DMS 101 cross sectional: unit 2
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
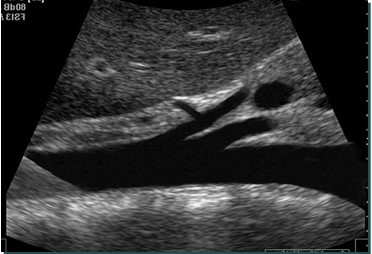
In this sagittal view, what is the structure in this image?
Celiac Trunk
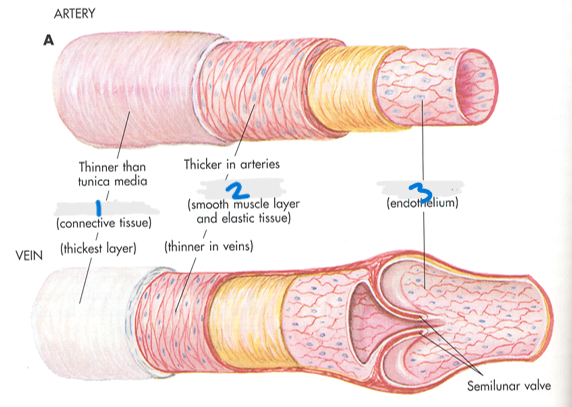
What is #1?
Tunica Adventitia
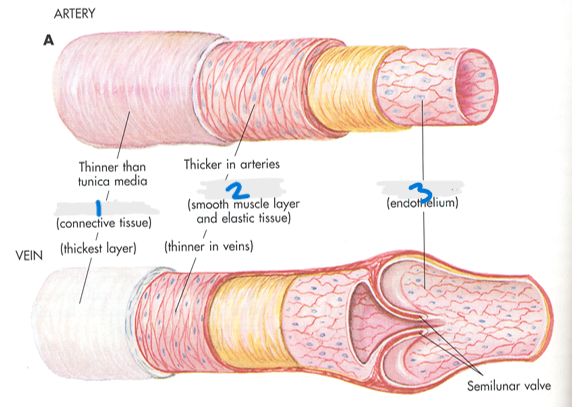
What is #2?
Tunica Media
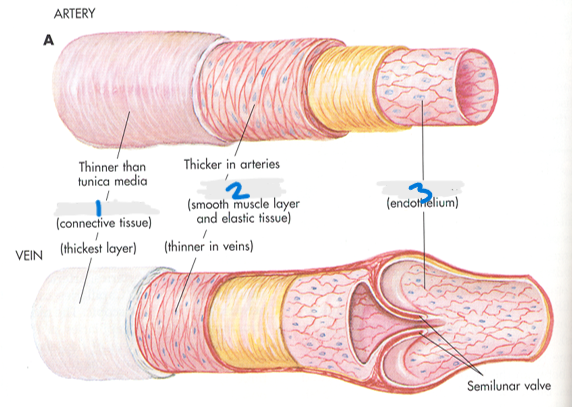
What is #3?
Tunica Intima
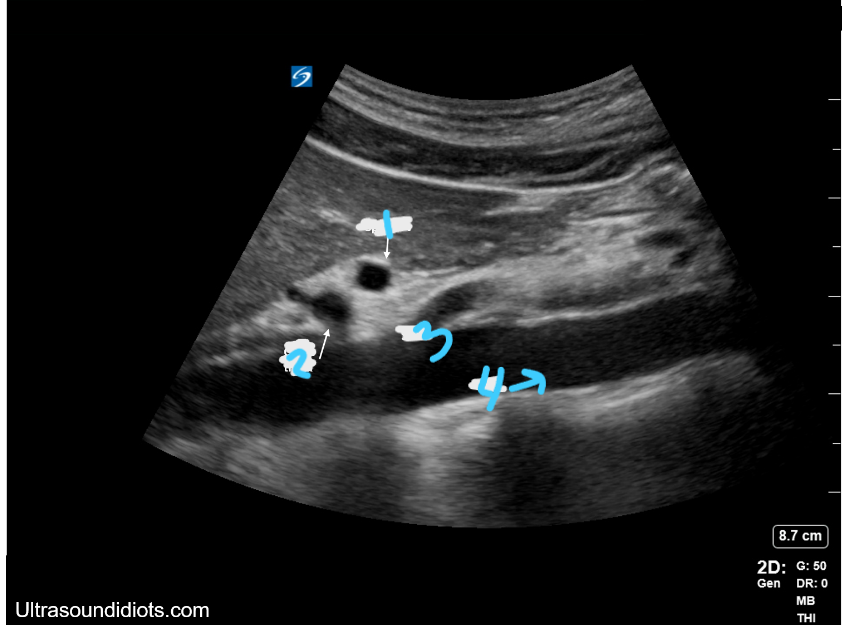
In this sagittal view, what is #1?
Splenic Vein
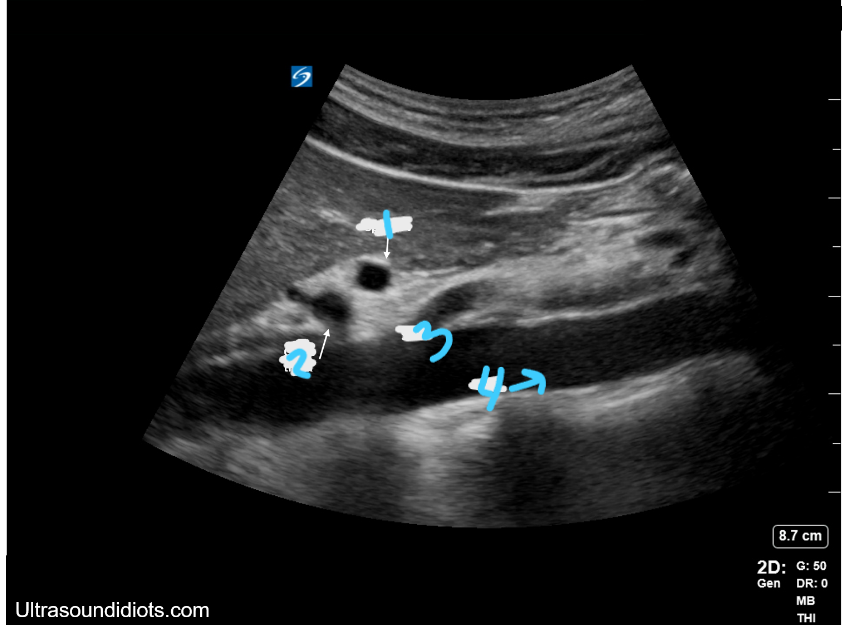
In this sagittal view, what is #2?
Celiac Trunk
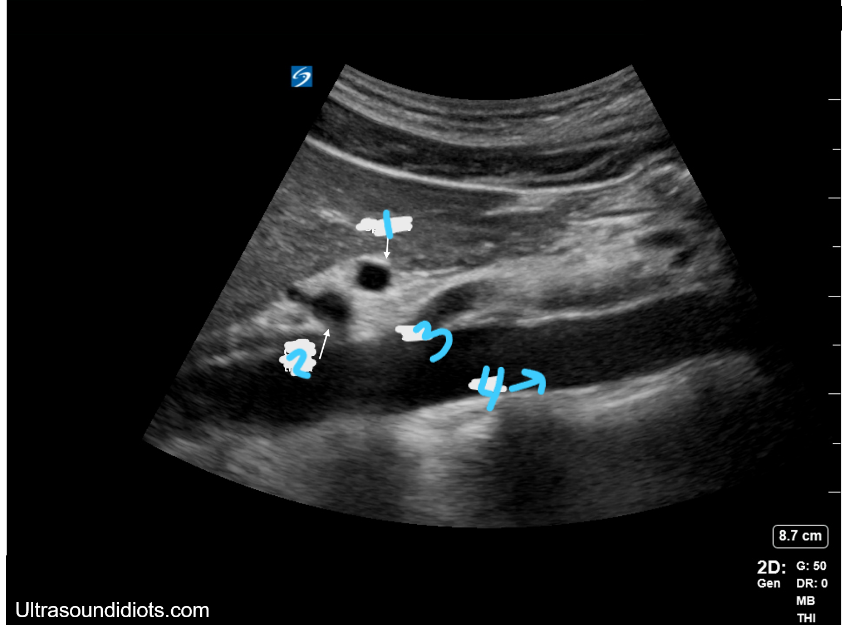
In this sagittal view, what is #3?
SMA
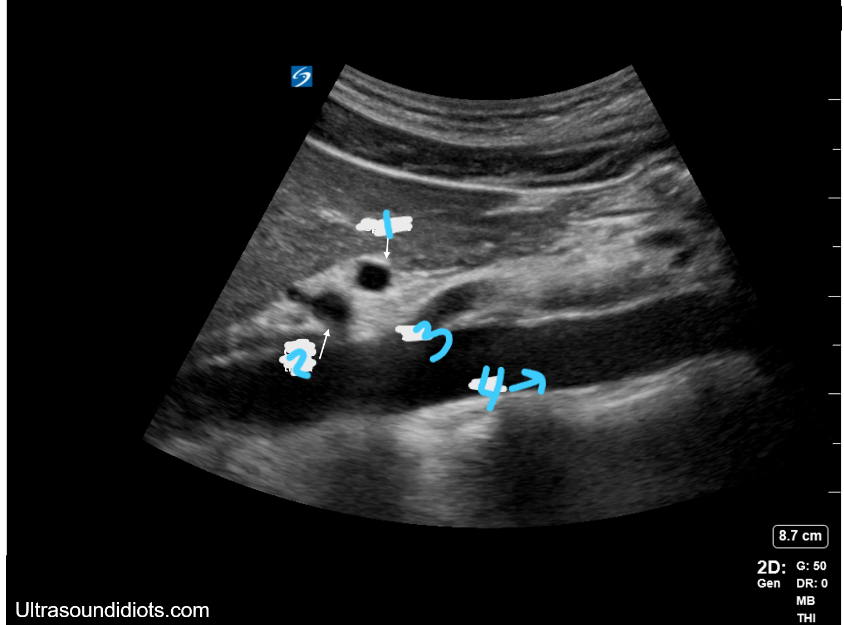
In this sagittal view, what is #4?
Aorta
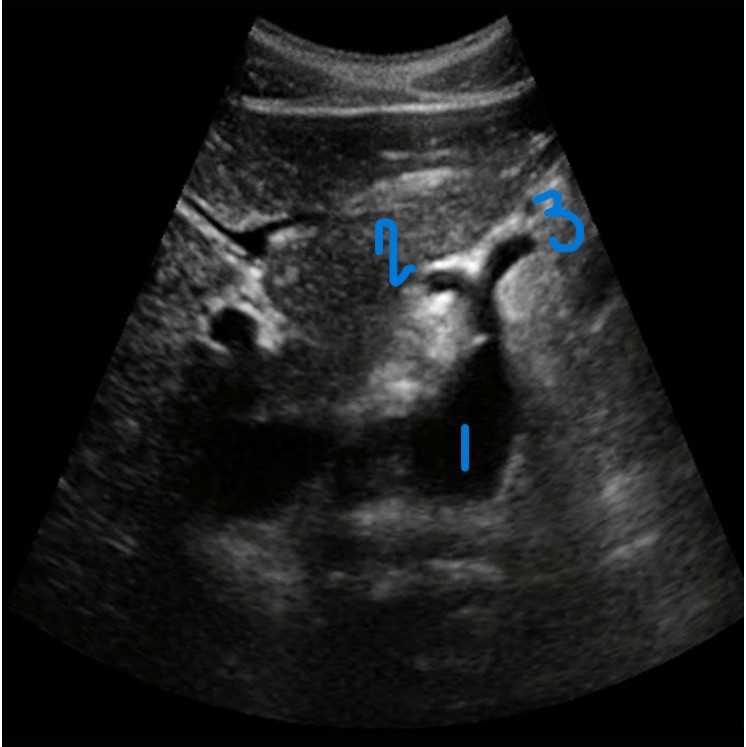
In this transverse view, what is #1?
Aorta
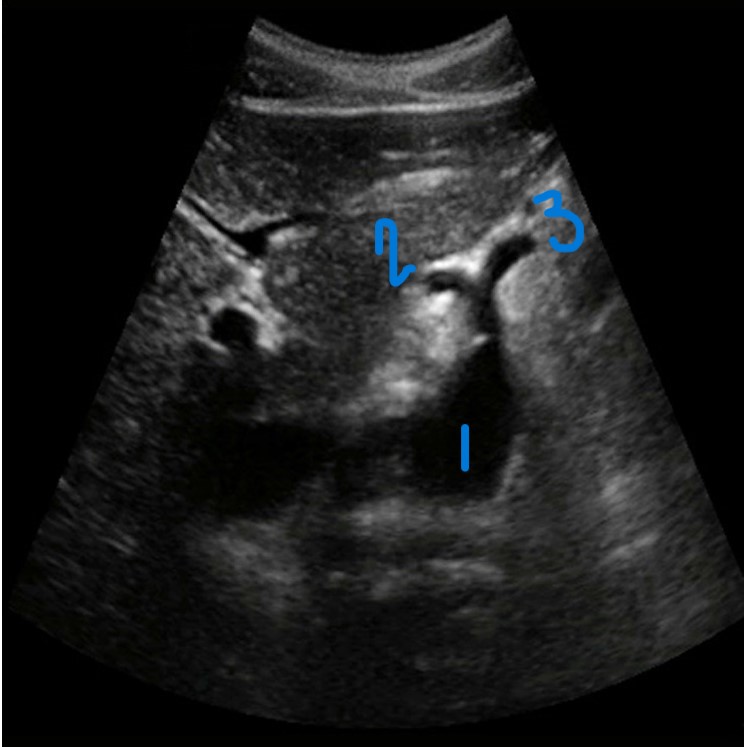
In this transverse view, what is #2?
Common Hepatic Artery
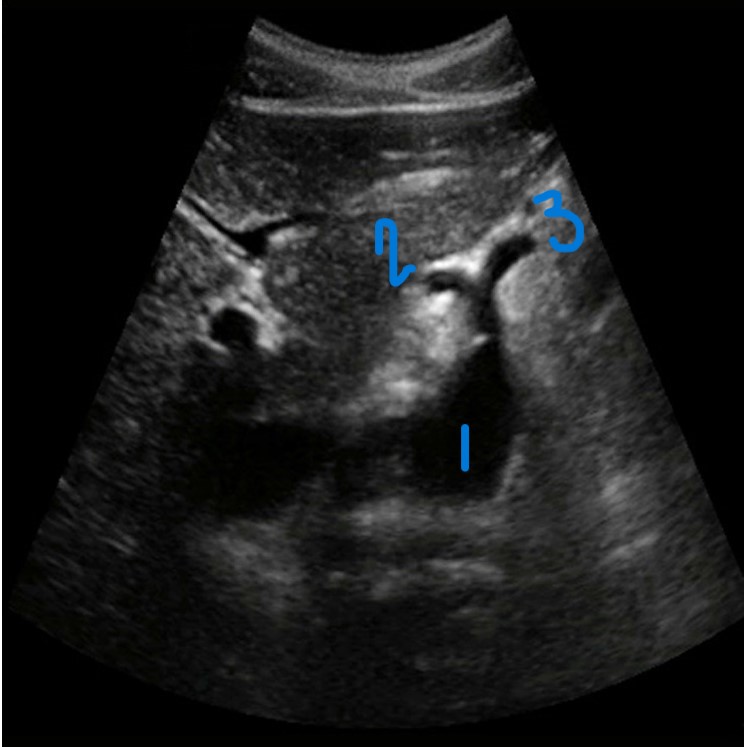
In this transverse view, what is #3?
Left Splenic Artery
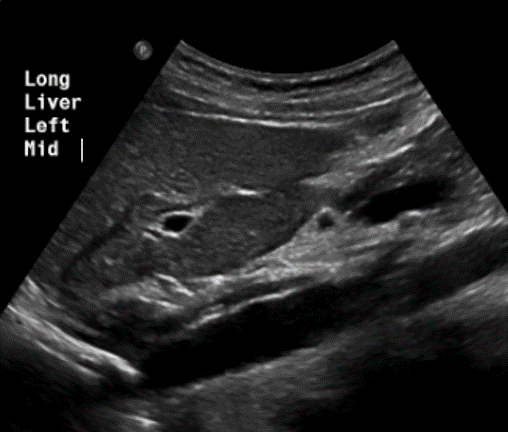
In this sagittal plane, what is this structure?
Aorta
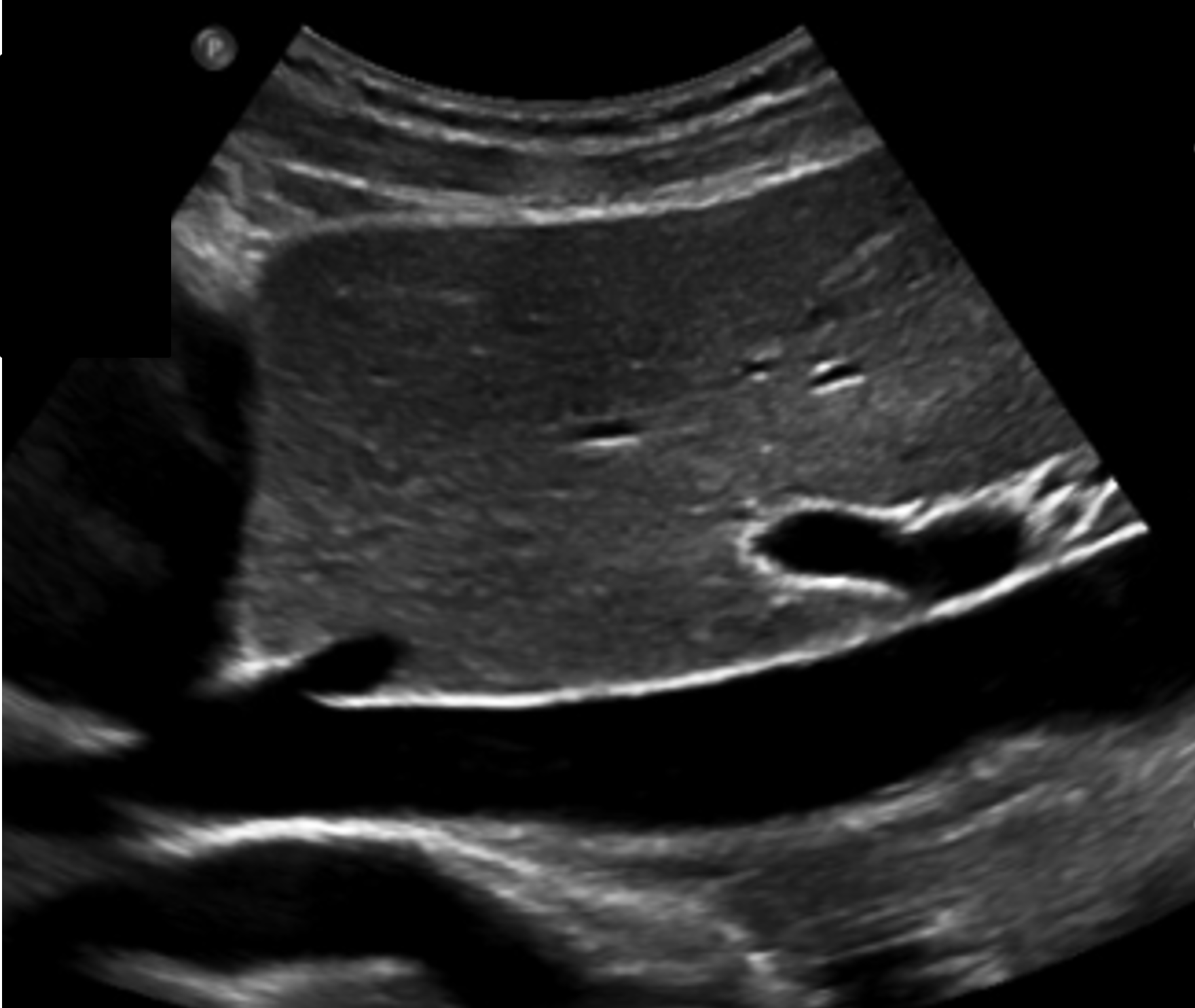
In this sagittal plane, what is this structure?
IVC
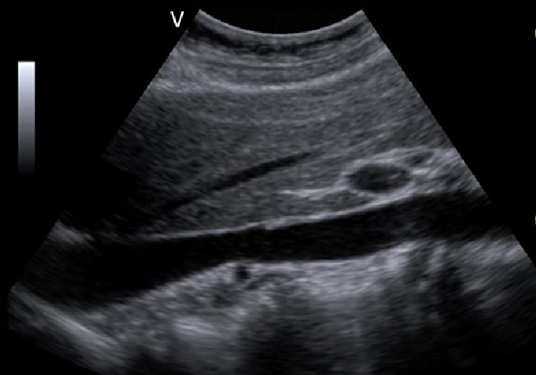
What is this structure?
IVC
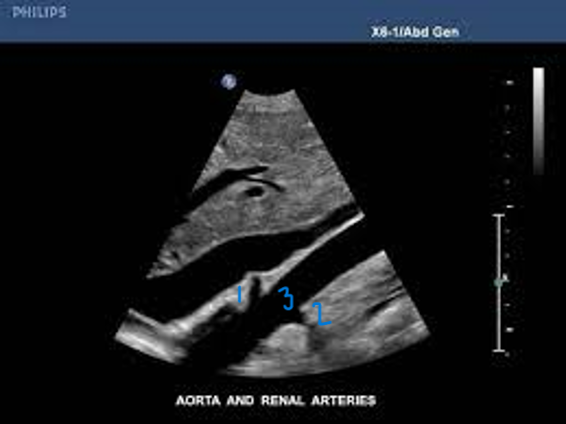
In this Sagittal-Coronal plane, what is #1?
Right Renal Artery
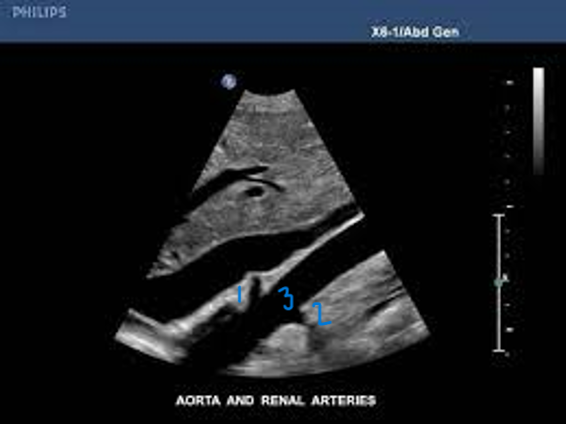
In this Sagittal-Coronal plane, what is #2?
Left Renal Artery
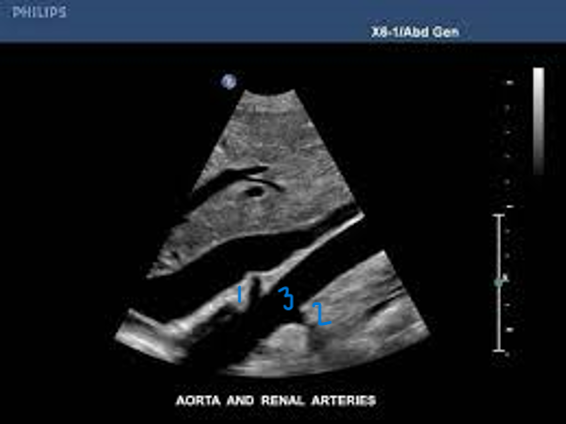
In this Sagittal-Coronal plane, what is #3?
Aorta
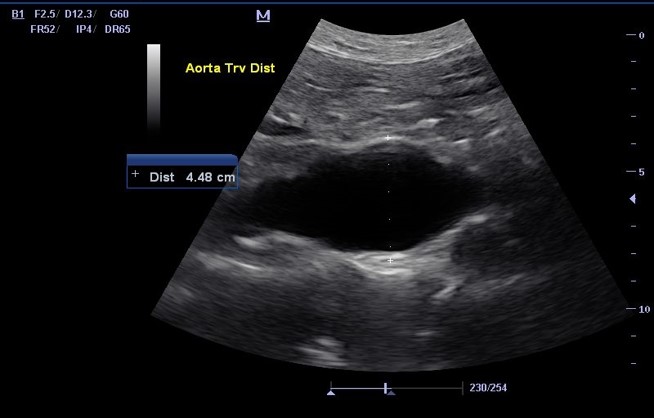
What is this structure ?
Abnormal Aorta
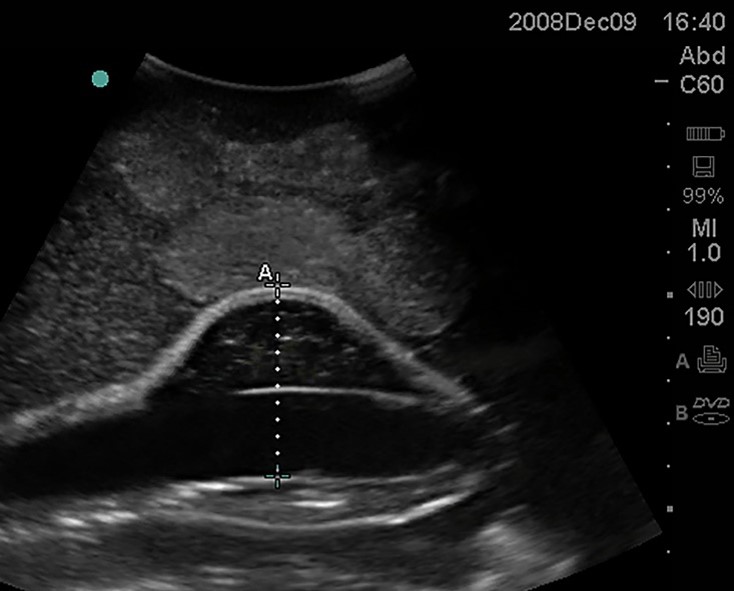
What is starting to from in this Aorta?
A blood clot
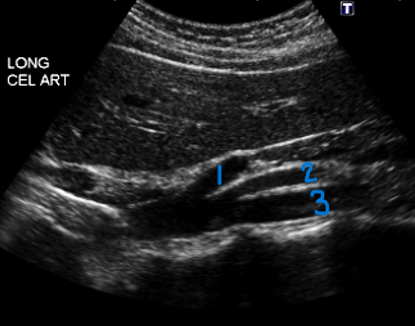
In this Sagittal view, what is #1?
Celiac Trunk
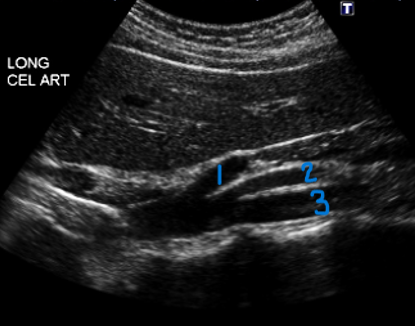
In this Sagittal view, what is #2?
SMA
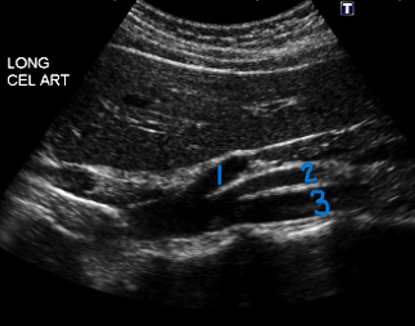
In this Sagittal view, what is #3?
Aorta
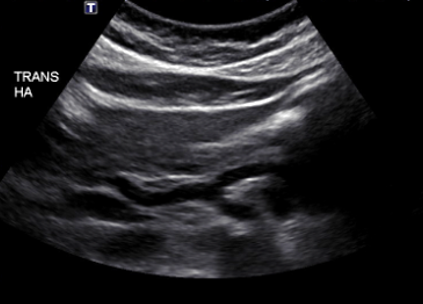
What is this structure in this the picture?
Celiac Trunk
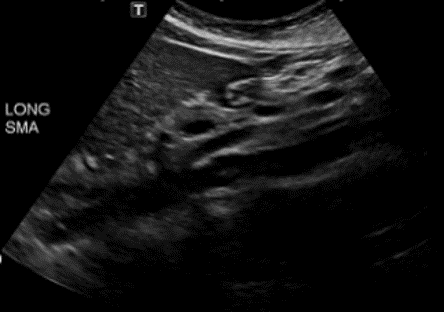
What is this structure?
Aorta with the SMA coming off the top
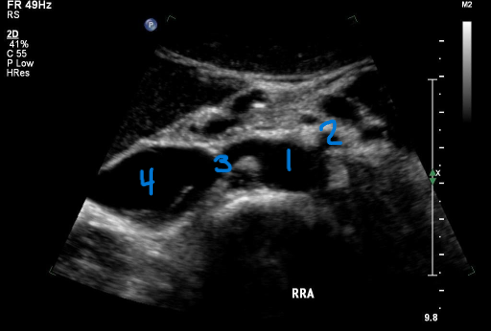
What number is known as the RRA
#3
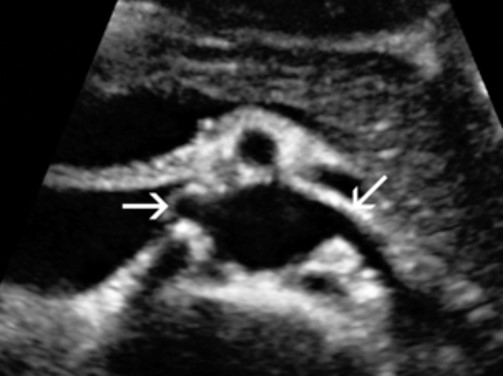
What is this structure?
The right and left renal arteries
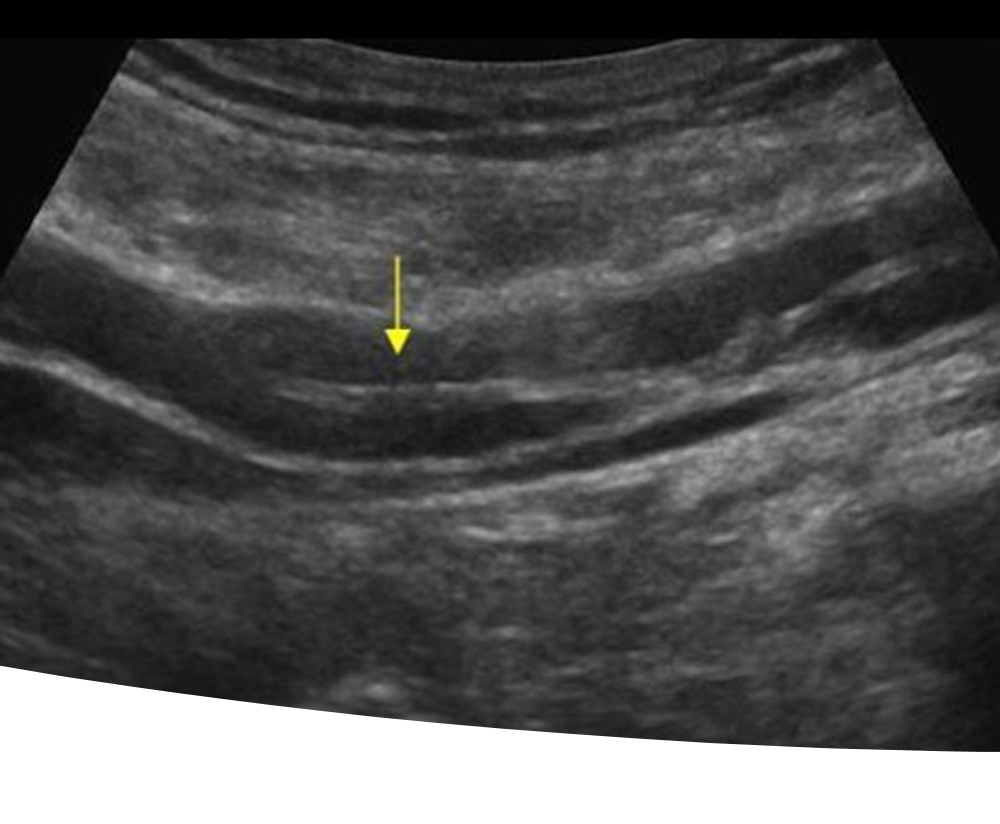
What is the structure in this picture?
The iliac arteries
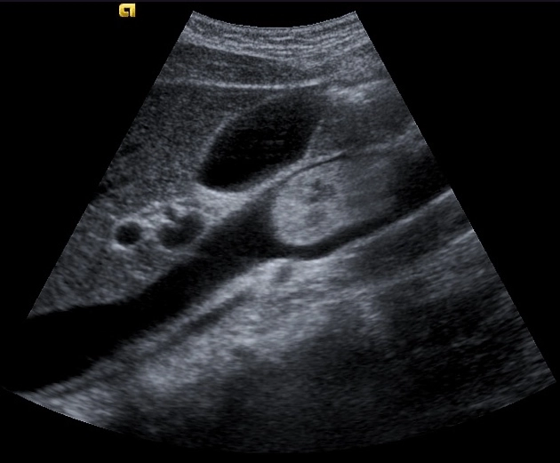
What is this image showing?
Tumor Invasion of the IVC
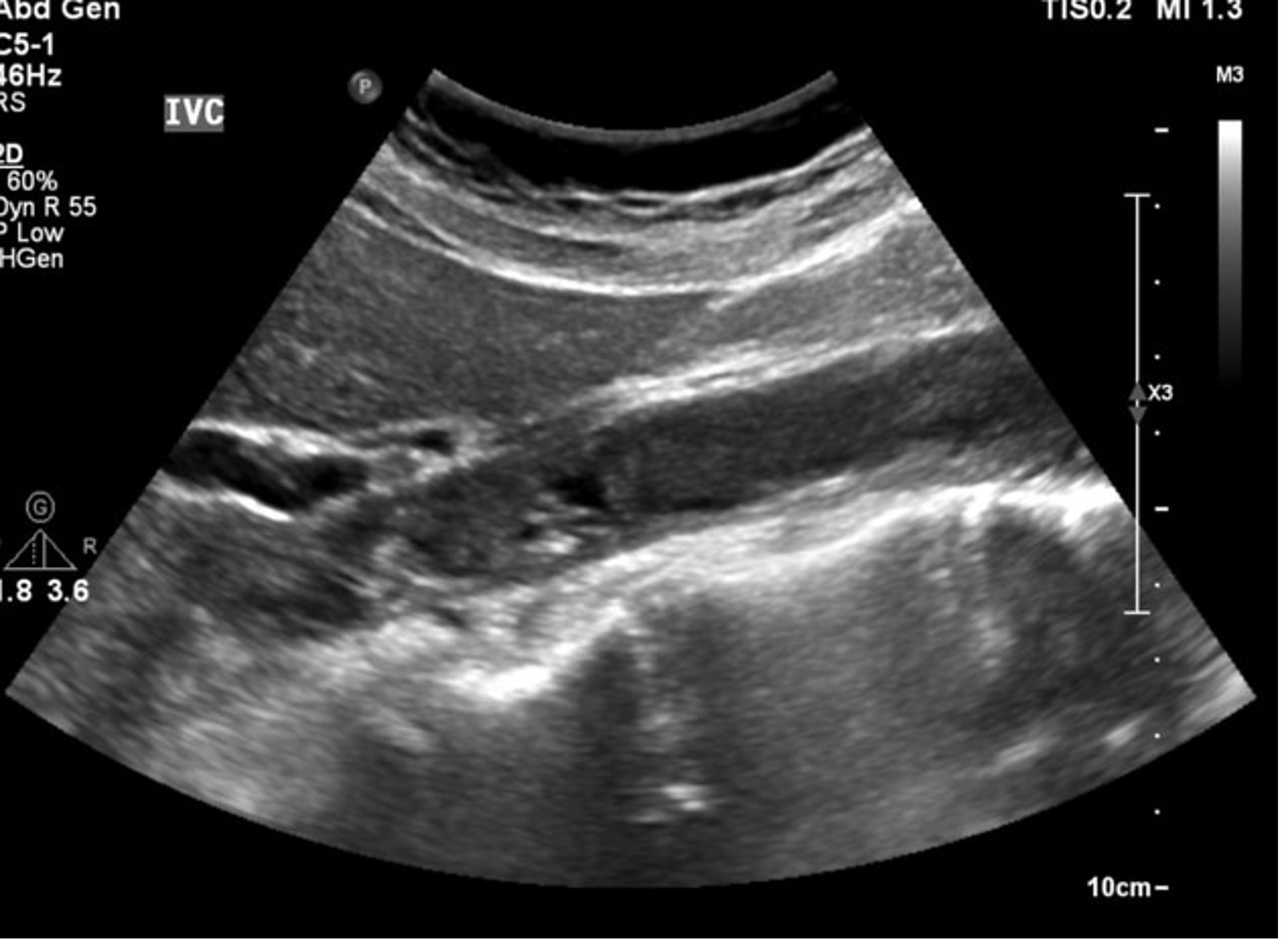
What is this image showing ?
Thrombus in the IVC
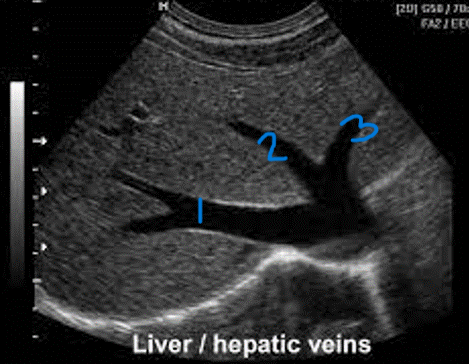
In this sagittal plane, what is #1?
RHV
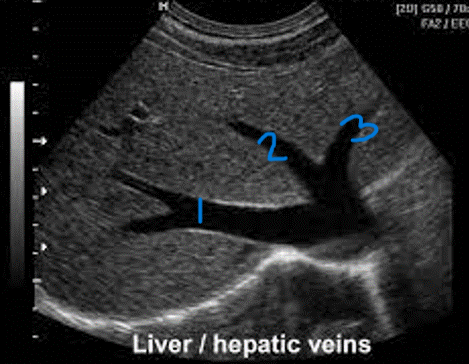
In this sagittal plane, what is #2?
MHV
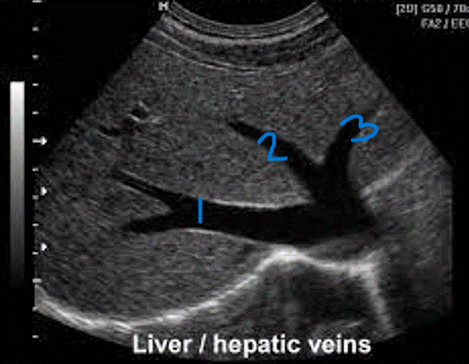
In this sagittal plane, what is #3?
LHV
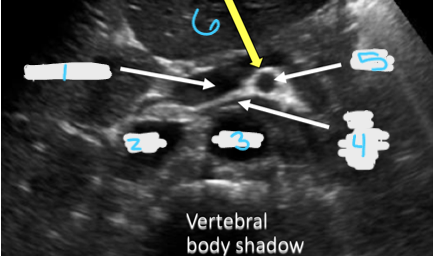
In this transverse view, what is #1?
Portal Vein
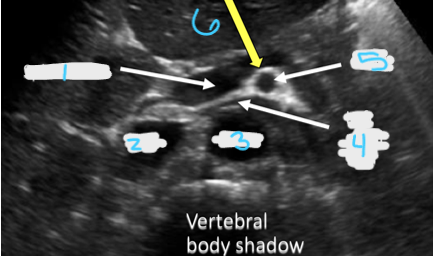
In this transverse view, what is #2?
IVC
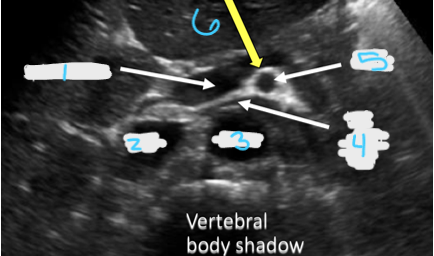
In this transverse view, what is #3?
Aorta
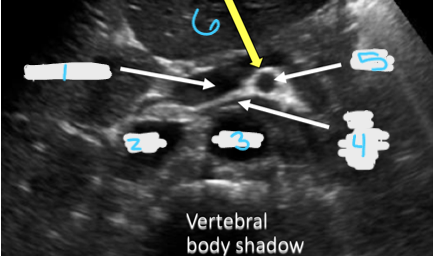
In this transverse view, what is #4?
Left Renal Vein
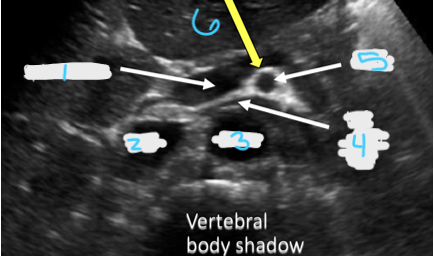
In this transverse view, what is #5?
SMA
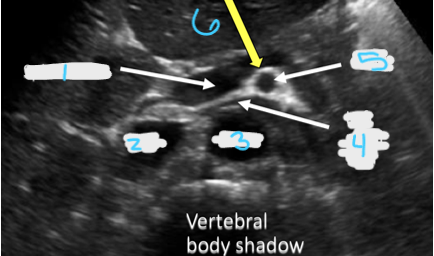
In this transverse view, what is #6?
Splenic vein
What part of the Aorta does DM sonographers scan?
Abdominal Aorta
What blood does the aorta work with?
Oxygen rich blood
Where does the aorta take blood?
To the whole body
Aorta’s have…
Strong, muscular walls that can handle high pressure
What can aorta’s have within them?
Atherosclerosis (narrowing of arteries), aneurysm, or blood clot
Arteries DO NOT…
Compress with pressure
Why do arteries not have valves?
The force of blood coming from the heart ensures flow only travels in one direction
What is the arterial structure?
Tunica adventitia (connective tissue), Tunica media (smooth muscle layer and elastic tissue), and Tunica intima (endothelium)
What layer of the arterial/venous structure is the thickest in arteries?
Tunica media
Which layer is thicker for veins?
Tunica adventitia
What is the aorta also known as?
The greater vessel
What is the function of the aorta?
Delivers oxygenated blood to the body from the left ventricle of the heart
Where is the abdominal aorta located?
Through the diaphragm at the Aortic Hiatus, posterior to the left lobe of the liver
What is designated as the Abdominal Aorta?
Diaphragm to bifurcation into iliac arteries
What is a retroperitoneal structure?
Anatomical elements that lie behind the peritoneum
What kind of structure is the aorta?
Retroperitoneal structure
What is the normal diameter of the proximal aorta?
2.0cm
What is the normal diameter of the mid aorta?
1.5cm
What is the normal diameter of the distal aorta?
.8-1.0cm
What is the diameter for aneurysmal in the aorta?
>3cm
What is the course of the aorta?
Superior to inferior
The aorta lies …
Slightly to the left of the patient’s midline
The IVC lies …
Slightly to the right of the patient’s midline
What does stagnant mean?
Not being pushed, no movement
What are the primary abdominal aortic branches?
Celiac Trunk, SMA, Renal Arteries, Gonadal Arteries, IMA, Common Iliac Arteries
Where does the Celiac Trunk arise from?
Anterior aorta, just distal to the diaphragm
Where does the Celiac Trunk supply blood too?
Abdominal Esophagus, Stomach, Liver, Gallbladder, Spleen, Part of duodenum and pancreas
What is the normal diameter of the Celiac Trunk?
Less than (<) one centimeter
What are the other names of the Celiac Trunk?
Artery, or Axis
What does the Celiac Trunk branch into?
Common Hepatic Artery, Left Gastric Artery, and Splenic Artery
Where does the Splenic Artery course?
Toward the patients left, posterosuperior margin of pancreatic body & tail
Where does the Splenic Artery terminate?
The splenic hilum by dividing into numerous branches
When looking at the Celiac Trunk, which plane is best to see the orgin?
Transverse
Where does the Common Hepatic Artery course?
Toward the patients right, superior border of pancreatic head
The Common Hepatic Artery branches into?
Gastroduodenal and Proper Hepatic Artery
Where does the Gastroduodenal Artery course?
Anterosuperior border of the pancreatic head
The Gastroduodenal Artery branches into?
Pancreaticoduodenal Artery
What does the Pancreaticoduodenal Artery do?
Allows communication between Celiac Axis & SMA
The Common Hepatic Artery is also split into the?
Porta Hepatis, RHA & LHA (follows the Portal Vein)
In the longitudinal view, what is visualized of the Celiac Trunk?
Only the orgin
In the transverse view, what is visualized of the Celiac Trunk?
T-shaped bifurcation of CHA & CA (“Sea-gull”) appearance
Where are the Adrenal (Suprarenal) Arteries located?
Direct from the Aorta, indirectly from branches of phrenic arteries, and sit superior / anterior to the Renal Arteries
Where does the Superior Mesenteric Artery arise from?
Anterior of the Aorta, 1cm distal (inferior) to the Celiac Trunk
What does the SMA supply blood to?
Distal Duodenum, small bowel, colon - right side, portions of pancreatic head
In the longitudinal view, what is visualized of the SMA?
Run parallel to Aorta, and may course slightly to the right
In the transverse view, what is visualized of the SMA?
Dense echogenic ring of connective tissue / fat
What is the origin of the Renal Arteries?
From the Aorta just distal to the SMA
What is important about the RRA?
Longer than LRA & courses behind the IVC
What is important about the LRA?
Lies posterior to SMA & anterior to the Aorta
The Renal Arteries…?
Divide into multiple branches as they enter the renal hilum
What do the Renal Arteries supply blood to?
Kidneys, adrenals, & ureters
Where do the Ovarian / Testicular (Gonadal) Arteries arise?
Anterolateral off Aorta caudad to Renal Arteries, and course inferiorly
Which arteries are not routinely identified with sonography?
Gonadal Arteries, Adrenal (Suprarenal) Arteries, and IMA
Where does the Inferior Mesenteric Artery arise?
ANTERIOR Aorta, DISTAL to renal arteries near umbilicus and course anteroinferior
What does the IMA supply blood to?
Colon and rectum
Where is the Iliac Arteries located?
Near the umbilicus the Aorta tapers and then bifurcates into Right and Left Common Iliac Arteries
Common Iliac Arteries divide into?
Internal & external branches
What does the Internal Iliac Branch supply blood to?
Pelvic organs
What does the External Iliac branch supply blood to?
Lower extremities
What blood does the IVC work with?
Oxygen poor blood
Where does the IVC take blood to?
Back to the heart
Veins carry …
The same volume of blood as arteries, but at a lower pressure