P - Waves S2023
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study for the Learning Check! (OWL book will be available)
Last updated 6:35 PM on 6/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
1
New cards
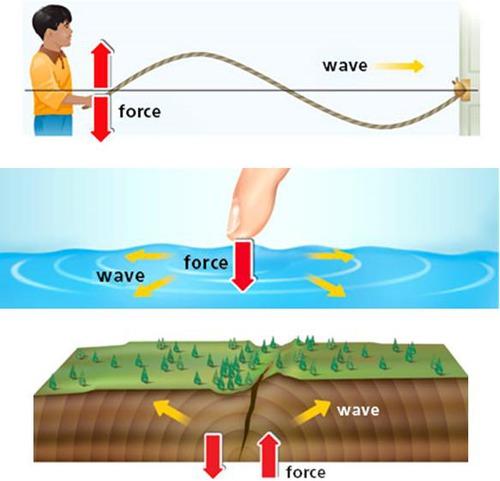
mechanical wave
a wave that travels through matter
2
New cards
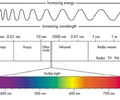
electromagnetic waves
transverse waves that transfer energy through matter and the vacuum of space; travel their fastest in the vacuum of space at 300,000 km/s
3
New cards
electromagnetic spectrum
includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays
4
New cards
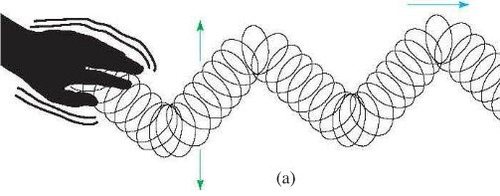
transverse wave
wave in which the particles of the medium move perpendicularly to the direction the wave is traveling
5
New cards
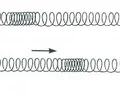
longitudinal wave
wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of wave motion
6
New cards
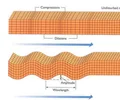
compression
part of a longitudinal wave where the particles of the medium are close together
7
New cards
rarefaction
part in a longitudinal wave where the particles are spread apart
8
New cards
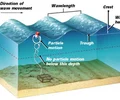
water waves
these are a combination of transverse and longitudinal waves
9
New cards
seismic waves
mechanical waves that move through Earth's crust (P waves are longitudinal, S are transverse)
10
New cards
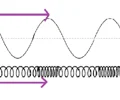
wavelength
horizontal distance between the crests or troughs
11
New cards
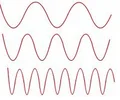
frequency
the number of wavelengths that pass a given point in one second; measured in Hertz (Hz)
12
New cards
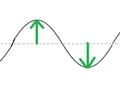
amplitude
height of a wave; greater height = greater energy (and greater loudness for sound waves)
13
New cards
color
a quality produced by light waves; CASE 1: when light hits an object, some wavelengths are absorbed by the object and some are reflected; this quality is produced by the wavelengths of light reflected; CASE 2: if an object emits light itself, this quality is produced by the wavelengths it emits
14
New cards
additive color
color that is produced by light that is emitted directly from a light source (red, green and blue produce white)
15
New cards
subtractive color
color that is produced by the mixing of pigments (cyan, magenta, and yellow produce black)
16
New cards
white light
contains all the wavelengths of the visible spectrum
17
New cards
blue skies
As white light from the Sun enters Earth's atmosphere, much of the red, yellow, and green wavelengths of light (mixed together and still nearly white) pass straight through the atmosphere to our eyes. The blue and violet waves, however, are just the right size to hit and bounce off of the molecules of gas in the atmosphere. This causes the blue and violet waves to be separated from the rest of the light and become scattered in every direction for all to see. The other wavelengths stick together as a group, and therefore remain white.
18
New cards
red sunsets
As the Sun gets lower in the sky, its light passes through more of the atmosphere to reach you. Even more of the blue and violet light is scattered, allowing the reds and yellows to pass straight through to your eyes without all that competition from the blues.
19
New cards
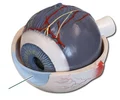
cornea
convex lens made of transparent tissue located on the outside of the eye
20
New cards
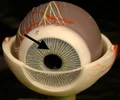
iris
colored part of the eye that regulates size of pupil
21
New cards
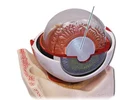
eye lens
the transparent structure behind the pupil that changes shape (when ciliary muscles relax & contract) to help focus images on the retina
22
New cards
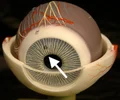
pupil
opening into the interior of the eye at the center of the iris
23
New cards
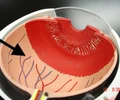
retina
layer of special light-sensitive cells in the back of the eye; where an image forms
24
New cards
rods
cells in the retina that are active in dim light
25
New cards
cones
cells in the retina that are active in bright light and detect color
26
New cards
sound wave
longitudinal wave caused by vibrations that only travel through matter (solids, liquids & gases)
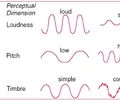
27
New cards
speed of sound
increases with increasing temperature and/or density (faster in solids than gases); formula s=d/t

28
New cards
outer ear
collects sound waves
29
New cards
middle ear
amplifies sound waves
30
New cards
inner ear
converts vibrations to nerve signals that travel to the brain
31
New cards
pitch
perception of how high or low a sound seems
32
New cards
vocal cords
two membranes in the throat that vibrate creating sound waves; muscles connected to these make them thicker and thinner like guitar strings
33
New cards
decibel scale
measures loudness of sound
34
New cards
sonar
uses reflected sound waves to locate objects under water
35
New cards
echolocation
the process of using reflected sound waves to find objects used by animals such as bats and dolphins
36
New cards
standing wave
waves that appear to be standing still
37
New cards
node
a point on a standing wave that has no displacement from the rest position
38
New cards
antinode
a point of maximum displacement midway between two nodes in a standing wave