neuroscience
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Neurobiology
anatomy and cell biology of the nervous system~
Neurophysiology
physiological basis of resting and action potentials~
Neurochemistry
neurotransmitters, synapses and receptor biology~
Neuropathology
outline of common neurological diseases~
Trajectories of change in brain structure and function across the lifespan
Structural topology develops non linearly across the lifespan and is strongly related to cognitive trajectories whereby the brain undergoes changes throughout life
Brain development was shown was to occur in five distinct epochs with turning points in childhood, midlife and old age
Five major phases represent key turning points at the ages of about 10, 30, 60 and 80
Even though the brain changes most significantly during childhood, it remains adaptable well into old age~
Examples of neurological abnormalities
Acquired neurological disorders
Neurological injury/ trauma
Genetic neurological diseases
Genetic susceptibilities towards neuropathology
Mental or neurodevelopmental disorders
Neurological co morbidities of common diseases
Medical treatment or drug related neuropathology
Pharmacogenetic diseases of the nervous system
Neurotoxicological insults to the nervous system
Neurological speech disorders
Aging related neurodegeneration~
Common neurological disorders
Brain trauma
Ischemic stroke
Haemorrhagic stroke
Motor neuron disease
Brain cancer
Dementia
Multiple sclerosis~
Common neurological diseases
Headache
Facial pain/ paralysis
Dizziness and vertigo
Syncope and epilepsy
Cerebrovascular disease
Cerebral tumours
Parkinsons's disease
Head trauma/ injury
Cerebral palsy
Cerebrellar ataxia
Spinal cord injury/ diseases
Peripheral nerve disorders
Motor neuron disease
Dementia
Huntingtons disease
Multiple sclerosis
Neuronal infectons~
Phineas Gage (1848)
Accident that put an iron rod through his skull, pentrating his left cheek and exited through skull
Observations made my Dr. John Harlow, who treated him afew months after accident
The balance between his " intellectual faculties and animal propensities" seemed gone. He could not stick to plans, uttered "the grossest profanity" and showed "little deference for his fellows"~
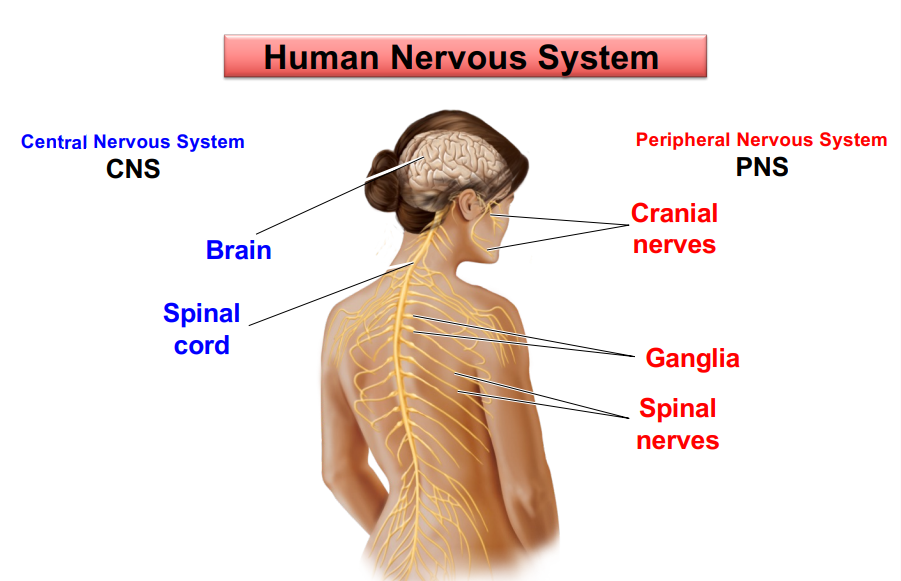
Central nervous system (CNS)
brain and spinal cord~
Behavioural and emotional issues associated with TBI (traumatic brain injury) and other brain disorders:
Emotional problems after traumatic brain injury ( frontal and temporal lobe)
Involuntary emotional expression disorder (IEED)~
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
neurons and axons outside the CNS~
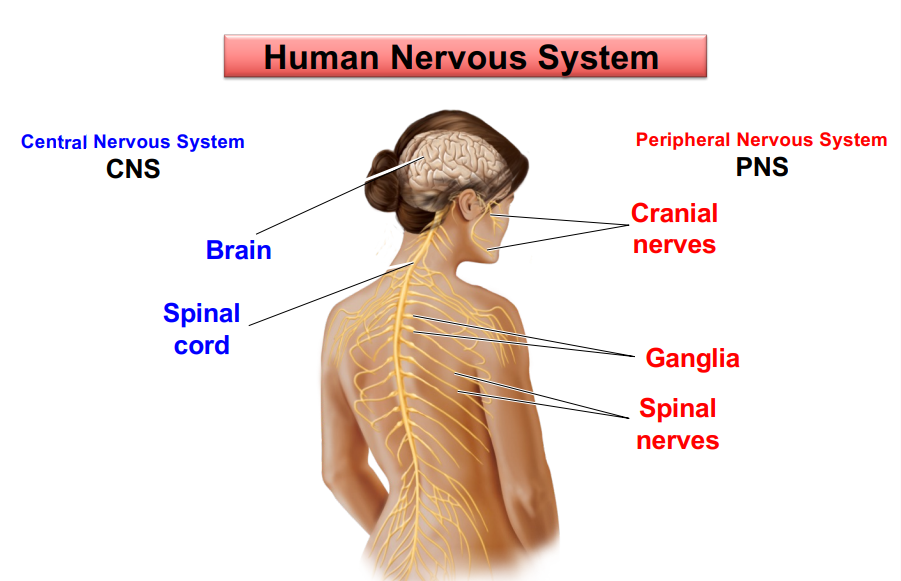
Peripheral nervous system sub parts
Somatic NS- voluntary movements
Enteric PNS- control of Gi system
Autonomic NS
Sympathetic NS- mobilisation during activity
Parasympathetic NS- 'housekeeping' during rest~
When did the modern human brain develop?
200,000 years ago~
Typical features of a nervous system
Segemnted structures
Bilaterally symmetrical organisation
Principle of crossed organisation of brain hemisphere
Brain and spinal cord are protected by encasement in cartileage and bone structures~
3 layers of meninges
Dura mater- outer thick layer
Arachnoid mater- numerous connections to inner layer
Pia mater- inner thin membrane on surface of brain and spinal cord~
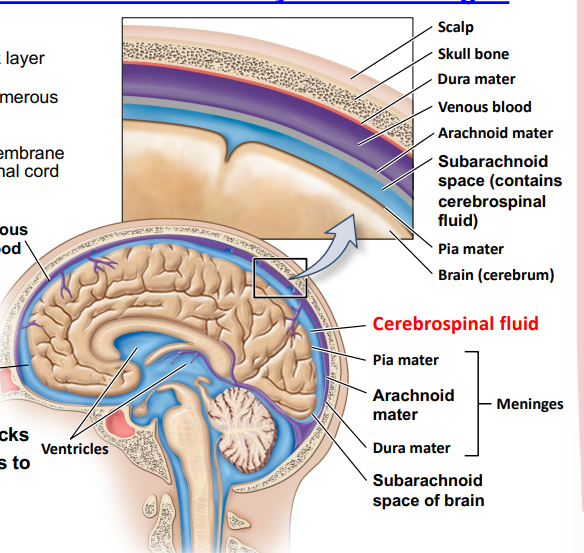
Cerebrospinal fluid
Circulates through subarachnoid space
Absorbs physical shocks
Transports substances to and from cells~
Evolution of human brain optimisation
Overall size and structure specialisation
Number of neurons and glia cells
Length of interconnections
Number of interconnections
High bioenergetic consumption
Elaborate memory system~
Neuroplasticity
CNS and PNS have relatively high potential for adaptation to environmental change and compensation of minor pathological insults~
Main brain functions (skilled movements and social behaviour)
Collection of essential information from surrounding environment- afferent (incoming) information => sensory information coming into CNS
Integration of essential information for creation of sensory reality- two directional neural information flow and signal integration
Production of commands to control muscle movement- efferent (outgoing) information=> motor pathway information leaving CNS
Highly sophisticated human cognitive functions~
Neuroscience of behaviour
Most complex behaviours probably comprise a mixture of learned and inherited actions, such as movements, vocalisations or thinking
Main types of behavioural patterns
Innate ( fixed) behaviours, dependent on heredity
Learned flexible behaviours, dependent on learning process
Wide ranging mammalian behaviour due to highly complex nervous system~
General principles of the nervous system
Perceptual world of the brain
Neuroplasticity: constant change in NS functioning
Crossed organisation of the brain hemispheres
Hierarchal and parallel organisation of brain systems
Divisions of sensory and motor systems exist throughout the NS
Brain function is both localised and distributed
NS functioning is based on integration of neuronal excitation versus inhibition~
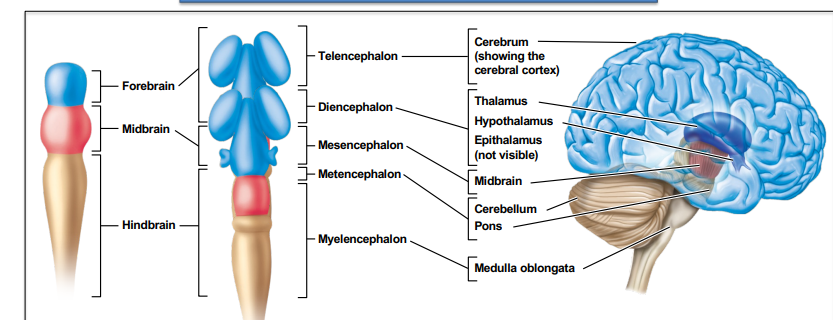
Three main brain divisions 1; forebrain
5 week embryo-- telencephalon and diencephalon
Adult-- cerebrum (showing cerebral cortex)
Thalamus--- – Relays sensory information to the cerebrum – Also sends outputs from the cerebrum to other parts of the brain – Gets input from all sensory systems except olfaction
hypothalamus - Produces hormones regulating pituitary gland, which regulates hormone secretion from other glands – Great importance for homeostasis of the body and the control of behaviour
epithalamus (not visible)- Structures with various roles in the production of cerebrospinal fluid, control of food and water intake, and rhythmic and seasonal behaviors – Pineal gland produces melatonin (hormone that controls sleep and wake cycles)~
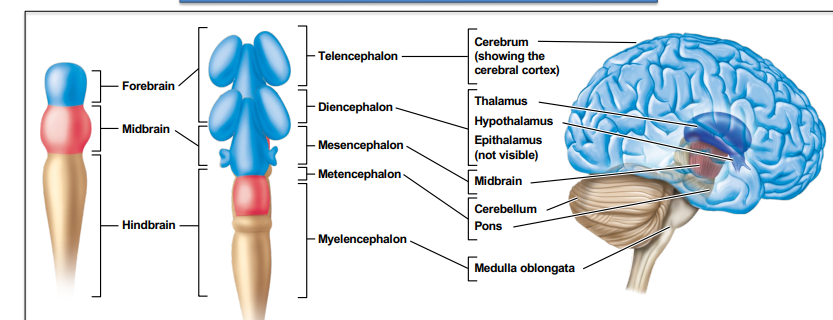
Three main brain divisions 2; midbrain
Three main brain divisions 2; midbrain:
5 week embryo-- mesencephalon- Processes several types of sensory input (vision, olfaction, and audition) & controls sophisticated tasks. Tracts pass this information to other parts of the brain for further processing and interpretation.
Adult-- midbrain~
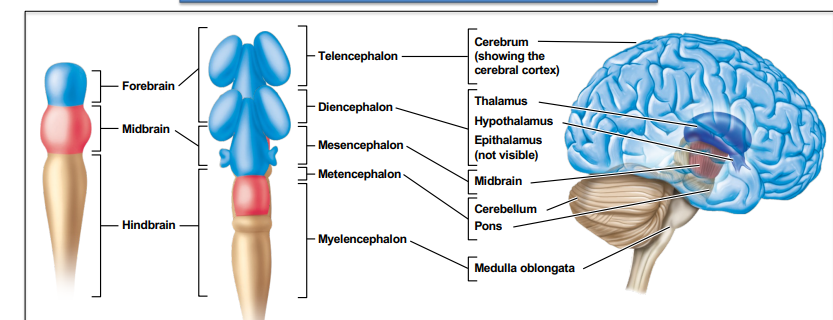
Three main brain divisions 3; hindbrain
5 week embryo--metencephalon and myelencephalon
Adult-- cerebellum pons- Responsible for monitoring and coordinating body movement
medulla oblongata- Coordinates many basic reflexes and bodily functions~