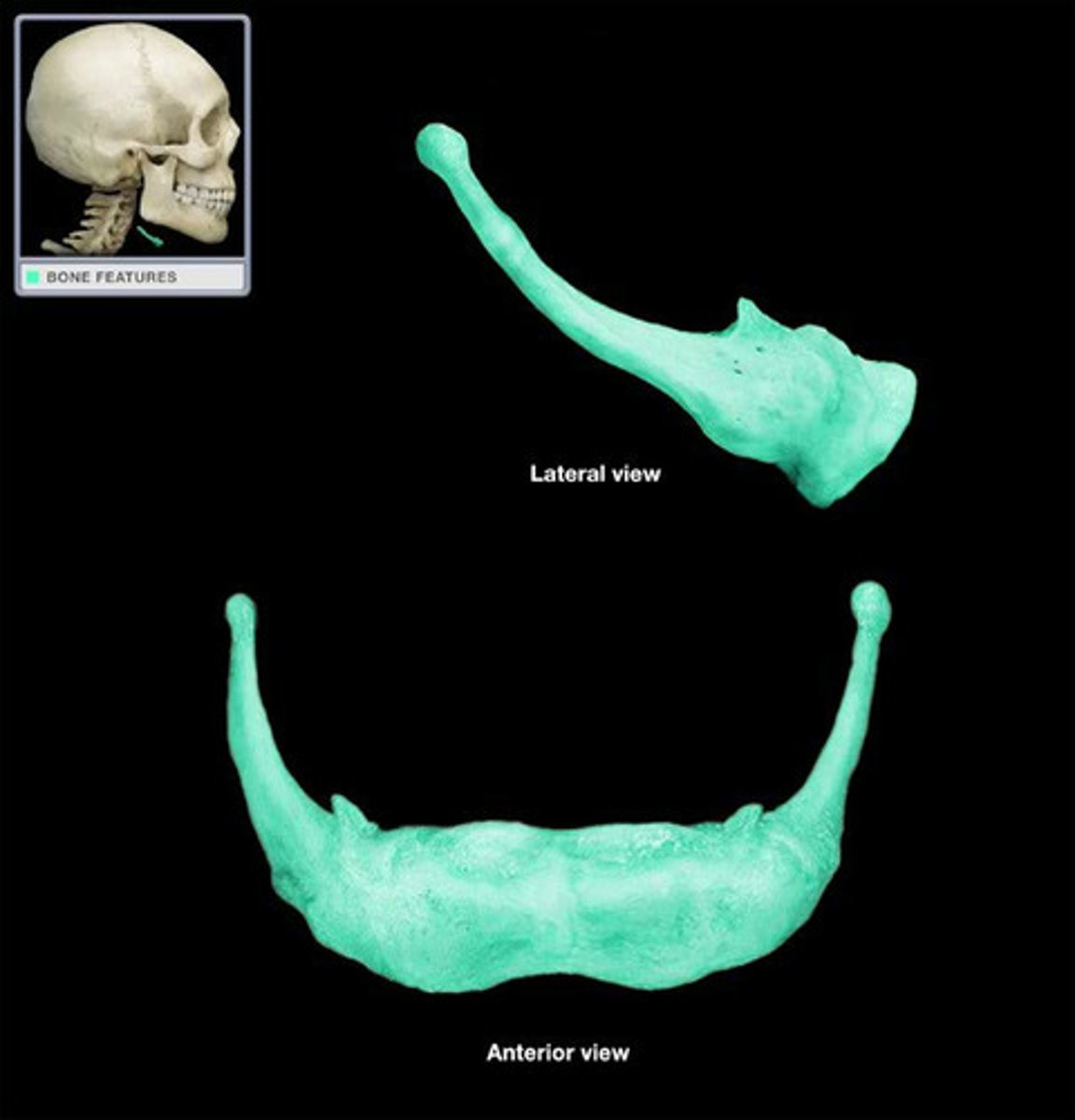
hyoid bone
a U-shaped bone
- a bone of the face
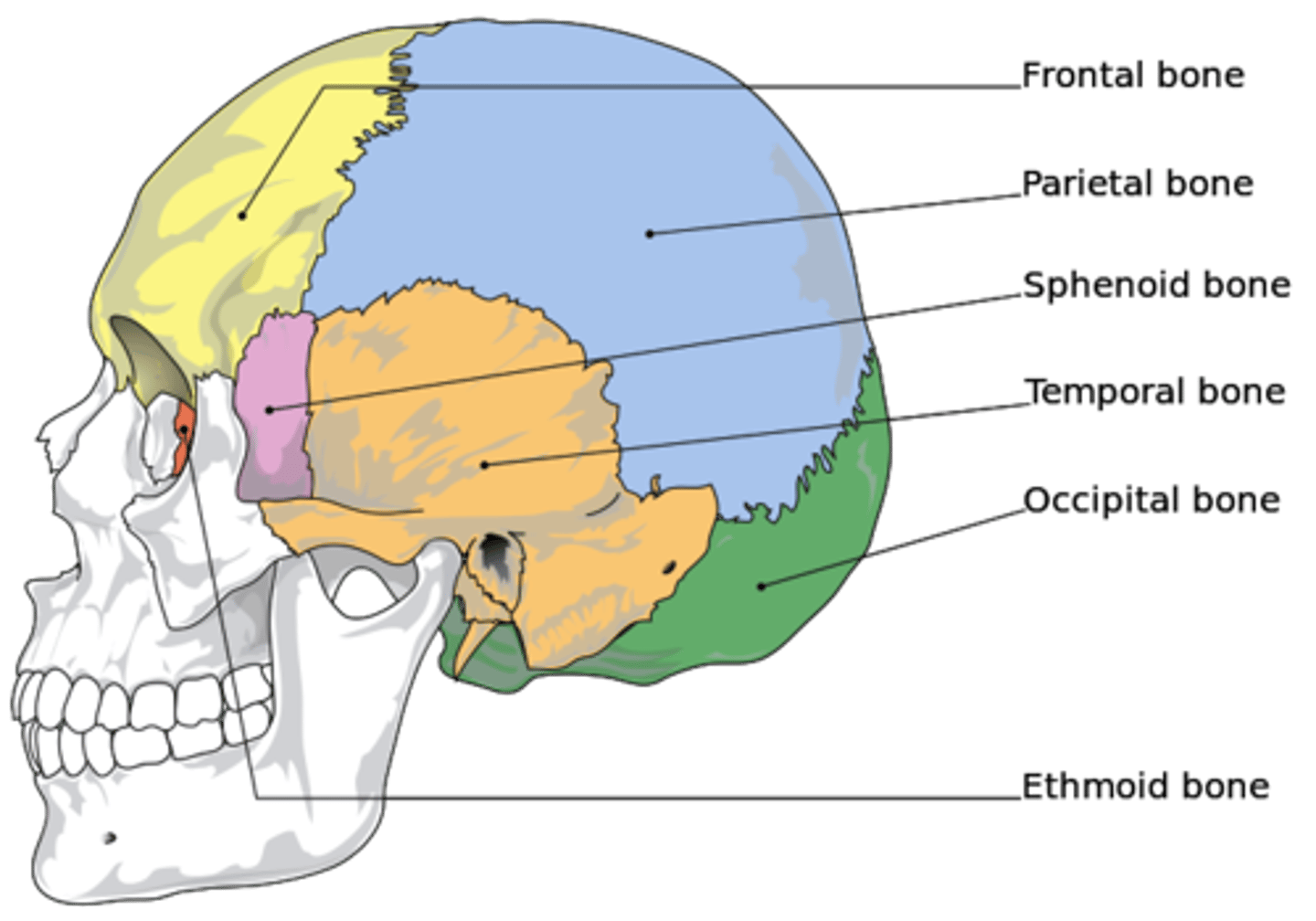
bones of cranial skeleton
• Ethmoid
• Sphenoid
• Frontal
• Parietal
• Occipital
• Temporal
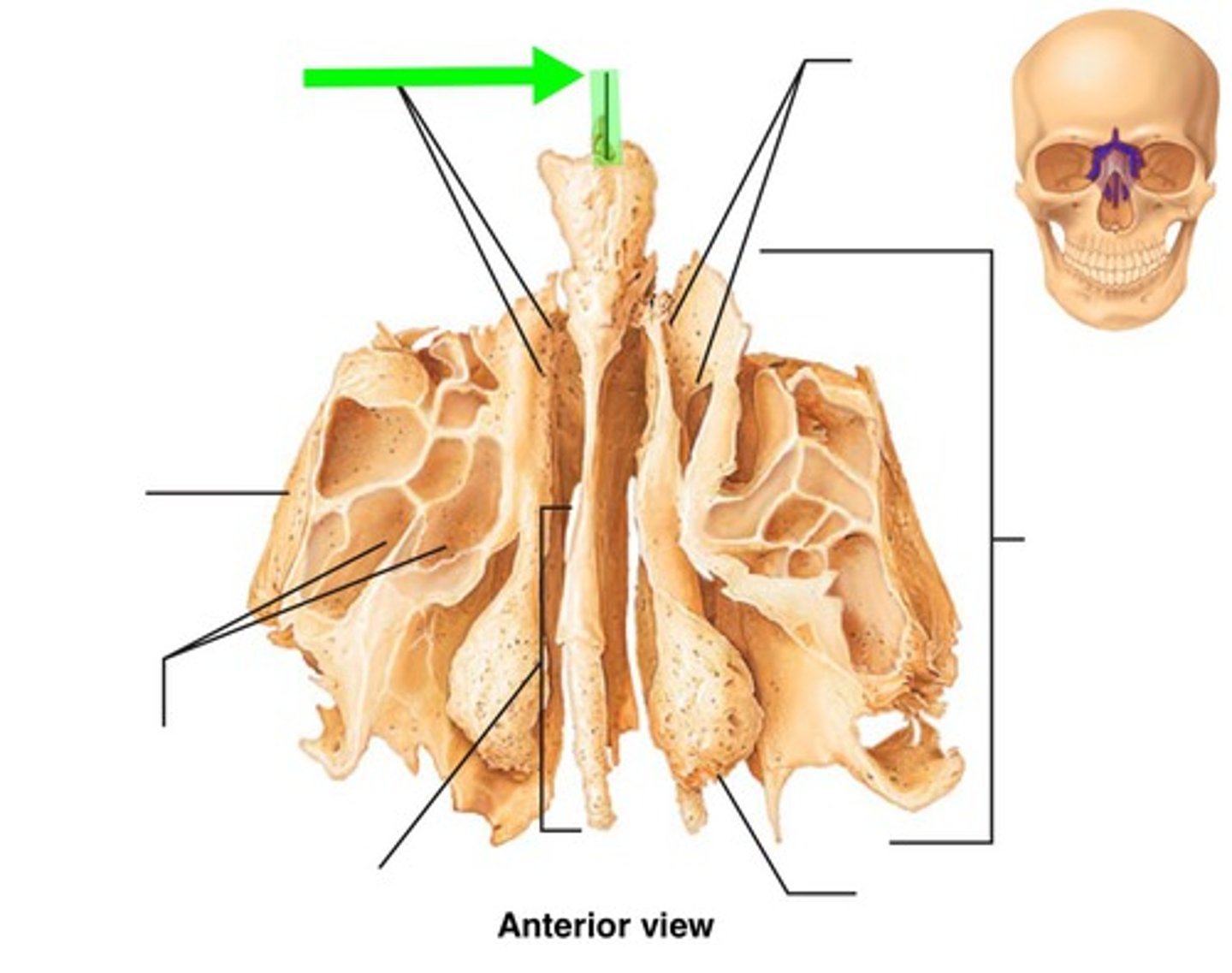
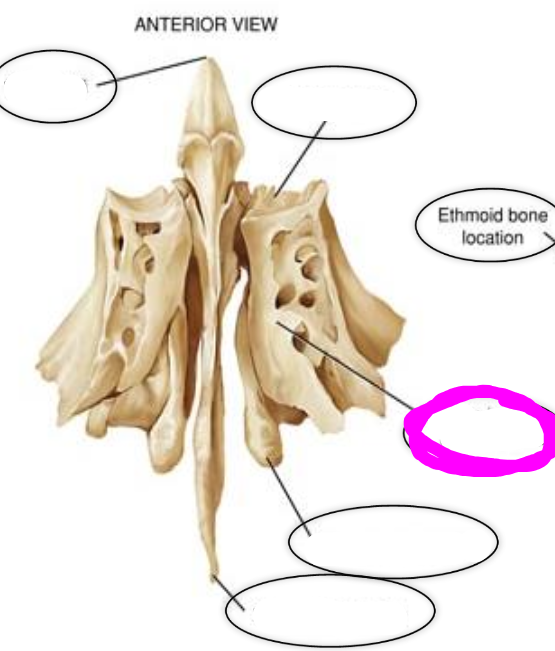
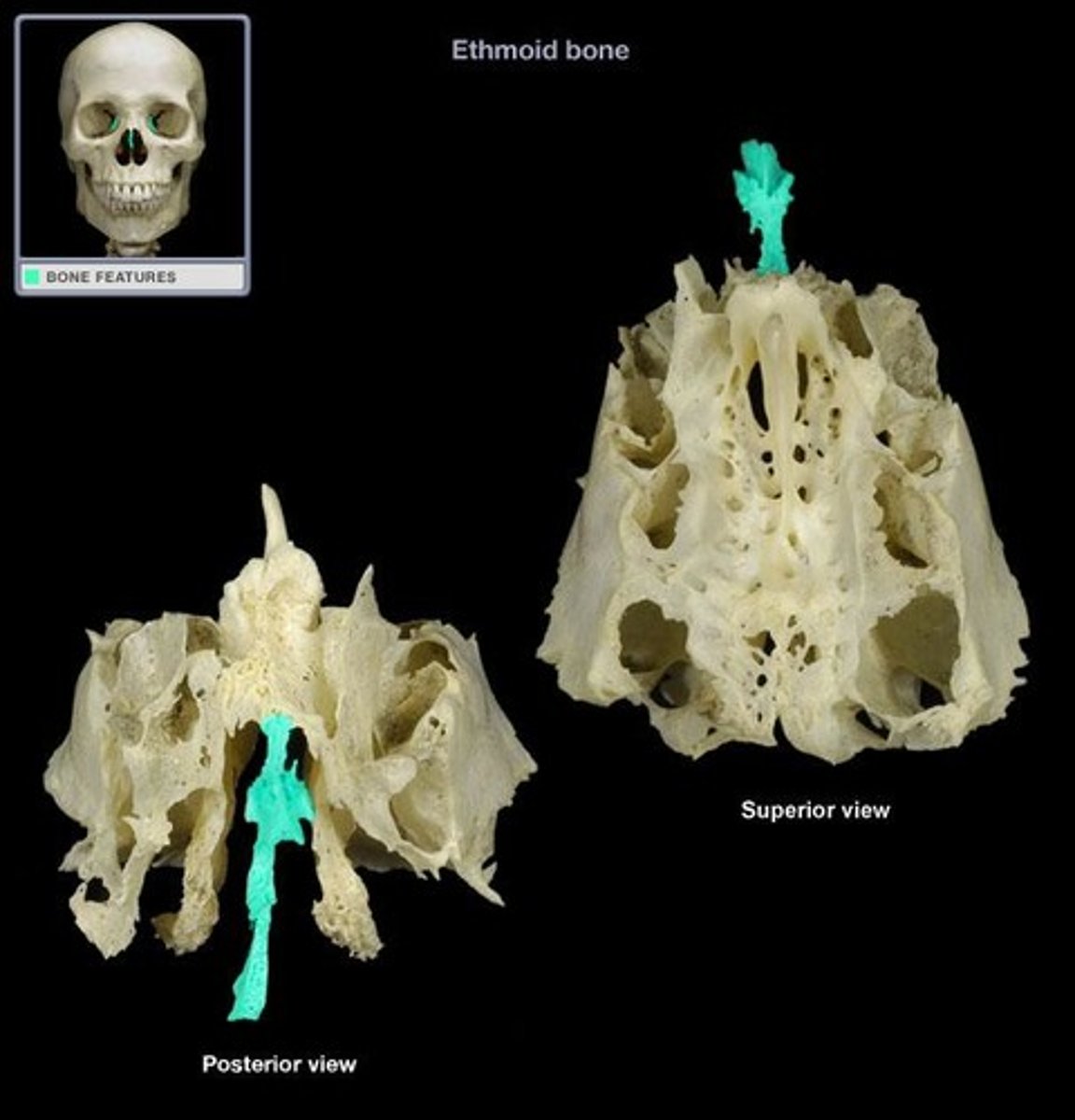
ethmoid (bones of the cranial skeleton)
contains the following:
1. Crista galli
2. Cribriform plate
3. Superior nasal concha
4. Middle nasal concha
5. Perpendicular plate
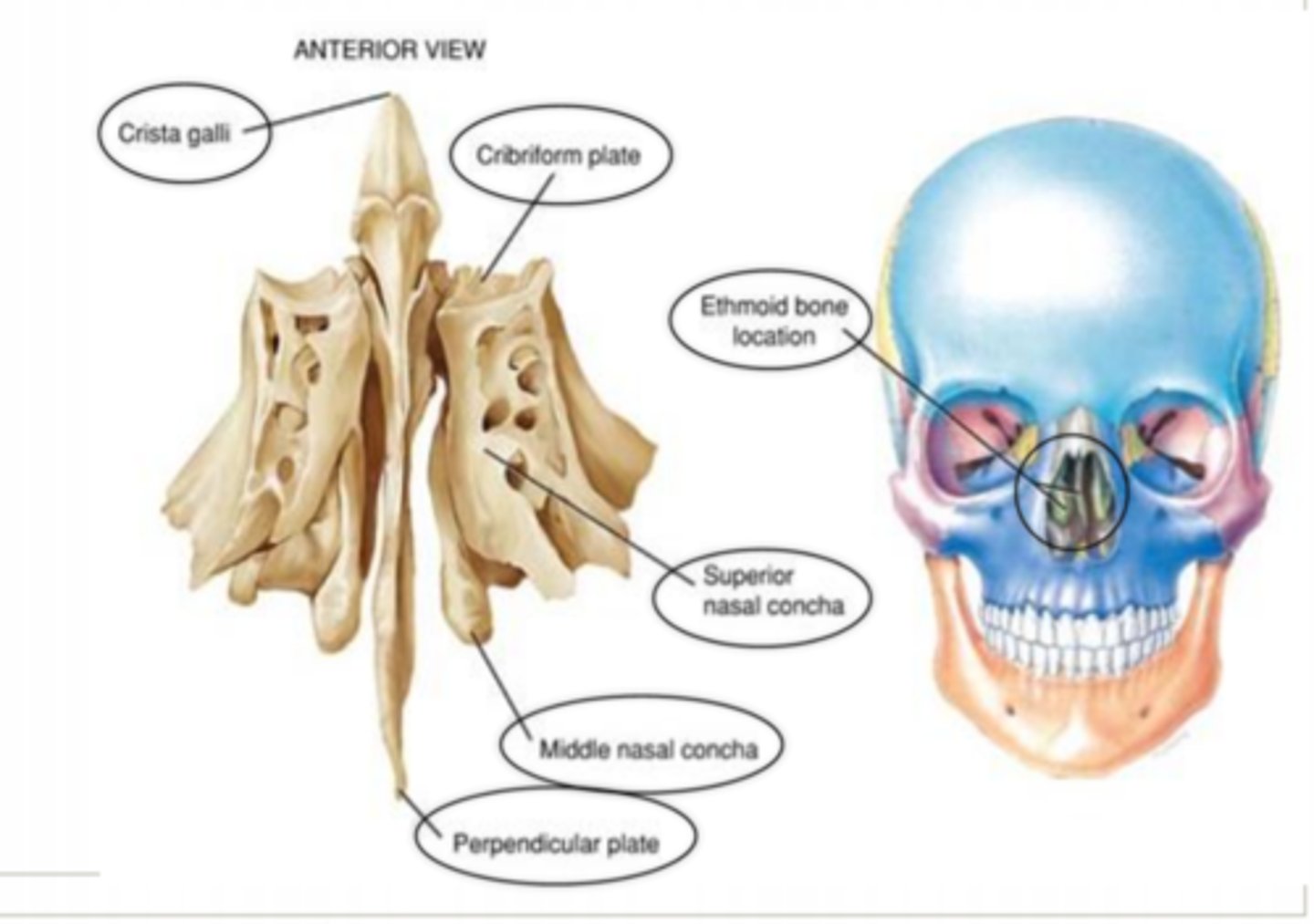
crista galli
extends superiorly into the cranial space
(ethmoid)
cribriform plate
separates the cranial cavity from the nasal cavities
allows passage of olfactory nerves
(ethmoid)

superior nasal concha
increases surface area to warm and humidify incoming air
(ethmoid)
middle nasal concha
increases surface area to warm and humidify incoming air
- middle
(ethmoid)
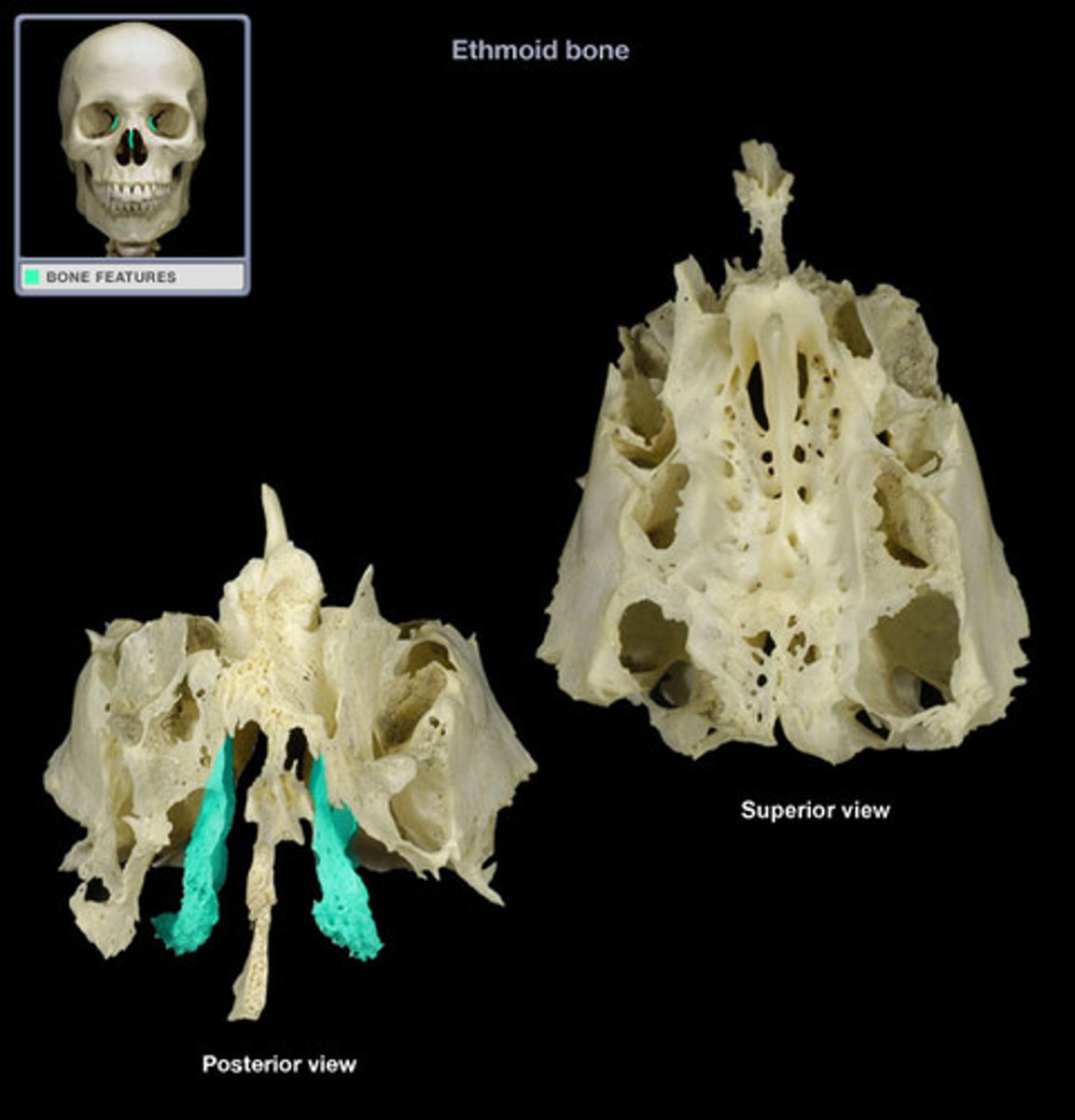
perpendicular plate
contributes to the structure of the nasal septum
(ethmoid)
sphenoid
wedge-shaped bone
great wings, lesser wings, hypophyseal fossa, lateral pterygoid plates, medial pterygoid plates
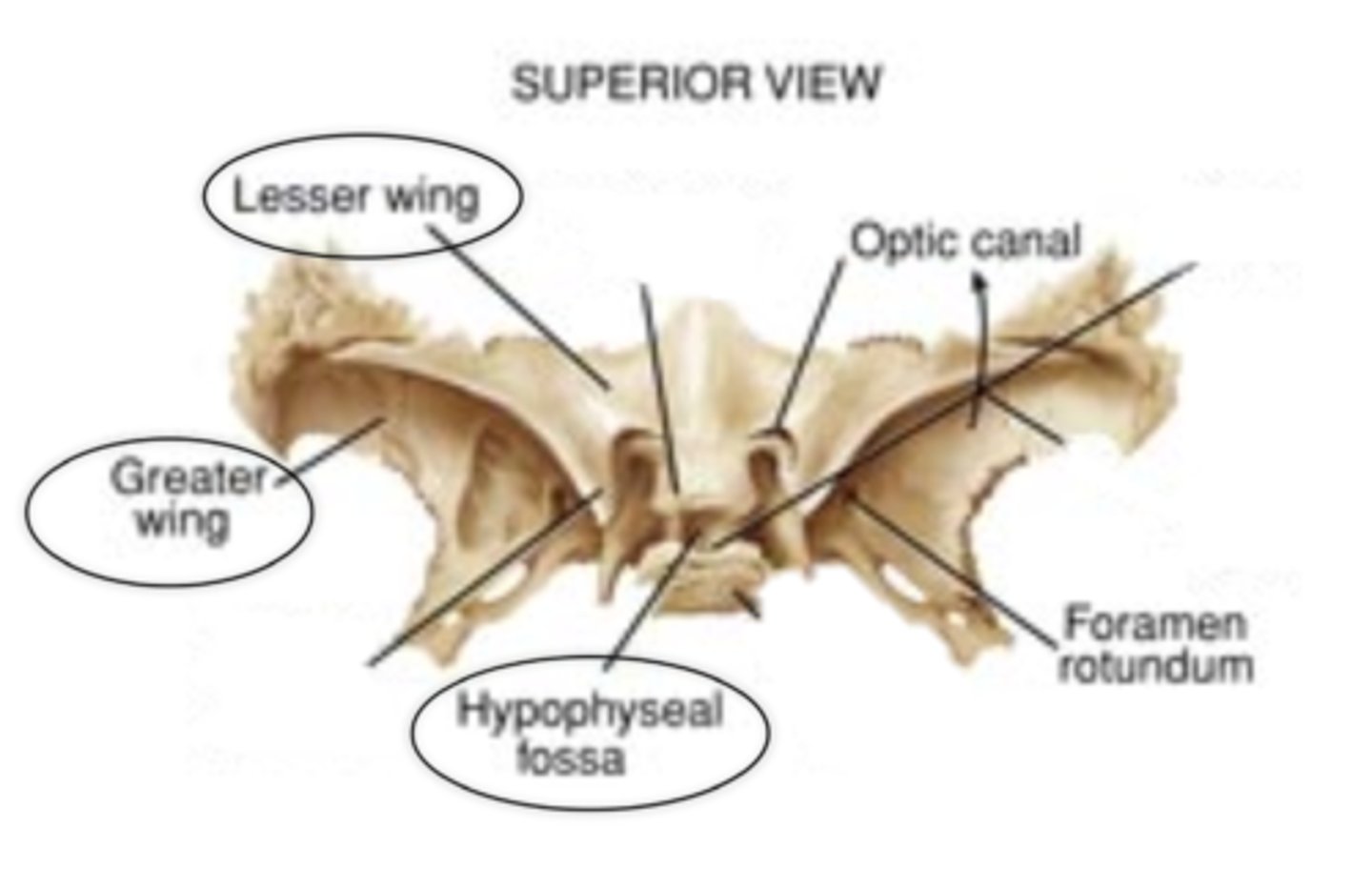
greater wings
(sphenoid bone)
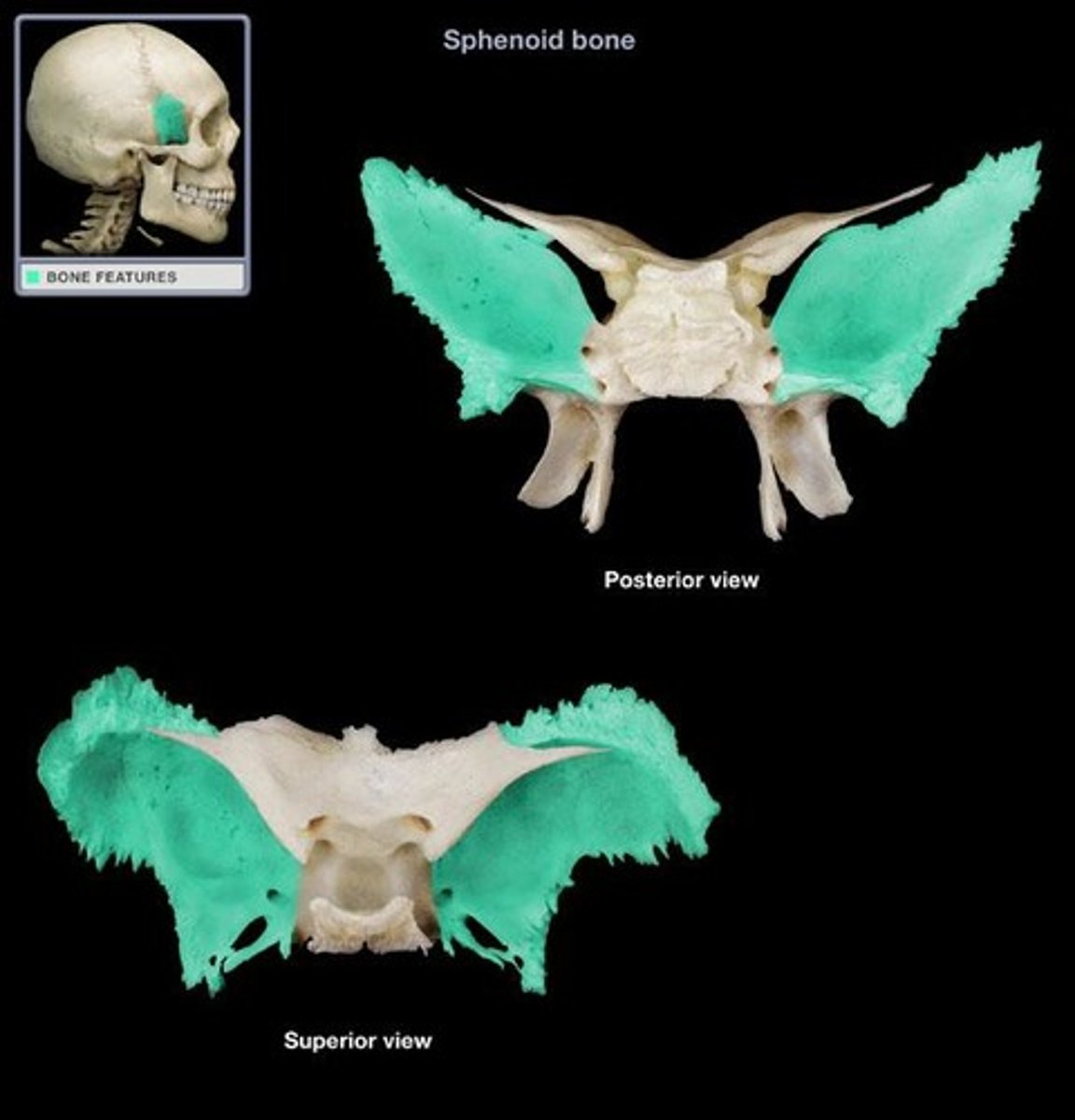
lesser wings
(sphenoid bone)
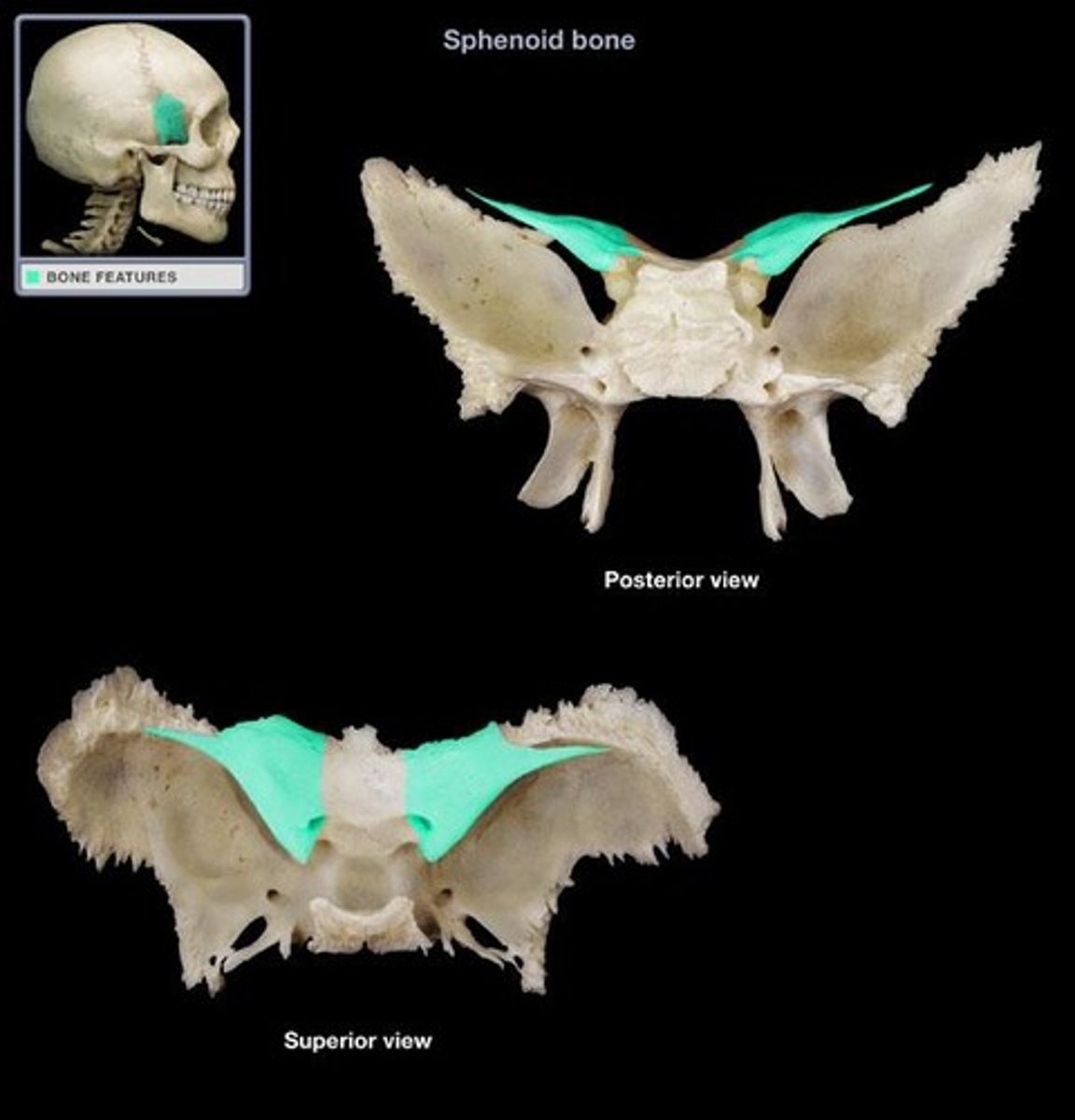
hypophyseal fossa (sella tursica)
houses the pituitary gland
(sphenoid bone)
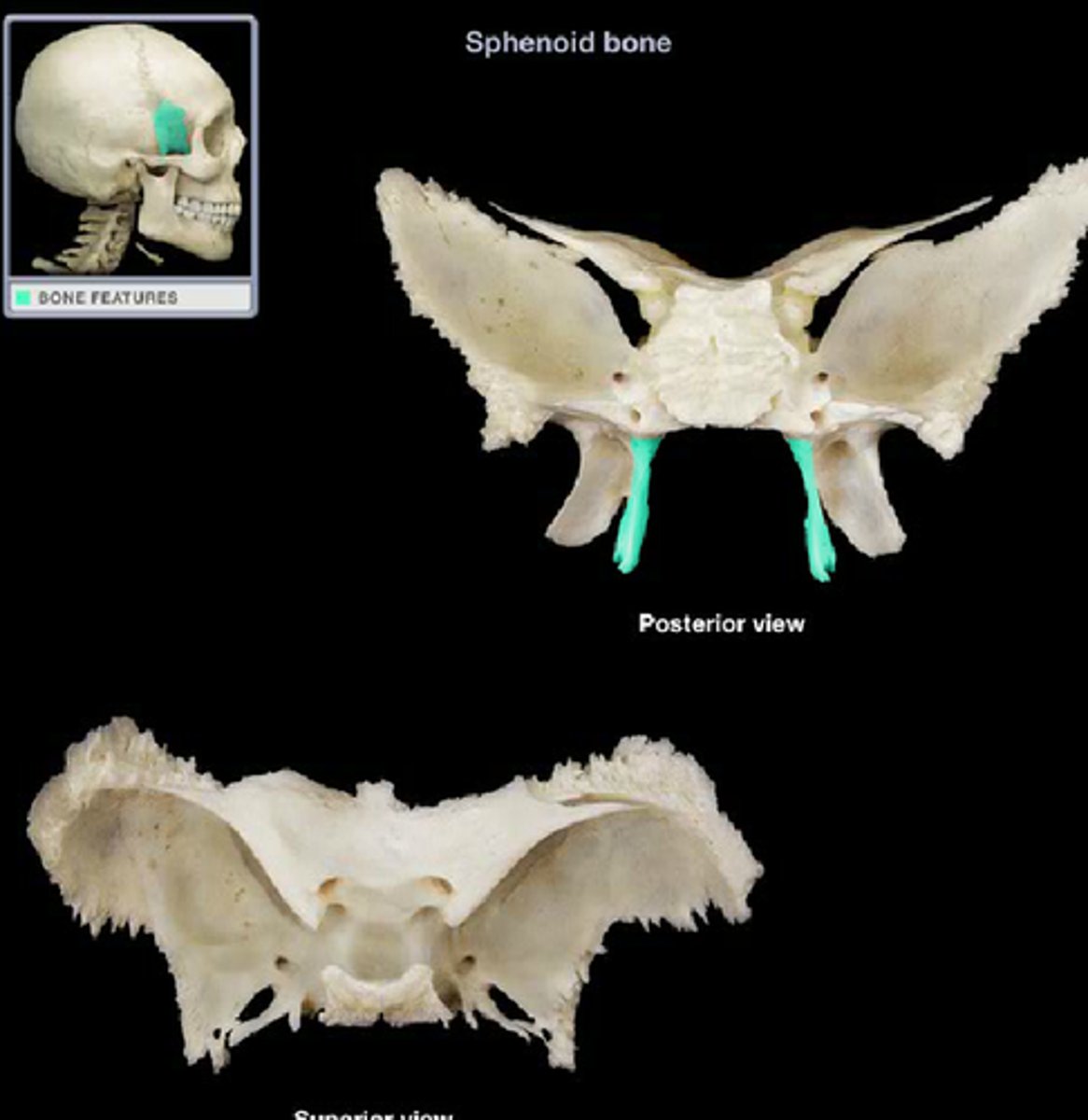
lateral pterygoid plates
point of attachment for muscles of mastication
(sphenoid bone)
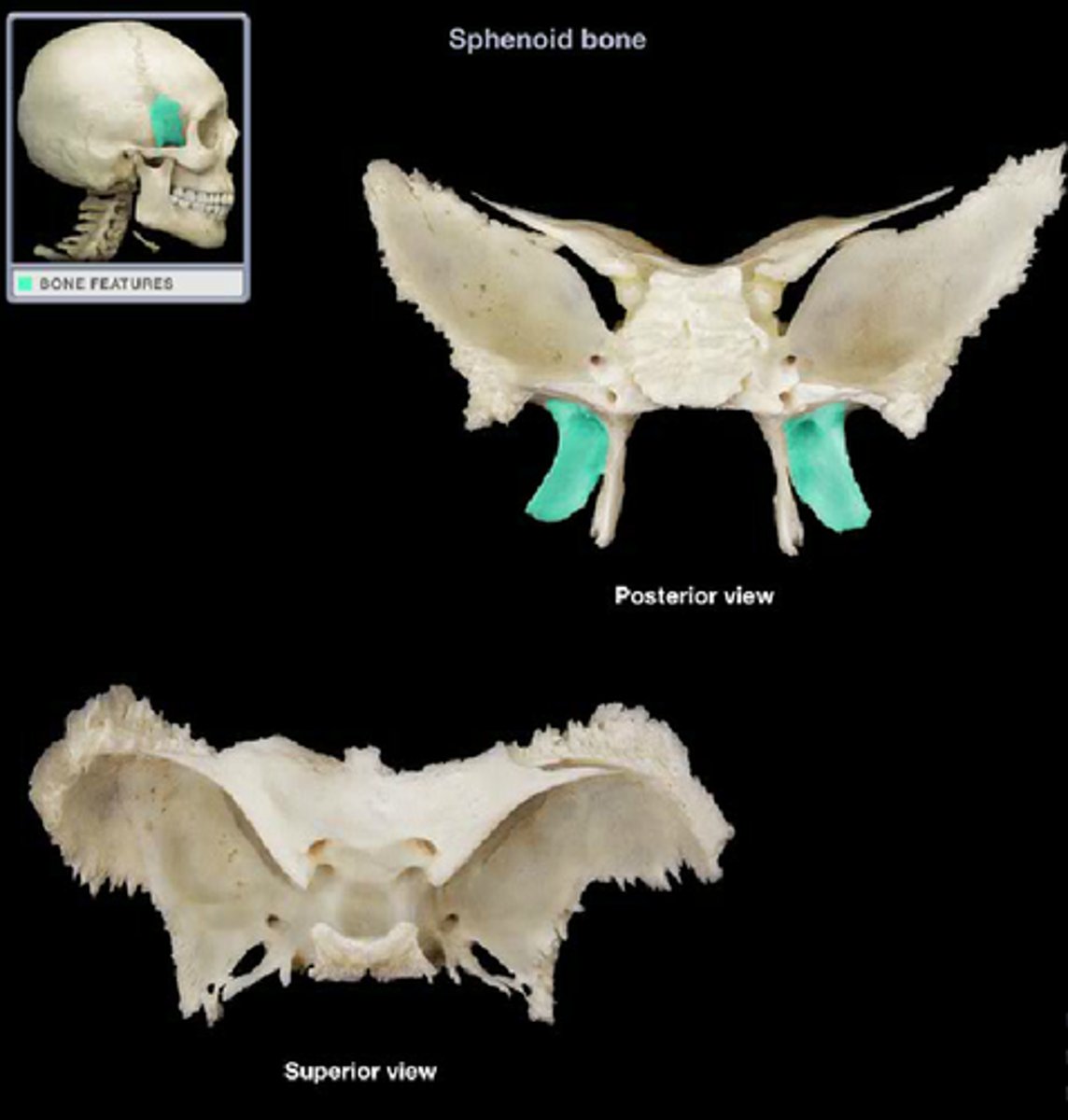
medial pterygoid plates
point of attachment for muscles of mastication
(sphenoid bone)
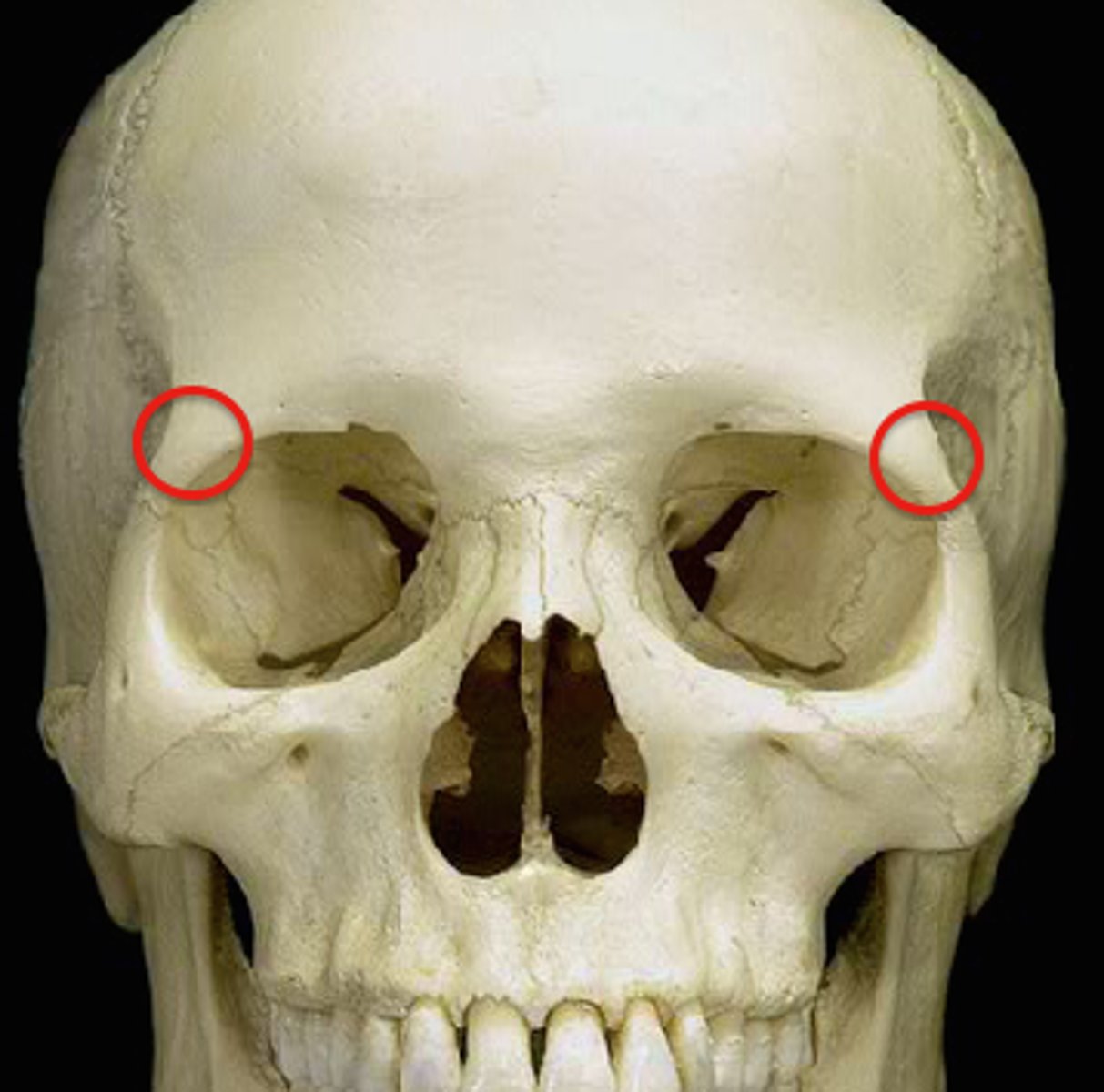
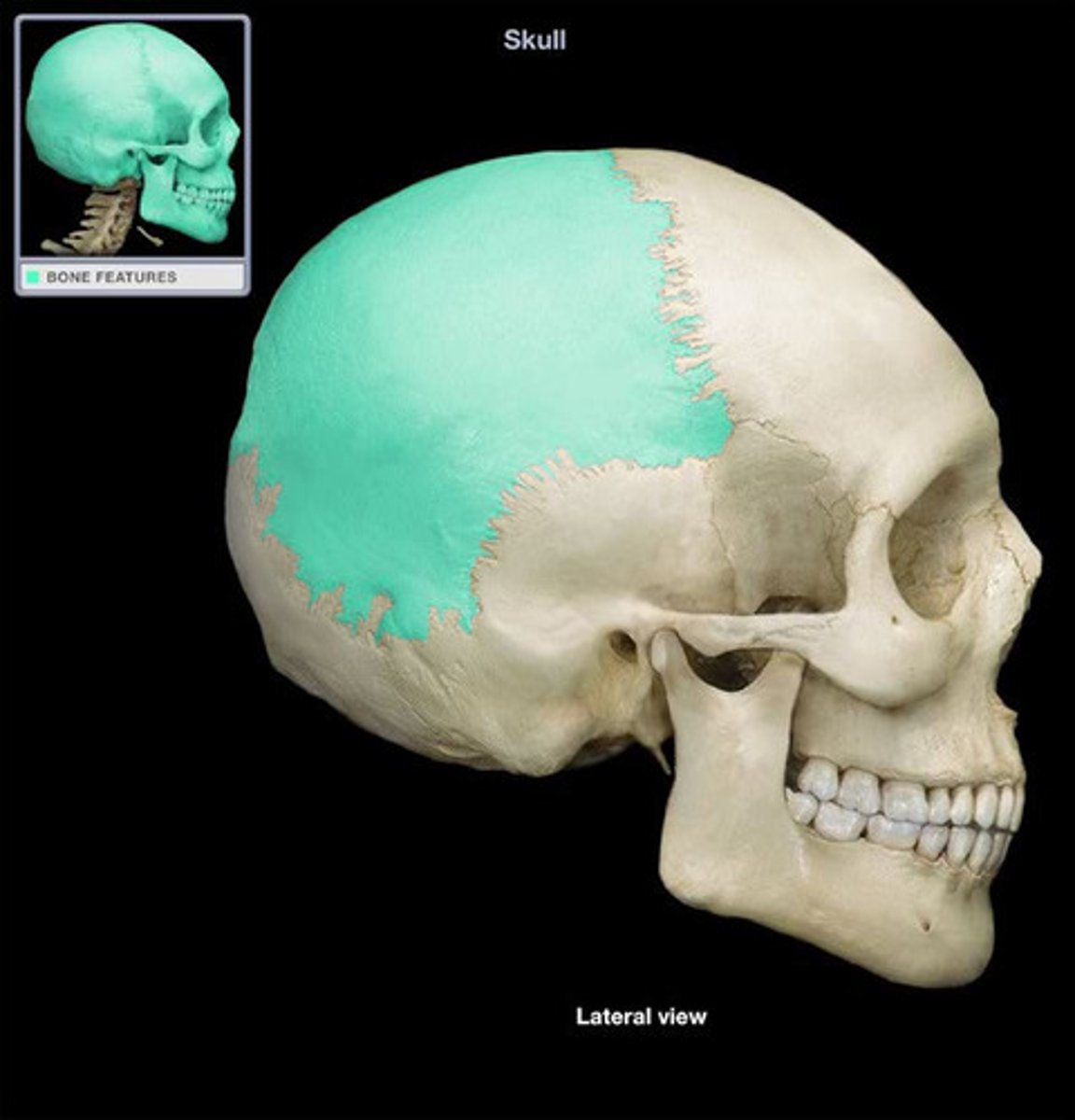
frontal bone
1. supraorbital margin
2. zygomatic process
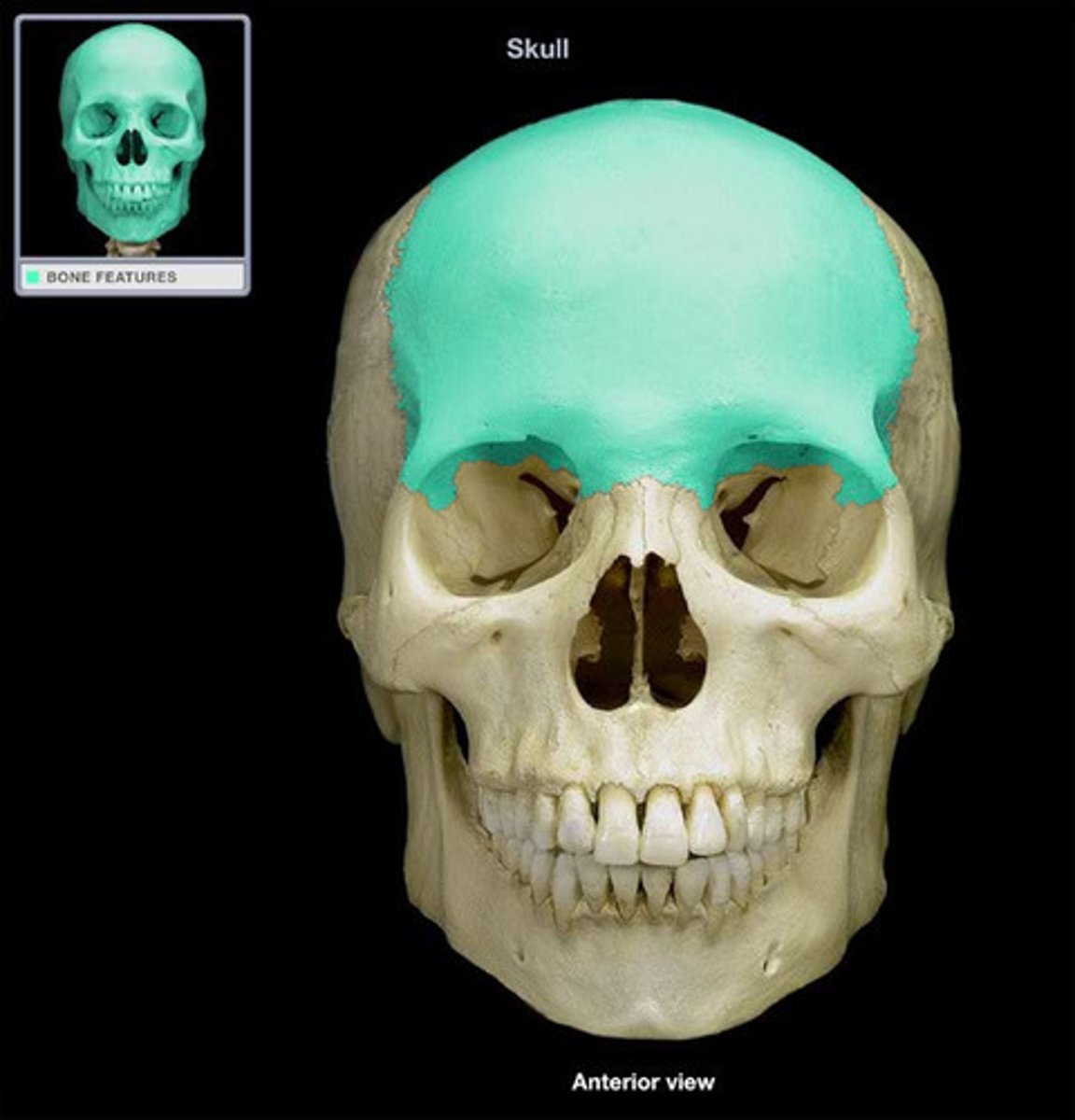
supraorbital margin
contributes to the orbital cavity
(frontal bone)
zygomatic process (frontal bone)
articulates with the zygomatic bone
(frontal bone)
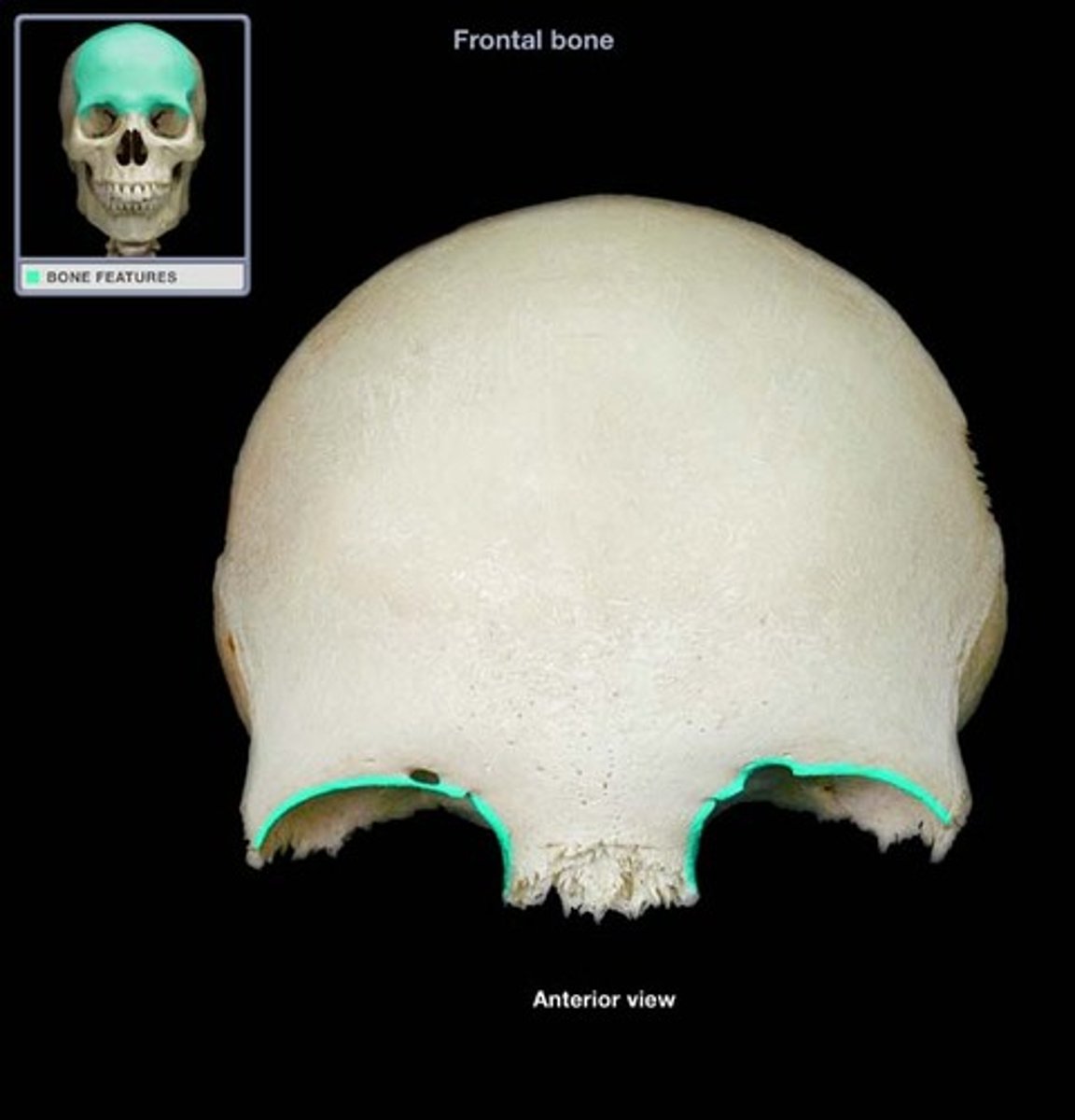
parietal bone
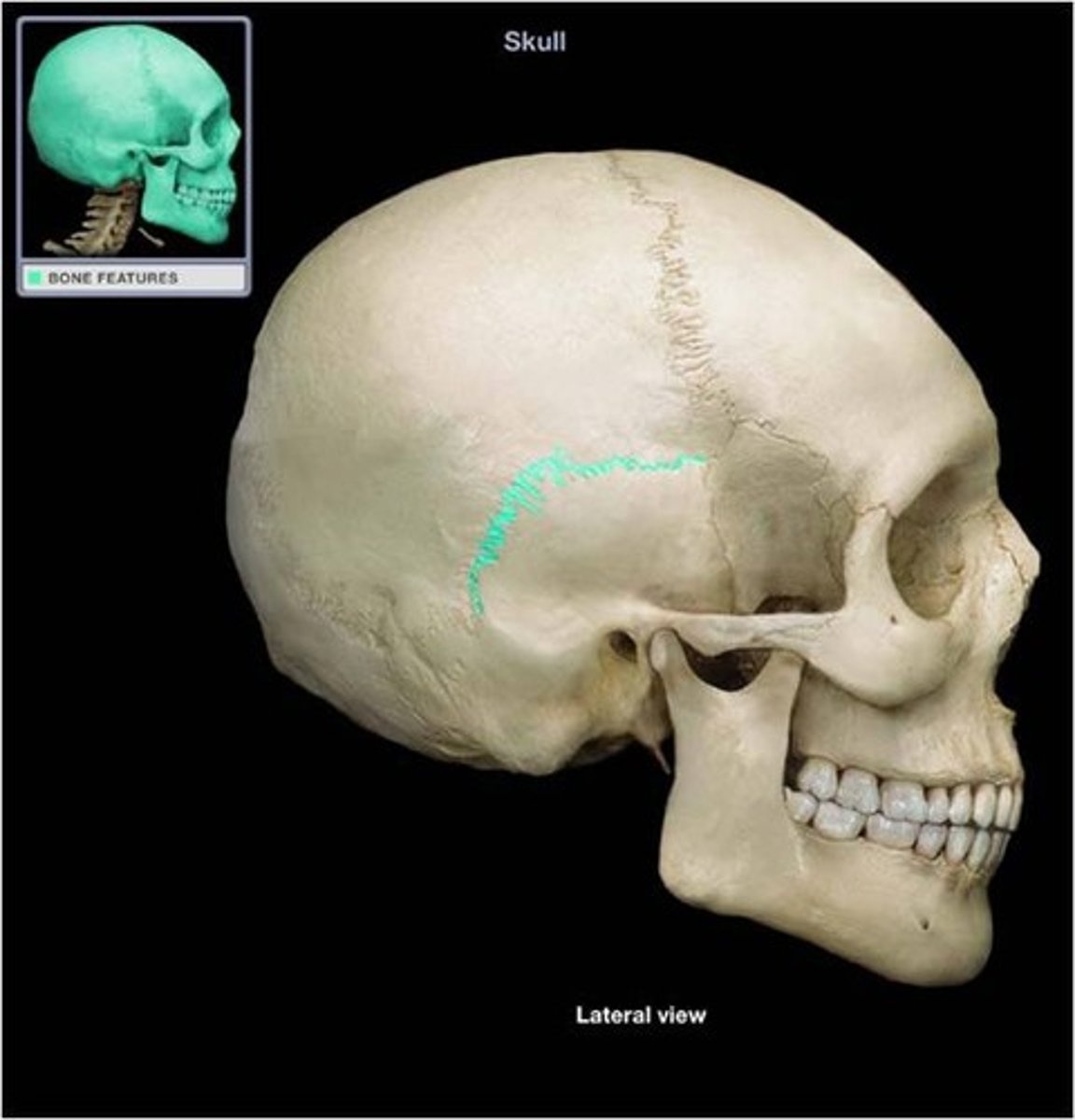
1. coronal suture
2. squamosal suture
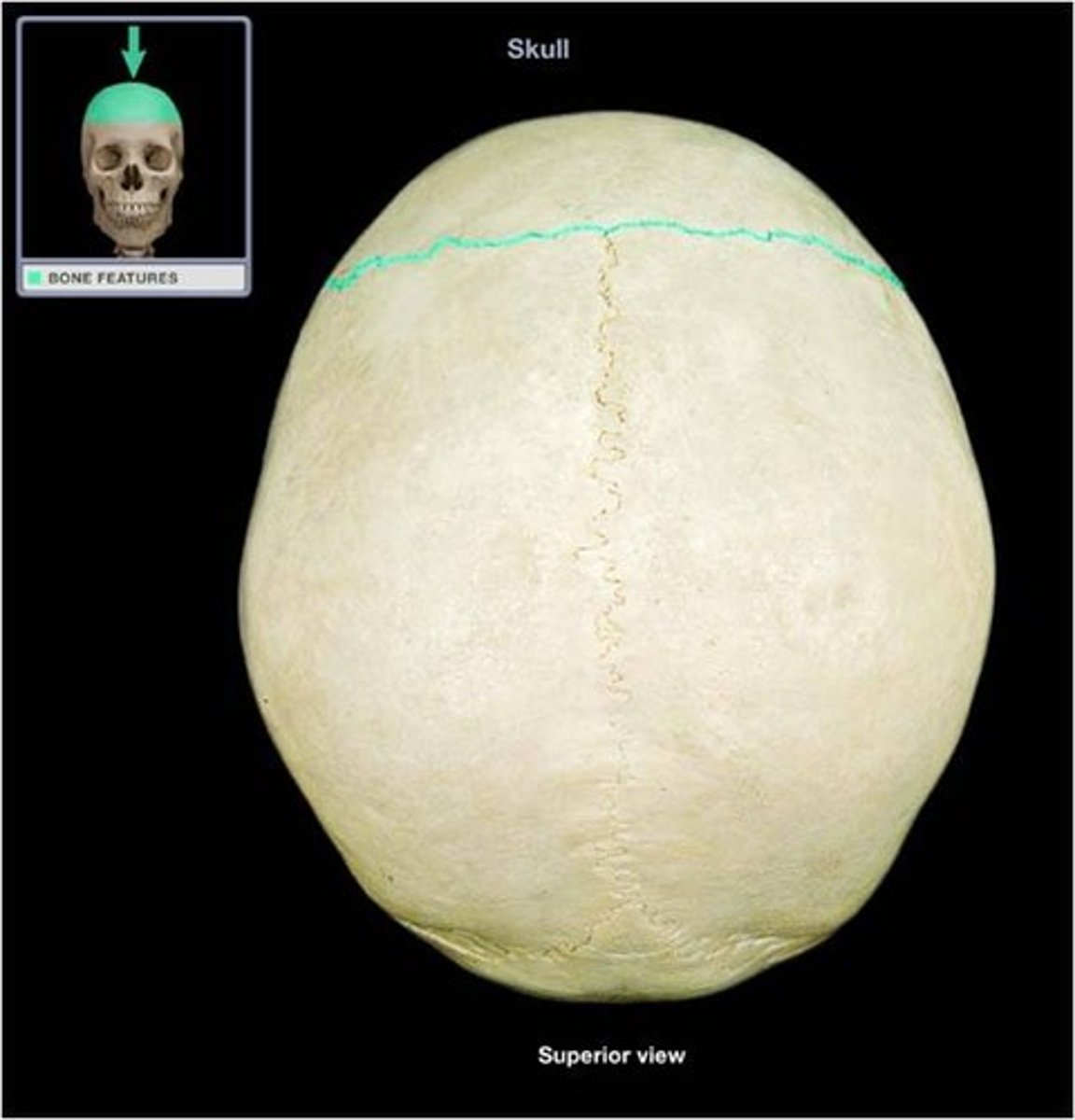
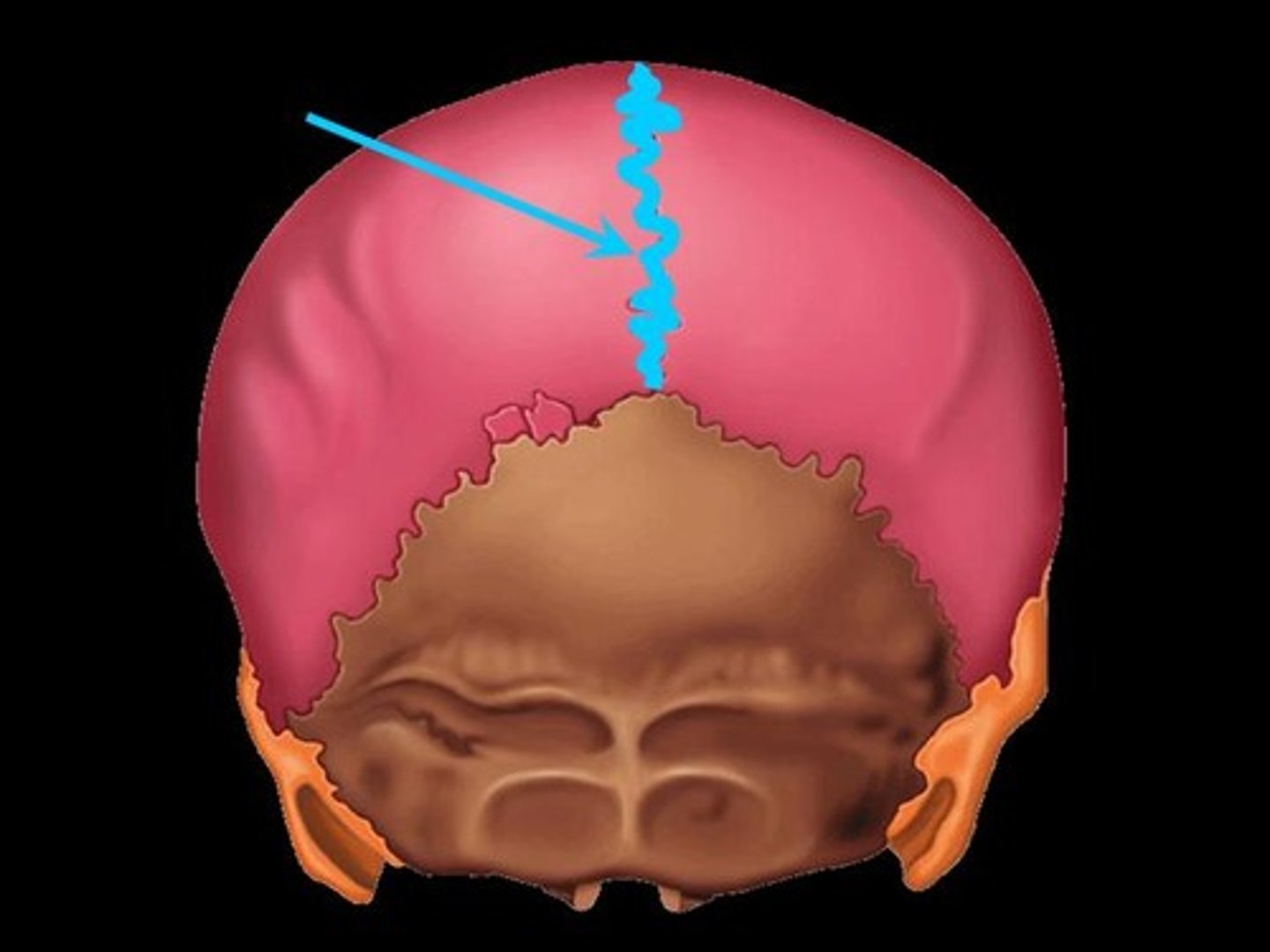
3. sagittal suture
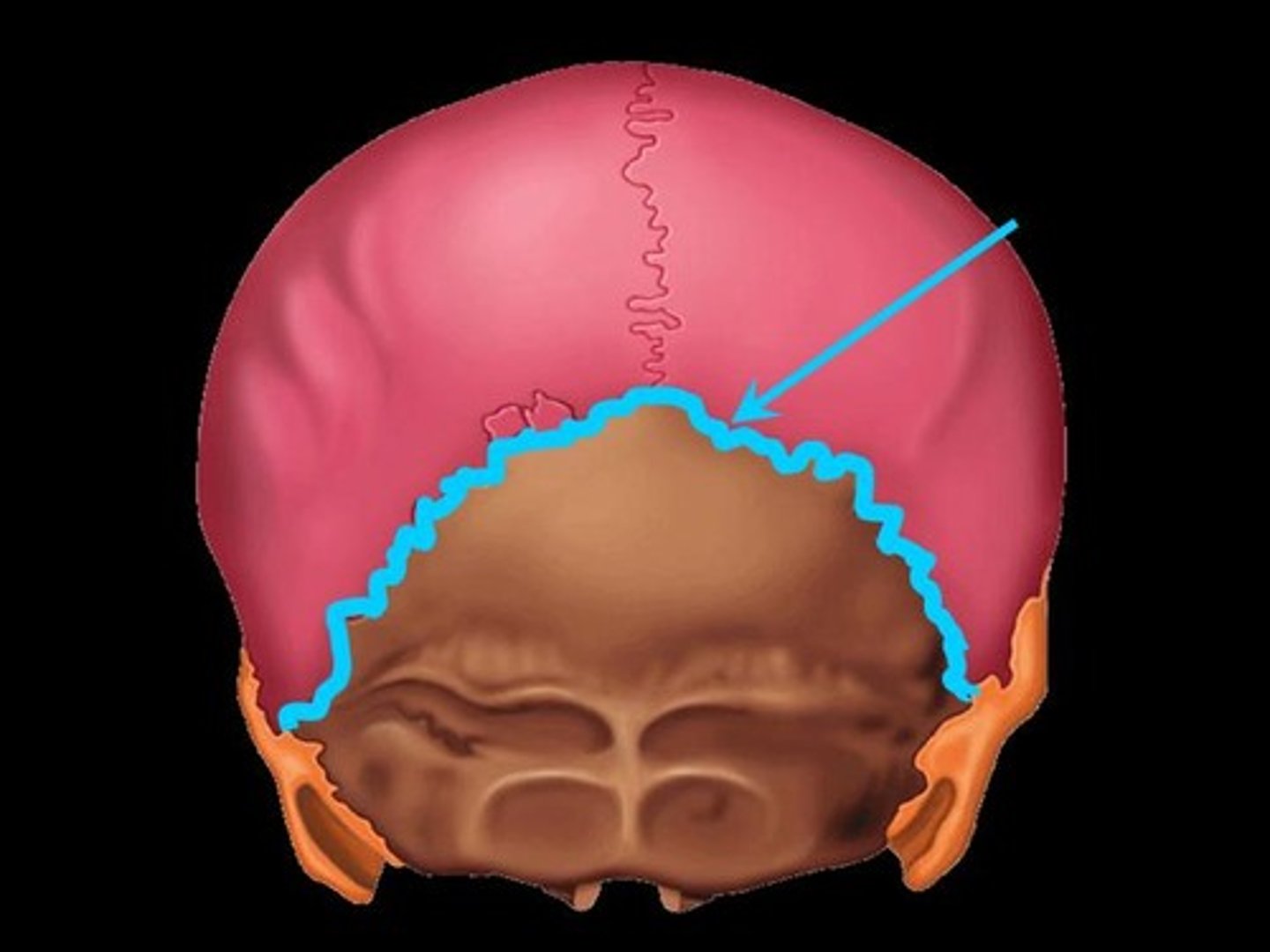
4. lambdoidal suture
coronal suture
between the frontal bone and parietal bone
squamosal suture
between temporal and parietal bones
lambdoial suture
between occipital and parietal bones
sagittal suture
between both parietal bones
Craniosynostosis
when the sutures of the skull become ossified prematurely
- can affect 1 or more of the sutures
- often requires surgery to separate the fused bones
- may/not be associated with genetic syndromes
- can affect brain development/learning
occipital bone
1. foramen magnum
2. condyles
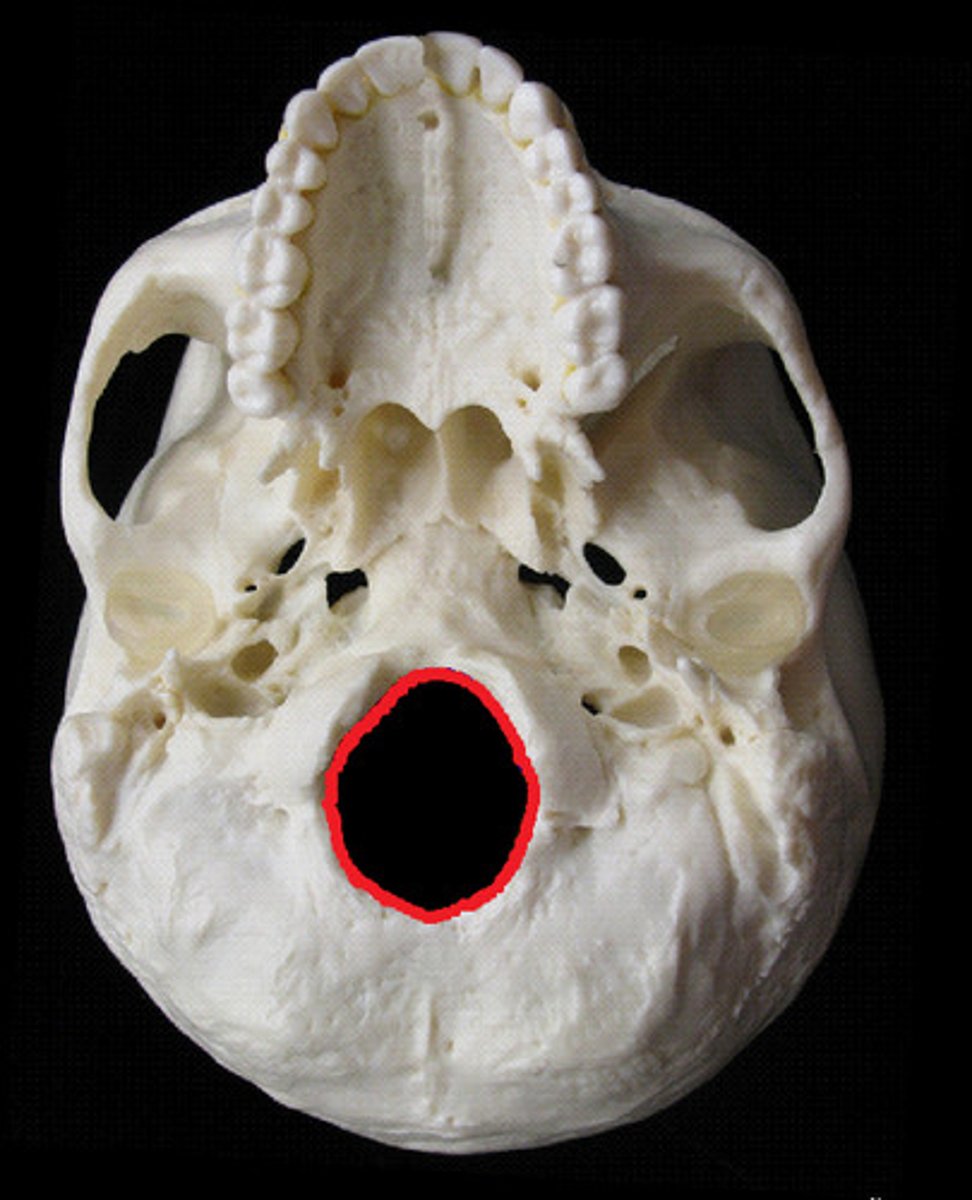
foramen magnum
allows for passage of the spinal cord to the brainstem
(occipital bone)
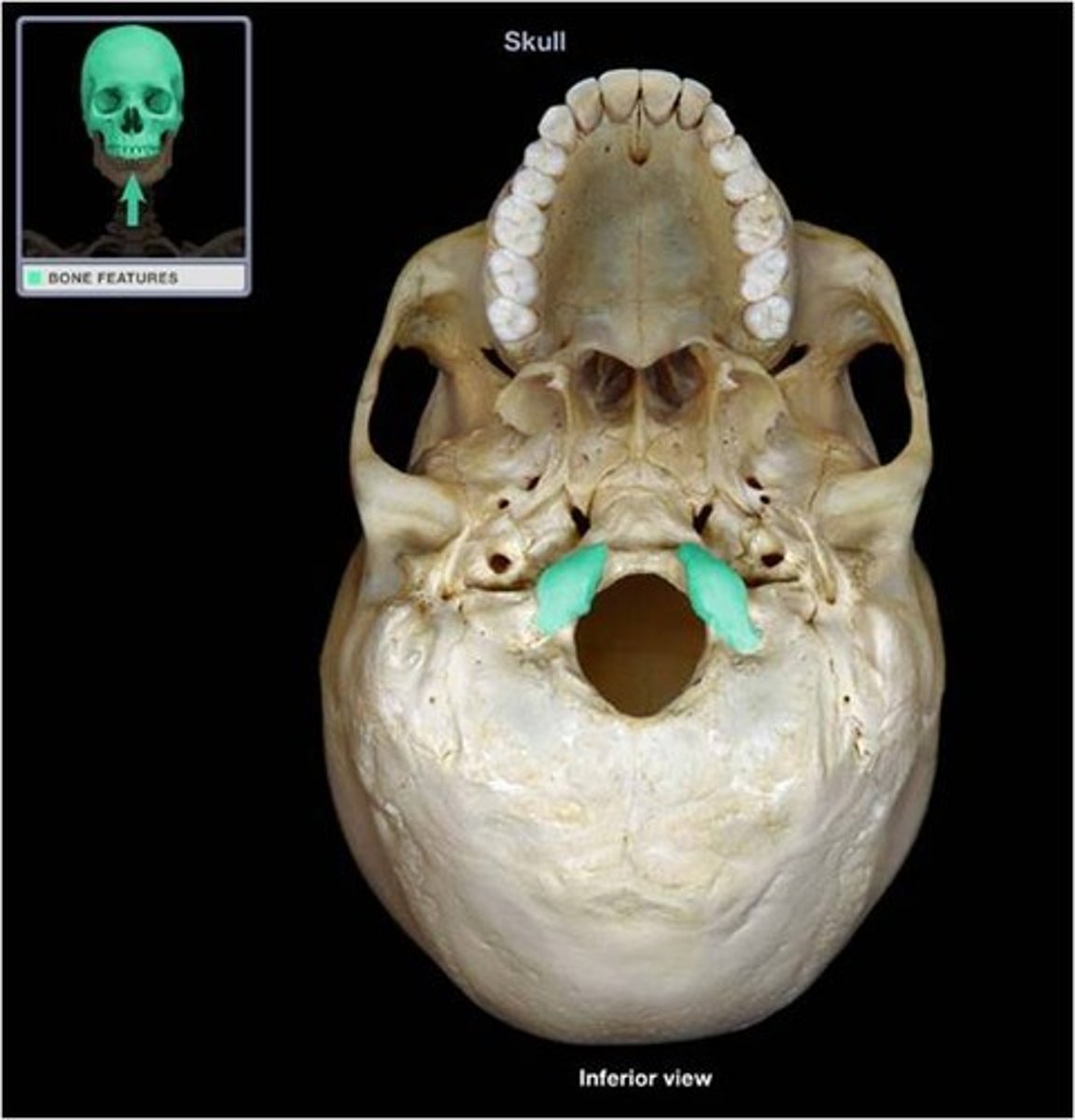
condyles
resting point for the first cervical vertebra
(occipital bone)
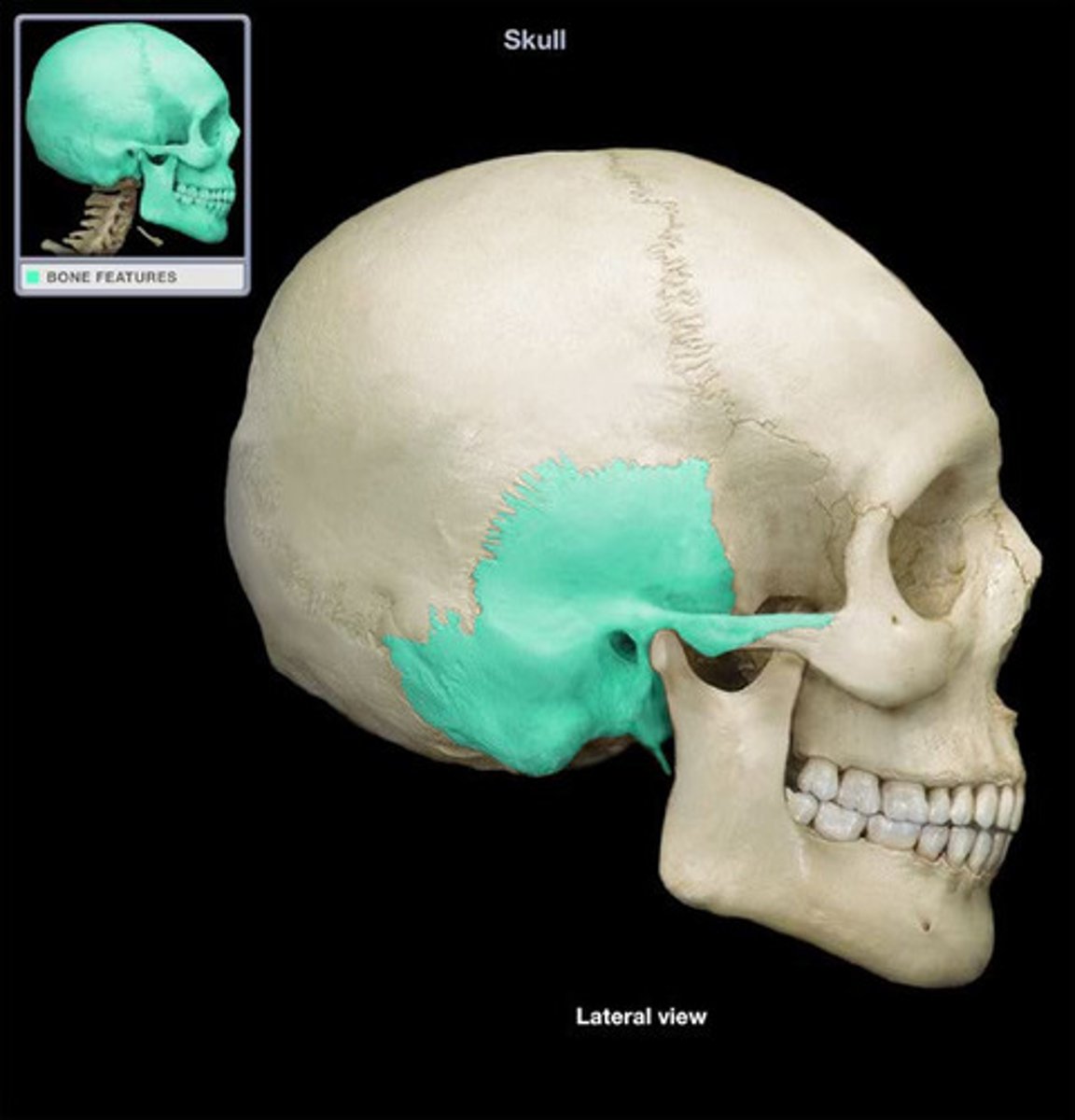
temporal bone
1. external auditory meatus
2. zygomatic process
3. mandibular fossa
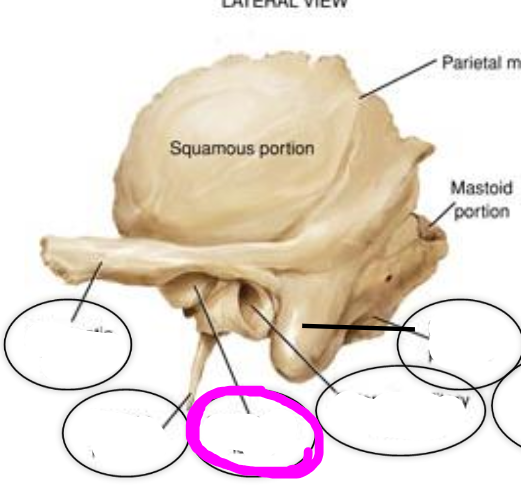
4. styloid process
5. mastoid process
6. petrous part
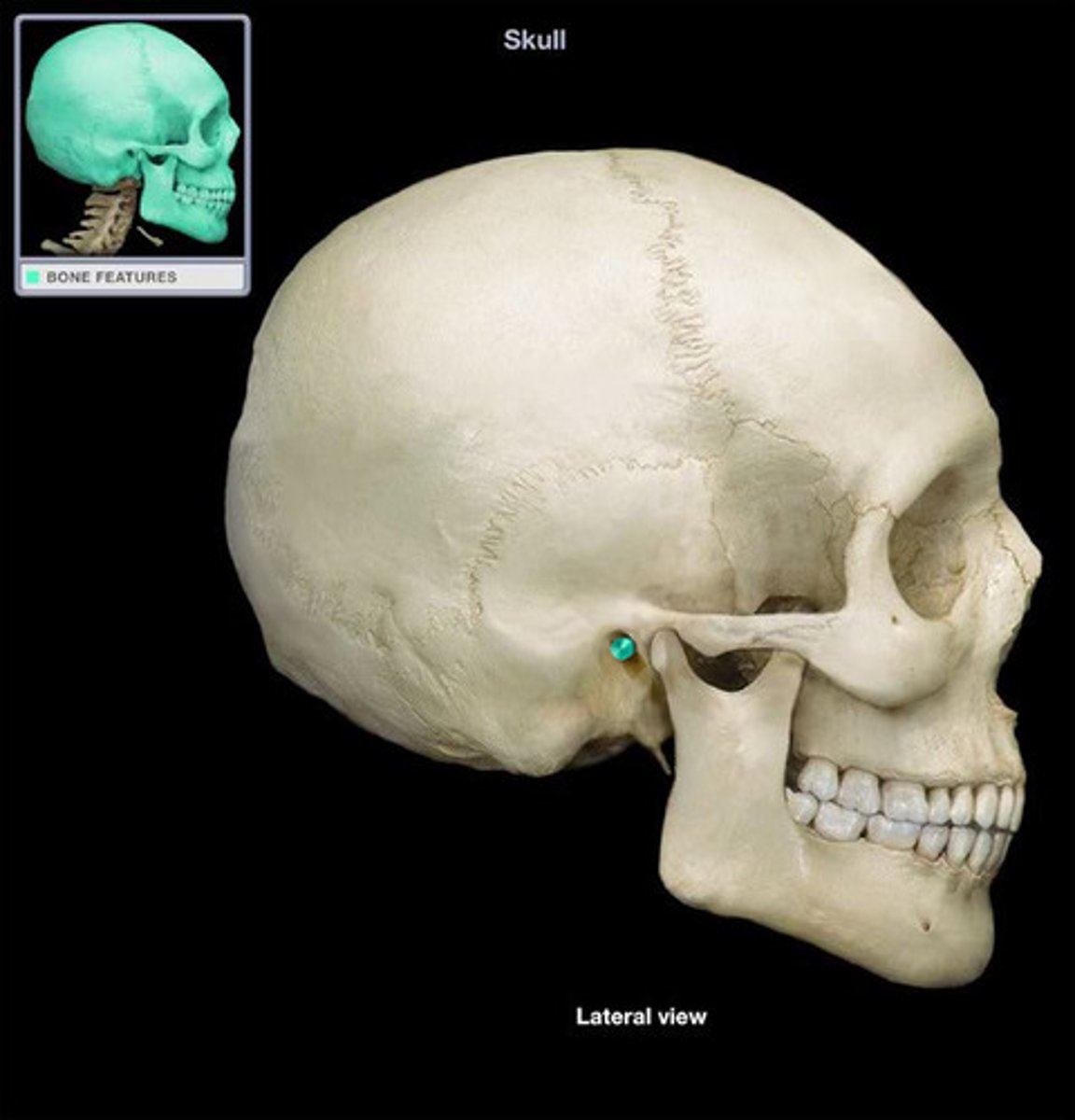
external auditory meatus
ear canal
(temporal bone)
zygomatic process (temporal bone)
articulates with the temporal process of the zygomatic bone to from zygomatic arch
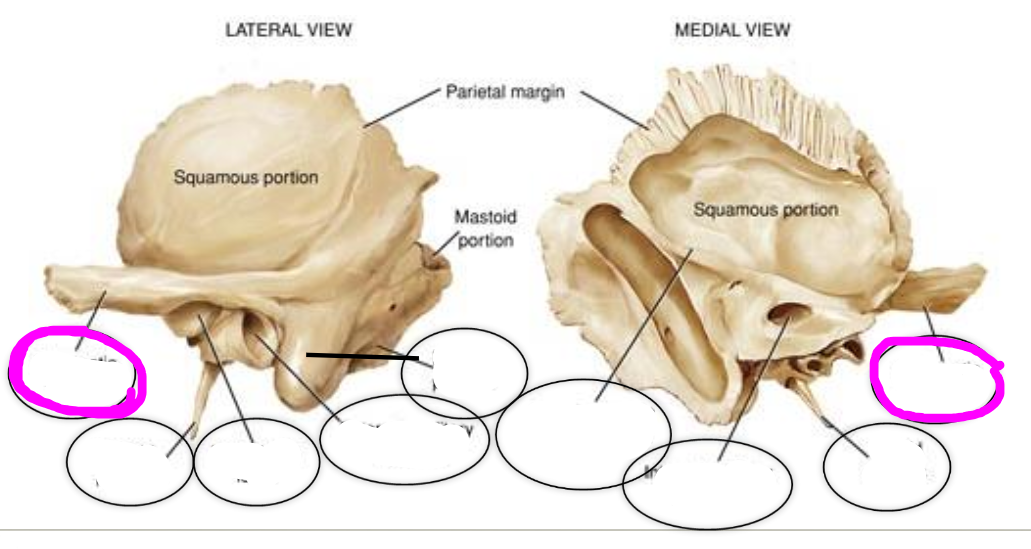
mandibular fossa
articulates with mandibular condyle to form the temporomandibular joint
(temporal bone)
styloid process
point of attachment for various muscles
(temporal bone)
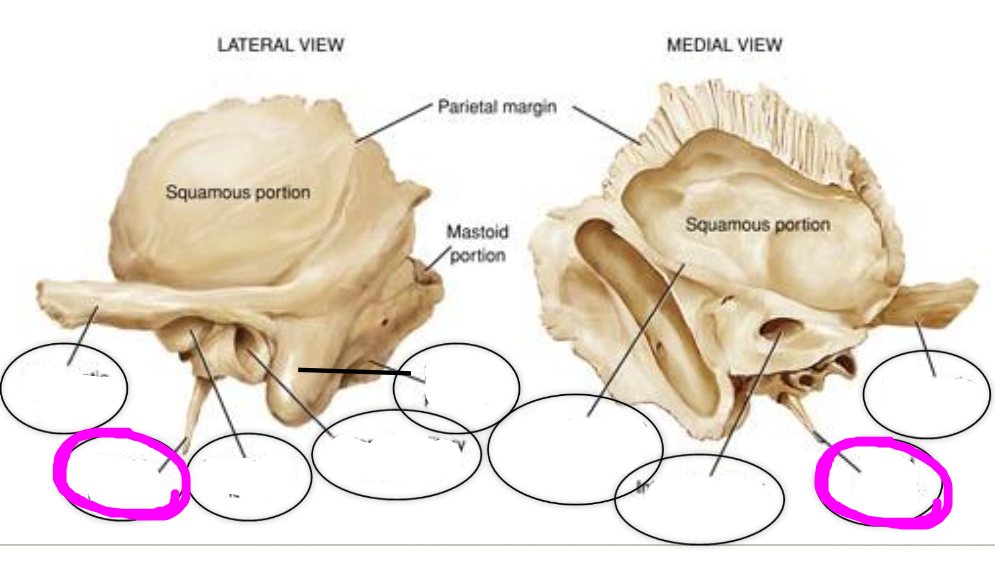
mastoid process
point of attachment for various muscles of the neck
(temporal bone)
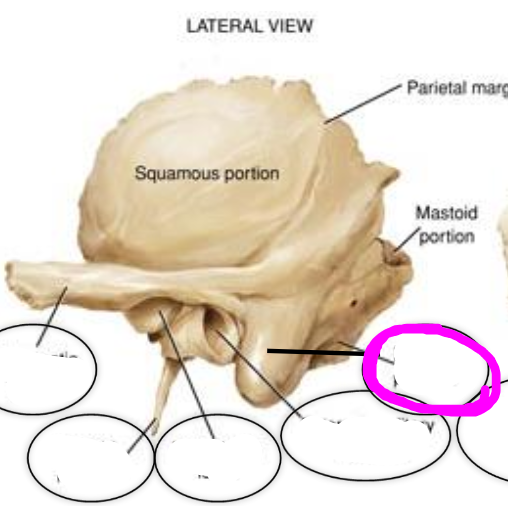
petrous part
houses the organs of hearing (cochlea) and equilibrium (semicircular canals)
(temporal bone)
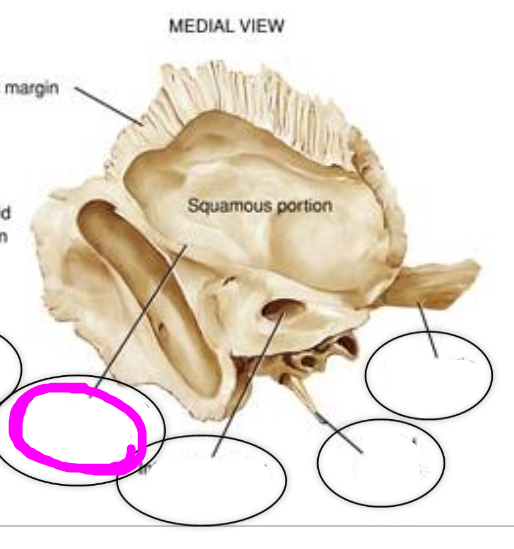
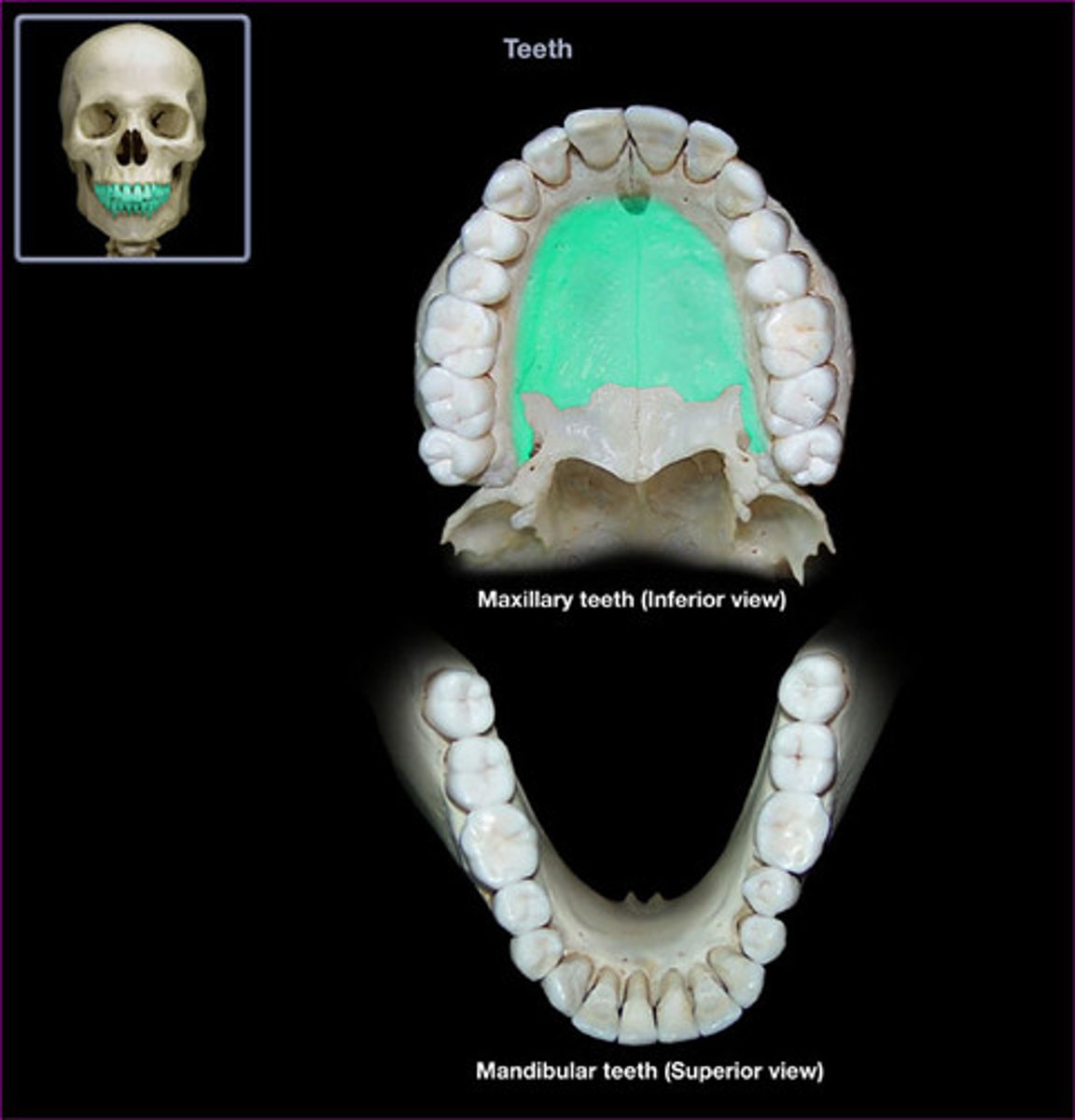
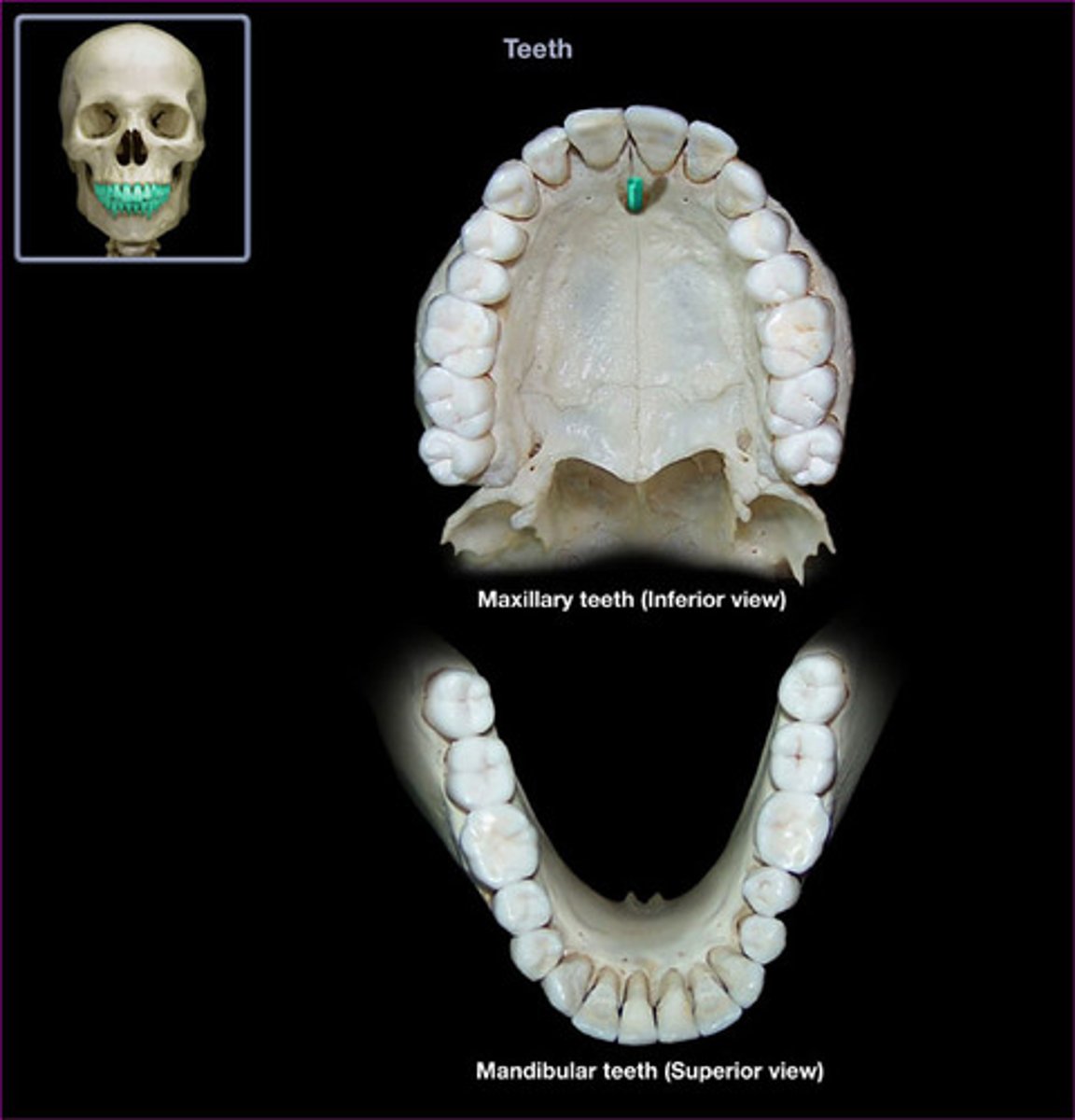
types of teeth
permanent dental arch:
- central incisor
- lateral incisor
- cuspids (canine)
- first bicuspids (premolar)
-second bicuspid (premolar)
- first molar
- second molar
- third molar (wisdom teeth)
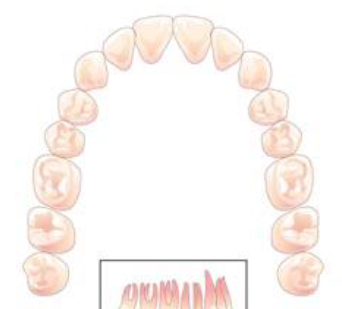
components of tooth
- crown
- root
- enamel
- dentin
- pulp
crown (tooth)
area above the gum line
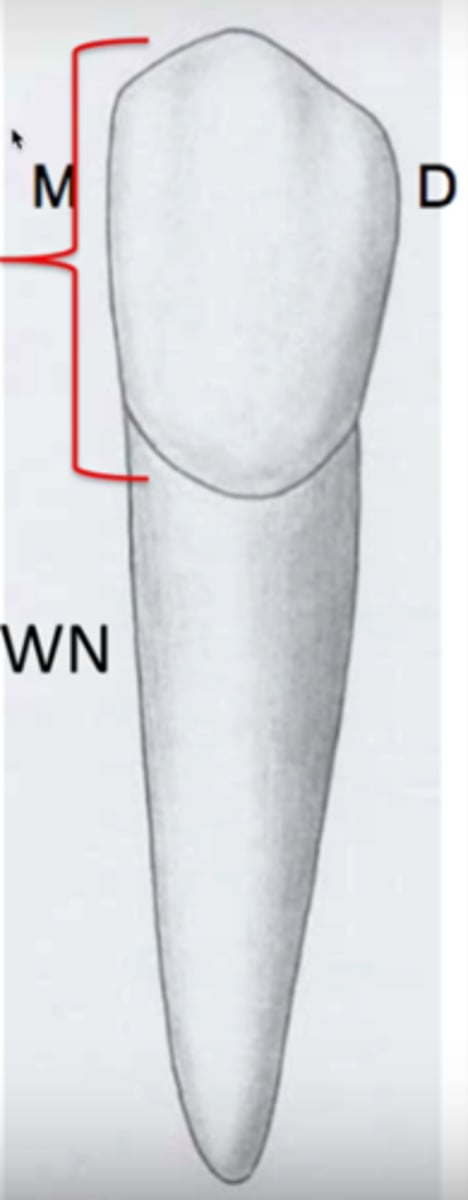
root (tooth)
below the gum line
enamel (tooth)
dense surface for protection
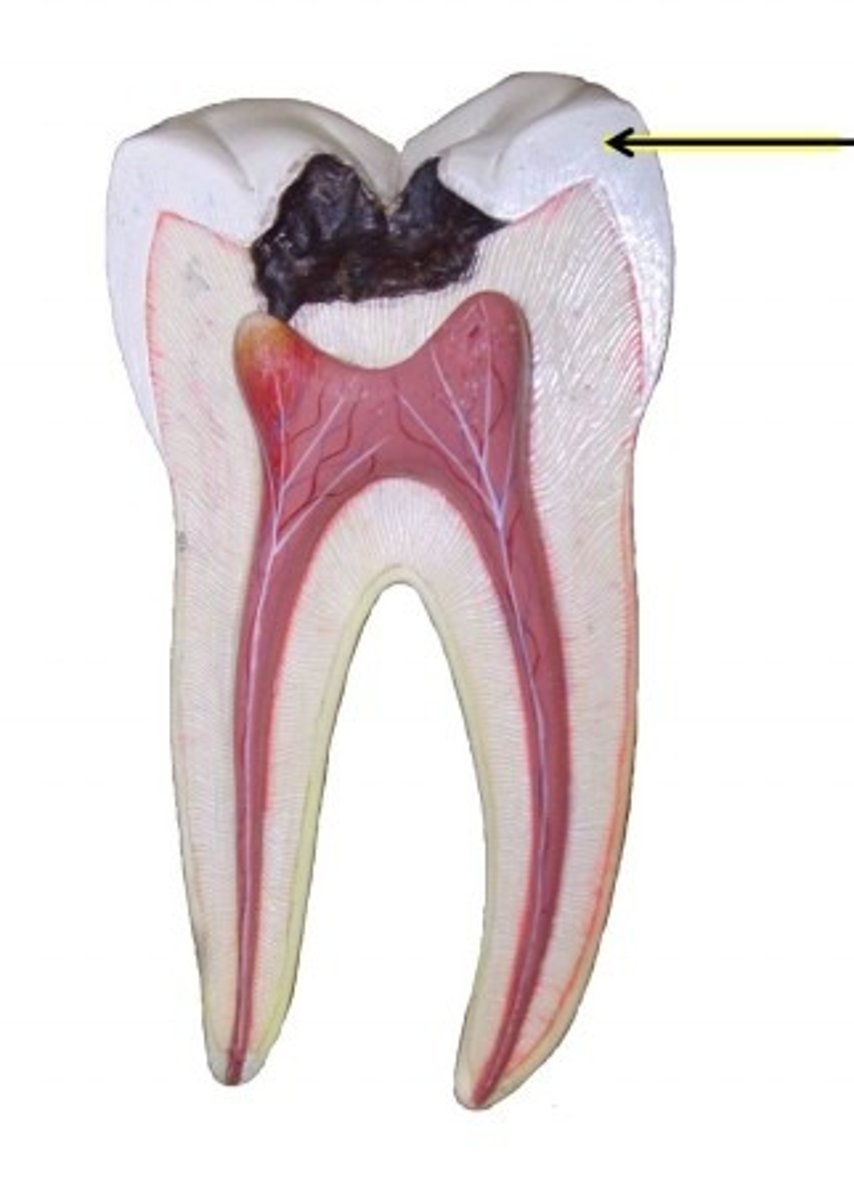
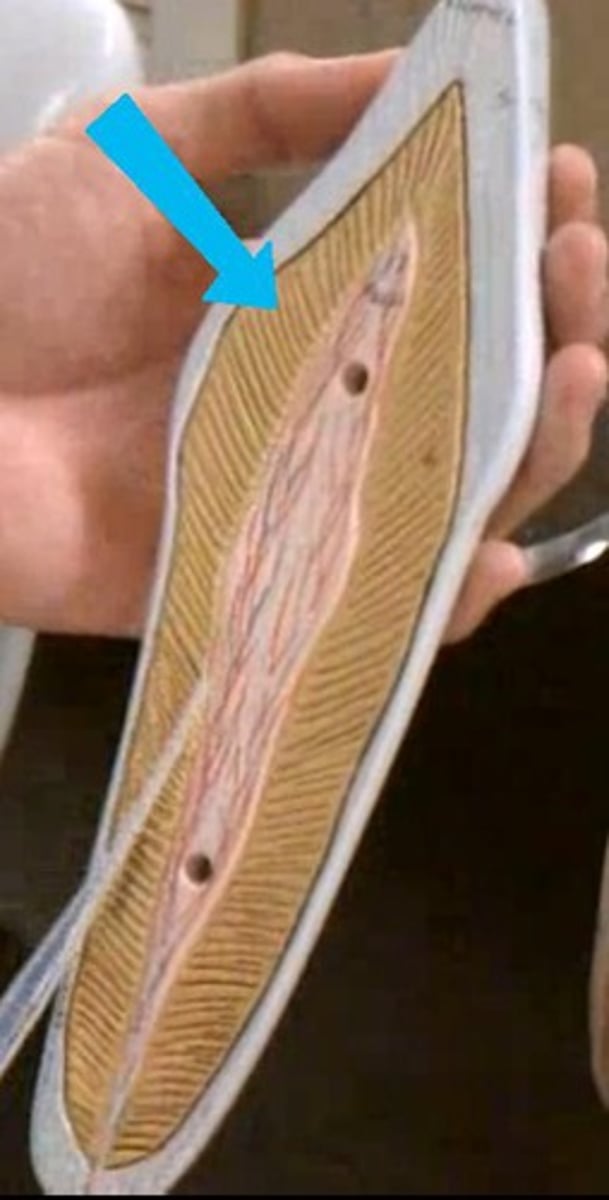
dentin
solid portion of tooth

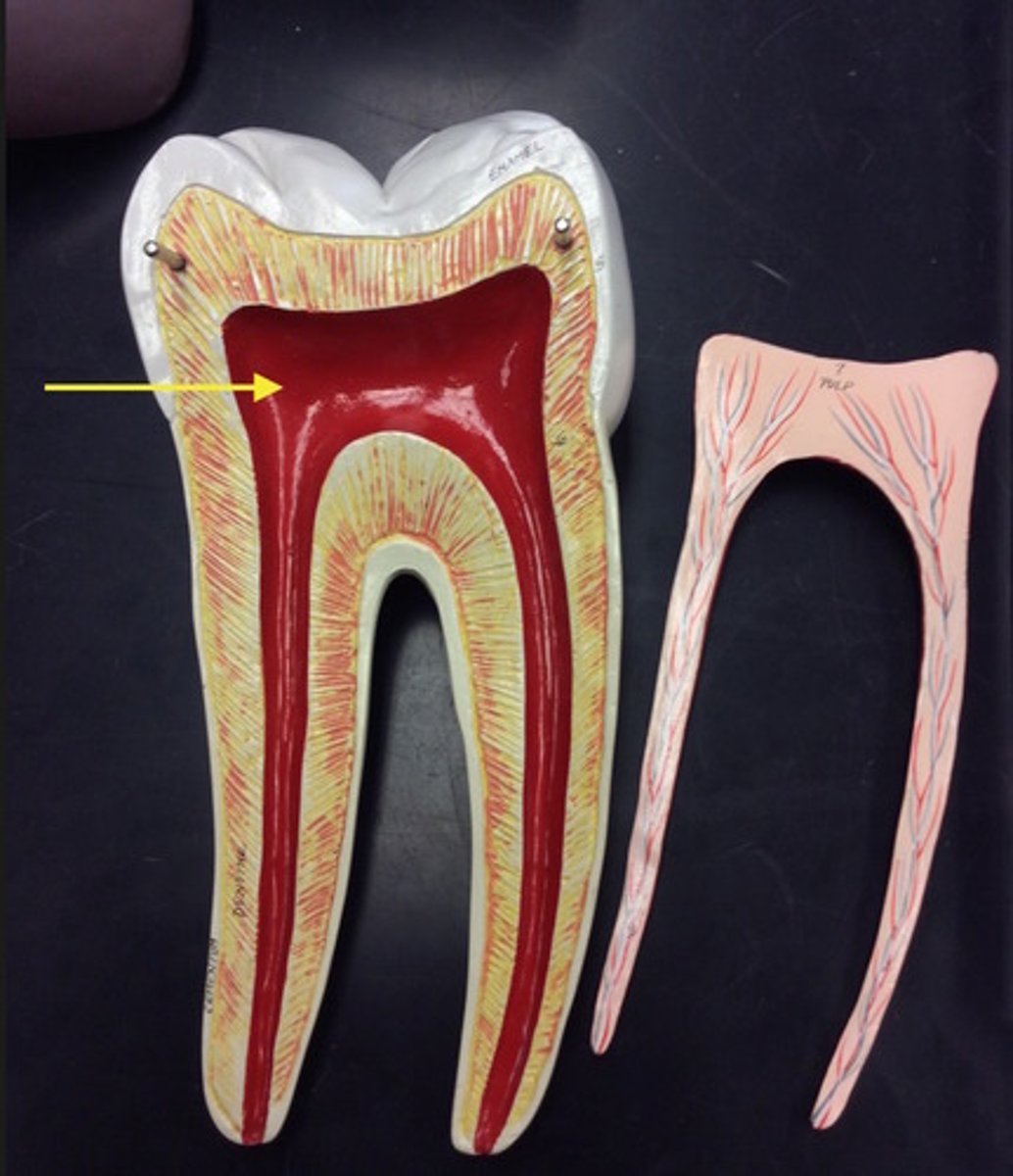
pulp
contains nerves and blood vessels within the tooth
dental development
1. deciduous teeth (shedding teeth)
- 10 teeth in each arch
2. permanent teeth (successional teeth)
- 16 teeth in each arch
dental occlusion
relationship of upper dental arch to lower dental arch when teeth come together
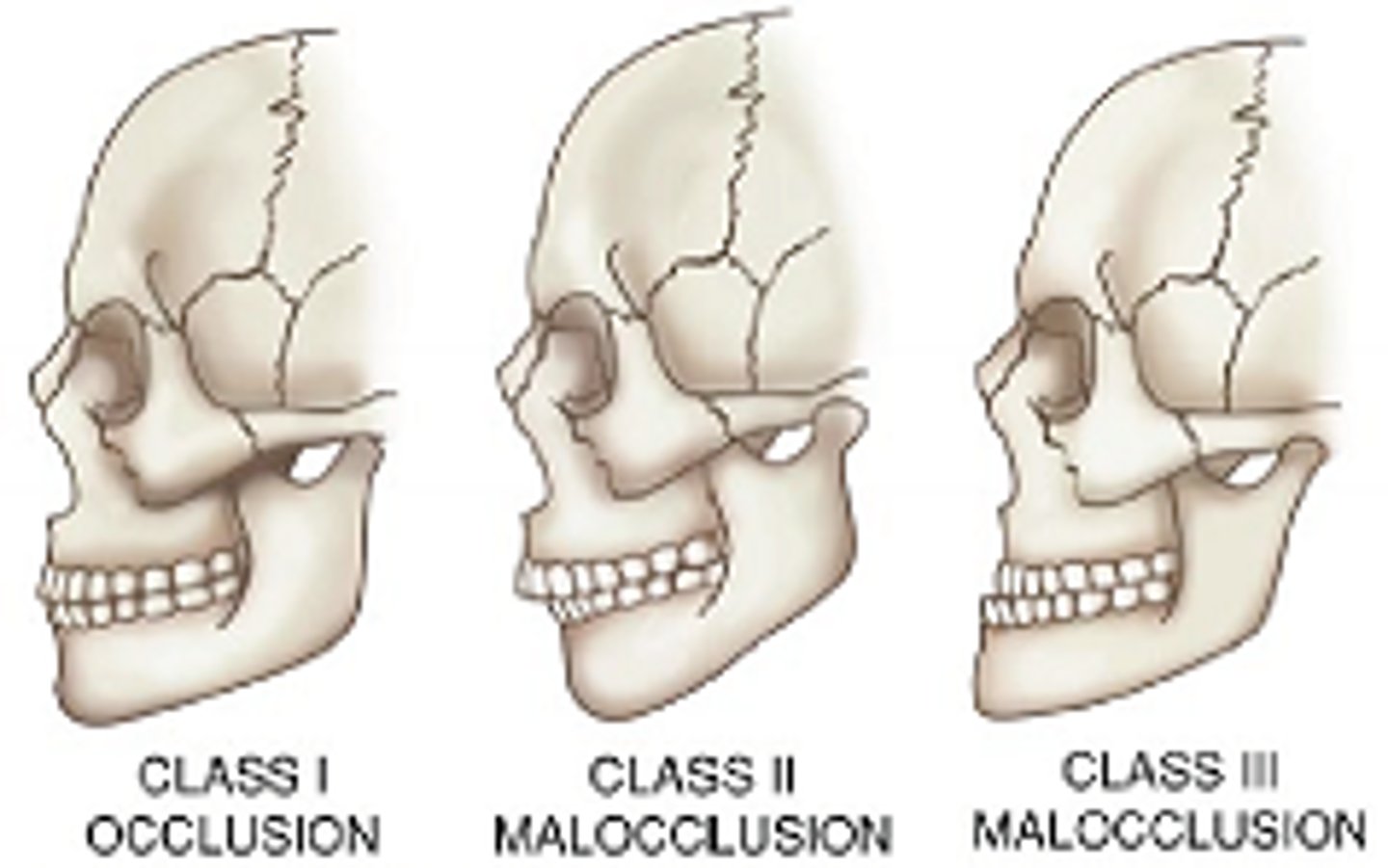
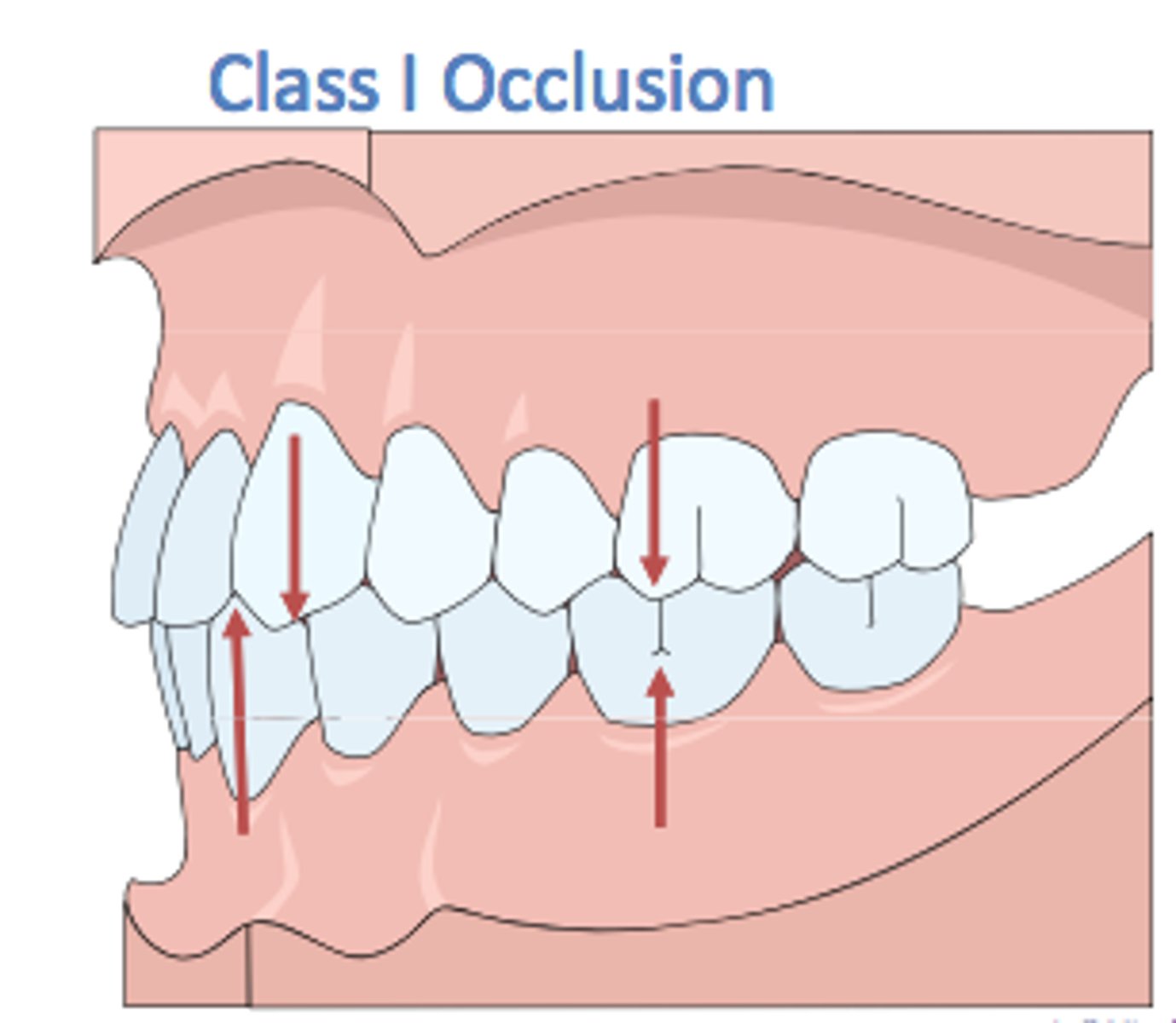
class I occlusion
- normal occlusion
- neutrocclusion
- first mandibular molar is one half tooth anterior to the first maxillary molar
class II occlusion
- malocclusion
- first mandibular molar is posterior to normal position
- mandible is retracted
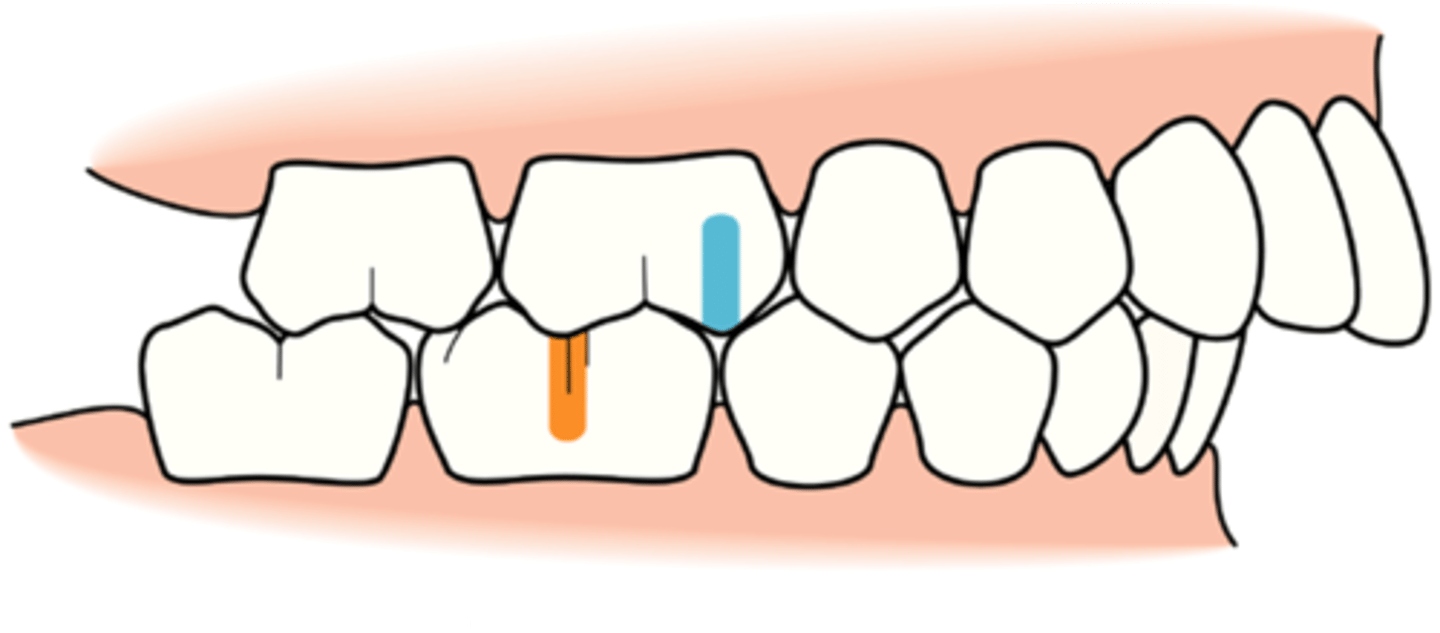
class III occlusion
- malocclusion
- first mandibular molar is anterior to normal position
- mandible is protruded
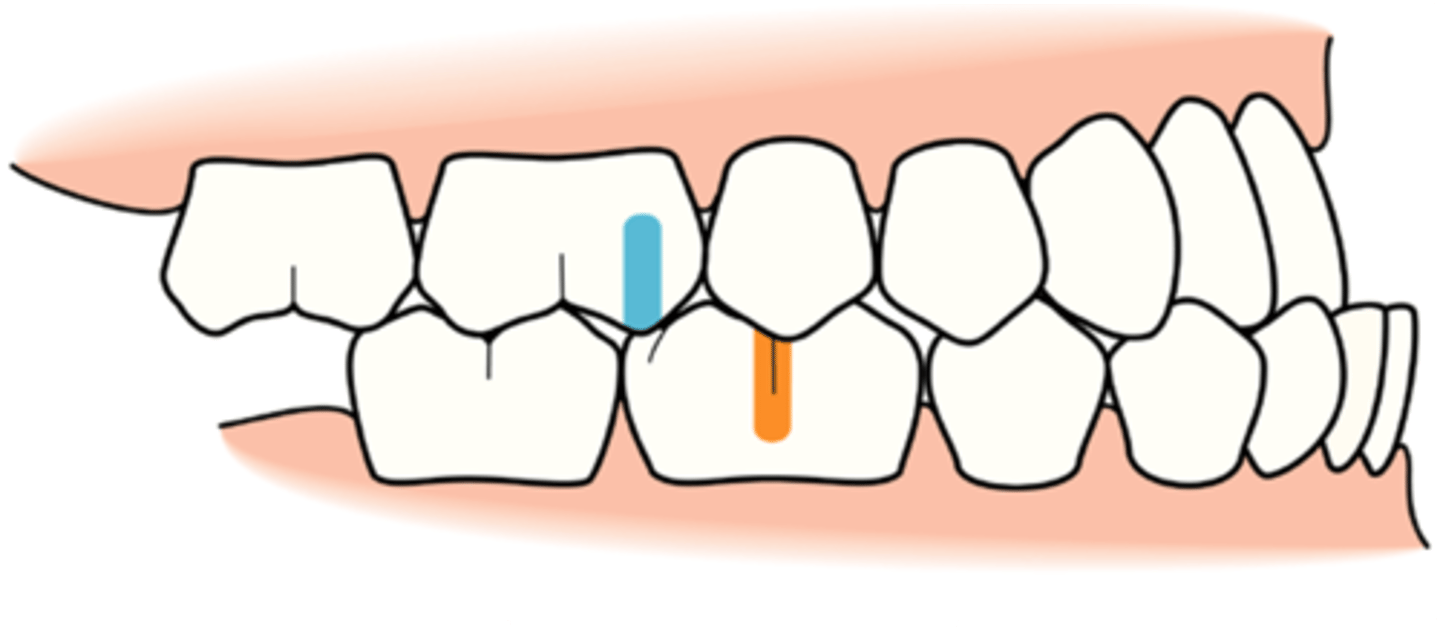
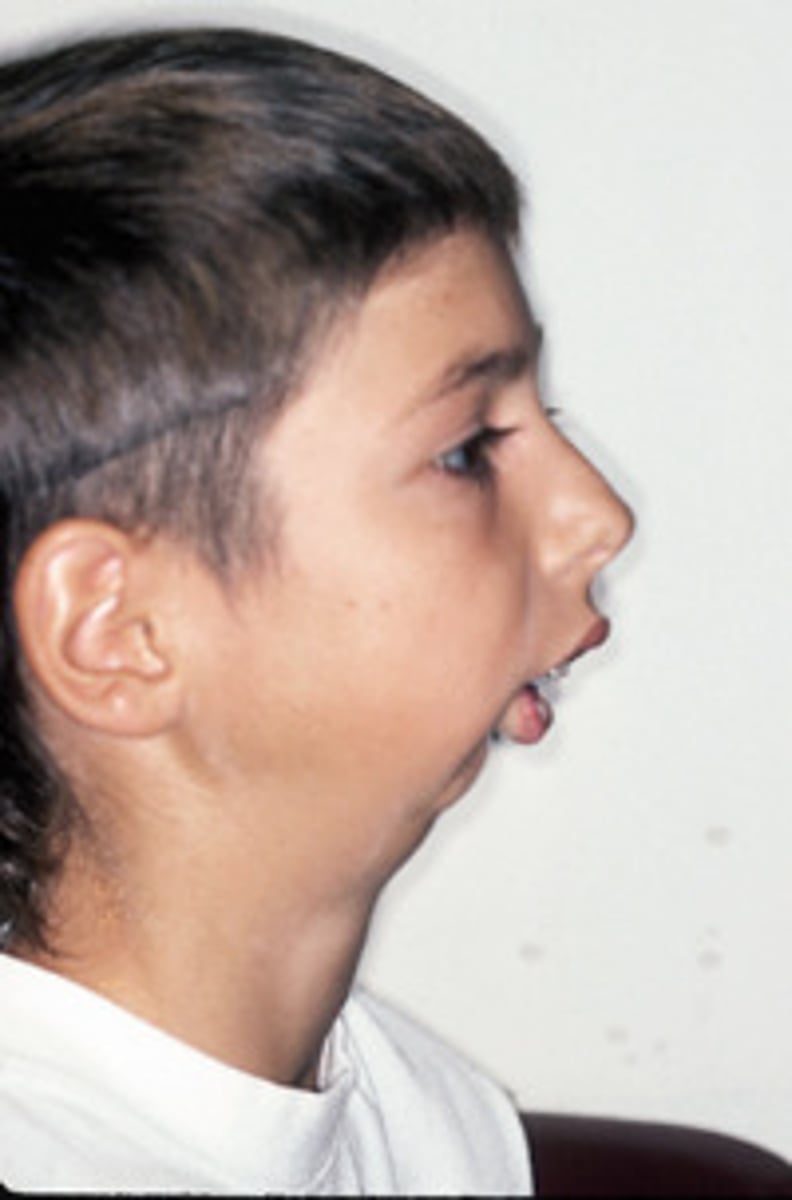
relative micrognathia
condition in which the mandible is small in relation to the maxilla
- may be part of other genetic syndromes
- may interfere with infant feeding
- may cause abnormal alignment of the teeth
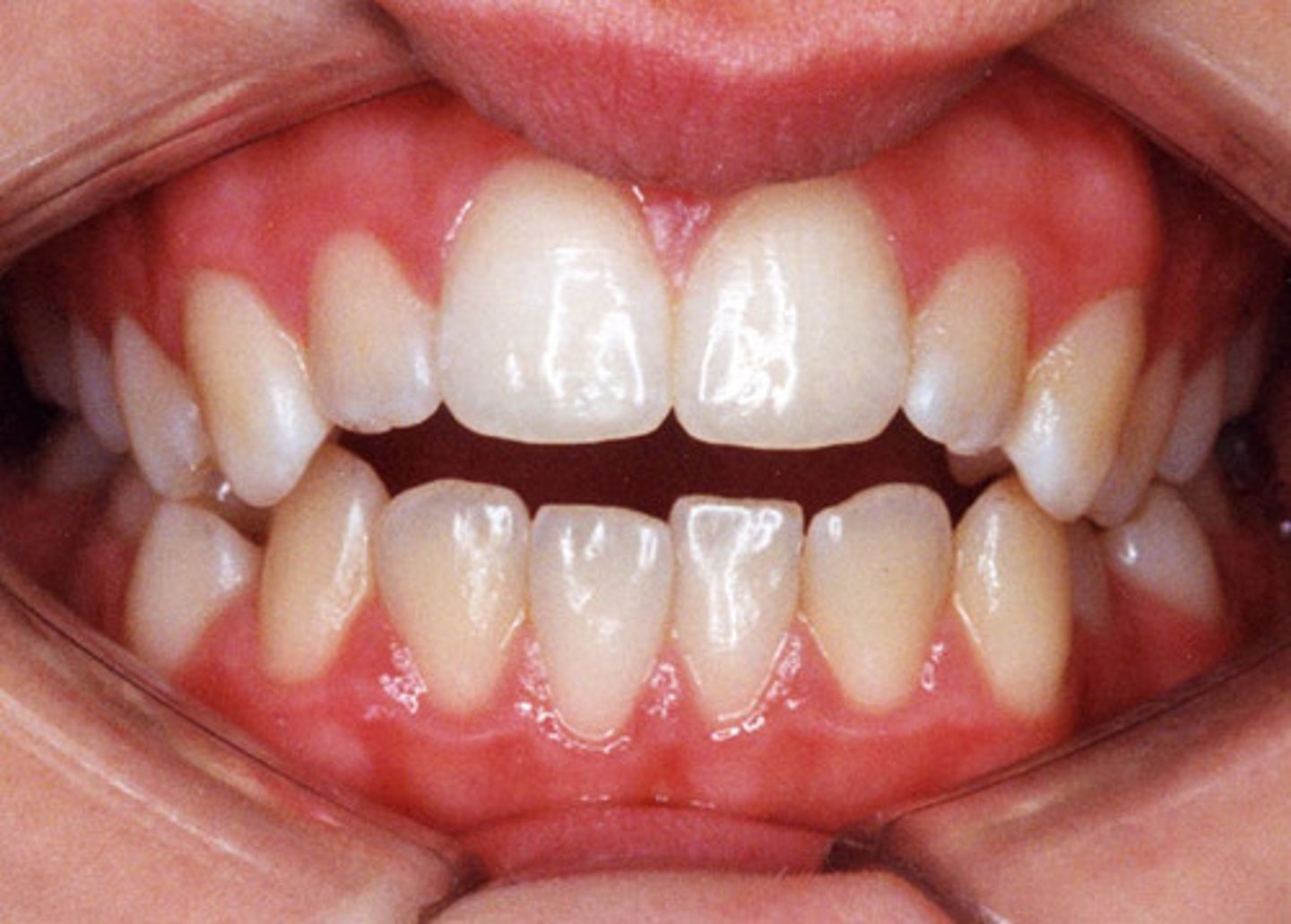
open bite
anterior teeth do not occlude ( do not touch when you bite down )
bc excessive eruption of posterior teeth
closed bite
posterior teeth do not occlude
- back teeth cant come together
bc excessive eruption of anterior teeth
cavity of the vocal tract
- oral cavity
- buccal cavity
- pharyngeal cavity
- nasal cavity
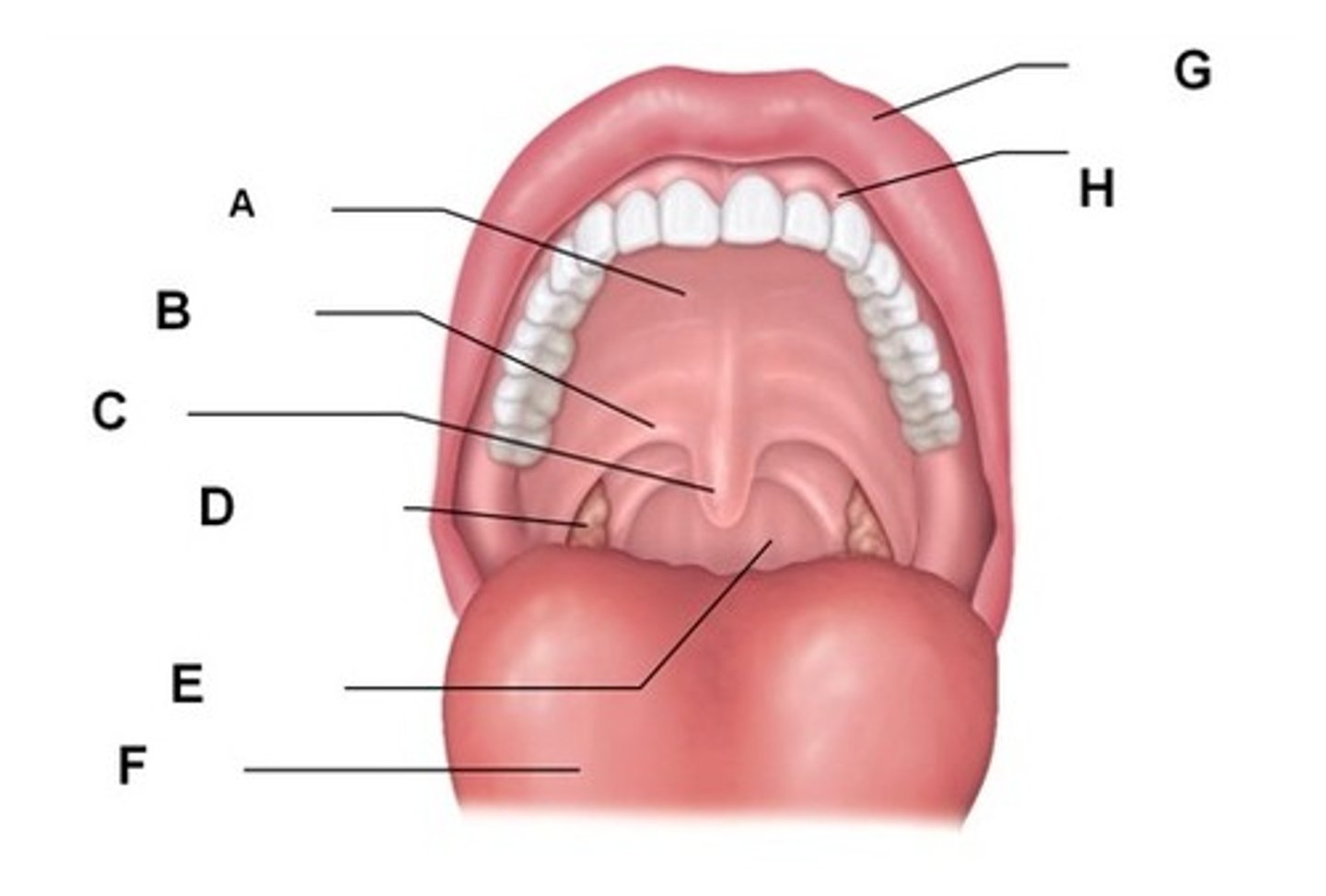
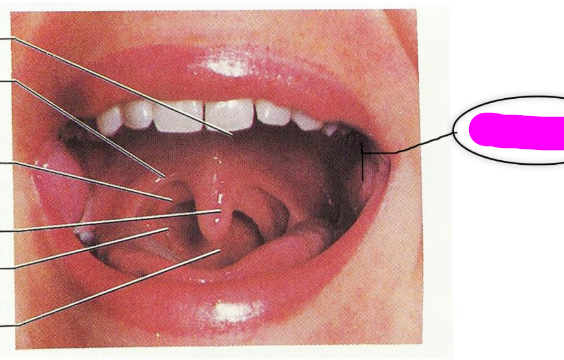
oral cavity
1. hard palate
2. rugae
3. soft palate (velum)
4. anterior faucial pillars (arches)
5. posterior faucial pillars (arches)
6. palatine tonsil
7. uvula
(cavity of the vocal tract)
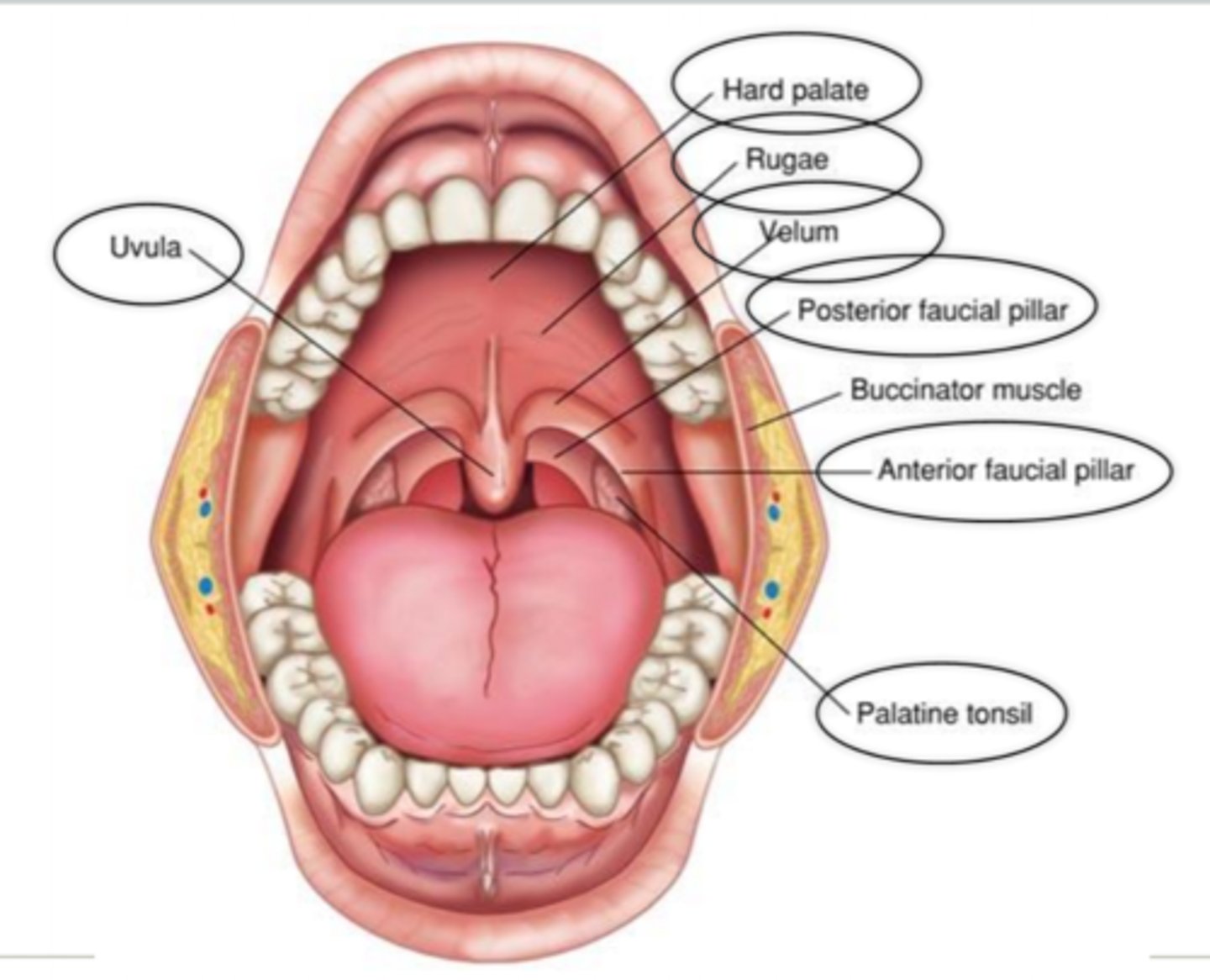
hard palate
(oral cavity)
rugae
folds of tissue
(oral cavity)
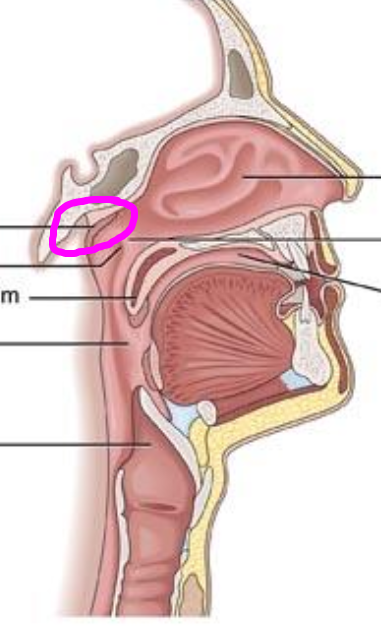
soft palate (velum)
moves posteriorly to separate oropharynx from nasopharynx
(oral cavity)
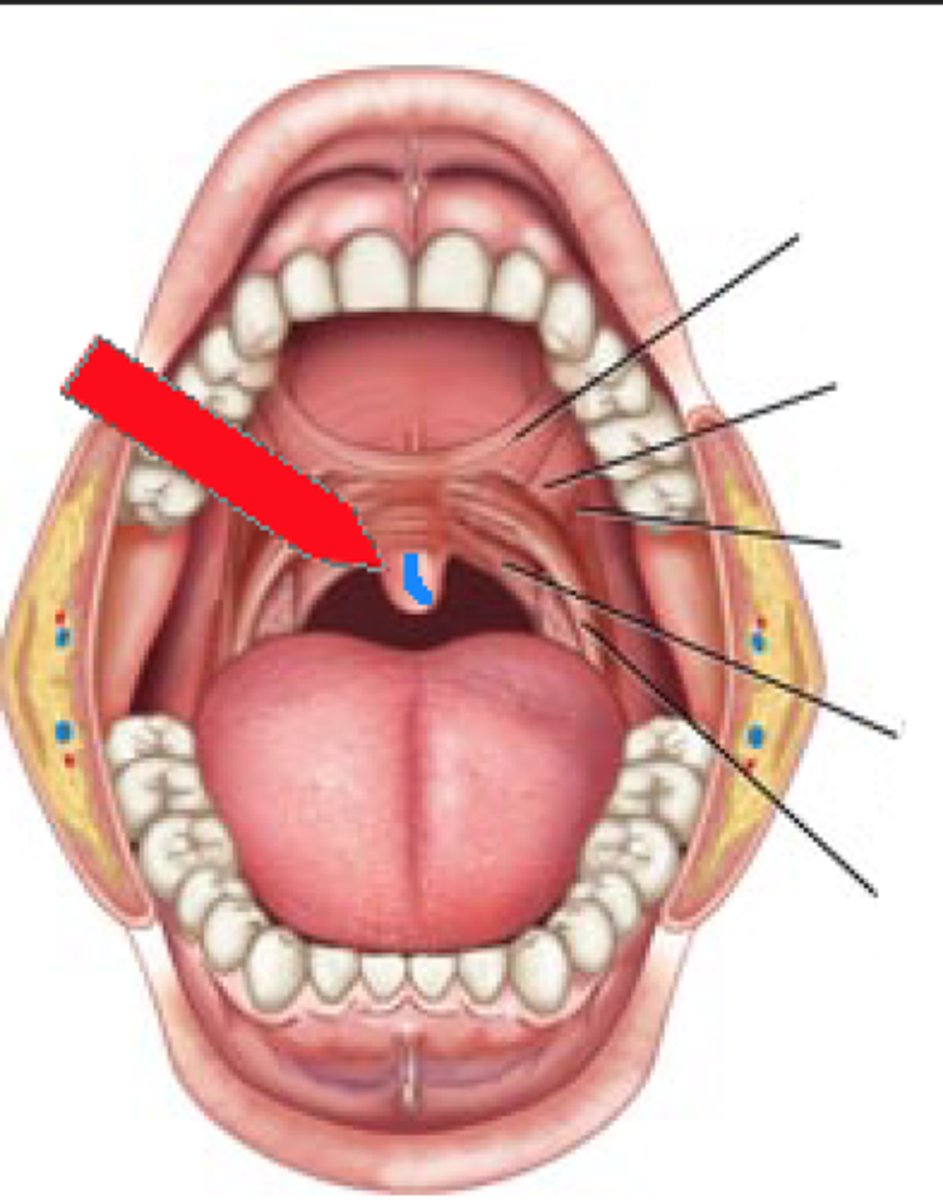
anterior faucial pillars (arches)
bands of tissue located in the posterior boundary of the oral cavity
(oral cavity)
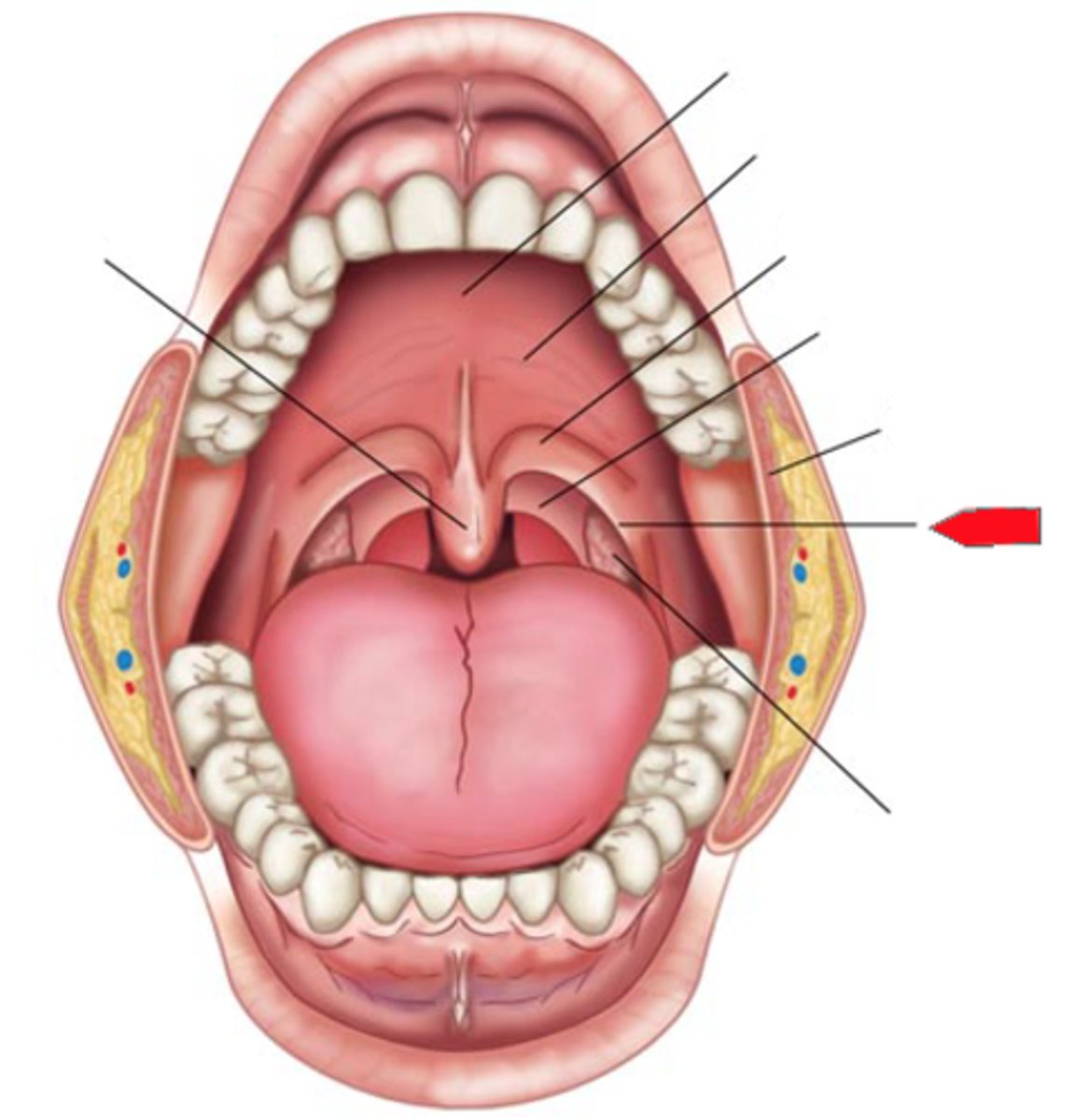
posterior faucial pillars (arches)
bands of tissue located posterior to the anterior faucial pillars
(oral cavity)
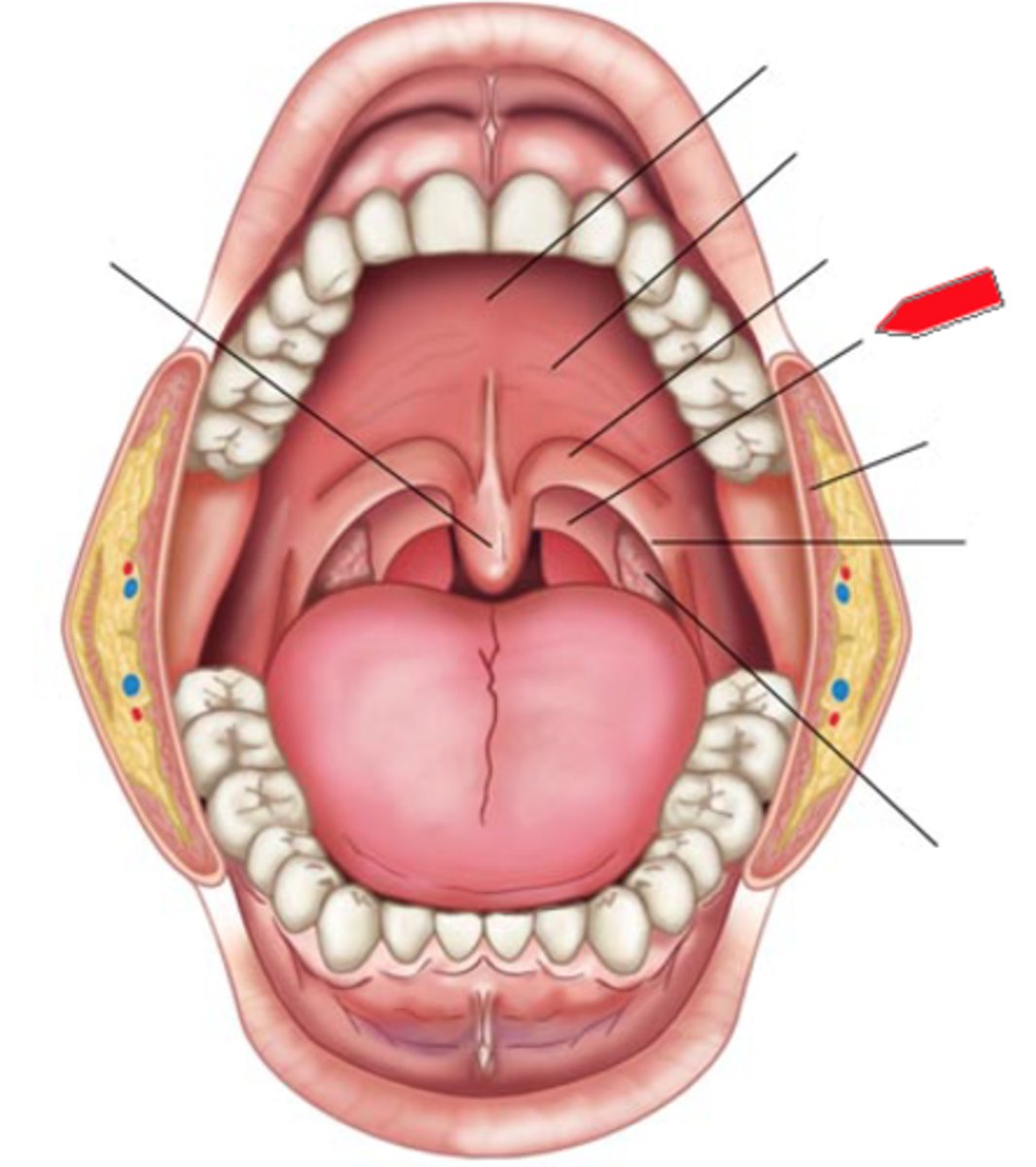
palatine tonsil
located between the two faucial pillars
(d)
(oral cavity)
uvula
may aid in speech sounds (non english), aids in velopharyngeal closure
(oral cavity)
buccal cavity
space between the teeth and the cheeks
(cavity of the vocal tract)
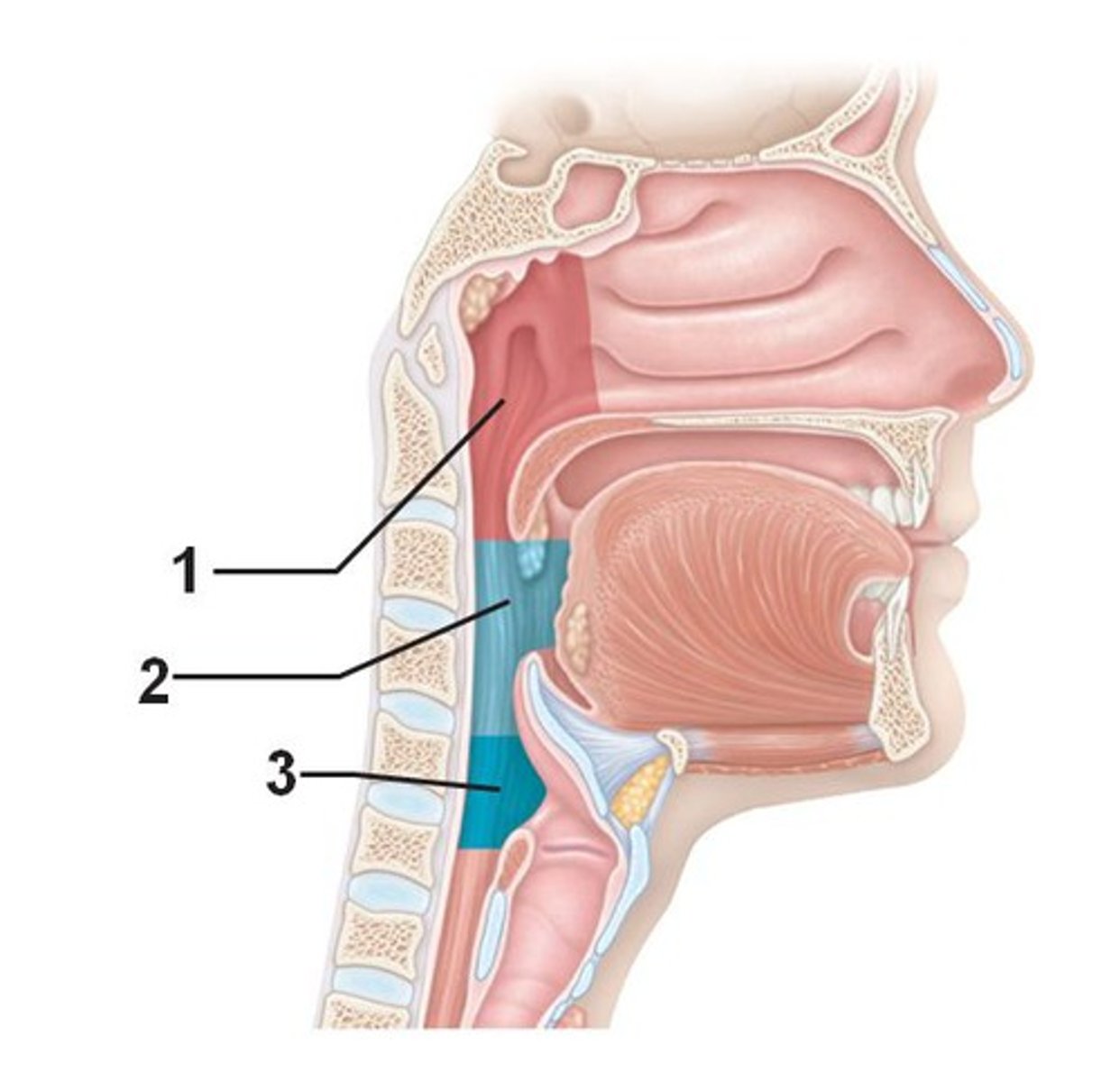
pharyngeal cavity (pharynx)
1. nasopharynx
2. oropharynx
3. laryngopharynx
(cavity of the vocal tract)
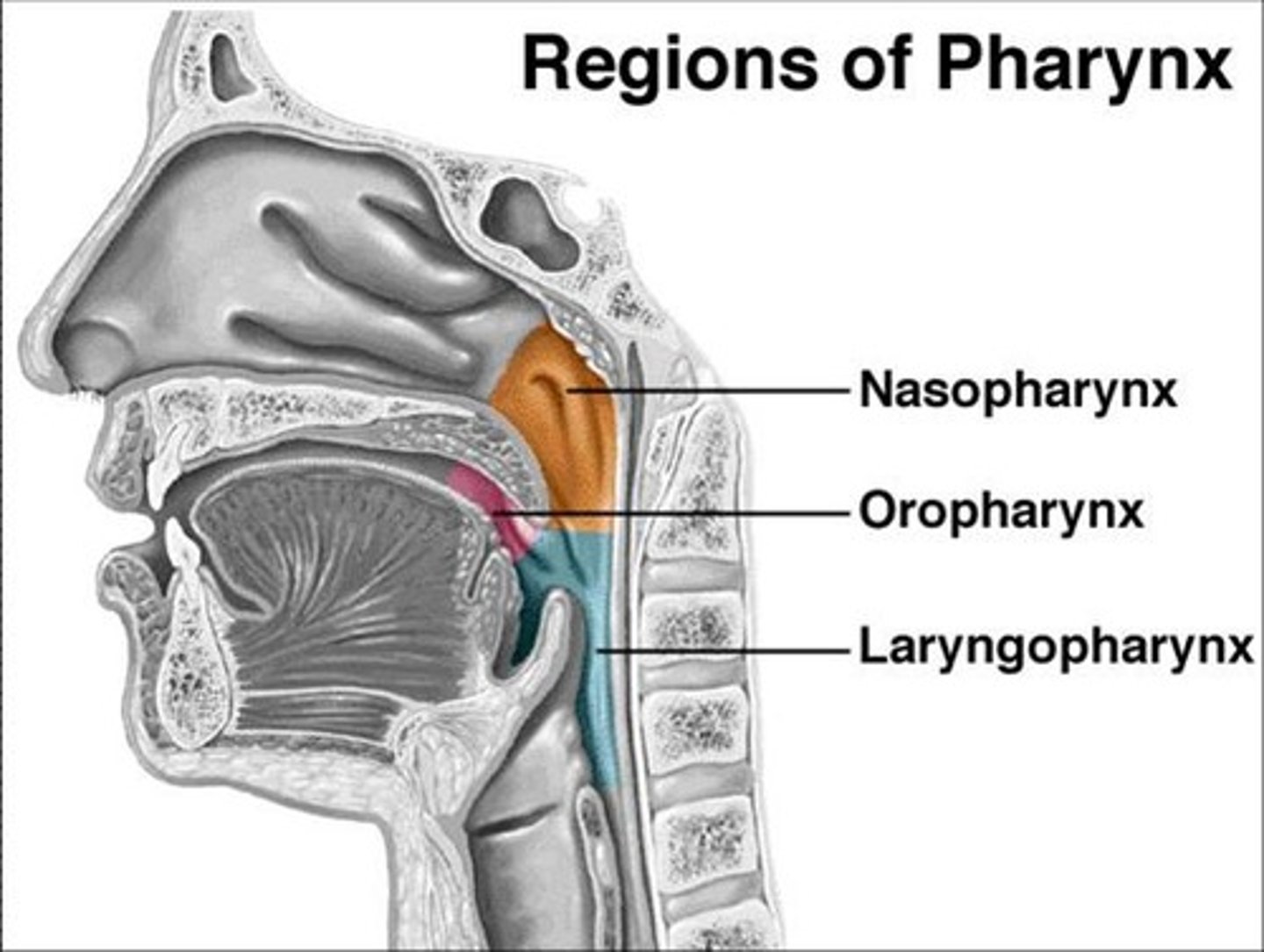
nasopharynx
space above the soft palate
1. eustachian tube
2. pharyngeal tonsil (adenoid)
(pharyngeal cavity)
eustachian tube
provides aeration of the middle ear
(nasopharynx)
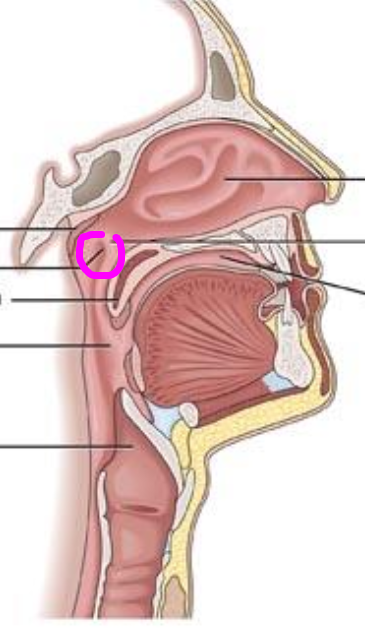
pharyngeal tonsil (adenoid)
located in the pharyngeal cavity
(nasopharynx)