Unit 3: Biological Basis of Behavior
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
neuron
building blocks of information system
dendrites
recives messages
axon
sends messages
myelin sheath
fat that makes electrons move faster
action potential
communications along nerves
refractory period
period of time when a neuron cannot fire
threshold
level of stimulation required to trigger an impulse
all-or-none responce
a neurons reaction of firing or not
synapse
junction between axon tip and body recieving neuron
neurotransmitters
chemical messeges that cross synaptic gaps
reuptake
reabsorption by sending neuron
endorphines
neurotransmitters linked to pain control
agonist
stimulates response
antagonist
blocks response
nervous system
the bodys electrochemical communication network
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
neurons that connect central nervous system
nerves
axons that connect with central nervous system
sensory (afferent) neurons
neurons that carry into to central nervous system
motor (efferent) neurons
neurons that carry information from central nervous system to muscles/glands
interneurons
neurons within central nervous system that communicate internally
somatic nervous system
division of peripheral nervous system
autonomic nervous system
controls glands and muscles
sympathetic nervous system
division of autonomic nervous system that arouses the body
parasympathetic nervous system
division of autonomic nervous system that calms the body
reflex
response to sensory stimulus
endocrine system
slow chemical communication system
hormones
chemical messengers that effect other tissues
adrenal glands
help arouse body in times of stress
pituitary glands
regulates growth
lesion
tissue distruction
EEG
measures electrical activity in the brain
CT scan
reveals layers of head/brain
PET scan
measures glucose
MRI
shows soft tissue
fMRI
series of MRI, allows us to see movement
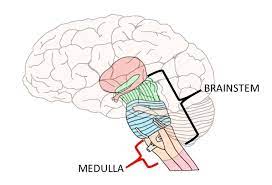
brainstem
responsible for survival functions
medulla
controls breathing, heart beat, digestion
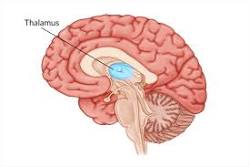
thalamus
makes sure bain sends signals to correct part
reticular formation
nerve network traveling the brainstem
cerebellum
stores memories
limbic system
system associated with emotions and drives
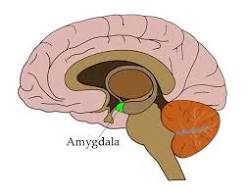
amygdala
responsible for intense “negative” emotions
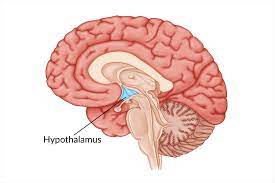
hypothalamus
regulates all biological drives
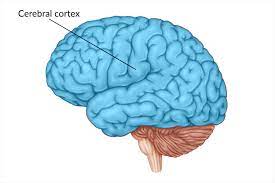
cerebral cortex
information processing center
glial cells
support and protect neurons
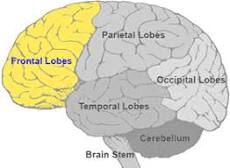
frontal lobes
regulates decision making
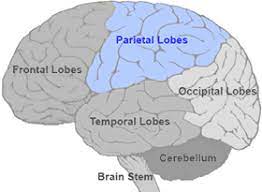
parietal lobes
recieves sensory input for touch and body position
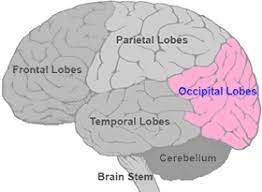
occipital lobes
area that gets information from visual fields
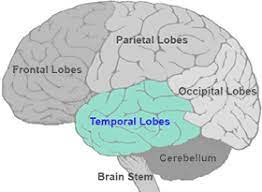
temporal lobes
recieves information from the opposide ear
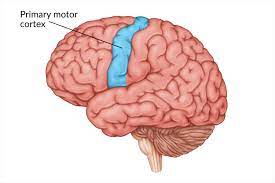
motor cortex
controls voluntary movement
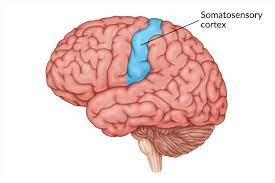
somatasensory cortex
registers/processes touch and movement sensations
association areas
involved in learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking
plasticity
the brains ability to change
corpus callosum
allows 2 hemispheres of the brain to communicate
split brain
condition that isolates the brains 2 hemispheres
consciousness
awareness of ourselves and our environment
dual processing
information is processed on conscious and unconcious tracks
heritability
humans can atribute to genes
epigenetics
study of environmental changes on gene expression
evolutionary psychology
study of evolutionary behavior and mind
natural selection
reproduction and survival will be passed on
paul broca
brocas area- language production
carl wernicke
wernickes area- language comprehention
michael gazzaniga
the split-brain phenomenon
charles darwin
theory of evolution and natural selection