Jewish History
Classical Judaism
- 66 CE: Jewish War to overcome Romans
- 70 CE: temple in Jerusalem was destroyed
- 600 CE: Islam comes to power
- Diaspora: dispersion; Jewish people having to live away from their ancestral homeland
- Own land at the crossroads of many major empires and have been conquered by many groups
Medieval Judaism
- 700s-1700s CE
- Lived under Muslim rule in Spain and Africa and Christian rule in Europe
- Under Muslim regime
- Relative peace and prosperity
- Still faced harassment, assault, rape
- Under Christian regime
- Great economic success as bankers
- Accused of starting black plague, killing Jesus, killing Christian children
- Often harassed/murdered by mobs
- Forced conversion
- Viewed as a “dangerous influence” to others
- Physically tortured
- Jewish movement in Europe
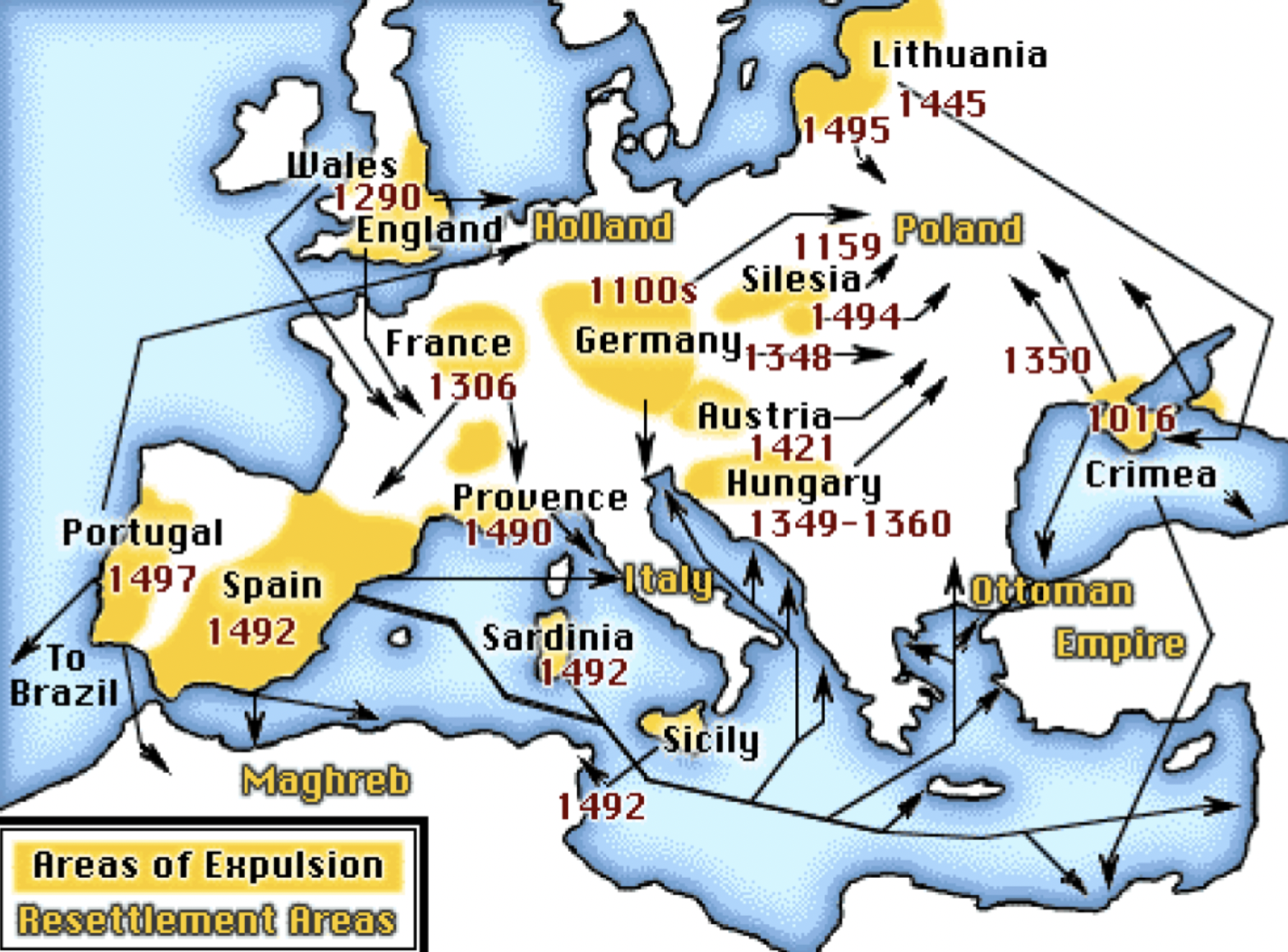
- Idea of genocide predates the Holocaust and Jewish history
- Despite persecution, Judaism is thriving
Philosophy and Mysticism
- Moses Maimonides (1135-1204)
- Wrote The Guide to the Perplexed
- Created the 13 Principles of Faith
- Belief in the existence of God
- God’s unity
- God’s spirituality and incorporeality
- God’s eternity and timelessness
- God alone should be the subject of worship and prayer
- Revelation through God’s prophets
- The preeminence of Moses among the prophets
- God’s law was given on Mount Sinai
- The immutability of the Torah as God’s Law
- God’s foreknowledge of human actions
- Reward of good and retribution of evil
- The coming of the Jewish Messiah
- The resurrection of the dead and human immortality
- Kabbalah: a belief that the best way to know God is through the heart and through love
- Developed in Spain in the 1200’s
- The Torah can be interpreted on multiple levels
- Alternative to traditional Judaism
Modern Judaism
- Hasidism: pious Judaism which emphasizes mysticism, a personal relationship with Yahweh, and a close community (focus on following Zaddik rather than studying Torah)
- Zaddik: a charismatic holy person
- Zionist: the belief in re-establishing a Jewish homeland by reclaiming the ancient Jewish ancestral homeland (modern-day Israel and Palestine)
- Since 1948, the state of Israel was recognized by the international community and the term refers to those who support Israel
- British Empire technically owned the area which would become Israel and gave it to Jewish people following international pressure after the Holocaust
- Believed to be needed because of anti-semitism
- Anti-Semitism: sentiment against Jewish people deriving from attitudes, exclusion, violence, and/or death
- Holocaust: the persecution of Jewish people by Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945
- Resulted in the deaths of 6 million Jewish people in Europe
- More than exile, inquisition—anything that’s been faced before
- Shook the faith of many Jewish people; common questions included
- Why did God let this happen?
- Some saw it as a punishment for abandoning tradition
- Some thought God broke his covenant
- One great response—Victor Frankl’s Man’s Search for Meaning
- State of Israel
- Jews emigrated to Israel before WWI
- Was part of the Ottoman Empire
- The League of Nations in 1922 recognized the need for a Jewish homeland
- Many international treaties before and after reaffirmed this
- This land was already occupied
- Palestinians and Jews both claim the land as their homeland
- Very complicated conflict
- Many countries declared war on Israel
Modern Divisions of Judaism
- Reform: Jewish people adapt to modern society
- Relaxed observance; speak English
- ~1/3 of Jewish people in the US
- Orthodox: follow the Torah
- Often live in separate communities
- Very strict
- Conservative: somewhat open to change, but still fairly strict regarding practices of liturgy and law
- Eg. follow the Sabbath
- Middle ground between other two branches
Torah
- Because you believe, you follow the law/Torah and act accordingly
- Daily life is governed by the Torah
- Permitted, forbidden, obligated, free, holy, profane (remember Islamic Sharia Law)
- Prayer
- Takes place three times a day
- Yarmulke: a skull cap, sign of respect for God
- Reminder that God is above you
- Worn after Bar Mitzvah
- Tallit: prayer shawl
- Tefillin: small boxes with scripture in them
- Home and Synagogue
- Worship takes place primarily in the home
- Mezuzah: parchment in a decorative case which designates the home as Jewish
- Food is to be Kosher
- Don’t eat pork, shellfish, any combination of meat with dairy
- Synagogue is huge since there is no temple
- Friday night is the Sabbath (time of rest)
- Services are led by Rabbis (religious leaders)
- Rabbi: one who has mastered the Talmud