respirometers and respiratory substrates
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What about a substrate determines how effectively it can be respired
The number of hydrogens
What is the RQ value for glucose/carbohydrates
1
What is the RQ value for Lipids
0.7
What is the RQ value for Proteins
0.9
How can an RQ value be calculated
from a balanced chemical equation
(Moles of CO2 given out)/(moles of O2 taken in)
What does a really high number RQ value above 1 mean about the respiration occuring
High proportion of anaerobic respiration occuring
What are the advantages of using this respirometer
simple to submerge in water bath to change temperature
Syringe resets respirometer easily
Scale easy to read
Movement of manometer scale should give volume of O2 taken up
What is the purpose of potassium hydroxide solution
Absorbs any CO2 produced so that only the oxygen is affecting the change in gas volume
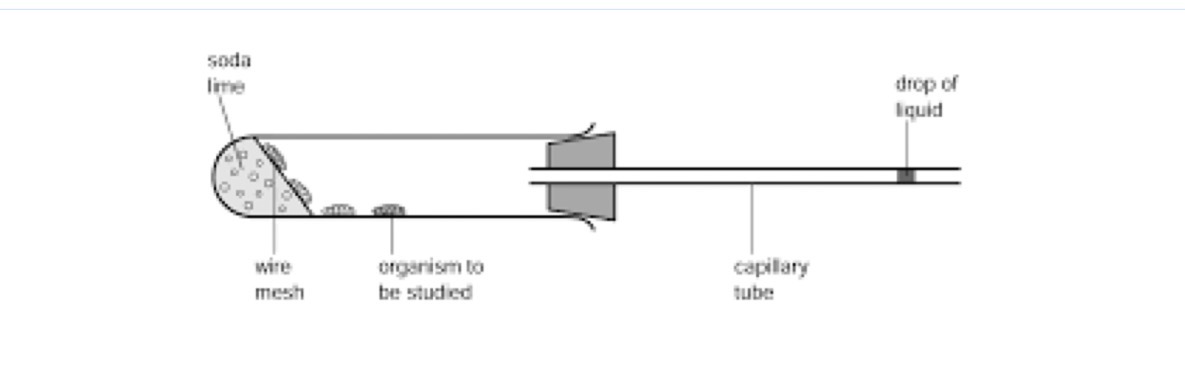
Explain this respirometer
the movement of liquid = volume of O2 produced
Soda lime added absorbs CO2 - gas shouldnt move as far as less gas produced
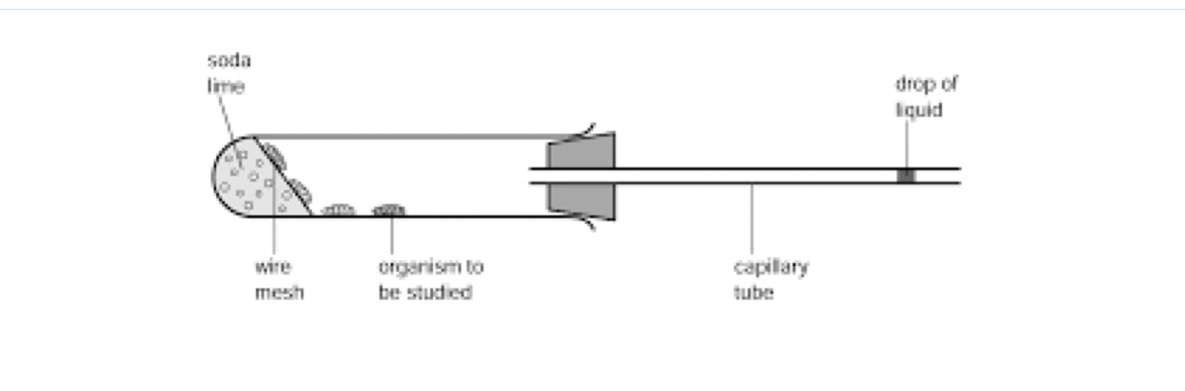
What are the limitations of this respirometer
no reset
No fixed scale
No control tube - need separate equipment
How would you find the volume of gas from a capillary tube from a respirometer
area of tube x length
πr² x distance moved
How would you find the RQ value experimental using a respirometer set up
measure volume of O2 consumed (with KOH)(VOL1)
Reset respiometer
Rerun experiment with no KOH (VOL2)
RQ = [(O2 consumed)-(O2consumed-CO2 produced)] / O2 consumed
RQ = [VOL1-VOL2]/VOL1