Acute/Chronic Pain- Dart
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2 hours
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
For acute pain, _______ opioids for the _________ duration are recommended if opioid use is warranted.
a. extended-release, minimum
b. immediate-release, minimum
c. extended-release, maximum
d. immediate-release, maximum
b.
What type of treatment is used for each kind of pain? (aka opioid, non-opioid)
idk how imp
mild: nonopioid ± adjuvant therapy
mild-mod: weak opioids ± nonopioid ± adjuvant therapy
mod-severe: strong opioids ± nonopioid ± adjuvant therapy
What are some non-pharm approaches to pain management?
ice/ heat
elevation
rest
immobilization
exercise
Examples of weak opioid agonists include…
idk how imp
Tramadol
codeine
hydrocodone
tapentadol
Examples of strong opioid agonists include…
idk how imp
Methadone
fentanyl
hydromorphone
meperidine
morphine
oxycodone
oxymorphone
What are Morphine Miligram Equivalents (MME) used to do?
used to monitor patient’s daily intake of opioids
____ MME/day is often used as a benchmark for when to use extra precaution with opioid prescriptions.
50 MME/day (risk of overdose x2 at 50 MME/day versus <20 MME/day)
Can MMEs be used to convert from one opioid to another?
NOOOO…
PRACTICE:
A pt. is currently taking oxycodone 10mg every 6 hours routinely and uses Hydromorphone 2mg for breakthrough pain. They have taken 2 doses of hydromorphone today. Calculate the pts. daily MME.
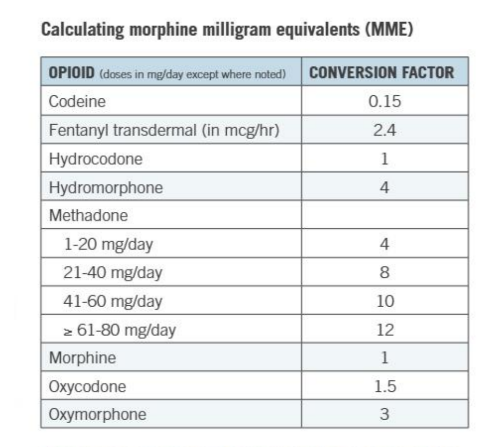
MME= strength x quantity x conversion factor
Will be given table on exam!!!!
Oxy = 10 × 4 × 1.5
= 60
Hydromorphone= 2 × 2 × 4
= 16
TOTAL MME= 76
_______ is preferred due to convenience, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility as a route of administration for opioids.
a. IV
b. IM
c. transdermal
d. oral
d.
With ______ administration you get the most rapid onset of effect.
a. IV
b. IM
c. transdermal
d. oral
a.
Why is IM admin not recommended for opioids?
painful
variable and inconsistent absorption
What is the benefit to transdermal ROA for opioids?
less constipation compared to oral
What is a PCA?
programmable pump for IV/SQ opioids
gives small dose constantly and/or frequently
For PCA, the safety mechanism is a _______________.
lockout interval (max amount of med a pt. can get in an hour)
What are the pros and cons of a PCA?
PROS | CONS |
|
|
With intrathecal (intraspinal) opioids, ______ has a longer duration of action as it will penetrate the spinal cord, and fentanyl has a quicker onset.
Morphine
With intrathecal opioids, epidural doses are 1/____th of IV doses, but intrathecal doses are 1/____th of epidural doses.
1/10th
(Ex: morphine 10mg IV = 1mg epidural = 0.1mg intrathecal OR you can also say IV dose → Epidural (1/10) → Intrathecal (1/100))
PRACTICE:
A physician wants to start his pt. on a morphine PCA pump with a lockout amount of 6mg/hr. Which option would NOT be a possible option?
a. Morphine 1 mg/hr and 0.5 mg q10 minutes PRN
b. Morphine 1 mg/hr and 0.5 mg q5 minutes PRN
c. Morphine 0.5 mg q5 minutes PRN
d. Morphine 1 mg q10 minutes PRN
b. (0.5 mg x 12 = 6 + 1 = 7 mg, but lockout amount is 6 mg)
Clinicians should reevaluate patients __-__ weeks after starting opioid therapy.
idk how imp
1-4
What does PDMP stand for and what is it’s purpose?
PDMP= prescription drug monitoring program
purpose: help prevent rx drug abuse as well as protect the community
The main difference between acute and chronic cancer pain is the duration. Acute cancer pain usually lasts how long? chronic?
acute= <3 months
chronic= >3 months
Describe what kind of analgesics should be used for each type of cancer pain (aka non opioids or opioids):
mild pain
mod-severe pain
severe pain/ pain crisis
mild pain: focus on nonopioids + adjuvant therapies
mod-severe pain: nonopioids, adjuvants, and short-acting opioids q3-4 hrs PRN
consider long-acting if need short-acting a lot
severe pain/ pain crisis: consider hospice
What is “breakthrough pain”?
pain flare—> usually associated with cancer pain
Typical breakthrough dose for breakthrough pain is ___-___% of the total daily opioid use every 2-6 hours as needed.
5-20%
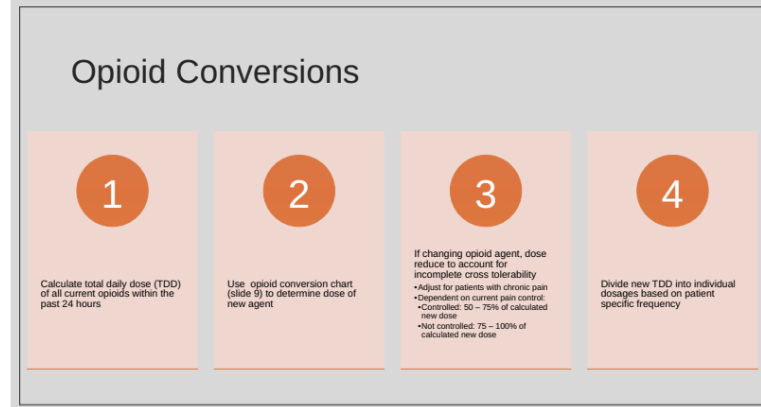
What are the steps to converting opioids?
calculate TDD of all opioids within last 24 hrs
use opioid conversion chart to determine dose of new agent
if changing opioid agent, must dose reduce to account for incomplete cross tolerability
adjust for pts. with chronic pain
dependent on current pain control:
controlled—> 50-75% of calculated new dose
not controlled—> 75-100% of calculated new dose
divide new TDD into individual dosages
When might you consider titrating from a short term opioid to long term opioid?
if requiring >/=2-3 breakthrough doses within 24 hours
if >25% of TDD take for breakthrough pain
Are adjuvants opioids?
no—> co-analgesics that are nonopioids
T/F: adjuvants contain APAP or an NSAID.
FALSE—> do not contain
Examples of adjuvants?
antidepressants
anticonvulsants
benzos
bisphosphonates
NMDA receptor antagonists
skeletal muscle relaxants
steroids
topical agents
Why do we taper opioids?
to avoid withdrawal in pts. on long term opioids
First line medication for pain management in pregnancy is _______.
Acetaminophen
When can NSAIDs technically be used in pregnancy?
only in 1st or 2nd trimester
What are the 4A’s of pain?
adverse effects
analgesia
ADLs
abuse issues
Compare tolerance, dependence, and addiction:
Description | |
Tolerance | |
Dependence | |
Addiction |
Description | |
Tolerance |
|
Dependence |
|
Addiction |
|
What are the 3 medications recommended to manage OUD?
methadone
naltrexone
buprenorphine
Answer the following about methadone:
agonist or antagonist?
used for mild, mod, or severe pain?
why is it used for withdrawal/ OUD?
full agonist
synthetic opioid used for severe pain
long half life and slow absorption—> reduces “high” sensation and slow elimination—> avoids emergence of withdrawal symptoms
Patients need to be fully withdrawn before ______ can be initiated to avoid precipitated withdrawal.
Naltrexone
_______ is an opioid receptor partial agonist and the most widely prescribed OUD medication.
Buprenorphine
Naloxone is an opioid ________ that rapidly temporarily reverses the effects of opioids. (fyi: do not confuse naltrexone with naloxone)
a. antagonist
b. agonist
a.
Which of the following about naloxone is INCORRECT?
a. can repeat dose q2-3 minutes if pt. doesn’t wake up
b. affects patients that do not have opioids in their system
c. comes in a nasal spray or injection
d. opioid antagonist
b. (does NOT affect pts. that do not have opioids in their system)
What did PA Act 139 do?
provides (limited) immunity from charges/prosecution
“good samaritan”
allows 1st responders to administer naloxone
allows non-profits to distribute naloxone
PRACTICE:
JZ has a history of OUD was recently admitted into the hospital. She takes methadone 120mg daily. Pharmacy has been consulted to make recommendations to improve her lower back pain. Which recommendation below would be a priority for this patient?
a. Increase home methadone dose to 140 mg and add topical agents
b. Decrease methadone dose to 5 mg every 8 hours for pain control
c. Hold home methadone and start oxycodone 10 mg every 6 hours
d. Continue home methadone 120 mg in addition to other pain management agents
d.