Biology Unit 3 Test 1
5.0(4)
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/57
Last updated 3:30 PM on 4/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
1
New cards
Homeostasis
It is the body’s process of keeping a set point while there are internal and external changes.
2
New cards
Meristematic Tissue
This is like the stem cells of the plant kingdom. It is a fast growing tissue that will change into one of the other types as the plant needs it.
3
New cards
Dermal Tissue
This is the outer protective tissues of the plant. The outer layer is called epidermis for herbaceous plants and is one cell thick. Periderm for woody plants and is several cells thick. Cork is an example.
4
New cards
Stomata
Which are guard cells that open the plant up to the air, or close it off to prevent water loss. Part of the Dermal.
5
New cards
Trichomes
Which are the fuzzy hairs that you can find on the stems and leaves of plants. They help to cool the plant and prevent water loss. part of the Dermal.
6
New cards
Root Hairs
Are specialized cells on the roots increase the surface area of the root with the soil so that the plant can absorb more water and nutrients. Part of the Dermal.
7
New cards
Ground Tissue
This is the base tissue of a plant and do jobs like photosynthesis, storage and support. It is the general main type of tissue in a plant.
8
New cards
Vascular Tissue
This is the arteries and veins of the plant that will transport things around the plant. It is comprised of two layers. Xylem and Phloem.
9
New cards
Xylem
Which transports water and nutrients up from the roots to the rest of the plant to use. Layer of Vascular Tissue.
10
New cards
Phloem
Which transports sugars down from the leaves to the rest of the plant to use as a fuel source. Layer of Vascular Tissue.
11
New cards
Roots
Take in water and nutrients from the soil. Anchor the plant against wind and erosion. To Store carbohydrates produced by photosynthesis.
12
New cards
Stems
Can be herbaceous or woody. Their main goal is support for the plant. Though herbaceous stems also help with photosynthesis.
13
New cards
Leaves
It’s main purpose is to carry out photosynthesis. The upper surface can be waxy to prevent water loss. It has guard cells that can open and close to allow for gas exchange.
14
New cards
Positive Feedback Loop
When some hormones tell the plant to do more of what it is doing.
15
New cards
Reflex Arc
A fast stimulus response that travels through the spine to protect the body.
16
New cards
Neuron
It is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. They function to transmit information throughout the nervous system. It consists of three parts: Cell Body, Dendrites, and Axon.
17
New cards
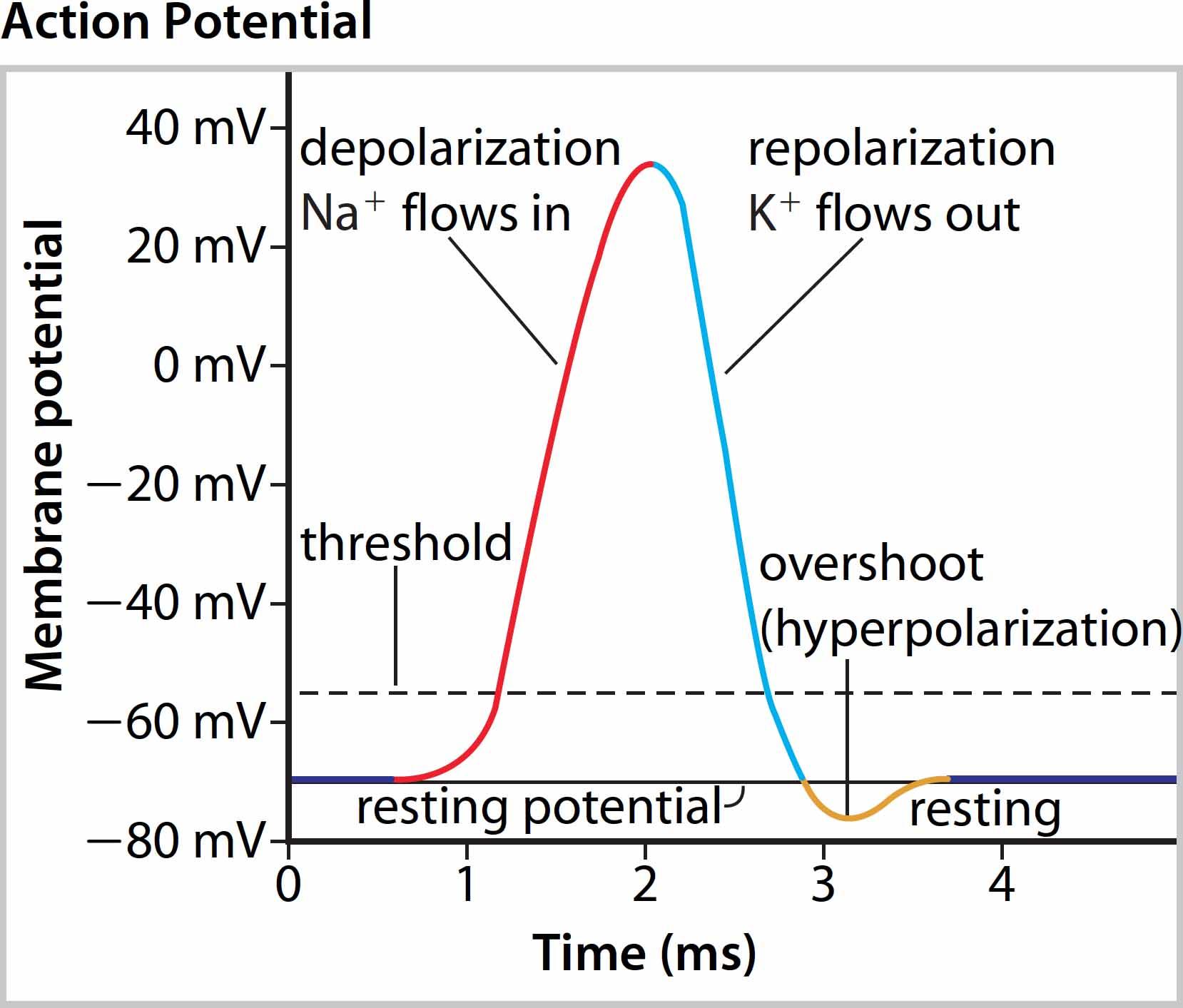
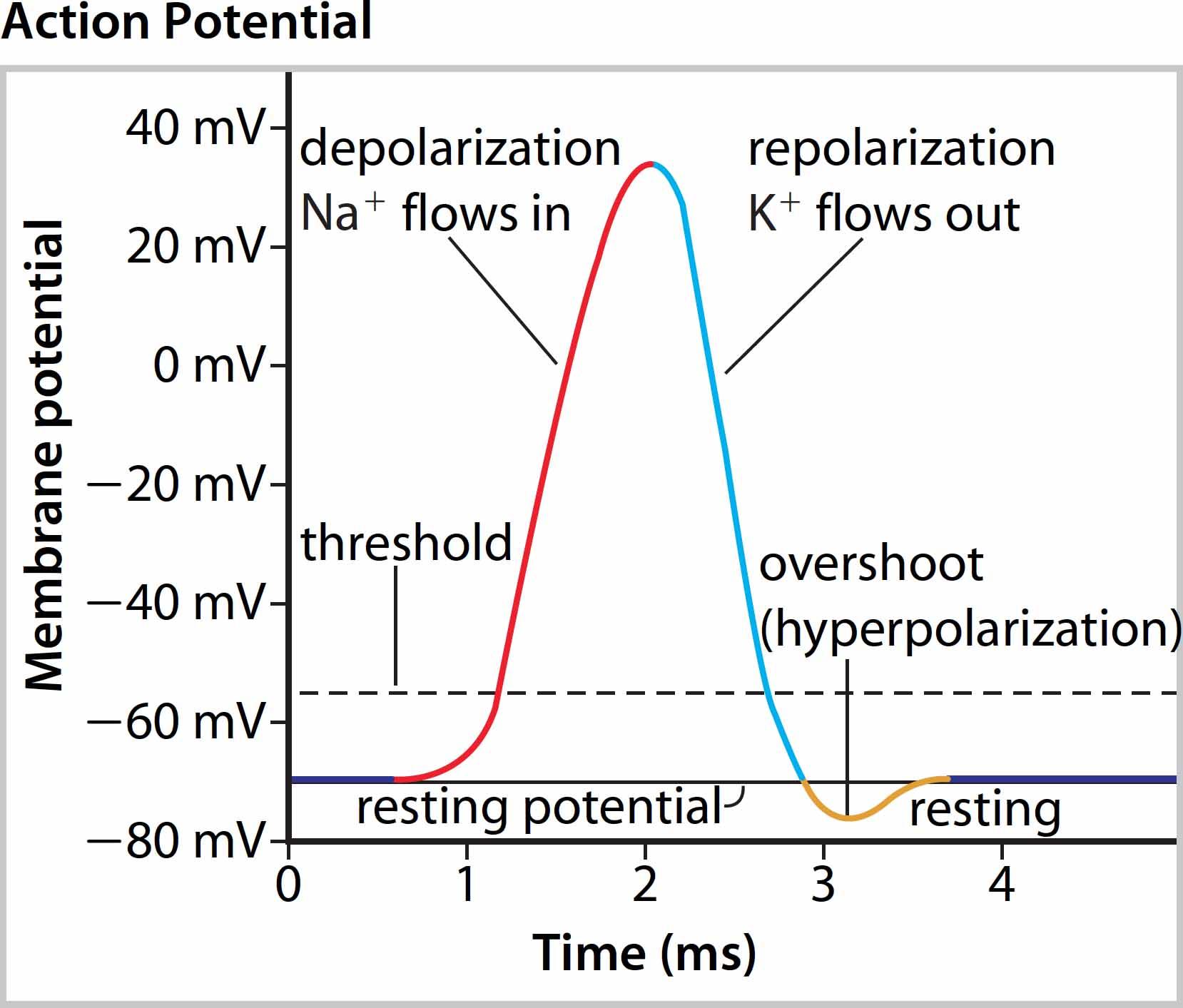
Resting Potential
* High concentration of sodium ions outside, low concentration of potassium ions
* Positive charges inside membrane due to high potassium, low sodium
* Specialized channels for movement of sodium and potassium
* Voltage difference of -70 mV
* Positive charges inside membrane due to high potassium, low sodium
* Specialized channels for movement of sodium and potassium
* Voltage difference of -70 mV
18
New cards
Threshold Potential
If there is enough stimulus and the membrane charge changes enough then the process cannot be stopped and the nerve will fire. If there is not enough, the cell will go back to Rest.
19
New cards
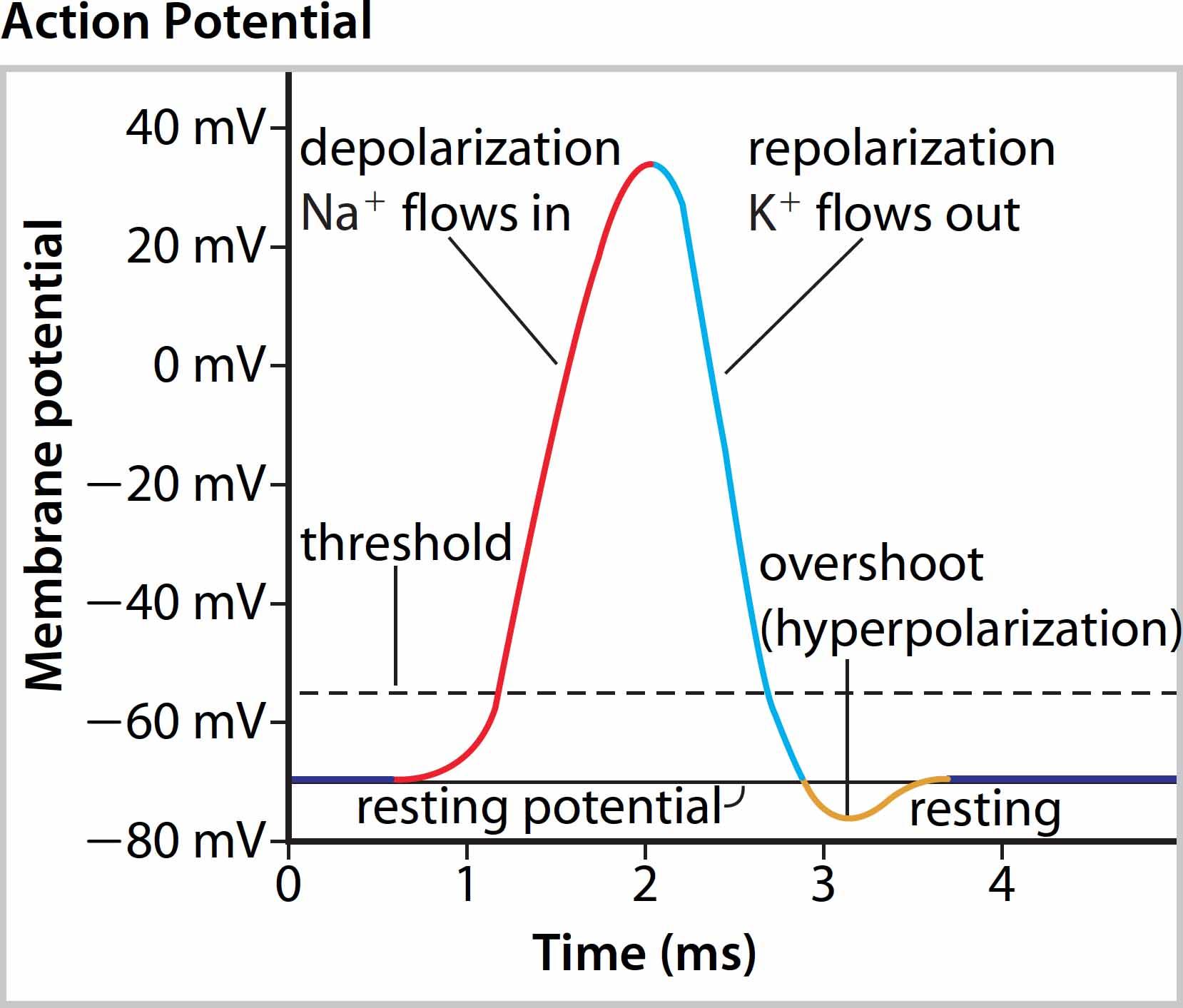
Depolarization
Because of some stimulus the cell begins to allow Na+ to leak in. This starts to change the membrane charge.
20
New cards
Repolarization
Now that the membrane charges are flipped we need to fix things back. Now K+ flows out and changes the charges back to where it was. The ions are now on the wrong side and have to be put back to get back to rest.
21
New cards
Synapse
The gap between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another.
22
New cards
Neurotransmitters
Are chemicals that are sent and received between the two cells and sends the message. Examples: Acetylcholine, Cholinesterase, Dopamine, Serotonin: Endorphins, and Norepinephrine.
23
New cards
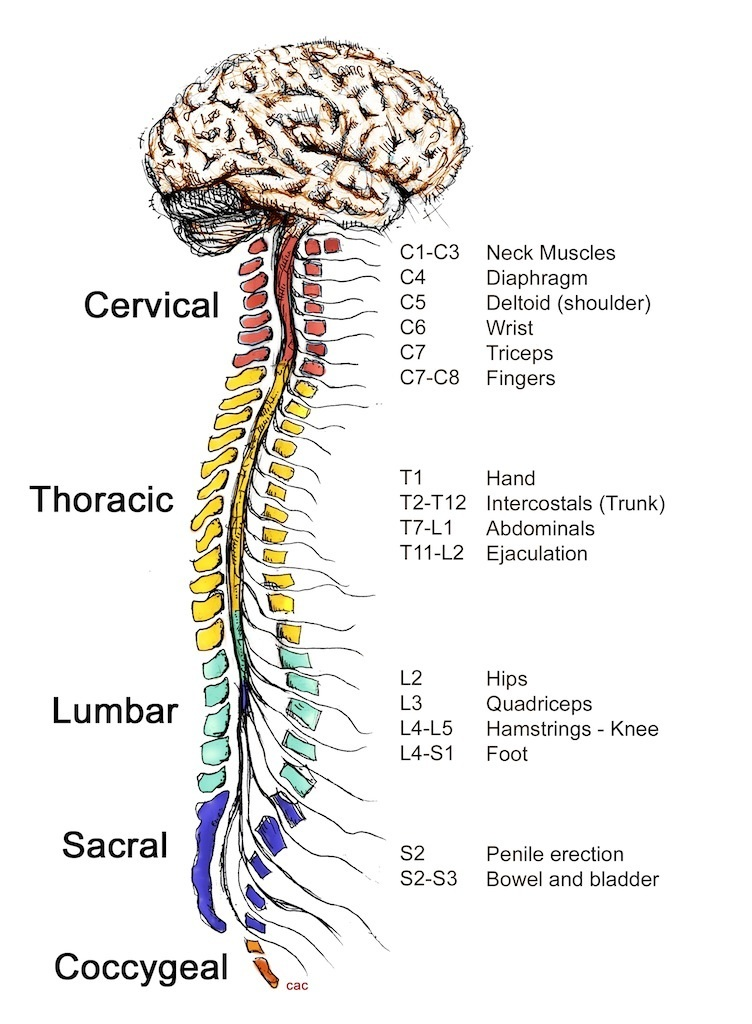
The Central Nervous System
Composed of the Brain and the Spinal Cord. The brain is the control center for processing information and deciding what to do. It sends information out from the brain and in from the body.
24
New cards
Peripheral Nervous system
Contains only nerves and connects the brain and spinal cord (CNS) to the rest of the body. It consists of: the Somatic Nervous System and the Autonomic Nervous System.
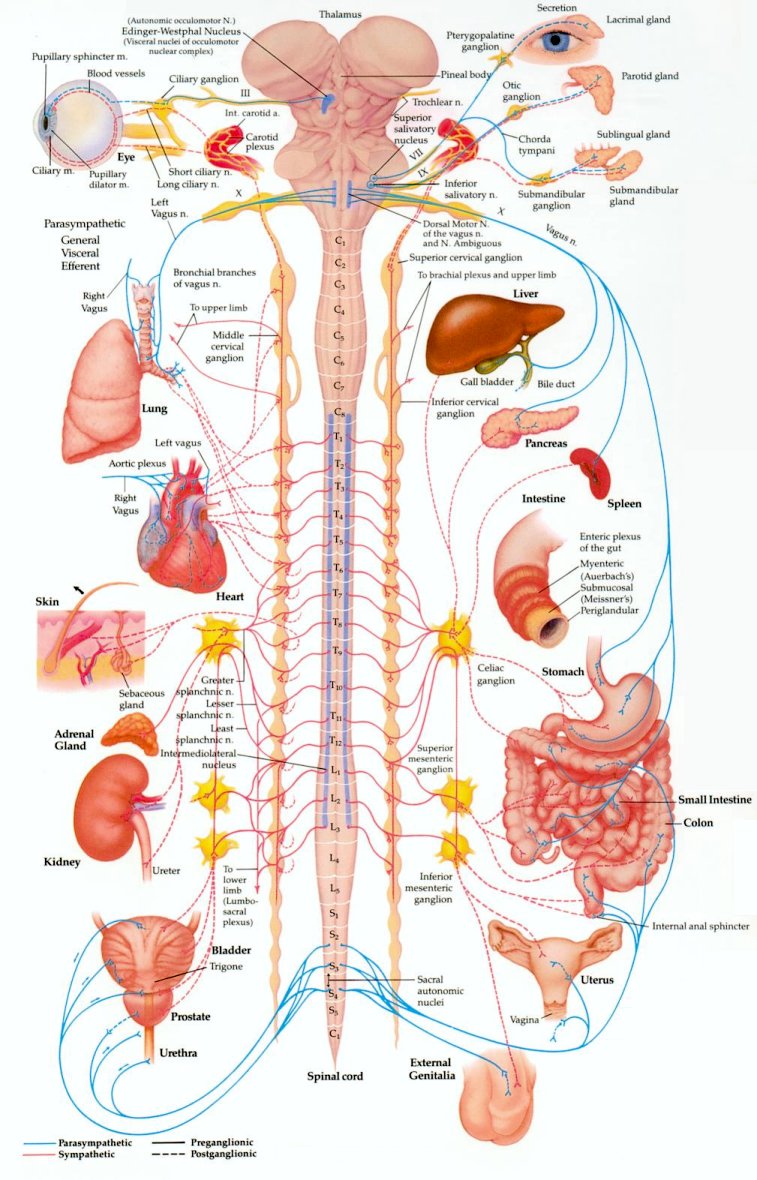
25
New cards
Somatic Nervous System
Composed of sensory nerves that carry impulses from the body’s sense organs to the CNS. Also made of motor nerves that carry commands from the CNS to the muscles. To some degree, the SNS is under conscious control.
26
New cards
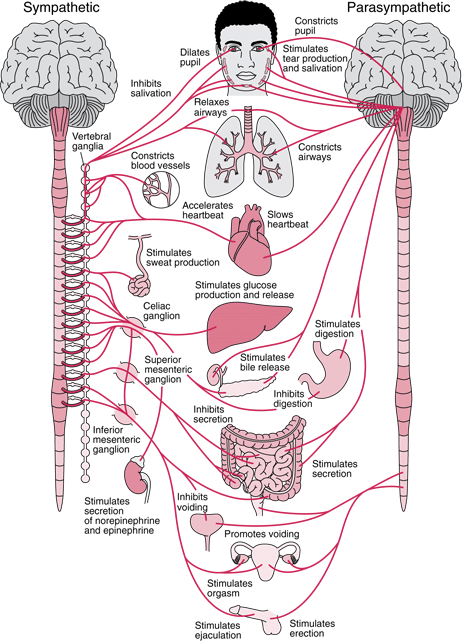
Autonomic Nervous System
Not under conscious control. Controls muscles in the heart, smooth muscle in internal organs such as the intestine, bladder, and uterus. Consists of the: Sympathetic Nervous System and Parasympathetic Nervous System.
27
New cards
Sympathetic Nervous Systems
Part of the nervous system that is dominant during times of stress. For example: Heart rate speeds up, blood pressure rises, pupils dilate, and breathing rate increases.
28
New cards
Endocrine System
Uses chemicals called hormones that travel in the bloodstream to send signals to other parts of the body.
29
New cards
Pituitary Hormones
Human Growth Hormone (HGH): Responsible for growth of the body. Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH): Responsible for stimulating the thyroid. Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH): Tells the Kidneys to keep more water. Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH): Stimulates the Adrenal glands in the fight or flight response.
30
New cards
Negative Feedback Loop
Can be identified when a level of something is detected and the response is to do the opposite of what is detected. Something is detected as high... lower it Something is detected as low... raise it.
31
New cards
Thyroxine Regulation
Hypothalamus secretes TRH (Thyroid Releasing Hormone). TRH stimulates the Anterior Pituitary to secrete TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone). TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete Thyroxine (which regulates growth and metabolism) .Thyroxine levels increase which affects the pituitary by inhibiting the release of TSH .Lower levels of TSH result in less stimulation of the thyroid and thus less thyroxine.
32
New cards
Insulin
Released when blood sugar levels are too high. Causes cells to become more permeable to glucose. Lowers blood sugar.
33
New cards
Glucagon
Produced when the blood sugar is falling too low. Opposite influence to insulin, triggers the release of glucose. Raises blood sugars.
34
New cards
Blood Glucose Regulation
Blood glucose levels are high, pancreas secretes insulin. Insulin triggers the storage of glucose as glycogen Insulin lowers blood glucose levels. Blood glucose levels become too low, pancreas secretes glucagon. Has opposite effects to that of insulin, glycogen broken down into glucose. Blood glucose levels are raised.
35
New cards
Dendrites
Cell like projections off cell body for receiving signals.
36
New cards
Cell Body
Contains, nucleus, cytoplasm, and organelles.
37
New cards
Nucleus
\
\
Contains cellular information.
\
Contains cellular information.
38
New cards
Schwann Cell
Forms Myelin sheath.
39
New cards
Nodes of Ranvier
\
Sections between Melin to conduct signal.
Sections between Melin to conduct signal.
40
New cards
Myelin Sheath
\
Insulator to prevent charge loss.
Insulator to prevent charge loss.
41
New cards
Axon Terminal
\
Bulb-like extensions at the and of axons to release neurotransmitters to the next axon.
Bulb-like extensions at the and of axons to release neurotransmitters to the next axon.
42
New cards
Medulla Oblongata
Control center for heart rate and breathing rate.
43
New cards
Pons
Has reflex centers involved in head movement.
44
New cards
Cerebrum
Memories and emotions are controlled by this part of the brain.
45
New cards
Cerebellum
Controls muscle coordination and balance.
46
New cards
Meninges
Protective membrane that surrounds the brain.
47
New cards
Midbrain
Controls important auditory and visual functions.
48
New cards
Hypothalamus
Controls homeostatic functions such as thirst and hunger.
49
New cards
Corpus Callosum
Connects the right and left hemispheres of the cerebrum.
50
New cards
Thalamus
Sorts sensory information.
51
New cards
Pituitary gland
Network of blood vessels and neurons connected to the hypothalamus. Produces hormones that regulates hormone production elsewhere (other glands).
52
New cards
Pineal Gland
Found deep in the center of the brain and secretes Melatonin, which is related to circadian rhythms. It is involved in the Sleep-Wake Cycle.
53
New cards
Thyroid
Located above the trachea in the neck. Produces Thyroxine: Increases metabolic rate (energy expended at rest). Also produces Calcitonin: Hormone which regulates calcium levels in blood.
54
New cards
Parathyroid
4 smaller glands set into the Thyroid They produce Parathyroid Hormone (PTH), which increases the level of calcium in the blood
55
New cards
Adrenal Gland
There are two. One found on top of each kidney. Each gland is made of an: Outer Cortex and Inner Medulla. Each are responsible for producing different hormones,
56
New cards
Adrenal Cortex
Produces Cortisol and Aldosterone. Both contribute to the long term stimulus of the immune system when the body is under stress. Fat and Protein Metabolism, rather than sugar. Blood pressure and volume increase.
57
New cards
Adrenal Medulla
Secrete Epinephrine and Norepinephrine. Increase blood pressure. Breathing rate increases. Muscles become energized. Rapid, short lived emergency response.
58
New cards
Pancreas
A small gland located near the intestine which produces Glucagon and Insulin in the Islets of Langerhans. Regulate body’s metabolism of sugar.