ans 214L practical 2
1/280
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
281 Terms
arth-, arthr
joint
carpus
wrist
chondr-
cartilage
-clast
to break
cost-
ribs
myel-
bone marrow
oss-, osteo-
bone
syn-
union
tarsus
ankle
osteology
the study of bones
portion of organic (ossien) bone
1/3 of the bone
portion of inorganic (tricalcium phosphate) bone
2/3 of the bone
exoskeleton
hard, outer skeleton that is outside of the body
found in arthropods (insects, arachnids, and crustaceans) and in mollusks with shells (clams and snails)
endoskeleton
this is a skeleton embedded within the muscle
domestic animals contain this type of skeleton
axial skeleton
consists of the bones of the skull, ribs (costae), vertebrae, and sternum
these parts are not highly mobile and serve to protect major organs
appendicular skeleton
consists of bones of the appendages or limbs, including wings, tails, legs, and arms
these parts aid in motion of the organism
heterotrophic bones
also known as splanchnic or visceral bones
bones embedded in the organs
some of these do not serve a function at this point
os rostrale
bones in the snout of the pig

ossa cordis
bones in the heart of cattle, sheep, and goats
os phrenic
bone in the diaphragm of camels
ossa penis
bones in the penis of carnivores (dogs and cats) and rodents

scleral rings
round bones found on the eyes of birds

hyoid apparatus
found in the tongue of avians and mammals

ossa
plural for os
epiphysis
the 2 ends of long bone
diaphysis
the shaft of long bone
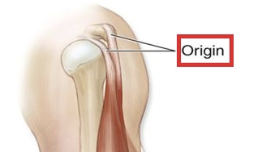
origin
the end of the muscle that is attached to a stationary part of the bone
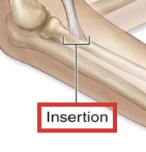
insertion
the end of the muscle that is attached to a mobile section of bone
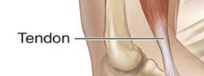
tendons
attach muscles to bone
ligaments
attach bone to bone
epiphyseal plate
a growth region of cartilage between the epiphysis and the diaphysis (active growth)
epiphyseal line
line formed in the bone when growth has ended, remnant of the epiphyseal plate
endosteum
membrane lining the medullary cavity
periosteum
membrane covering the outer surface of the bone composed of connective tissue
bone itself does not have nerves; the periosteum is full of nerve and is what causes pain when the bone breaks
medullary cavity
hollow area in the center of the bone where bone marrow is located, the bone marrow produces blood cells
diploe
spongy bone and is also known as cancellous bone
compact bone
dense, hard layer of bone
yellow bone marrow
composed of adipocytes and stem cells
red bone marrow
gives rise to red blood cells, platelets, and some white blood cells
long bone
dumb-bell shaped, wide, expanded ends, narrow, cylindrical midsection
ex- bones of the limbs, except for the ankle and wrist bones in humans and analogous bones in livestock and the patella
long bones aid in movement and carry the weight of the body
ex- femur, fibula, and tibia

flat bone
flat in 2 dimensions, thin and curved, mostly dipole surrounded by thin layer of compact bone
primarily function is to provide protection to vital organs
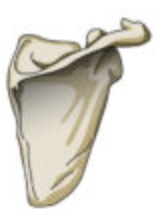
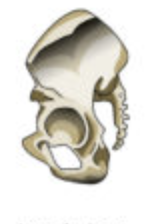
ex- most skulls bones, the scapulae, sternum, costae, and the os coxae (ischium, ilium, and pubis%
short bone
round or cubicle in shape
these bones reduce friction and concussion
ex- human wrist and ankle, knee and tarsal, and carpals

irregular bone
bones of vertebral column
sesamoid bones
bones that form in tendons and aid in the movement
ex- patella
pneumatic bone
bones that contain spaces filled with air
these spaces can serve numerous functions, in birds the hollow bones allow for flight due to reduced weight, and in mammals, the sinus cavities help warm and condition air as it is inspired
air pockets/spaces/cavities- birds have open respiratory systems meaning that inspired air moves through their bones, not just their lungs
excavation in the skull- paranasal sinuses, frontal sinuses, maxillary sinuses
joints
points at which 2 or more bones meet
this area is lined with cartilage which provides cushion and smooth movement
not all joints function in the same manner
fibrous/immovable joint
bones in this joint do not move
they may overlap or interlock and are held together by fibers
cartilaginous/slightly moveable joint
allows for some movement
bones are held together by ligaments and padded with cartilage
synovial/freely moving joint
largest group of joints in the body
they have a wide range of motion
immovable joint movement
non mobile
joints found in the skull
hinge joint movement
extension and flexion
elbow or knee
pivot joint movement
rotation of one bone around another
joint just below the skull between C1 and C2
ball-and-socket joint movement
flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, and rotation, this includes the shoulder (human) and hip joints (mammal)
condyloid joint movement
flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, and circumduction, found in the wrist and foot
gliding joint movement
allows for smooth gliding motions, found in the wrist and vertebrae
saddle joint movement
flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, and circumduction, found in the thumb
fibula
in latin or greek refers to a brooch
the fibula bone is named this because it functions to hang muscle, much like a fibula brooch would hang a toga
bones in early life
are not solid
are first cartilage tissue then they ossify into hard and strong bones
calcium and phosphorus diet of animals
is very important for bone health
when there is a deficiency in of calcium in the diet, the body will pull calcium from the bone to make up for the lack of it in the diet
-algia
pain
-lysis
breakdown
macro-
large
micro-
small
-pathy
disease
-penia
lack
-phagia
to eat
pre-
before
beak
function in prehension
shape and size of this will vary among species and this has a lot to do with diet
mouth
entrance to gastrointestinal tract
birds do not have teeth
palatine cleft
passage between oral and nasal; cavities
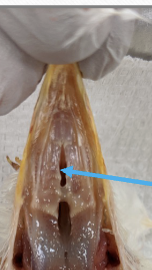
oropharynx
the combine oral and pharyngeal space
there is no sharp distinction between mouth and pharynx in the bird
pharyngeal space is a joint are for digestive and respiratory tract
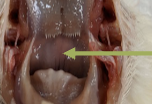
toungue
aids in taste
flat, and triangular in shape with papillae that point towards the back of the mouth
ensures that food goes away only in one direction
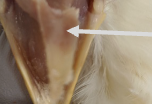
infundibular cleft
common opening of the eustachian tubes (canals extending from the middle ear that control pressure within the middle ear)
in avians this is continuously open to permit pressure equalization during flight
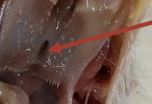
laryngeal cleft
opening into larynx that closes to block food from going into the larynx
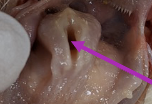
salivary glands
secrete mucin, bicarbonate, and water
chickens and turkeys do not produce salivary amylase
larynx
transports air from oropharynx to trachea
birds do nor have vocal cords in the larynx
trachea
transports air from larynx to bronchi
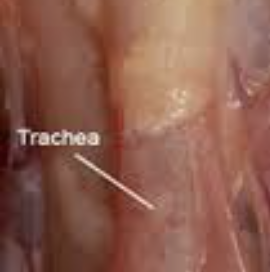
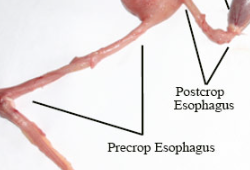
esophogus
thin-walled distensible tube with small amount of muscle compared to mammals
passageway for feedstuffs from the oropharynx to crop, and then from the crop to proventriculus
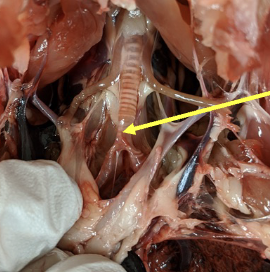
syrinx
responsible for vocalization in birds
this is a Y-shaped organ at the base of the trachea
vocalization is produced by syringeal muscles, tympanic membranes, and the clavicular air sac
infundibular cleft
common opening of the eustachian tubes
the eustachian tubes are canals that extend from the middle ear
this remains open continuously to permit pressure equalization in flight
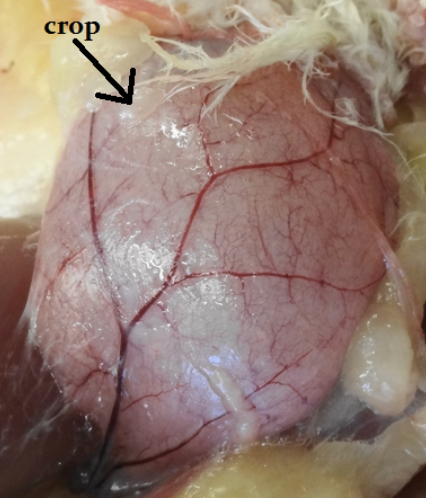
crop
organ for the storage and the moistening of ingested feed
chicken heart
birds have a 4 chambered heart
chicken liver
similar functions as in mammals, process nutrients; produces bile
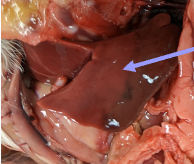
chicken gallbladder
stores bile
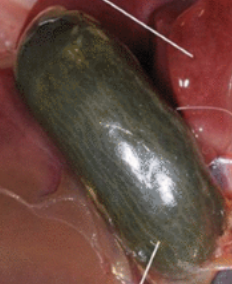
chicken spleen
part of the immune system; lymphocyte production
recycles red blood cells
more round in shape as compared to mammalian spleens which are flat
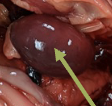
chicken proventriculus
the glandular stomach of a chicken
functions similarly to the mammalian stomach (secretion of pepsinogen, HCL, mucous, and gastrin)
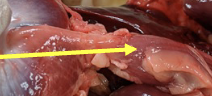
chicken ventriculus/gizzard
muscular organ responsible for grinding feed
ingested rocks and pebbles lodge here where they function similarly to teeth
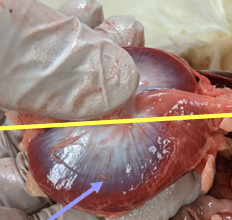
chicken small intestine
functions similarly to the mammalian small intestine and is divided into the same 3 sections
does not produce lactase
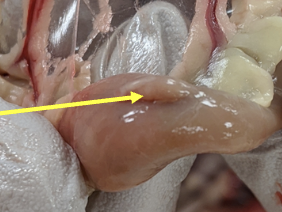
duodenum
the first section of the small intestine and the
shortestreceives bile and pancreatic secretions in addition to receiving ingesta from the ventriculus
initiates intestinal digestion of protein and starch
jejunum
middle portion of the small intestine is usually the longest
its proportion of the small intestine varies with the species
digestion of protein and carbohydrates is fairly complete here
absorption of amino acids, monosaccharides, calcium, and iron occurs here
ileum
last section of the small intestine
absorption of bile salts, water, electrolytes, and vitamin B12 occurs here
connects to the large intestine
a constriction at this point called the ileocecal valve regulates the flow of material from the ileum into the large intestine
meckel’s diverticulum
yolk stalk remnant
marks the juncture of the jejunum and ileum
part of the immune system
lymphocyte production
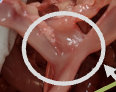
ceca
chickens have two ceca
microbial fermentation of residual starch and some cellulose occurs here
absorption of fermentation products such as volatile
fatty acids and vitamins as well as water occur herebirds do not have an appendix
avians have TWO ceca (hence why it is the plural form of cecum)
colon
the colon is very short in the bird
absorption of fermentation products from the cecum such as volatile fatty acids and vitamins as well as water occurs here
fermentation, if any, is limited
urine is stored here prior to excretion
ileocecal junction
the point at which the ilium and the ceca meet
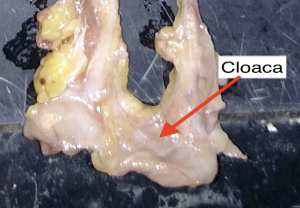
cloaca
the juncture of the ureters, colon, and reproductive system in birds
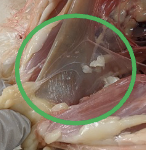
hepatic portal system
collects nutrients absorbed from digested tract
transports these directly to the liver
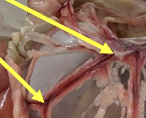
mesentery
the folds of the peritoneum that connect and anchor the small intestine
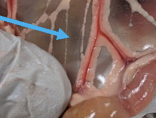
bursa of fabricius
located dorsal to the cloaca and easily found in chicks but regresses by sexual maturity
responsible for the production of B-lymphocytes
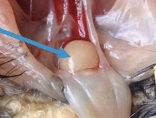
kidneys
lobulated in birds
located in the synsacral cavity
the synsacrum is the fused ischium and ilium