Sophia Koh Chapter 15 ~ Communication & Sciences Disorders
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Factors influencing impact of hearing loss:
Individual
Contextual
Technical
Characteristics of Hearing Loss (HL):
understanding covos, detecting subtle changes (variations in pitch), communicating in noisy environments
POTENTIAL:
withdrawal from activities, avoidance of social interactions, loss of confidence
Acquired hearing loss is possible at:
any age
Decibel (dB):
unit of sound pressure
Sound Pressure Level (SPL):
pressure level of sound (measured in dB)
Hearing Level (HL):
standardized scale
accounts for varying ear sensitivity across frequencies
Normal Hearing Range: -10 to 15 dB HL
Hearing loss: > 15 dB HL
Test battery components for hearing eval:
comprehensive case history
otoscopy
pure tone audiometry (?) & bone conduction
speech audiometry
immittance testing (alternations/fluctuations of TM & integrity of nervous system in response to stimuli)
Speech Recognition Threshold (SRT):
measures the intensity at which speech is audible 50% of the time
Procedure for SRT:
Spondees presented (equally stressed 2-syllable words ~ ex. mushroom, baseball)
Patient repeats (determined when 50% of words correctly identified)
Should correlate w/ pure-tone average (PTA) of 500, 1000, & 2000 Hz
Word Recognition Score (WRS):
assesses speech understanding at comfortable loudness level
Procedure for WRS:
Present phonemically balanced word lists
Patient repeats words:
Score calculated as percentage of words
Provides info on speech clarity perceptions
Helps in determining amplification needs/rehabilitation strategies
Pure-Tone Audiometry:
(procedure we use to determine how sound is traveling through the outer, middle, and inner ear)
preformed for each ear individually
uses audiometer
measures different frequencies in Hertz (Hz)
measures intensity in decibels (dB)
Transducers:
Supra-aural headphones
Insert earphones
Speakers
Bone conduction oscillator
Pure-Tone Audiometry Procedure:
conducted in sound-treated booth
subject/behavioral test
patient responds when tone is heard → hand raising, fairy wands, etc.
“masking” used for asymmetrical hearing (introducing noise to the non-test ear during a pure-tone audiogram)
air conduction (degree, how severe)
bone conduction (what TYPE)
Bone Conduction Pathway
alternative route for sound to reach inner ear
bypasses outer & middle ear
Process:
Sound vibrates bones of the skull
Bony labyrinth set into sympathetic vibration
Cochlea responds similarly to air conduction
Important for distinguishing types of hearing loss
Audiometer Frequencies (octave intervals typically tested):
125 Hz
250 Hz
500 Hz
1000 Hz
2000 Hz
4000 Hz
8000 Hz
Mid-octave frequencies often included:
750 Hz
1500 Hz
3000 Hz
6000 Hz
Audiogram:
graph displaying hearing sensitivity
inverted scale:
vertical axis (dB HL) (lower dB # at top; higher dB # at bottom)
horizontal axis (frequencies Hz) (low frequencies on left; high frequencies on right)
Symbols used for audiogram:
Air Conduction
Right ear: red O
Left ear: blue X
Bone conduction (mastoid):
Right ear: Red <
Left ear: Blue >
(Different symbols used when masking is applied)
Threshold of Audibility:
softest sound detectable 50% of the time (expressed in dB HL)
plotted on audiogram for each frequency & ear
Speech Audiometry:
Assesses: how individuals hear speech stimuli
Complements pure-tone audiometry
2 main components:
Speech Recognition Threshold (SRT)
Word Recognition Score (WRS)
Importance of Comprehensive Hearing Eval:
combines objective & subjective measures
provides detailed info on:
degree & type of hearing loss
impact on speech understanding
potential benefit from amplification
guides treatment & management decisions
essential for developing personalized intervention plans
crucial for monitoring hearing changes overtime
Types of hearing loss:
conductive
(outer, middle)
sensorineural
(inner, auditory nerve)
mixed
Conductive Hearing Loss:
impairment in air conduction
bone conduction is always w/ in norm. limits (WNL)
Causes of conductive hearing loss: Outer Ear
Occulsion of the external auditory canal:
Ear wax buildup
Debris from infection
Tumors, burns, congenital partial/complete closure
Causes of Conductive Hearing Loss: Middle Ear
Otitis media (middle ear infection)
often in childhood
Other causes:
fluid formation acting as a sound barrier, thickening/destruction of the tympanic membrane, damage to ossicular chain, tumors, trauma, Chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction
Treatment for Conductive Hearing Loss:
Medical intervention
Myringotomy for Chronic Eustachian tube Dysfunction
Prompt treatment for otitis media
Audiologic intervention:
Indicated for prolonged treatment of hearing loss
Hearing aids
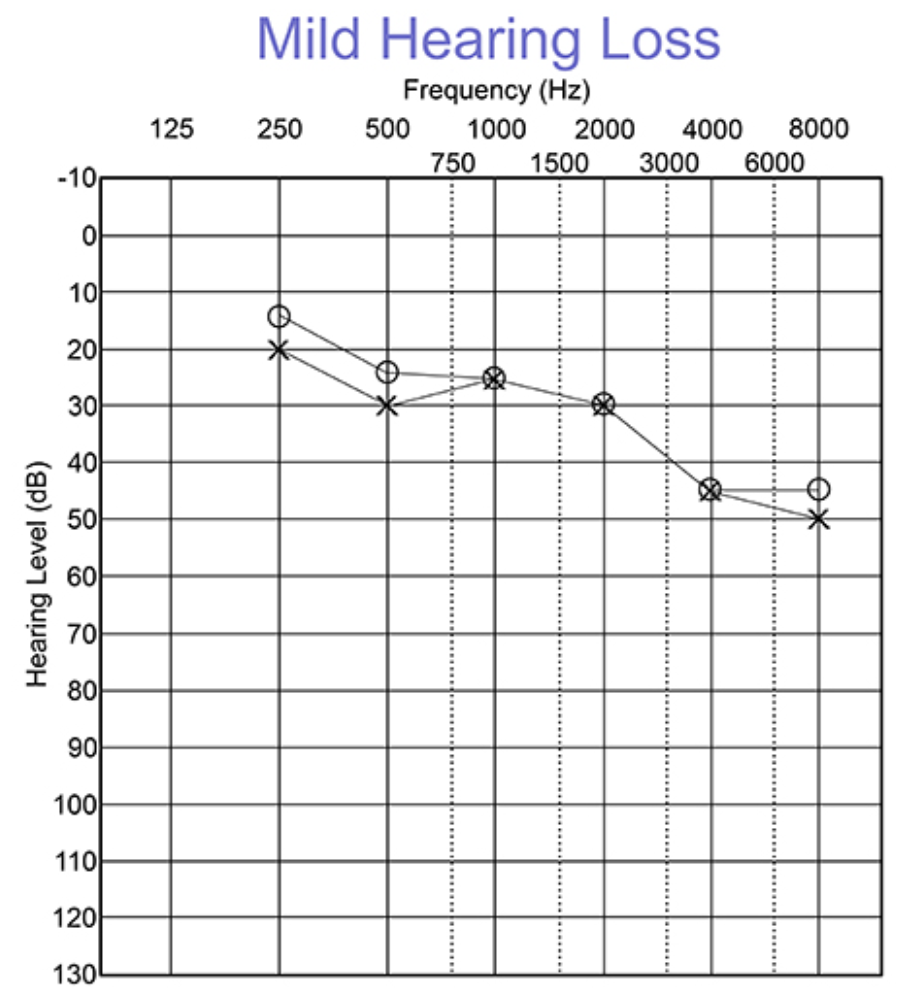
Audiogram Interpretation for Conductive hearing loss:
air conduction thresholds elevated
bone conduction thresholds within normal range
significant air-bone gap
(suggests issues in outer or middle ear)
Sensorineural Hearing Loss:
damage to inner ear (cochlea) or auditory nerve
Characteristics:
mild to total hearing loss
No air-bone gap
Poorer Word Recognition Thresholds (WRTs)
Causes of sensorineural hearing loss (COCHLEAR):
Prenatal causes:
maternal alcohol/drug abuse
Perinatal causes
birth complications (umbilical strangulations)
Postnatal causes
prolonged otitis media
aging process
Causes of sensorineural hearing loss (AUDITORY NERVE):
Acoustic neuroma
tumor on vestibular branch of auditory nerve
usually unilateral (affects 1 ear)
Symptoms
Tinnitus (ringing/roaring sounds)
progressive hearing loss
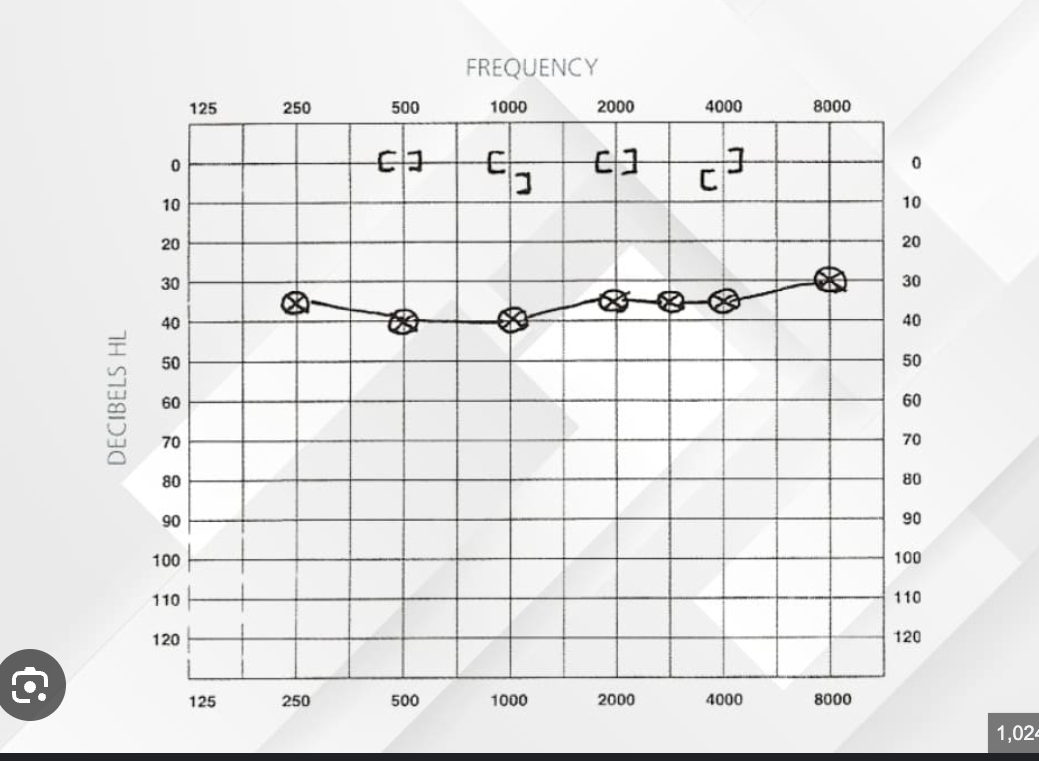
Audiogram features for sensorineural hearing loss:
both air & bone conduction thresholds elevated
no significant air-bone gap
often shows sloping configuration
(indicates cochlear or auditory nerve damage)
Mixed Hearing Loss:
combination of conductive & sensorineural hearing loss
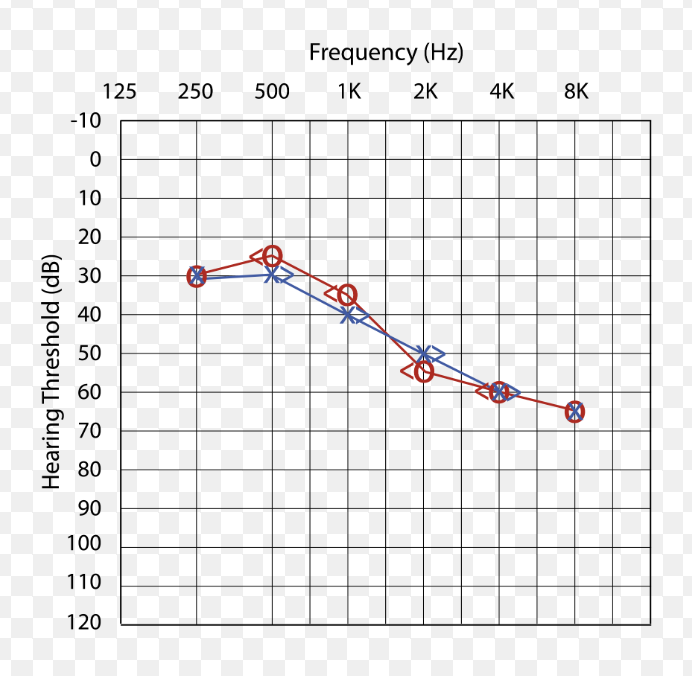
Audiogram for mixed hearing loss:
air & bone conduction thresholds outside normal limits (elevated)
air-bone gap present, but bone conduction also affected
(suggests combo of conductive & sensorineural issues)
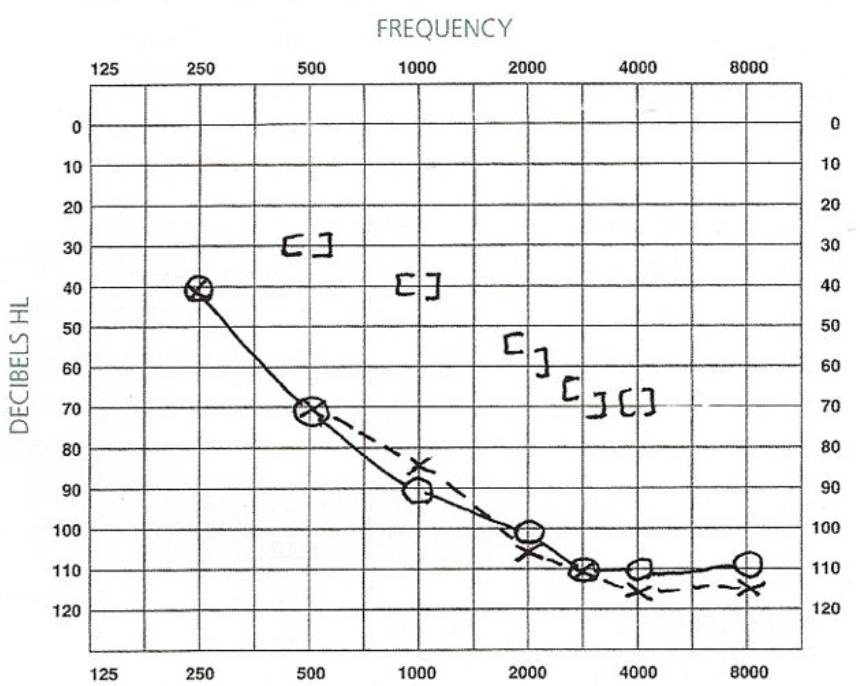
Mixed hearing loss measurement & interpretation:
Measurement:
sensorineural component
air-bone gap (ABG) - difference between air & bone conduction thresholds
Interpretation:
smaller ABG
larger ABG
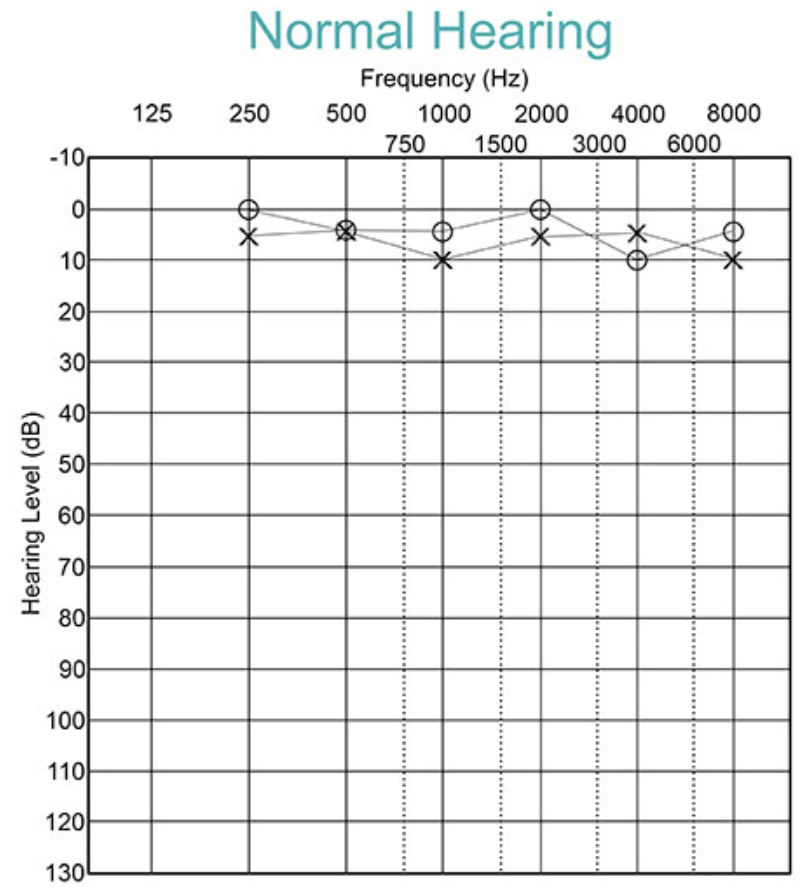
Audiogram Interpretation: Normal Hearing
Thresholds below 15 dB HL at all frequencies
No significant difference between air & bone conduction
indicates optimal hearing sensitivity
Impact of Hearing Loss on Speech Discrimination:
Word Recognition Thresholds (WRTs)
Normal: excellent
Conductive: generally good
Sensorineural: poorer, often correlated with degree of loss
Implications:
Conductive: may benefit from amplification (signal just needs amplification)
Sensorineural: may have persistent speech discrimination difficulties even w/ amplification (signal itself is degraded)
Importance of early intervention:
language development in children
improves quality of life & communication in adults
Ex. of reading audiograms:
“Within normal limits sloping to moderately-severe sensorineural hearing loss.”
“Mild conductive hearing loss.”
Degree of Hearing Loss Chart:
0-15 normal
16-25 slight
26-40 mild
41-55 moderate
56-70 moderately-severe
71-90 severe
91-120 profound