Inner Ear
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Acute Labyrinthitis (vestibular neuritis)
Inflammation of the labyrinth as a result of a viral or post-viral disorder affecting the vestibular portion of CN VIII
prednisone, anti-emetics, meclazine (antivert)
Patient presents to the ER for vertigo and hearing loss in their right ear. Patient reports that they have recently gotten over a cold. Patient notes nausea/vomiting. On a physical exam, you note a unstable gait. What treatments can we use in the 1st 48 hours to treat this condition?
vestibular rehab
Long term treatment of vestibular neuronitis labyrinthitis
rule out other causes of vertigo
Concerning acute peripheral vestibulopathy, why do we need to refer to ENT?
none
What is the confirmatory test you can use to determine the diagnosis of neruo-labyrinthitis?
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (bppv)
A 77 y/o male presents to the ER for sudden onset nausea vomiting. While collecting a history you discover that the patient has a history of a TM rupture. Patient also reports tinnitus and short episodes of vertigo that occur when he moves his head. What are we thinking team?
tinnitus
The perception of noise or ringing in the ears that affects 1/5 people and is a symptom of an underlying injury such as age-related hearing loss or ear injury
ringing, buzzing, roaring, clicking or hissing
Tinnitus can be described by
ENT, audiology
Concerning tinnitus who do we refer to
lessen awareness and impact, aimed at underlying abnormality
When treating tinnitus what is the goal of treatment?
Acoustic neuroma (vestibular schwannoma)
A benign schwannoma of CN VIII that affects about 3,000 per year in the US, usually people 30-60 y/o.
asymmetric hearing loss, tinnitus, vertigo
What are the initial symptoms of an acoustic neuroma?
facial numbness/weakness (compression of CN V/VII)
Symptoms of progressive vestibular schwannoma
asymmetric SNHL (Sensorioneural hearing loss)
What will an audiogram in an acoustic neuroma show?
Nodular advancing lesions in the internal auditory canals
What will a MRI in a vestibular schwannoma show?
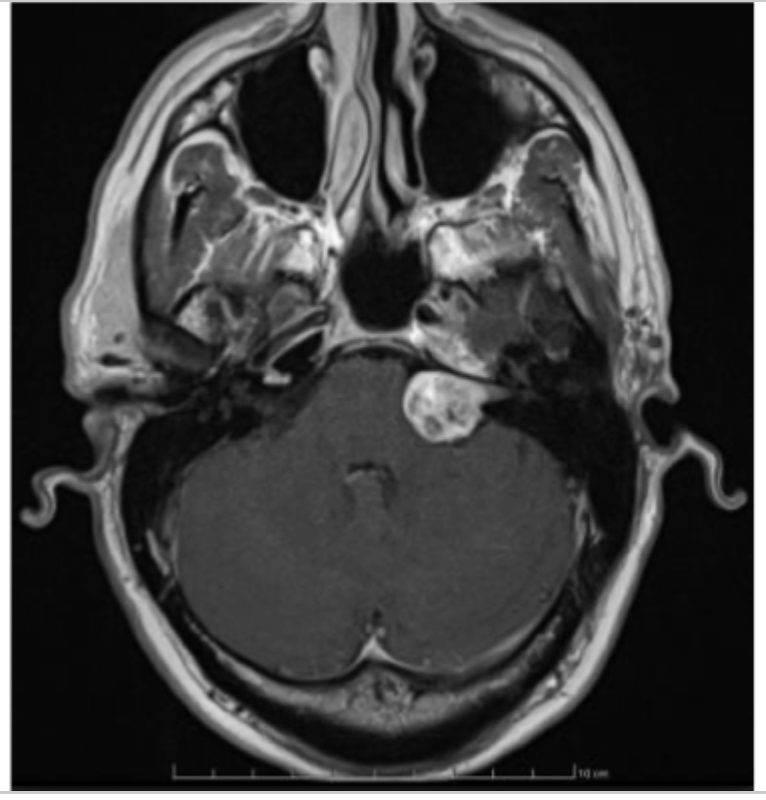
surgical removal, radiation
In acoustic neuroma how are you treating large tumors, young patients, or significant hearing impairment?
observation (yearly imaging/audiometry)
In acoustic neuroma how are you treating older patients, small tumors, or limited hearing loss?
Meniere’s Disease
What is an inner ear problem characterized by an abnormal accumulation of endolymph fluid within the inner ear (endolymphatic hydrops) from an unknown cause?
Sodium and water retention
What is a possible cause of Meniere’s disease?
avoid triggers, low sodium diet (2-3 g/day), vestibular rehab, diuretics (hydrocholorothiazide), vasodilator (betahistamine)
Patient presents to the ER for extreme bouts of dizziness. Patient reports these episodes last 20 minutes to 12 hours and she loses hearing in the right ear. They note tinnitus and ear fullness - all on the right side. A physical exam shows low sensorineural hearing loss in her right ear. What are the long term treatments for this condition?
fluctuating asymmetric hearing loss (SNHL), tinnitus, vertigo
Triad of Meniere’s disease
vestisbular schwannoma, MS, TIA, migraine (vertigo/vestibular), BPPV
Differentials of Meniere’s Disease
SNHL on the affected side
Audiometry for Meniere’s disease will show
abnormal on the affected side
Vestibular testing for Meniere’s disease will be
rule out tumors, aneurysms, MS, etc
Why do you do an MRI in a Meniere’s disease workup?
2 or more spontaneous episodes of vertigo (20min-12 hours), audiometrically documented low-mid frequency SNHL in affected ear, fluctuating aural symptoms (tinnitus, reduced/distorted hearing/fullness) in affected ear, symptoms not better accounted for by another vestibular diagnosis
Criteria to diagnose Meniere’s disease
No (educate your patients and address expectations)
Is there a cure for Meniere’s?
reduce frequency and severity of vertigo attacks, reduce/eliminate tinnitus and hearing loss associated with attacks, alleviated chronic tinnitus and disequilibrium, minimize disability, prevent progressive hearing loss
Goals in managing Meniere’s disease
Vestibular suppressants (clonazepam, diazepam), anti-emetics (promethazine, ondasetron)
Acute treatment for Meniere disease