Grade 11 - Physics Semester 1
5.0(2)Studied by 97 people
Card Sorting
1/101
Last updated 4:04 AM on 3/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
1
New cards
Kinetic Particle Model (KPM) states
that all particles are constantly moving.
2
New cards
Theoretically, at absolute zero
particles are not vibrating and have no energy.
3
New cards
Absolute Zero (Zero Kelvin)
-273.15°C
4
New cards
Thermal energy is
internal energy of an object due to kinetic energy.
5
New cards
The more thermal energy means
The higher the temperature
6
New cards
Temperature is
measurement of an average kinetic energy of an object system.
7
New cards
Kinetic energy is
energy of movement, based on work required for an object to move between 2 points.
8
New cards
Heat is
thermal energy that transfers from a 'hot body' to a 'cold body'
9
New cards
Internal energy is
kinetic energy (K.E) + potential energy (P.E) \= K.E & P.E
10
New cards
Conduction is
heat is transferred through contact between particles. A higher vibrating gives energy to a lower vibrating particle.
11
New cards
Convection is
bodies or currents of particle redistribute due to density. A fluids heat up they expand and get less dense.
12
New cards
Radiation
heat energy is transferred as wave energy (electromagnetic waves). It may transfer through a vacuum.
13
New cards
The addition of energy into a system (no phase change) invokes a
transformation to kinetic energy of particles.
14
New cards
An increase in particle vibration (energy) means
an increase in temperature
15
New cards
Phase change is
change of materials state, eg; solid liquid or gas.
16
New cards
All vibrating particles
emit radiation
17
New cards
If vibration increases, then
the radiation output initially increases, however it will vary.
18
New cards
If energy absorbed is less than energy emitted then
potentially, heat loss has occurred.
19
New cards
Energy removal/loss can occur through
conduction, convection, and radiation.
20
New cards
Specific heat capacity is
the amount of energy required to heat 1kg of a material by 1°C.
21
New cards
Direct proportionality is
Q ∝ m, where m\=mass and Q\= heat energy.
22
New cards
Explain Q ∝ m
when m changes, Q changes in the same way.
23
New cards
If something has a higher heat capacity then
more heat energy is needed
24
New cards
Explain the process of phase changes
When matter changes state (solid, liquid, gas) molecular bonds are restructured. the bond restructuring requires energy for bonds and forces to form/breakdown/rearrange. While this occurs, additional energy does not affect the average kinetic energy, thus the heat energy, meaning there is no temperature change. The process of changing state/ phase change requires energy gain/ loss as the material/ medium has a change in P.E.
25
New cards
Latent heat is
hidden energy, which is unique for every material/ medium. This is the required P.E during phase change.
26
New cards
Calorimetry is
the process of measuring the amount of heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction.
27
New cards
The Zeroth law states that
objects in thermal contact will eventually reach a thermal equilibrium.
28
New cards
All forms of energy has
the ability to transform into another form of energy.
29
New cards
Energy cannot be
created or destroyed
30
New cards
During transformations,
particles undergo a change. At the micro level, bonds and vibration of particles change. At the macro levels object transform by possibly moving, rotating, rolling etc.
31
New cards
Mechanical work is
energy used for the object to transform.
32
New cards
first law of thermodynamics is
energy is always conserved, irrelevant of the transformation. Total energy remains constant. Law of conservation of energy is always obeyed.
33
New cards
In mechanical systems energy is
'lost' to the environment as heat/sound/friction
34
New cards
Efficiency is
how effective a system or action may execute the required operation
35
New cards
Protons and neutrons are \_____ times \_______ than electrons
2000, heavier
36
New cards
The four main forces are
gravitational force (gravity), electromagnetic force (ESF), strong nuclear force (SNF), weak nuclear force (WNF)
37
New cards
Electromagnetic force is aka
electrostatic (ESF), electro repulsive, or coulomb force
38
New cards
ESF causes protons to
repel
39
New cards
ESF is a
non-contact force
40
New cards
Proton - proton
proton on proton; a way of describing the interaction.
41
New cards
proton-proton and electron-electron interactions are caused by
repulsive force
42
New cards
proton-electron interactions are caused by
attractive force (ESF)
43
New cards
The strongest force is
strong nuclear force
44
New cards
The weakest force is
gravitational force
45
New cards
SNF is
a contact force
46
New cards
fm is a
femtometre, (a quadrillionth of a metre).
47
New cards
SNF overcomes
ESF within 1.5 fm.
48
New cards
SNF only occurs within
the nucleus
49
New cards
When SNF acts within 1.5 fm
larger nuclides become less stable
50
New cards
As protons increase
protons cannot touch each other which causes an imbalance in SNF and ESF, causing the isotope to be unstable.
51
New cards
Neutrons balance out the
stability of nuclides, binding nucleons
52
New cards
Serge plots are
plots of all stable and unstable isotopes.
53
New cards
Serge plots show
0
54
New cards
If the isotope doesn't have enough neutrons
positrons are emitted from protons, causing the proton to become a neutron
55
New cards
Protons emitting B+ decay, it causes the segre plot to
move left or up
56
New cards
Positrons are
positive leptons
57
New cards
Leptons are
an elementary particle of half-integer spin that does not undergo strong interactions.
58
New cards
As the number of protons increase, an atom becomes
heavier and the ESF increases
59
New cards
When there are too many neutrons,
neutrons emit an excited electron, and becomes a proton
60
New cards
an excited electron is
(e- decay or β- decay)
61
New cards
too many neutrons means that
the nucleus needs to get rid of mass or energy
62
New cards
When neutrons emitting e- decay or β- decay, it causes the segre plot to move
right and down
63
New cards
Heavier isotopes require
more SNF and more neutrons than protons
64
New cards
If N/Z is not a stable nuclide
natural radioactive decay (emission) may occur
65
New cards
Decay includes
alpha decay, beta (+ or -) decay, gamma emission (U1-4) and other forms.
66
New cards
Naturally occurring stable isotopes are
less likely to undergo radioactive decay
67
New cards
Emission includes
energy emission for stability, and sometimes particle emission for stability
68
New cards
A parent nuclide is
nuclide before decay
69
New cards
A daughter nuclide is
nuclide after decay or emission
70
New cards
Neutron emission is when
nucleus mass reduces, however the atomic number doesn't change
71
New cards
Proton lost is when
nucleus mass and atomic number reduces, therefore the particle changes, eg, carbon to boron.
72
New cards
Rounding in exams
the answer should have the same number of digits as the least accurate number in the operation.
73
New cards
Percentage uncertainty is the same as
relative uncertainty
74
New cards
Absolute uncertainty \=
1/2 x (increment)
75
New cards
Percentage uncertainty \=
(abs unc/ measurement) x 100
76
New cards
The steps for calculating uncertainty of a line with error bars are
calculate the (T\=gradient (m) + y-intercept) of the l.o.b.f, minimum line and maximum line. Then calculate the absolute uncertainty of the gradient (Abs Unc Gradient (m) \= (max gradient-min gradient)/2). The final equation is then,
T \= ((l.o.b.f m) ± m)t + ((l.o.b.f) ± Abs Unc of y-int)
T \= ((l.o.b.f m) ± m)t + ((l.o.b.f) ± Abs Unc of y-int)
77
New cards
What does it mean to find the mathematical relationship
You must calculate the gradient with the formula T\=kt, and explain the relationship using x ∝ y.
78
New cards
Absolute Uncertainty formula
max-min/2
79
New cards
Formula for an equation
T \= kt, where k is the gradient and t is the y-intercept
80
New cards
Words to describe graph trends
positive, negative, linear, constant rate of change
81
New cards
Formula for absolute zero
0 Kelvin \= -273°C
82
New cards
Specific Heat capacity formula
Q \= mc∆T
83
New cards
Explain Q\=mc∆T
Q \= heat energy (if Q\>0J, temp increases, if Q
84
New cards
Latent Heat formulas
Q \= mLv and Q \= mLf
85
New cards
Explain Q\=mLv and Q\=mLf
Q \= heat energy (joules)
m \= mass (kg)
Lv \= Latent heat of vaporization (Jkg-1)
Lf \= Latent heat of fusion (Jkg-1)
m \= mass (kg)
Lv \= Latent heat of vaporization (Jkg-1)
Lf \= Latent heat of fusion (Jkg-1)
86
New cards
Lv and Lf of a substance is
Lv the amount of energy per kg required to change a substance from/to liquid state to/from gas state. Lf is the same except from/to solid to/from liquid state.
87
New cards
Formula for thermal equilibrium
Total energy of Q1 \= Total energy of Q2
Q1T \= Q2T
Q1T \= Q2T
88
New cards
To calculate thermal equilibrium, the formula is
∆Q1 \= -∆Q2
89
New cards
Formula to calculate the change in internal energy
∆u \= Q±W
90
New cards
Formula for efficiency
η \= (energy output/energy input) x 100
91
New cards
Symbols, mass and charge of alpha decay
The mass is 2 protons and 2 neutrons, and it has a +2 charge.
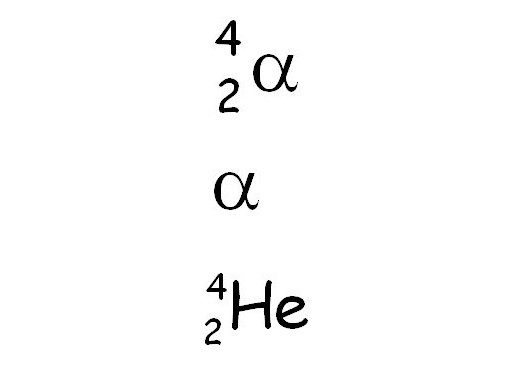
92
New cards
Symbols, mass and charge of beta positive decay
The mass is 1 positron, and it has a +1 charge.

93
New cards
Symbols, mass and charge of beta negative decay
The mass is 1 charged electron, and it has a -1 charge.
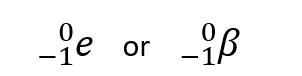
94
New cards
Symbols, mass and charge of gamma emission
Gamma emission are waves, therefore there is no mass or charge.
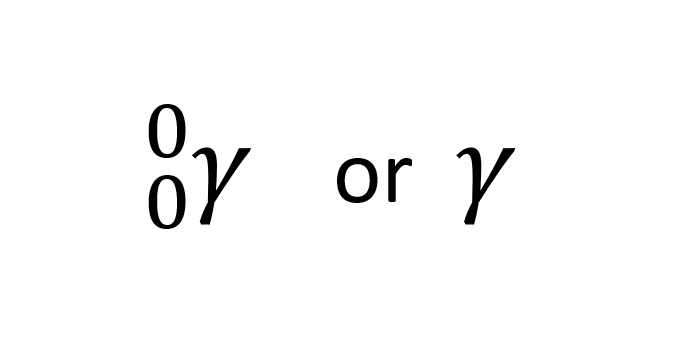
95
New cards
Ionisation ability meaning
the capability to remove electrons from atoms and molecules in the matter through which they pass.
96
New cards
Ionisation ability for the decay
From highest to lowest it goes, alpha, beta +, beta -, gamma.
97
New cards
Penetration ability meaning
the power (length) of an electron beam transmitted for a substance.
98
New cards
Penetration ability for decay
from highest to lowest it goes, gamma, beta -, beta +, alpha.
99
New cards
Against gold foil, alpha particles
are blocked/deflected
100
New cards
Against gold foil, beta + and -
have minimal deflection