cambridge computer science as unit 6 and 7
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
cambridge computer science as, mrs. preston
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
The set of instruction are grouped into instruction for:
a. _____ movement
b. input and output of ______
c. _____ operations
d. unconditional and conditional _____
e. _____
data
data
arithmetic
jumps
comparison
Machine code consist of a sequence of _____
instructions
An instruction contains an _____
opcode
An instruction may not have an _____ but up to 3 _____ are possible
operand, operands
Different processors have _____ instructions sets associate with them
different
Different processors will have comparable instructions for the same operation, but the coding of the instruction will be _____
different
Define opcode
Defines the action associated with the instruction
Define operand
Defines any data needed by the instruction
Define machine code instruction
A binary code with a defined number of bits that comprises the opcode and, most often, one operand
What determines the number of bits needed for the opcode?
number of different opcodes in instruction set
What 3 factors does the opcode determine?
operation, address mode, register addressing
Why does the control check the opcode when an instruction arrives in the CPU?
To determine what action it defines
Machine code allows the programmer to _____ the processor
directly control
Writing a substantial program as a sequence of machine code instruction would take a _____ and most likely contain _____
very long time, several errors
Do all processors use the same assembly language?
No
Define assembly language
A low-level language related to machine code where opcodes are written as mnemonics and there is a character representation for an operand
Define assembler
A program used to translate an assembly language program into machine code
What is used to translate a program written in assembly language must into machine code?
Assembler
List advantages of using assembly language
code being easier to write
allows special features to be included in assembly language program
List examples of special features included in an assembly language program
comments
symbolic names for constants
labels for address
macros
directives
Define macro
A sequence of instructions used more than once in a program
Define directive
An instruction to the assembler program
Use of symbolic programming allows programmers to write assembly code without worrying about _____
where to store the code in memory
Define label
A sequence of characters that identifies a location within source code
Are labels used in symbolic addressing?
Yes
Are labels used in relative addressing?
No
Are labels used in absolute addressing?
No
What are the 2 ways that it is possible to write code without symbolic memory?
relative and absolute addressing
What is assumed when using relative addressing?
A special function base register, BR, contains the base address
Give examples of things an assembler must do with assembly language code before translating
a. removal of comments
b. replacement of a macro name used in an instruction by the list of instructions that constitute the macro
c. removal and storage of directives to be acted upon later
During first pass in a two-pass assembler is needed to identify what?
Addresses for forward references
During first pass in a two-pass assembler, how is the code read?
line by line
During first pass in a two-pass assembler, what is created?
Symbol table
During first pass in a two-pass assembler, what happens when a symbolic address is first encountered?
It is entered into the symbol table
During first pass in a two-pass assembler, when a symbolic address is first encountered, what additional actions must occur and when will it occur?
A corresponding address is added when the address can be identified
During first pass in a two-pass assembler, what must the assembler do as it reads the code?
Count instructions
During second pass in a two-pass assembler, what does the look up table provide?
Binary code for each opcode
Where can the binary code for every opcode in the set defined for the processor be found?
Look up table
Assuming no errors are found, what will the second pass produce?
A machine code program
In machine code, what do most instructions have and what is it?
An operand, a 16-bit binary number
In machine code, what does the operand usually represent?
An address
In machine code, for which instructions does the operand represent a value?
SUB, LDM
In machine code, which instructions have no operand?
IN, END
In machine code, which instructions is a special case?
INC
What makes the instruction INC special?
the operand in assembly code identifies the register
machine code: identified with opcode, no operand needed
Define addressing mode
When the instruction uses a value this defines how the operand is used to find a value
In our simple processor, how many bits of the opcode in the machine code instruction are used to define the addressing mode?
2
If our simple processor used four bits of the opcode in the machine code instruction to define the addressing mode, how many modes would be possible?
4
List all the different addressing modes, give the mode and how the operand is used
immediate: the operand is the value used
direct: the operand is the address with the value used
indirect: the operand is the address with the address with the value used
indexed: the operand is the address added with the IX value to find the value used
Explain the options available for immediate addressing
#n: denary value n
#B00110000: binary value equivalent to denary 48
#&30: hexadecimal value equivalent to denary 48
What does IX represent?
Index Register
What does data movement involve?
Loading data into register, storing data in memory
What does ACC represent?
Accumulator
How many input instructions exist?
1
How many output instructions exist?
1
Which, if any, input or output instructions have an operand?
None
How does the execution of a conditional begin?
A conditional jump begins by checking the flag
When a jump instruction is executed, what happens to the program counter?
It is overwritten with the new address
An assembly language contains assembly language _____ plus _____ that provide information to the assembler
instruction, directives
A two-pass compiler identifies _____ addresses for _____ addresses in the first pass
relative, symbolic
Assembly language instructions can be categorized as
data movement, input/output, compare and jump, arithmetic, shift and logical
What is used to monitor/control a device?
Bit manipulation
What can a monitoring system be used to create?
A record of the conditions of a system
A monitoring system is usually used to detect what?
When a particular physical property is outside a desired range
What is a measuring device that records a value that can be transmitted to the computer?
Sensor
What is a thermocouple?
A sensor for measuring temperature and outputs an electrical voltage changing with the temperature
What prevents a sensor from taking action?
It does not have built-in intelligence
What must happen if the sensor detects values in the danger range?
Sound an alarm
Give at least six examples of sensors
pressure, humidity, carbon monoxide, pH levels, sound, different types of infrared sensors, motion sensors
Define sensor
A hardware device that measures a property and transmits a value to a controlling computer
Define actuator
A hardware device that receives a signal from a computer and adjusts the setting of a controlling device
True or False: An environment is monitored so that it can be controlled
False
True or False: An environment that is controlled must be monitored
True
True or False: A sensor is used to monitor a system
True
True or False: A sensor must be recording data continuously
False
True or False: An actuator is used to control an environment or a system
True
True or False: If a sensor detects a problem in a controlled environment, it must send a signal to the appropriate actuator to correct the problem
False
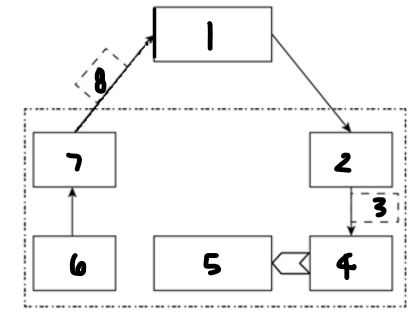
Label each component: 1
computer or microprocessor

Label each component: 2
digital-to-analogue converter
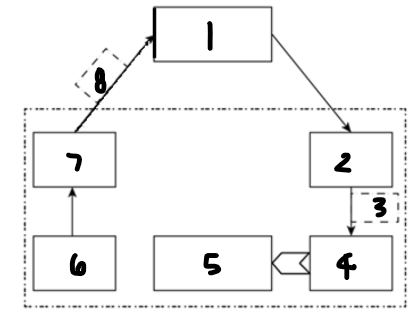
Label each component: 3
analogue control signal
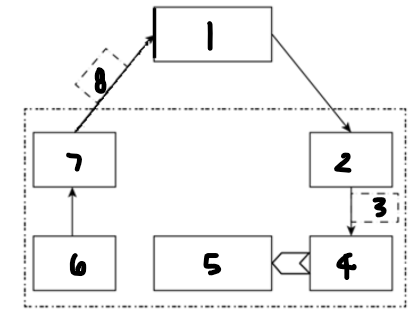
Label each component: 4
actuator

Label each component: 5
controlled device
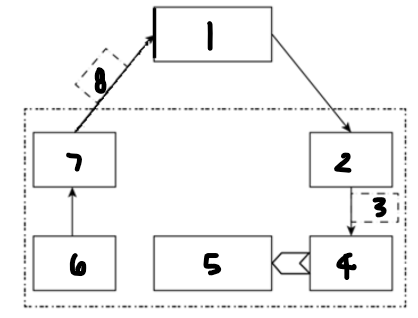
Label each component: 6
sensor
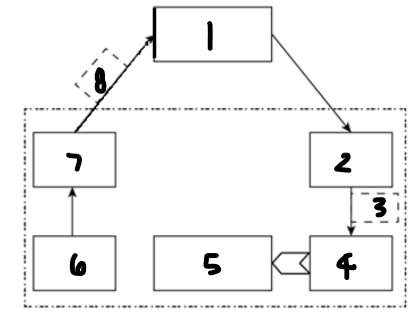
Label each component: 7
analogue-to-digital converter
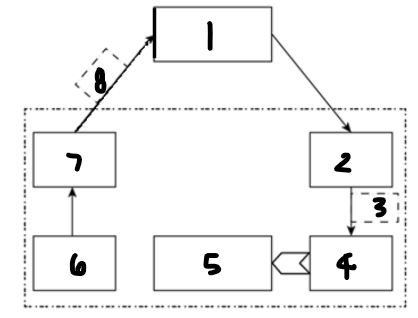
Label each component: 8
digital measured value
What is essential in a control system?
Feedback
A microprocessor functions as the controller and compares what values?
The actual output and desired output
What does the microprocessor do with the values?
Transfer to the actuator based on the difference between the actual and desired outputs
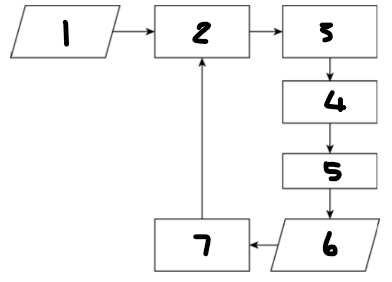
Label each component: 1
desired value for process output
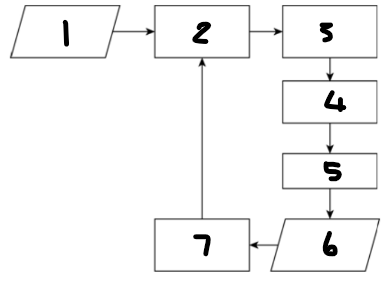
Label each component: 2
controlling computer
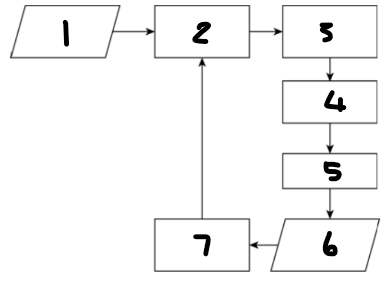
Label each component: 3
actuator
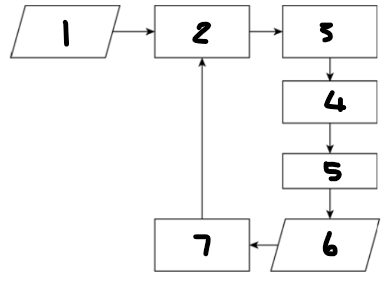
Label each component: 4
controlling device
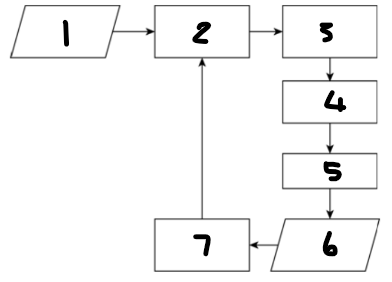
Label each component: 5
process
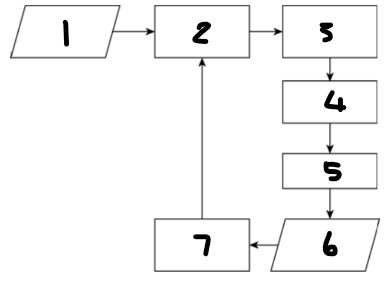
Label each component: 6
process output
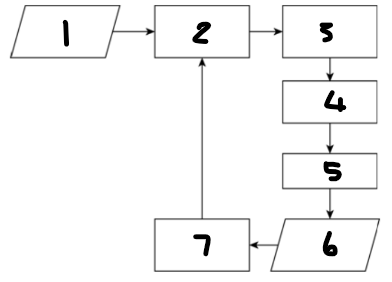
Label each component: 7
sensor
How many Boolean variables are needed if a single property is to be monitor, can be too high, too low or in range?
2
How many Boolean variables are needed if a single property is to be monitor, can in range or out of range?
1
What does it mean to toggle a switch?
To change the value of the flag it represents
A monitoring system contains
a sensor
A control system contains
a sensor and actuator