Chapter 3 patient assessments and side effects
1/189
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
190 Terms
What is the definition of patient assessment in radiation oncology?
A clinical plan that identifies the unique needs of the patient and how those needs will be addressed by the health care team.
What are the 3 key components of patient assessment?
Determines the nature of the problem
selects an intervention for that problem
evaluates the effectiveness of the intervention.
What approach does patient assessment in radiation oncology utilize?
Multidisciplinary approach
Who are some of the practitioners involved in the multidisciplinary approach to patient care?
Surgical oncologists, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, radiation therapists, oncology nurses, dietitians, social workers, spiritual counselors, and patient navigators.
What role do patient navigators play in healthcare?
They provide patients with guidance on medical, social, and financial services throughout the healthcare system.
How is a therapeutic relationship defined in healthcare?
The relationship between a healthcare worker and a patient that is aimed at engaging with each other to effect beneficial change in the patient.
What is the foundation of a therapeutic relationship?
Engagement with the patient in a professional, competent, and empathetic way.
What types of messages are included in a therapeutic relationship?
Both verbal and nonverbal messages from both the therapist and patient.
What is the significance of nonverbal messages in communication?
Research shows that nonverbal messages can provide more information than verbal messages.
What are some characteristics of helpful verbal messages?
Nonjudgmental, avoids medical jargon, uses moderate tone and rate of speech, clarifies understanding, uses verbal reinforcers.
What are some examples of nonhelpful verbal messages?
Preaching, blaming, patronizing, using an unpleasant tone of voice, being demanding.
What are helpful nonverbal behaviors in patient communication?
Appropriate eye contact, appropriate use of touch and smiling, nodding head to convey understanding.
What are some nonhelpful nonverbal behaviors?
Poor eye contact, frowning, yawning, slouching, sloppy appearance.
What is an example of a cognitive response to a patient's concern?
"Unfortunately, your sore throat will likely worsen as treatments progress. Are you using your magic mouth wash?"
What is an example of an affective response to a patient's concern?
"Sounds like the idea of a feeding tube is really frightening. Typically, what happens if it gets too sore is the doctor will give you a couple days off from treatment to allow time for your throat to heal a bit before continuing on with treatments."
What is reflective listening in healthcare communication?
-Communicating understanding of the patient's concerns by clarifying content that was omitted or implied.
-involves empathetic response
What does empathy involve in the context of patient care?
Identifying with the feelings, thoughts, or experiences of another person.
What are some of the most helpful verbal responses in patient communication?
Minimal verbal responses, reflecting, paraphrasing, probing, clarifying, interpreting, checking out, informing, confronting, and summarizing.
What is included in a general health assessment?
The collection of data regarding the past and present health of the patient.
How is the general health assessment typically conducted in radiation therapy?
- Collect past and present medical info.
-During consultation, either in an interview fashion or through a written self-report survey, the patient fills out.
What types of information should be assessed for cancer patients?
Medical, nutritional, social, lifestyle information, and the impact of cancer on the patient's life.
What is the significance of unexplained weight loss in cancer patients?
It is often one of the first signs of cancer, particularly in head & neck, lung, and upper gastrointestinal cancers.
What is the MST in nutritional assessment?
The Malnutrition Screening Tool, which assesses weight loss, appetite, and dietary intake.
What does the PG-SGA tool measure?
It is the gold standard full-assessment tool measures many factors that contribute to overall nutritional health
How is percent weight change calculated in nutritional assessment?
(Usual weight - actual weight) / Usual weight x 100.
What does a 20% weight loss indicate in cancer patients?
It is classified as severe weight loss.
What is cachexia in the context of cancer?
A complex metabolic syndrome characterized by loss of muscle with or without loss of fat mass, leading to weight loss and reduced physical function.
-"wasting away disorder
-associated with anorexia, muscle breakdown
What are the three stages of cachexia?
1) Precachexia - managed with nutritional support;
2) Cachexia - managed with pharmacologic approaches
3) Refractory cachexia - palliative care only.
What is the role of radiation therapists in patient assessment?
They assess critical changes in patient status and can recommend interventions or referrals to nurses or doctors.
What are common characteristics of pain experienced by cancer patients?
Pain can be sharp, stabbing, throbbing, burning, or aching, and may arise from the cancer itself or as a result of treatment.

Why is maintaining good nutrition challenging for cancer patients?
Due to treatment side effects and the psychological impact of the disease.
What is the impact of cachexia on cancer treatment outcomes?
It results in reduced physical function, decreased response to anticancer therapy, and increased morbidity.
How often is weight assessed during the treatment of cancer patients?
At least once per week during the on-treatment visit (OTV) with the nurse and physician.
What factors contribute to the nutritional assessment of cancer patients?
Weight loss, dietary intake, symptoms affecting eating, and functional capacity.
What is the psychological aspect of pain in cancer patients?
Pain is influenced by both physiological and psychological factors.
What is the primary goal of nutritional assessment in cancer patients?
To monitor and maintain nutritional status during treatment.
What lifestyle factors should be assessed in cancer patients?
Alcohol and tobacco use, sleep patterns, stress, and personal beliefs.
What is the role of family and friends in the social assessment of cancer patients?
Their support is crucial for the patient's emotional and psychological well-being.
What is the significance of pain assessment in cancer care?
It helps in managing one of the most feared consequences of cancer.
How does cachexia affect children differently than adults?
In children, it presents as growth failure, while in adults it manifests as weight loss.
What is the importance of regular assessments by radiation therapists?
To ensure timely interventions and adjustments in patient care based on their changing status.
What are some barriers that may affect a cancer patient's ability to eat?
Anorexia, early satiety, taste changes, and physical barriers.
What is the purpose of pain assessment?
To establish a baseline for treatment, help the clinical team focus on interventions, and evaluate ongoing interventions.
What are the dimensions of physical pain assessment?
1) Physiologic (organic cause)
2) Sensory (intensity, location, quality)
3) Affective (emotional response)
4) Sociocultural (cultural and family)
5) Behavioral (medication intake and activity level)
6) Cognitive (understanding, attitudes, level of cognition)
What is the difference between acute pain and chronic pain?
Acute pain has a sudden onset and may be an emergency, while chronic pain is present for 3 months or longer.
What tools are used to estimate functional performance?
1. Karnofsky performance scale (ratings from 100 to 0),
2. ECOG performance status (ratings from 0 to 5).
What is myelosuppression?
A reduction in bone marrow function that can lead to anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and pancytopenia.
What are the consequences of anemia?
Decrease in red blood cells impairs oxygen-carrying capacity, leading to pale skin, fatigue, and weakness.
What does leukopenia indicate?
A decrease in white blood cells that increases the risk of infection.
What is thrombocytopenia?
A decrease in platelets that results in decreased blood clotting ability.
What are the normal blood count values for WBCs?
5,000-10,000 per mm3.
What are the normal blood count values for RBCs?
3.9-5.4 million per mm3.
What are the normal blood count values for platelets?
150,000-425,000 per mm3.
What are the normal blood count values for hemoglobin?
12-16 g/dL.
What are the normal blood count values for hematocrit?
37-47%.
What are the normal vital signs for temperature?
96.8°F-98.6°F (oral).
What is the normal pulse rate?
60-100 bpm (beats per minute).
What are the normal respiratory rates?
12-18 breaths per minute.
What is the normal blood pressure range?
90-140 mm Hg systolic and 60-80 mm Hg diastolic.
What is the normal oxygen saturation level?
95-100% saturation.
What is quality of life (QoL) in the context of cancer patients?
A person's subjective sense of well-being derived from their current life experience.
What are the three domains of QoL?
1) Physical, 2) Psychological, 3) Social.
What are common emotional themes in cancer patients?
Fear/anxiety, loss of independence, uncertainty about treatment outcome, and effects of cancer treatments.
What are effective coping strategies for cancer patients?
Information seeking, participating in religious activities, and positive thinking.
What are signs of depression in cancer patients?
Sad mood
lack of interest in activities
significant weight changes
insomnia or hypersomnia
fatigue
feelings of worthlessness
recurrent thoughts of death.
When should a therapist refer a patient to a specialist for depression?
If the patient has persistent depression or if symptoms worsen.
Most difficult challenge for patients undergoing radiation treatment?
maintaining good nutrition
most feared consequence cancer
pain
purpose of pain assessment
-establish baseline for treatment and interventions
-help focus on the best interventions
ongoing evaluation of chosen intervention
pancytopenia
deficiency of all types of blood cells (RBC, WBC, platelets)
hematopoietic tissue
-Very sensitive to chemo and radiation
- increased sensitivity when both are used
When do we conduct weekly blood draws for cancer patients?
-when radiation field includes a large amount of bone marrow
-patient has both chemo and radiation
5 major psychological themes under the psychological domain of QoL
1. fear/anxiety
2. loss of independence
3. uncertainty of treatment outcome
4. Radiation oncologist's enthusiasm for treatment
5. The debilitating effect of cancer treatment
Emotions that cancer patients go through
-loss of self-esteem
-depression
-resentment
-isolation
-rejection
-discouragement
anxiety
response to perceived threat at emotional level
what feeling are associated with anxiety
vague unpleasant and uneasy feelings
tools for assessing anxiety
-state-trait anxiety inventory
- generalized anxiety disorder 7
depression
perceived loss of self esteem that results in a cluster of affective behaviors and cognitive emotions
non-effective coping skills
-denial of emotions
- social isolation
-blaming other
physical assessment
-done on a daily basis to monitor for critical changes
-recommend and refer to nurse or doctor
When do acute side effects of radiation therapy occur
during treatment
When do chronic/late side effects of radiation therapy occur
3 months- years after treatment
What is acute fatigue
tiredness, lack of emotional resilience, mental slowness
Causes of acute fatigue
-disease
-treatment
-anemia
-meds
-chemo
pain
stress
infection
What percentage of cancer patients experience acute fatigue?
50-75%
when do cancer patients experience acute fatigue?
first 2-3 weeks of treatment
how long does acute fatigue last
months to years
assessment for acute fatigue
scale
pts words/ appearance
labs (anemia)
management for chronic fatigue
- proper nutriton
- exercise
- blood transfusion ( anemia )
meds/ therpapy
Acute skin reactions
2/3 weeks to develop; resolve 1/2 months post treatment
factors that affect severity of acute skin reactions
-dose & fraction
- types of radiation (proton/electron)
-Bolus
chemo sensitization drugs
bolus
used to bring radiation closer to skin,
causes worse acute skin reactions
dermatitis
- Acute skin reaction
-irritated skin (dry)
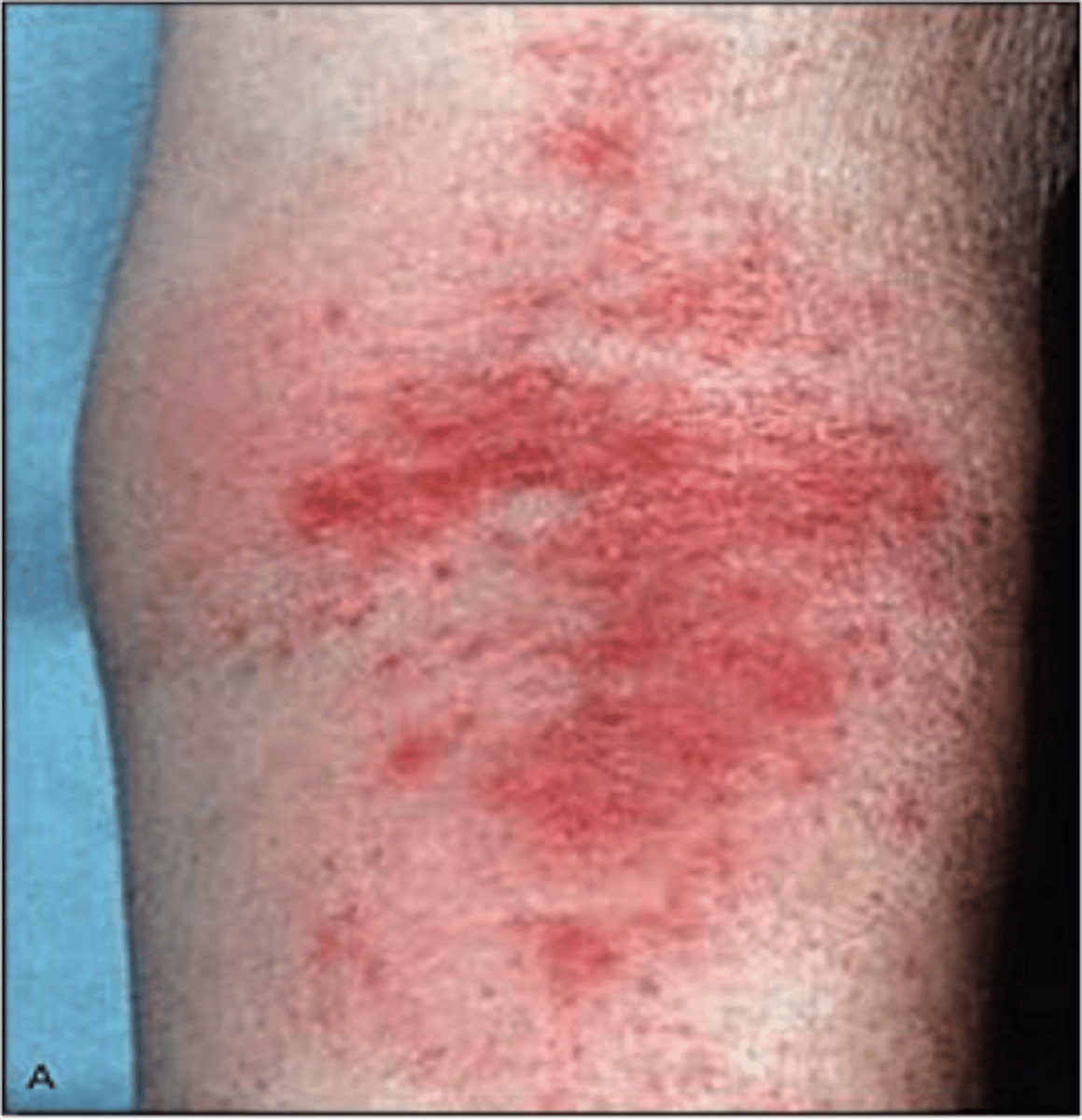
erythema
-- Acute skin reaction
-redness of the skin
-occurs at 3000-4000 cGy
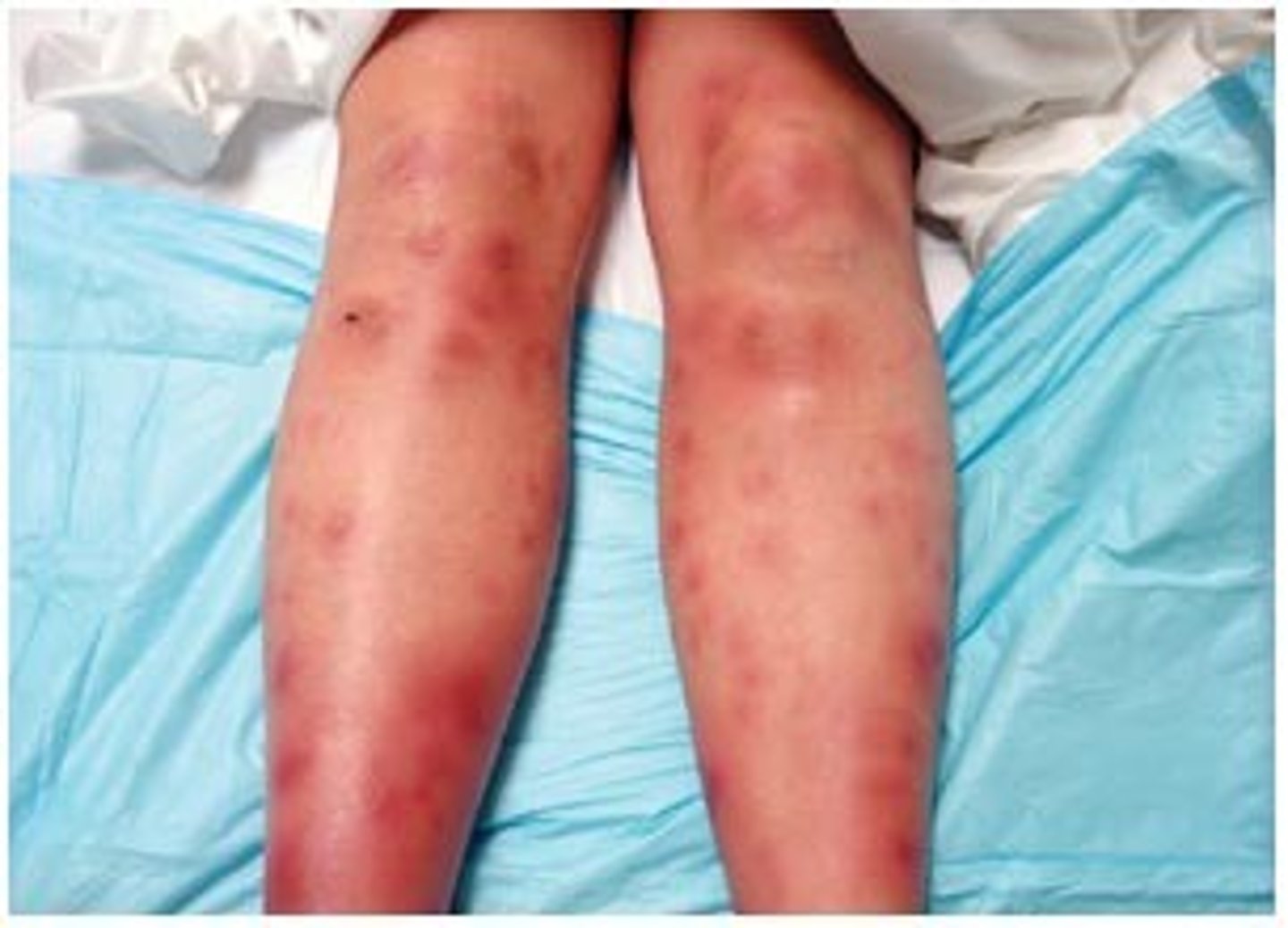
Dry desquamation
-skin breakdown
-occurs at 4000-6000 cGy
- Acute skin reaction
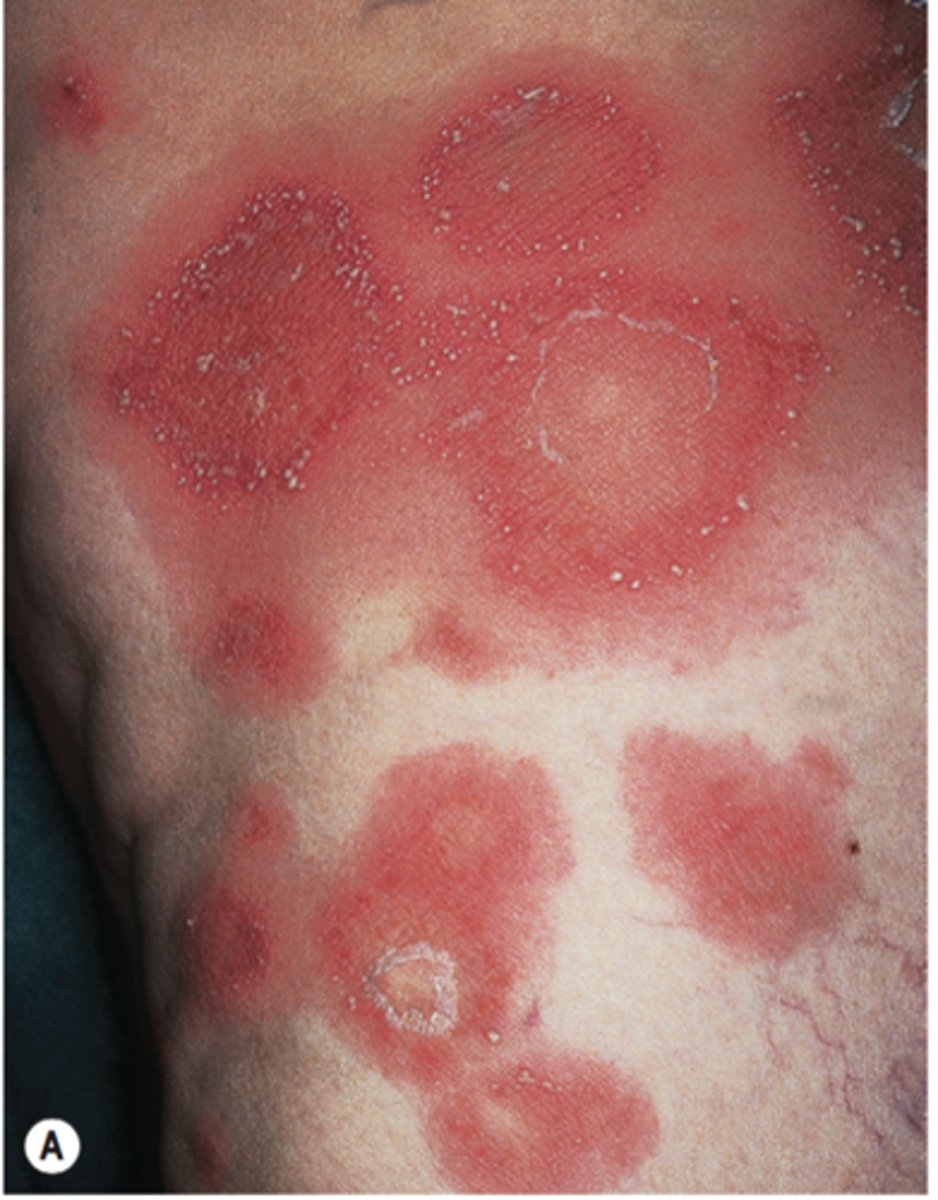
Moist desquamation
-skin breakdown with pus
-can lead to infection
-occurs at 4000-6000 cGy
- Acute skin reaction
radiation recall
-severe rash like sunburn around the treatment area
-occurs when the patient gets chemo and radiation concurrently
- Acute skin reaction
Fibrosis
-thickening/ hardening of skin
-chronic skin reaction
atrophy
-reduction in skin thickness
-regression of sebaceous glands
-chronic
Telangiectasia
-dilated superficial blood vessels, spider veins
-chronic