VPH 121 LE 2 Lec 1: Observational Study
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Observational Study
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Observational Study
Conducted to observe exposures that are not assigned by the researcher
Definition: Causation
Diseases do not occur randomly
prove causation by:
describe chain of events from cause to effect
study at a molecular level
Assessing association
assessment of exposure and risk indicator
calculation of risk or odds of having a disease
Assessing causation
calculation of risk or odds of having a disease
Factors in calculating the risk or odds of having a disease
predictive
diagnostic
management
Goals of Epidemiology
describe the health status of a population
explain causality or association
predict disease occurrence
control the spread of diseases
Types of Descriptive Study
Case Report
Case Series
Case Report
single occurrence of an unusual case
qualitative > quantitative
Case Series
multiple occurrences of an unusual case
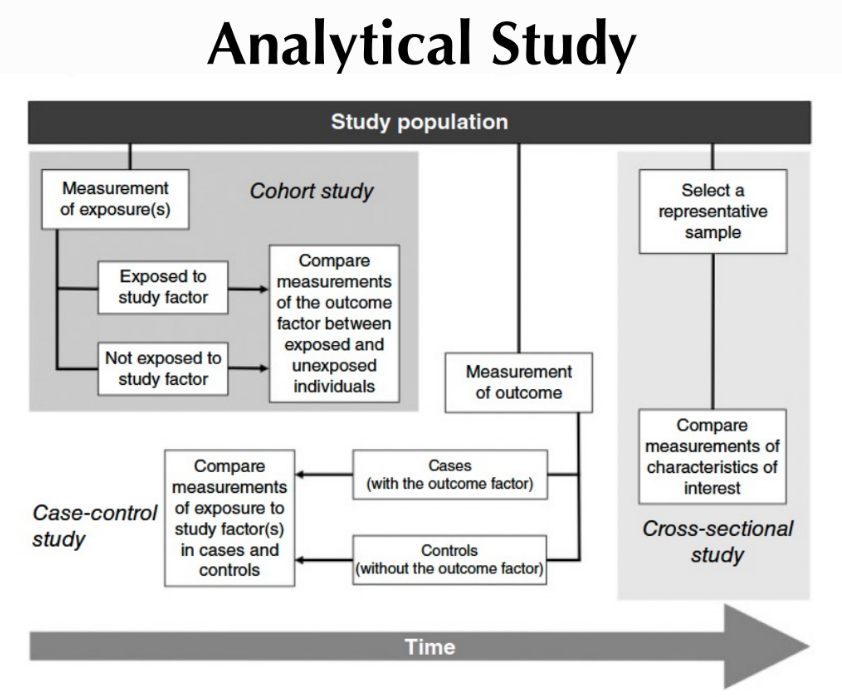
Types of Analytical Study
Cohort
Case Control
Cross-sectional
First three rules of Evan
Higher prevalence in exposed
Exposure to a cause should be present more in disease population
Higher incidence in exposed
Most effective study in causal hypotheses
Cohort study
two types of cohort study
prospective
retrospective
Advantages of Cohort Study
Calculation of incidence
Flexible in choosing variables
Investigate multiple outcomes and potential risk factors
Rare exposures
Progression of the disease
Temporal cause and effect relationship
Second choice if experimental studies are unethical
Disadvantages of Cohort Study
Sampling error
Large population size for rare diseases
Long duration of follow-up
Difficulty in follow-up
High cost
Confounding variables
Relative Risk
Ratio between cumulative incidence
Risks between the exposed and unexposed groups
Relative Risk
RR < 1
RR = 1
RR > 1
not an exposure; protective effect
no association
high likelihood of an association
Attributable Risk
Absolute measure of excess risk in the exposed from the unexposed group
Attributable Risk
AR < 0
AR = 0
AR > 0
not a risk factor; protective factor
absence of additional risk
excess absolute risk
Type of study used when studying diseases with low incidence and conditions with long follow-ups
Case Control Study
Case Control Study
Selects diseased and disease-free populations
no measure of disease frequency
Advantages of Case Control Study
Rare diseases
Diseases with long incubation or latent periods
Fast conduct
Low cost
Few subjects are required
Available records
Absence of risk
Multiple exposures
Disadvantages of Case Control Study
Sampling error
Poor quality of records
Difficulty in validation
No control on variables
Selecting control group
No assessment of temporal sequence
Rare exposures
Limited to one outcome
Odds Ratio
Ratio between odds of disease in exposed and unexposed groups
Odds Ratio
OR < 1
OR = 1
OR > 1
less association
not associated
highly associated
Cross-Sectional Study
Random selection and examination of a population at one point in time
Describing disease occurrence at the time of collection
Challenge in investigating causal hypotheses
Advantages of Cross-sectional Study
Estimation of prevalence or positivity rate
Fast conduct
Moderate cost
Records can be used occasionally
No risk to subjects
Multiple exposures and outcomes
Disadvantages of Cross-sectional Study
Rare diseases and exposures
Diseases with short duration
Uncontrolled extraneous variables
Estimation of incidence
Temporal pattern
Poor quality of records
Flowchart for Choosing Analytical Study