US Physics Unit 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
1
New cards
The diagnostic ultrasound imaging (sonography) method has 2 parts:
1. Sending ___ __of__ __*into the body, and 2.) using*__ ____ received from the anatomy to produce an of that anatomy__
1. Sending ___ __of__ __*into the body, and 2.) using*__ ____ received from the anatomy to produce an of that anatomy__
pulses, ultrasound, echoes, image
2
New cards
Ultrasound gray-scale scans are ________ images of tissue cross-sections and volumes
pulse echoes
3
New cards
the brightness of an echo as presented on the display, represents the ______ of the echo
strength
4
New cards
A linear scan is composed of many _________ scan lines
vertical, parallel
5
New cards
A sector scan is composed of many scan lines with a common ______
orgin
6
New cards
A linear scan has a _______ shape
rectangular
7
New cards
the shape of a sector scan is similar to a ___ __of__ _____
slice, pie
8
New cards
A sector scan can have a ___ __or a__ ____
pointed, curved
9
New cards
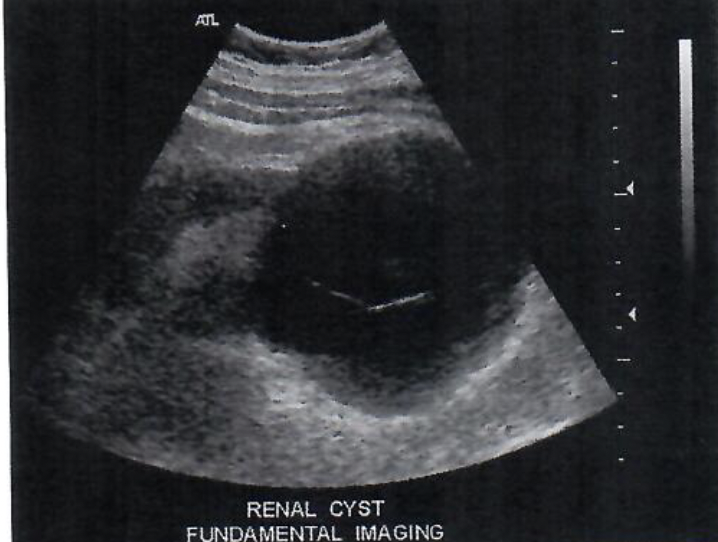
This is an example of an image in which the scan lines do not orginate at a common ______
orgin
10
New cards
Sonography is accomplished by using a pulse-echo technique. the important info gained from this technique includes the ___ __from which each echo orginated and the__ ___ __of each echo. from this info, the instrument can determine the echo__ __*and*__ _______ on the display__
location, strength, location, brightness
11
New cards
the ________ is the interface between the patient and the instrument
transducer
12
New cards
transducers generate ultrasound ____ __and receive returning__ _____
pulses, echoes
13
New cards
echo info in 3D is presented on ______ displays
2D
14
New cards
Acquisition of a 3D echo data volume requires scanning the ultrasound through several tissue _______
cross-sections
15
New cards
the doppler effect is a change in echo______
frequency
16
New cards
the change in echo frequency is due to _____
motion
17
New cards
the motion that produces the Doppler effect is that of the _______
reflector
18
New cards
in medical applications the flow of ____ __is comonly the source of the doppler effect. doppler info is applied to__ __*for audiable evaluation and to*__ _________ for visual analysis.__
blood, loudspeakers, displays
19
New cards
the visual display of doppler info can be in the form of a ______-Doppler display or a__ ______- doppler display
spectral, color
20
New cards
Color-Doppler displays can present Doppler-___ __and Dopppler-_______ info in color
shift, power
21
New cards
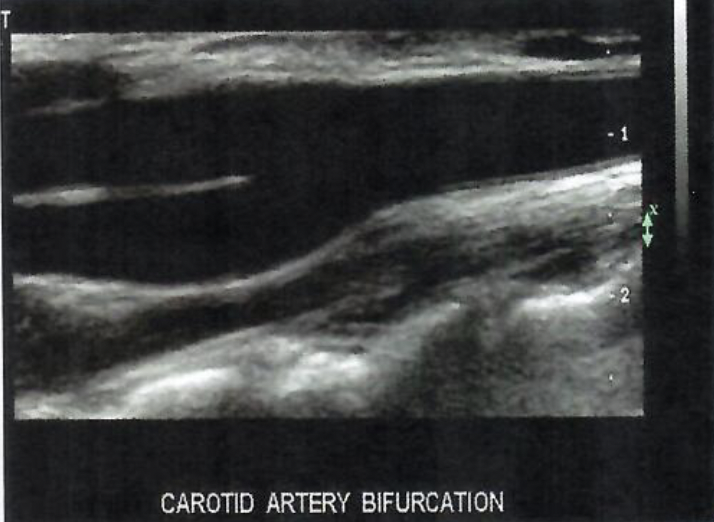
This shows a
2D linear image
22
New cards
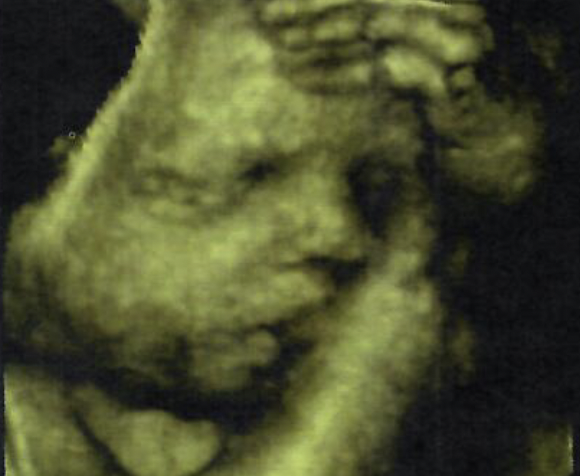
This shows a
3D gray-scale image
23
New cards
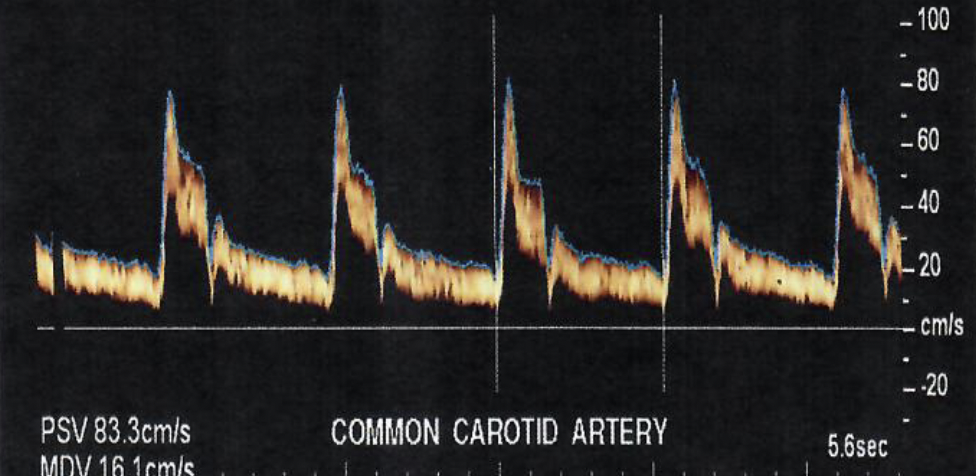
This shows a
spectral display
24
New cards
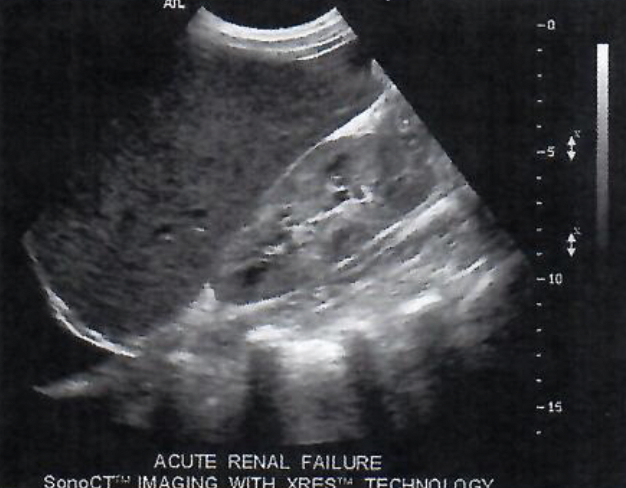
This shows a
modified sector image
25
New cards
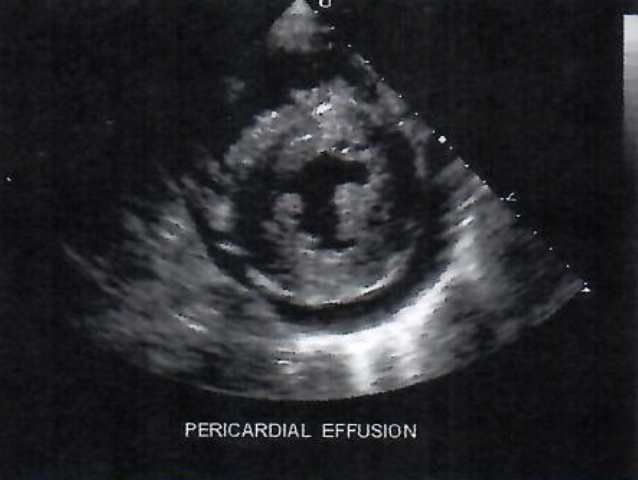
This shows a
2D Sector image
26
New cards
One line of echo information is called the
scan line
27
New cards
The brightness of the displayed echo corresponds to its
strength
28
New cards
1 inch = ____cm
2\.54 cm
29
New cards
1cm= ____mm
10
30
New cards
79mm=____cm
7\.9cm
31
New cards
04\.mm=____cm
0\.04cm
32
New cards
Express 10 in exponential notation
10^1
33
New cards
Express 1,000,000 in exponential notation
10^6
34
New cards
Express 1/100 in decimal form
0\.01
35
New cards
Express 1/100 in exponential notation
10^-2
36
New cards
Express 1/1,000,000 in decimal form
0\.000001
37
New cards
What prefix describes 1/1,000,000
micro
38
New cards
Express 1/1,000,000 in exponential form
10^-6
39
New cards
What is the logarithm of 10
1
40
New cards
What is the logarithm of 0.01
\-2
41
New cards
Every measurement has 2 parts:
unit, magnitude
42
New cards
10^9
giga (G)
43
New cards
10^6
mega (M)
44
New cards
10^3
kilo (k)
45
New cards
10^2
hecto (h)
46
New cards
10^1
deca (da)
47
New cards
10^-1
deci (d)
48
New cards
10^-2
centi (c)
49
New cards
10^-3
milli (m)
50
New cards
10^-6
micro (u)
51
New cards
10^-9
nano (n)
52
New cards
billions and billonths
giga and nanomi
53
New cards
millions and millionths
mega and micro
54
New cards
thousands and thousandths
kilo and milli
55
New cards
hundreds and hundredths
hecto and centi
56
New cards
tens and tenths
deca and deci
57
New cards
log10000
4
58
New cards
log1000
3
59
New cards
log100
2
60
New cards
log10
1
61
New cards
log0.1
\-1
62
New cards
log0.01
\-2
63
New cards
log0.001
\-3
64
New cards
log0.0001
\-4
65
New cards
Binary numbers are between ____
0-1
66
New cards
motion of an object can be described by 2 terms:
velocity and acceleration
67
New cards
Equation for force
F=(m)(acceleration)
68
New cards
accleration
the rate of change in velocity per unit of time, how fast the velocity is changing
69
New cards
if velocity is constant then acceleration is
0
70
New cards
velocity
the rate of change of the position of an object with time
d/t
d/t
71
New cards
Force
push or pull of an objectwo
72
New cards
work
the force applied times the distance over which it is applied
W=F (d)
W=F (d)
73
New cards
Power (P)
the rate of doing work
74
New cards
energy
the ability to do work