Nervous System: HESI Science Portion (Anatomy)
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
What are the main organs of the Nervous System?
brain, spinal cord, nerves and supporting structures and cells called neuroglia
What are the 2 main subdivisions of the Nervous System
the central and peripheral divisions
What is the Central nervous system (CNS)?
Consists of the brain and spinal cord, which are enclosed and protected by the cranium and vertebral column, respectively. They are the main control center of the body.
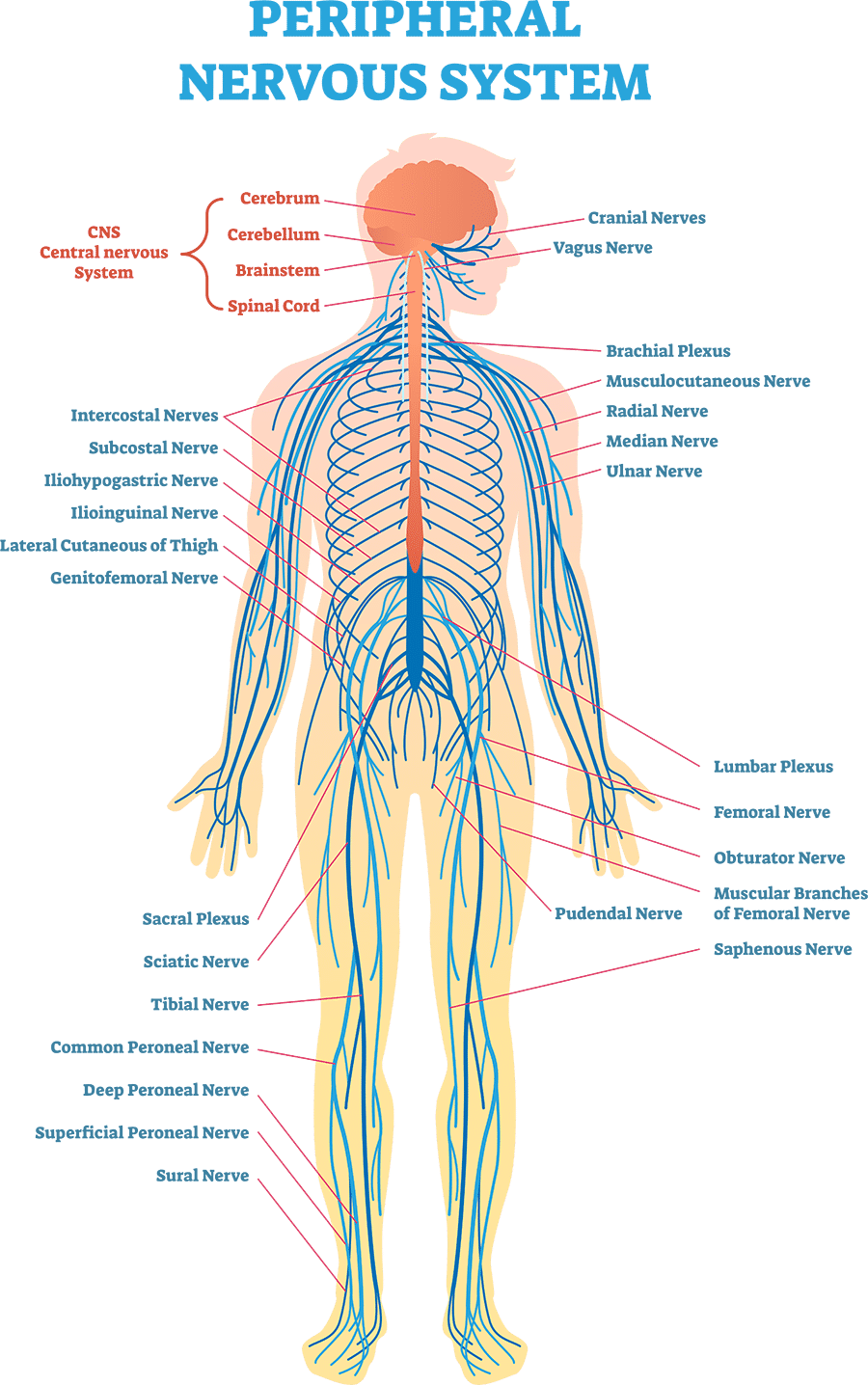
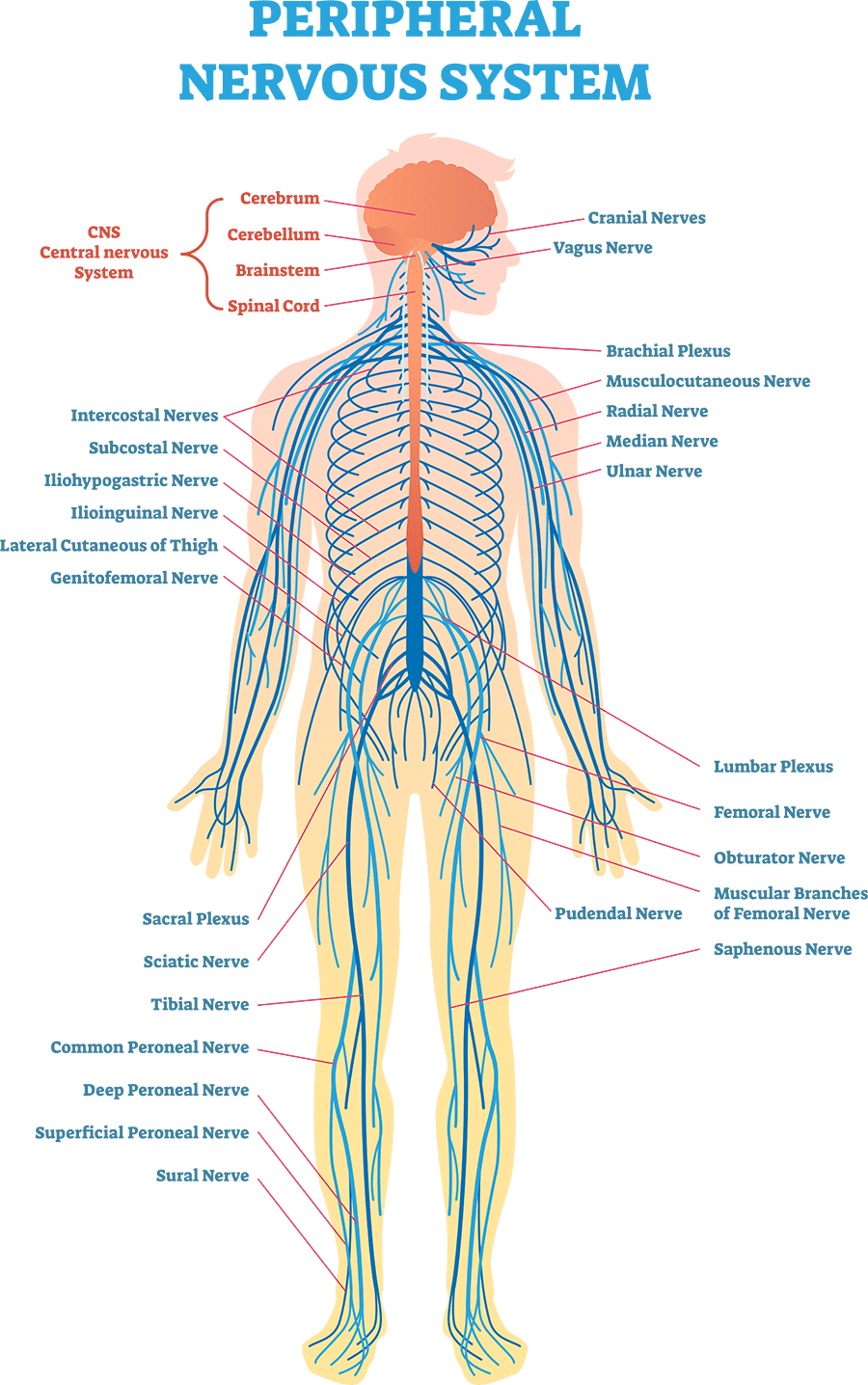
What is the Peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
Consists of the rest of the nervous system – the nerves and ganglia. A nerve is a bundle of nerve fibers wrapped in connective tissue, while ganglia are knot-like swellings in a nerve where neuron cell bodies are concentrated.
What are the 2 divisions that control our body’s internal functions?
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic divisions of the human nervous system
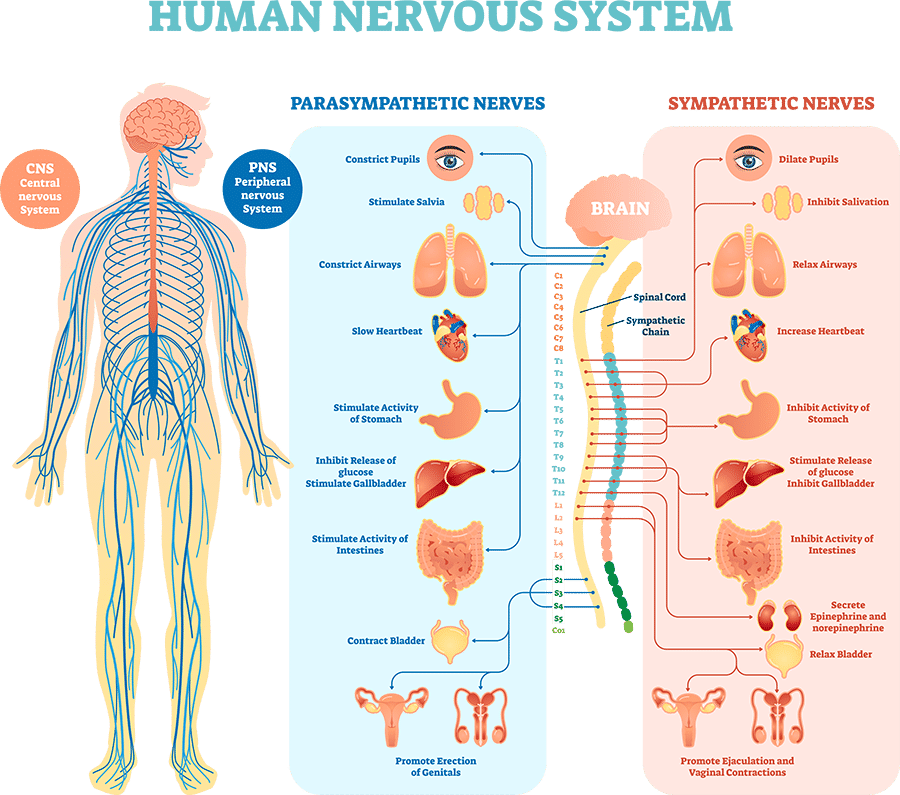
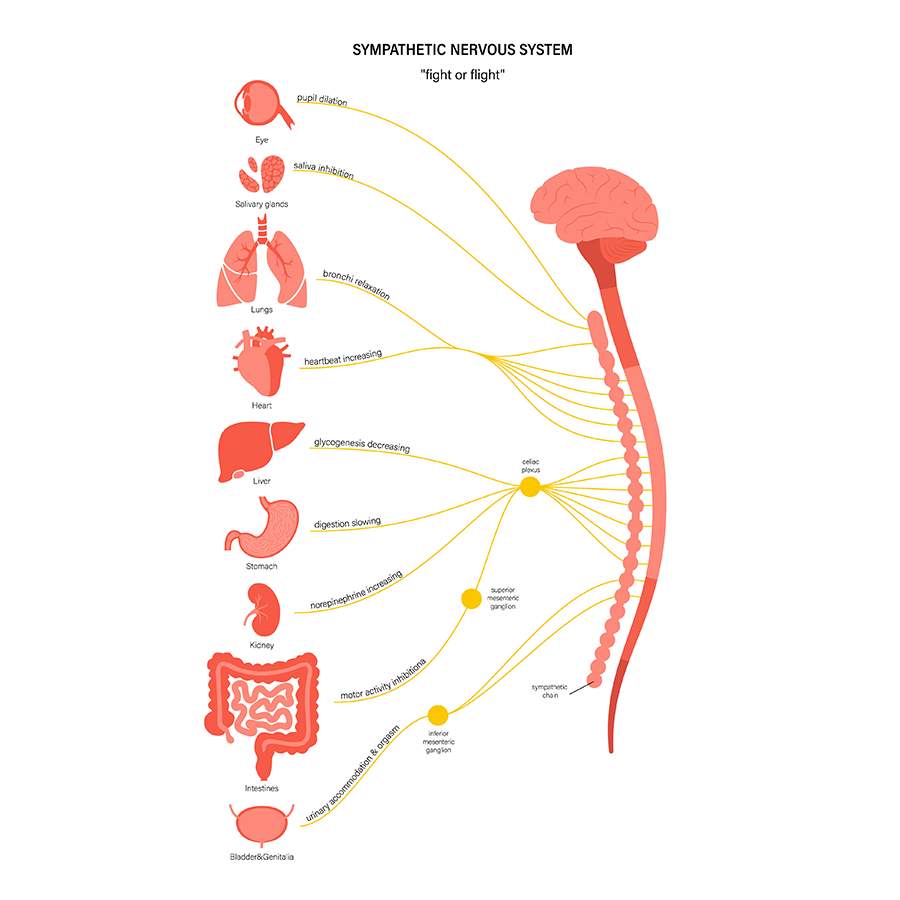
What is the Sympathetic Division?
The first division, which controls our “fight or flight” response. This is where the body is signaled into action, such as by creating an acceleration in heartbeat and respiration.
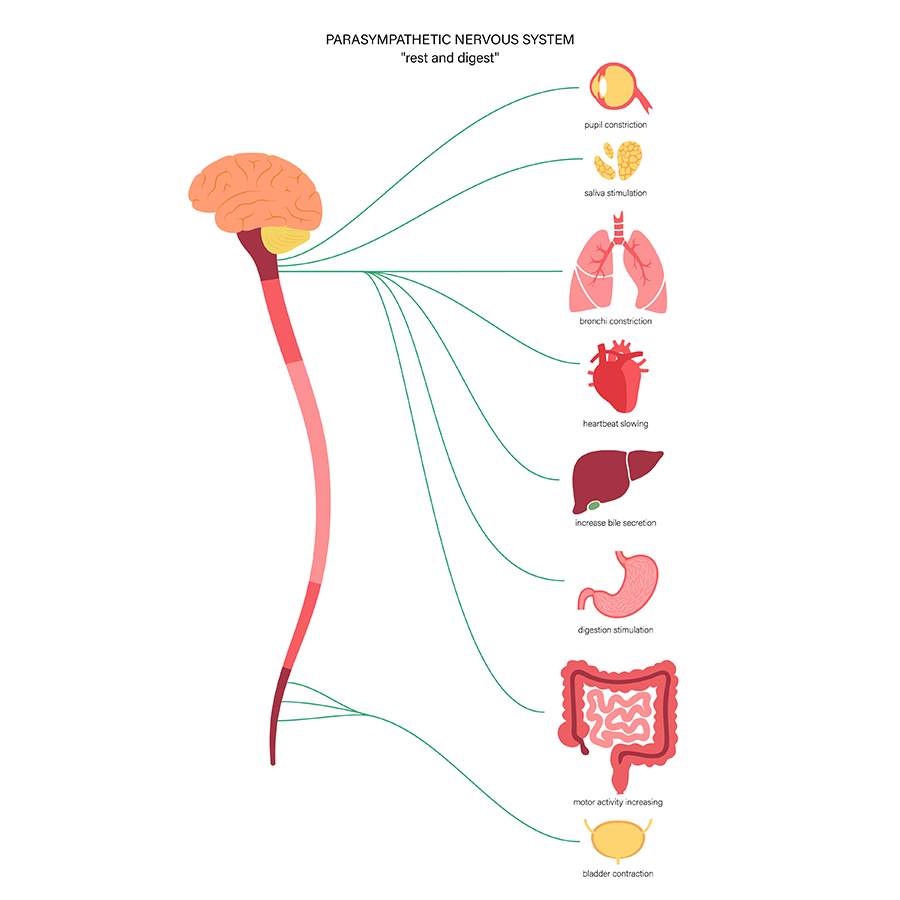
What is the Parasympathetic Division?
The second division, that controls our “rest and digest” functions, tends to have a calming effect. It does that by slowing the heart rate and breathing and stimulating the digestive and urinary systems to preserve energy and digest food to get it ready for when there is an action.
What are the main functions of the Nervous System?
Communicate with and control organs’ functions and growth.
Memory
Learning
Emotions
Sensations
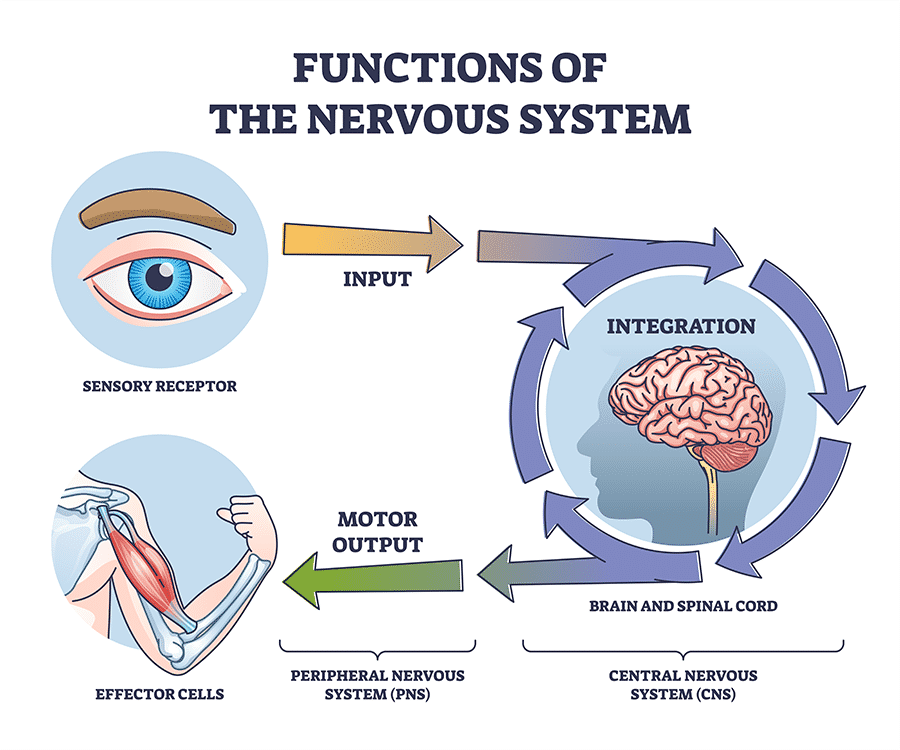
What are the steps for Processing Information in the Nervous System?
Sensory: Sensory neurons detect stimuli and transmit the information up to the CNS.
Integration: the brain takes sensory information, creates a coded message, and then sends signals through the Central Nervous System, mainly in the brain, where the message is decoded based on past information. This is done through interneurons that receive and carry out signals within the CNS.
Motor: After the command is issued from the CNS, the motor neurons send signals out to muscles and gland cells and the actual response to the original stimulus is performed.