Complement (F)
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:49 AM on 12/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
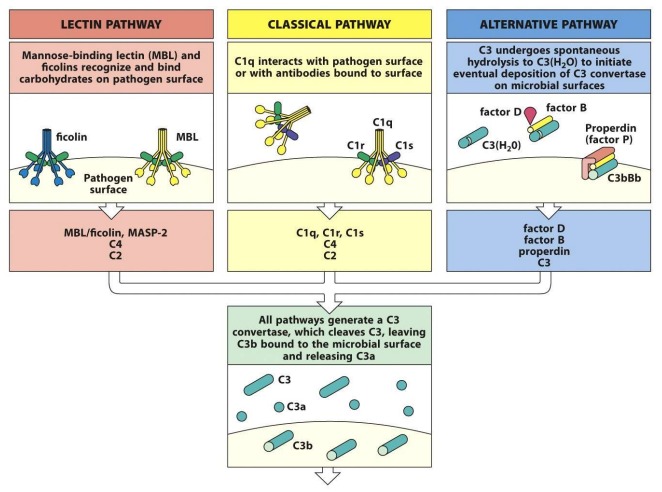
What are the three pathways of complement activation?
Classical (Antibody activated)
Alternative (Recognition of foreign surface structures by complement)
Lectin (Polysaccharide structures of microbes)
Alternative (Recognition of foreign surface structures by complement)
Lectin (Polysaccharide structures of microbes)
2
New cards
What does complement achieve?
Complement facilitates both the lysis of target cells and serves as an opsonin, enhancing phagocytosis of labeled targets
3
New cards
What is the end goal of all three complement activation pathways?
To activate complement component C3 and eventually C5
4
New cards
Explain: Proteolytic Cleavage
Cleavage of complement proteins yields 2 fragments
The larger of the two is designated as the b fragment and the smaller fragment is the a fragment
In general the larger fragment binds to nearby targets and is proteolytically active whereas the smaller fragments diffuse away and act as proinflammatory mediators distally
The larger of the two is designated as the b fragment and the smaller fragment is the a fragment
In general the larger fragment binds to nearby targets and is proteolytically active whereas the smaller fragments diffuse away and act as proinflammatory mediators distally
5
New cards
Which fragment is proteolytically active?
The larger fragment is proteolytically active and binds to nearby fragments. This is usually the B fragment, except for C2 where A is the larger active fragment.
6
New cards
What do small fragments achieve?
Smaller fragments diffuse away and act as proinflammatory mediators
7
New cards
Outline the steps of the Classical Pathway
1\. C1q binds to two Fc regions of antibodies (2 IgG molecules or 1 pentameric IgM molecule) on a target. This activates C1r
2\. C1r cleaves C1s
3\. C1s cleaves and activates C2 and C4
4\. C4 is efficiently cleaved due to high serum levels. Following cleavage C4b is quickly inactivated by hydrolysis (iC4b) However some C4b settles on and covalently bonds to a nearby surface and remains proteolytically active
5\. Cleavage of C2 is less efficient due to much lower serum concentrations. To compensate for this C2 binds to C4b on the target surface. C4b holds the C2 in close proximity to the active C1 and facilitates cleavage of C2 releasing C2b and leaving C2a associated with C4b on the target surface.
6\. This forms the C4b2a complex: C3 convertase
7\. C4b2a cleaves C3, C3b associates with C4b2a and produces C4b2a3b: C5 convertase. (Any C3b that does not covalently bind to the target surface is inactivated through hydrolysis (iC3b))
2\. C1r cleaves C1s
3\. C1s cleaves and activates C2 and C4
4\. C4 is efficiently cleaved due to high serum levels. Following cleavage C4b is quickly inactivated by hydrolysis (iC4b) However some C4b settles on and covalently bonds to a nearby surface and remains proteolytically active
5\. Cleavage of C2 is less efficient due to much lower serum concentrations. To compensate for this C2 binds to C4b on the target surface. C4b holds the C2 in close proximity to the active C1 and facilitates cleavage of C2 releasing C2b and leaving C2a associated with C4b on the target surface.
6\. This forms the C4b2a complex: C3 convertase
7\. C4b2a cleaves C3, C3b associates with C4b2a and produces C4b2a3b: C5 convertase. (Any C3b that does not covalently bind to the target surface is inactivated through hydrolysis (iC3b))
8
New cards
What is C1 comprised of?
C1 is comprised of C1q (binds antibody), C1r (regulatory), and C1s (serine protease - does the cutting)
9
New cards
What are the targets of C1, which is cleaved first? Why?
C1 has two targets: C4 and C2.
\
Due to the high serum levels of C4, it’s cleavage is very efficient. C2 is found in lower concentrations, thus it’s cleavage is less efficient.
\
Due to the high serum levels of C4, it’s cleavage is very efficient. C2 is found in lower concentrations, thus it’s cleavage is less efficient.
10
New cards
What is C3 Convertase comprised of in the classical pathway?
C4b2a
11
New cards
What is C5 Convertase comprised of in the classical pathway?
C4b2a3b
12
New cards
How does the Lectin Pathway differ from the Classical pathway? How are they similar?
\
\
Unlike the classic pathway - the lectin pathway does not involve antibodies. Instead of C1q, the lectin pathway utilizes either Mannose Binding Lectin (MBL) or Ficolins.
\
However, the steps following the cleavage of C4 are identical in both pathways. Including the composition of the C3 and C5 convertases.
\
Unlike the classic pathway - the lectin pathway does not involve antibodies. Instead of C1q, the lectin pathway utilizes either Mannose Binding Lectin (MBL) or Ficolins.
\
However, the steps following the cleavage of C4 are identical in both pathways. Including the composition of the C3 and C5 convertases.
13
New cards
Outline the steps of the Lectin Pathway
1\. Mannose Binding Lectin (MBL) or Ficolins bind to the cell surface activating MASP-1 (C1r equivalent)
2\. MASP-2 (C1s equivalent) cleaves C4.
4\. C4 is efficiently cleaved due to high serum levels. Following cleavage C4b is quickly inactivated by hydrolysis (iC4b) However some C4b settles on and covalently bonds to a nearby surface and remains proteolytically active
5\. Cleavage of C2 is less efficient due to much lower serum concentrations. To compensate for this C2 binds to C4b on the target surface. C4b holds the C2 in close proximity to the active MASP-2 and facilitates cleavage of C2 releasing C2b and leaving C2a associated with C4b on the target surface.
6\. This forms the C4b2a complex: C3 convertase
7\. C4b2a cleaves C3, C3b associates with C4b2a and produces C4b2a3b: C5 convertase. (Any C3b that does not covalently bind to the target surface is inactivated through hydrolysis (iC3b))
2\. MASP-2 (C1s equivalent) cleaves C4.
4\. C4 is efficiently cleaved due to high serum levels. Following cleavage C4b is quickly inactivated by hydrolysis (iC4b) However some C4b settles on and covalently bonds to a nearby surface and remains proteolytically active
5\. Cleavage of C2 is less efficient due to much lower serum concentrations. To compensate for this C2 binds to C4b on the target surface. C4b holds the C2 in close proximity to the active MASP-2 and facilitates cleavage of C2 releasing C2b and leaving C2a associated with C4b on the target surface.
6\. This forms the C4b2a complex: C3 convertase
7\. C4b2a cleaves C3, C3b associates with C4b2a and produces C4b2a3b: C5 convertase. (Any C3b that does not covalently bind to the target surface is inactivated through hydrolysis (iC3b))
14
New cards
What is C5 Convertase comprised of in the lectin pathway?
C4b2a3b
15
New cards
What is C3 Convertase comprised of in the lectin pathway?
C4b2a
16
New cards
What do Mannose Binding Lectins attach to on the cell surface?
Mannose and Fucose residues
17
New cards
What do Ficolins bind to on the cell surface
Oligosaccharides containing acetylated sugars
18
New cards
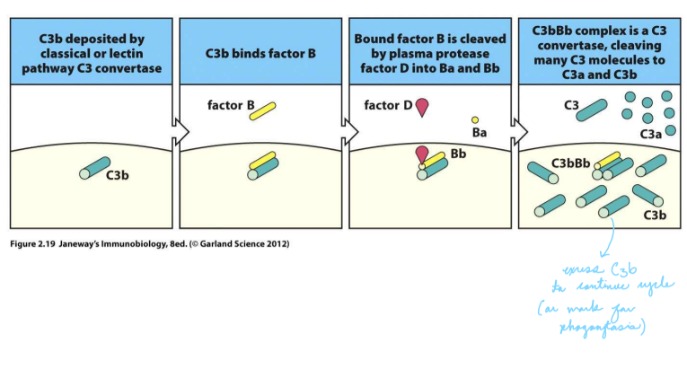
Outline the steps of the Alternative Pathway
Under normal circumstances, a small amount of circulating C3 undergoes spontaneous activation – a process known as “tick-over”. This activated C3b is rapidly inactivated through hydrolysis.
1\. If the activated C3b happens to bind to a “activating” surface, it remains active
2\. C3b binds Factor B
3\. Factor D cleaves B
4\. Bb remains bound to C3b, producing C3bBb: C3 convertase
5\. The C3 convertase facilitates the large scale cleavage of C3 producing more C3b
6\. This additional C3b can bind to the C3bBb to from C3bBbC3b: C5 convertase
1\. If the activated C3b happens to bind to a “activating” surface, it remains active
2\. C3b binds Factor B
3\. Factor D cleaves B
4\. Bb remains bound to C3b, producing C3bBb: C3 convertase
5\. The C3 convertase facilitates the large scale cleavage of C3 producing more C3b
6\. This additional C3b can bind to the C3bBb to from C3bBbC3b: C5 convertase
19
New cards
What is the difference between an activator surface and a non-activator surface?
Activator surfaces:
Bacterial Cell Surfaces. C3b bound to an Activator Surface has a high affinity for binding factor B. Binds Factor P (properdin) which stabilizes C3bBb activity
\
Non-Activator surfaces:
Mammalian cell surfaces. Rich in negatively charged residues. Negatively charged residues bind large amounts of Factor H. Factor H prevents C3b from binding Factor B. Factor H binds C3b, facilitating its inactivation by Factor I.
Bacterial Cell Surfaces. C3b bound to an Activator Surface has a high affinity for binding factor B. Binds Factor P (properdin) which stabilizes C3bBb activity
\
Non-Activator surfaces:
Mammalian cell surfaces. Rich in negatively charged residues. Negatively charged residues bind large amounts of Factor H. Factor H prevents C3b from binding Factor B. Factor H binds C3b, facilitating its inactivation by Factor I.
20
New cards
What is the role of factor P, where is it found?
Factor P is bound to activator surfaces by factor B. Factor P stabilizes C3bBb activity
21
New cards
What is the role of factor H, where is it found?
Factor H binds to the negative surfaces of mammalian cells. Factor H binds to Cb3 and prevents it from binding factor B. The binding of factor H to C3b facilitates inactivation by Factor I.
22
New cards
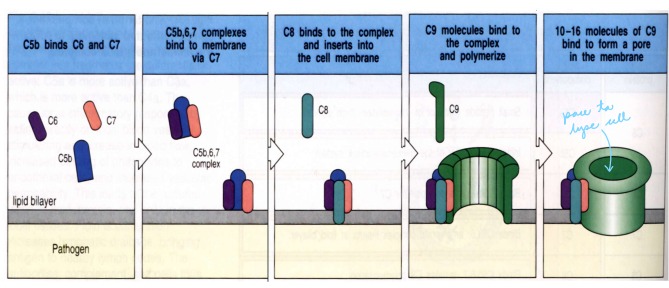
Outline the steps of the common terminator pathway.
1\. C5b produced by initiation pathway (any of the three) binds C6 and forms C5b6
2\. C5b6 binds C7 which induces a conformational change that reveals a hydrophobic domain that inserts into the cell membrane
3\. If the C5b67 complex is properly inserted into a membrane it binds C8
4\. C5b678 recruits 10-16 C9 molecules
4\. The 10-16 C9 molecules polymerize side by side to form a pore in the membrane
\
The membrane attack complex is completed.
2\. C5b6 binds C7 which induces a conformational change that reveals a hydrophobic domain that inserts into the cell membrane
3\. If the C5b67 complex is properly inserted into a membrane it binds C8
4\. C5b678 recruits 10-16 C9 molecules
4\. The 10-16 C9 molecules polymerize side by side to form a pore in the membrane
\
The membrane attack complex is completed.
23
New cards
What does C5 Convertase achieve in all three initiation pathways?
Cleaves C5 to produce C5b and proceed to the common terminator pathway
24
New cards
What is C3 Convertase comprised of in the alternative pathway?
C3bBb
25
New cards
What is C5 Convertase comprised of in the alternative pathway?
C3bBbC3b
26
New cards
What identical products are produced in all three pathways? What are their roles?
All pathways generate a C3 convertase which cleaves C3 leaving C3b bound to the microbial surface and releasing C3a.
\
C3a and C5a recruit phagocytes to the site of infection and promote inflammation
C3b on a cell surface tags cells for phagocytosis (acts as an opsonin)
\
C3a and C5a recruit phagocytes to the site of infection and promote inflammation
C3b on a cell surface tags cells for phagocytosis (acts as an opsonin)
27
New cards
In addition to cell lysis, what effector functions can be mediated by complement?
Opsonization
Cellular activation
Inflammation
Cellular activation
Inflammation