Lecture 38-39 - Perennial ryegrass staggers, moldy corn, nicotine, ivermectin, salt
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What are examples of tremorgenic syndromes involving grasses?
perennial ryegrass staggers, dallis grass staggers-paspalum staggers, bermuda grass staggers, phalaris staggers, annual ryegrass staggers
What is the common tremorgenic syndrome in the PNW?
perennial ryegrass staggers

What is perennial ryegrass staggers caused by?
Lolitrems, a toxin produced by Acremonium lolii, an endophyte that grows in the lower leaf sheath, complete flower head, and seed of Lolium perenne
What is an an endophyte?
A fungi with a symbiotic relationship with the plant

When does perennial ryegrass staggers tend to occur?
late summer, fall if grazing or anytime of overgrazed // anytime in hay
Tremorgenic syndromes like perennial ryegrass staggers is a __ cell problem leading to __ like clinical signs and has __ morbidity and __ mortality.
Purkinje,
cerebellar,
HIGH,
LOW
What animals are susceptible to tremorgenic syndromes like perennial ryegrass staggers?
all grazing animals or ones that eat hay
When is the onset of clinical signs of tremorgenic syndromes like perennial ryegrass staggers?
variable onset, hours to days depending on if grazing or contaminated hay
What clinical signs do you see with tremorgenic syndromes like perennial ryegrass staggers?
fine muscle tremors, rhythmic palsy of head/neck/limbs, exaggerated when forced to move or eyes covered, looks almost normal at rest

True or False? It is common to see seizure activities as part of the clinical signs for tremorgenic syndromes like perennial ryegrass staggers.
False. Very rare to no seizure activities are seen.
What is the prognosis for tremorgenic syndromes like perennial ryegrass staggers?
recover within days to weeks
How do you diagnose tremorgenic syndromes like perennial ryegrass staggers?
history of feed access
HIGH morbidity, LOW mortality, clinical signs
Analyses of representative feed
fungal ID: ±, fungal culture: -
loliterm analysis: +++ (have established safe/toxic doses)
How do you control for Tremorgenic syndromes like perennial ryegrass staggers ?
remove animals from source
avoid overgrazing, use rotational grazing
assume grass infected until proven otherwise
What is equine leukoencephalomalacia also called?
moldy corn poisoning

Equine leukoencephalomalacia or moldy corn poisoning is a __ problem! What and where is it found?
mycotoxin,
Fusarium molds in corn and screenings produce fumonisins
True or False? Equine leukoencephalomalacia is a problem in the PNW.
False. Equine luekoencephalomalacia is a problem in the East and Midwest US, not in PNW yet!
Fumonisins cause __ disease in __ species — but is __ to all.
different, different,
hepatotoxic
When is the onset of clinical signs of equine leukoencephalomalacia or moldy corn poisoning?
1-4 weeks
What are the clinical signs of equine leukoencephalomalacia or moldy corn poisoning?
Neurotoxic syndrome: blindness (unilateral or bilateral), head pressing, aimless walking, stupor, glossopharyngeal paralysis // delirium, recumbency, seizures, death
Equine leukoencephalomalacia or moldy corn poisoning has __ morbidity and __ mortality.
LOW,
HIGH
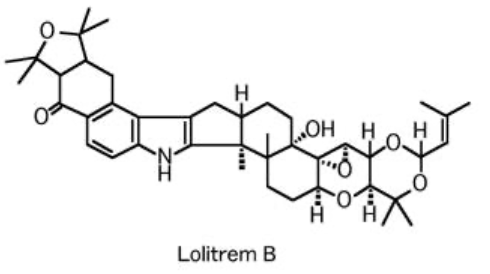
Describe the lesions seen with moldy corn poisoning
necrosis of subcortical white matter, one or both hemispheres, asymmetrical
hepatic necrosis, fibrosis, biliary hyperplasia
How do you diagnose equine leukoencephalomalacia?
corn or corn screenings
clincial signs and postmortem lesions
anlayses
representative sample of feed for fumonisin
tissue sphinganine/sphingosine ratios - limited
Describe the treatment for equine leukoencephalomalacia
No treatment - not reversible
True or False? Fumonsin from moldy corn poisoning, is not a health concern to humans as lack of residues in LA.
False. Fumonsin is a public health concern with correlated fumonisin in diet to increased risk of esophageal cancer. Residues are not a concern.
What are sources of nicotine toxicity?
cigarettes, chewing tobacco, nicotine gum, nicotine patches, insecticides // liquid cartridge and refills for e-cigs
True or False? Nicotine is generally not palatable.
True.
Describe the MoA of nicotine toxicity
direct stimulant on nicotinic Ach receptors causing either sympathetic or parasympathetic effects
short half life and rapid elimination by kidneys
Describe the clinical signs of nicotine toxicity
start with initial stimulation and as progresses see paralysis due to continuous depolarization and fatigue
vomiting, lacrimation, urination, diarrhea, hyperactivity, tremors, seizures if dose high enough
death from respiratory paralysis
How can you diagnose nicotine toxicity?
nicotine residues
How do you treat a nicotine toxicity?
patient dependent; consider decontamination - lavage, AC unclear if binds to nicotine, control CNS excitation, oxygen support, fludis
Ivermectin, moxydectin, eprinomectin, selamectin, abamectin, doramectin, milbemycin are all what?
antiparasitics that come in oral, injectable, pour-on forms
Ivemectins and similar antiparasitics are considered relatively __ and used in many __ across many __.
safe, species, ages
How does ivermectin toxicity occur?
Anytime to anyone - dogs like to lick up spilled ivermectin for horses or ivermectin in horse feces!
accidental access, overdosing, sensitive individuals either intrinsic mutation or temporary acquired

What species of K9s tend to have MDR1 mutation aka ABCB1?
American standard collie (70%), Australian shepherds (50%), Long-haired whippets (65%), shelties, mixes…

What species should never get ivermectin products? (NAVLE)
turtles and tortoises (chelonians)

Describe the MoA of ivermectin toxicity and half life
potentiates GABA and glutamate-gated chloride channels - mostly inhibitory effects, CNS depression
LONG half-life, 95% excreted in feces
Why do dogs (and cats) with intrinsic mutations like the MDR1 (ABCB1) mutation specifically lead to ivermectin sensitivity?
mutation lacks production of p-glycoproteins, so pump at blood brain barrier and biliary/renal excretion pumps not functioning and drugs like ivermectin (which rely on p-glycoproteins) accumulate
How does temporary acquired sensitivity to ivermectins occur?
P concurrently given 2 drugs that are p-glycoprotein substrates, second drug competes for limited P-gp binding sites, resulting in higher levels of one or both drugs, regardless of MDR1 status
Ivermectin: A normal dog would have TD ___ mcg/kg, while MDR1 homo/heterozygous dog would have a TD of ___ mcg/kg.
2550,
100
When is the onset of clinical signs with ivermectin toxicity?
variable (dose, route), 4-6 hours vs 10-12 hours
most dogs within 12 hours
Describe the clinical signs of ivermectin toxicities
ataxia, anorexia
depression, lethargy, weakness, recumbency (little ols)
salivation, decreased HR+RR
temporary blindness,
coma
tremors, seizures
True or false? Death from ivermectin toxicity is common.
False. Death is not common, however, a higher dose with seizure symptoms is a poor prognosis.
How do you diagnose ivermectin toxicity?
history of use/access
depression-comatose-blindness-tremors // high exposure or mutants → seizures can occur
nonspecific clin path/lesions, some retinal changes
chemical confirmation - 95% excreted in feces, fat, liver bile serum confirms exposure only
How do you treat ivermectin toxicity?
decontaminate!! both AS/S consider AC (multiple), cholestyramine?
AVOID benzodiazepines because GABA agonist and may prolong depression
aggressive supportive care (e.g. prevent sores, aspiratoin with obtunded P)
IV lipid therapy (likely not work in mutants) - mixed results
Describe the prognosis for ivermectin toxicity?
Majority recover over time and do well if avoid secondary complications (24 hours to 31 days!)
True or False? The severity of signs from ivermectin toxicity is a good predictor of prognosis, especially ones that have uncontrollable seizures.
False. The severity of signs from ivermectin toxicity is NOT a good predictor EXCEPT ones that have uncontrollable seizures
New report: ___ for cats, topical eprinomectin and praziquantal, cats with mutation are experiencing severe __ signs.
Centragard,
neurologic
What are sources of salt?
whey, electrolyte supplements, play dough, ice melts, mix/math errors, use as emetic, craft “salt dough”, ingesting sea water
osmotically active compounds like paintballs, single or repeated AC

What can cause salt poisoning // water intoxication?
not enough water or drinking TOO much water after hypernatremic!
What animals are susceptible to hypernatremia or too much salt or water intoxication?
occur in any animal, any time
Describe the MoA of hypernatremia (why is it a problem?)
hypernatremia → fluid shifts from intracellular to intravascular → cells shrink → cell death, capillary hemorrhage → neurological signs
hypernatremia → passive diffusion of Na into CSF, neurons → high levels inhibit glycolysis → no energy for active transport to move Na out → water follows Na → more neurologic signs
All resulting in fluid shifts in CNS → cerebral edema and hemorrhage
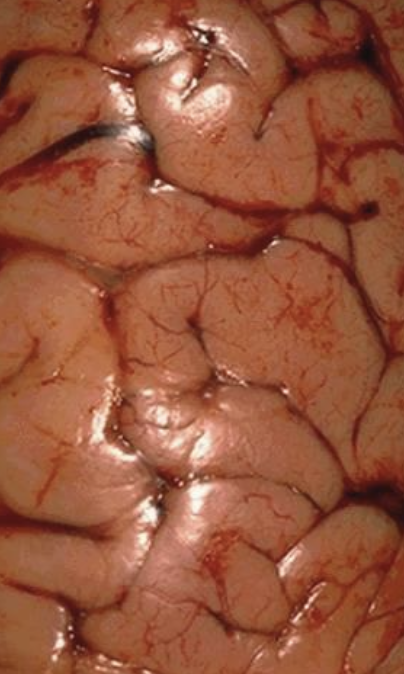
What might be a consequence of sudden rehydration when a P has been hypernatremic?
Na trapped in CSF + neurons, will draw more of the water in, exacerbating cerebral edema
What are the clinical signs of salt toxicity ?
CNS predominate
vomiting-regurgitation, diarrhea, anorexia initially;
fluid shifts in CNS → wandering, circling, head pressing, blind, dog sitting, tremors, seizures, excessive thirst, death
What lesions do you see with salt toxicity?
cerebral edema, malacia in all - polioencephalomalacia
eosinophilic meningoencephalitis in SWINE only (within first 48 hours)
What is the histologic lesion seen in SWINE only with salt toxicity/water deprivation/water intoxication within first 48 hours?
eosinophilic meningoencephalitis (perivascular eosinophilic cuffing)
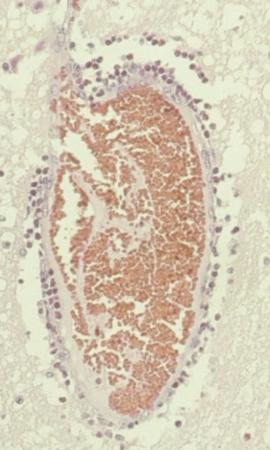
How do you diagnose salt toxicity?
history: lack of water, new feed, sources
clinical signs: CNS, generally group problem, single in SA
confirmation: know fluid/hydration status to interpret Na levels
high serum or CSF or cerebral Na levels
lesions if present
Too much water: cerebral edema and similar signs but hyponatremia systemically

How do you treat salt toxicity/water deprivation or water intoxciation?
remove source
decontaminate if appropriate AS vs S: NO AC!!
check baseline Na levels q2-4h, once normal after 12hrs OK
careful re-hydration - if Na levels go up quickly, can lower quickly, if Na levels go up slowly, must lower slowly
remove fluid if edema is an issue