Eukaryotic Pathogens: Helminths
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What are Helminths?
Worms (Flat- like tapeworms & Round- Egg infective & Larvae infective)
Host susceptibility
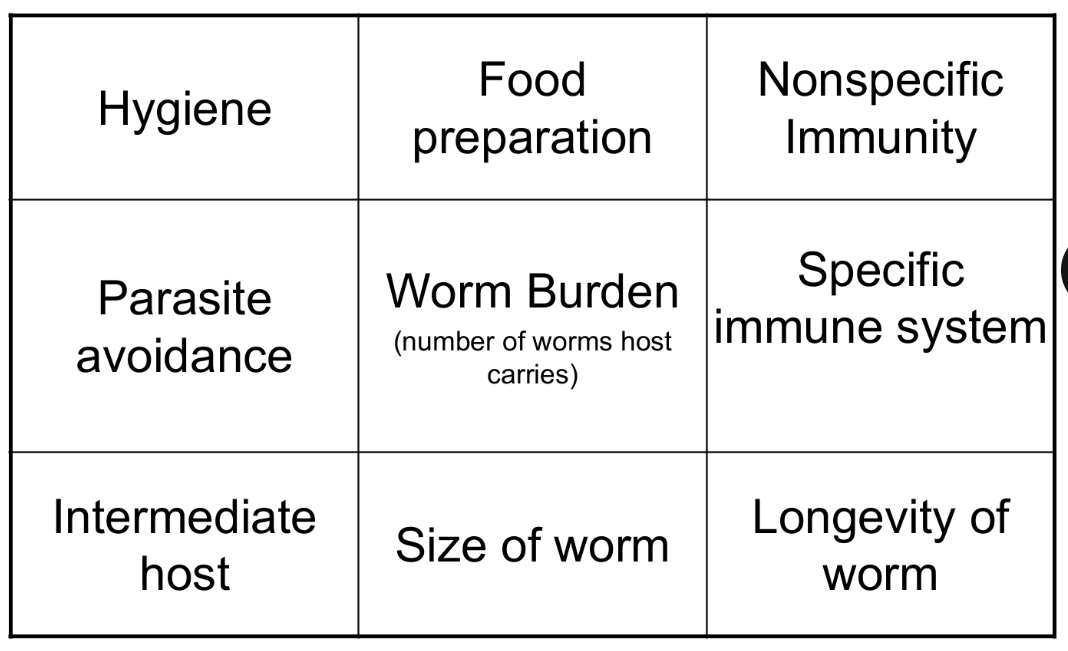
Pathogenesis Direct & Indirect damage
Direct Damage
Blockages (worm size, migration, granulomas (mass of inflamed tissues)
Pressure
Tissue necrosis, migration, turnover
Indirect damage
Inflammation
Hypersensitivity
Mucosal Changes
They have…
Little to no digestive system
Very simple nervous system
Little or no means of locomotion
A complex reproductive system, sometimes with multiple hosts (definitive and intermediate)
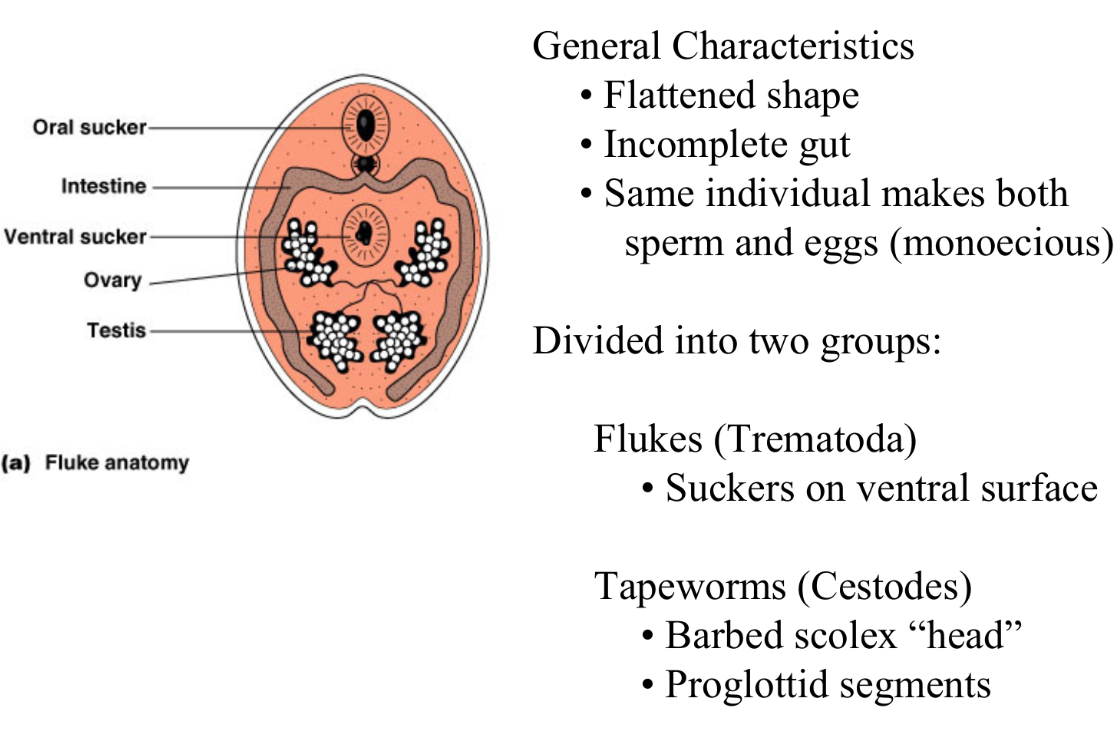
Flatworm characteristics
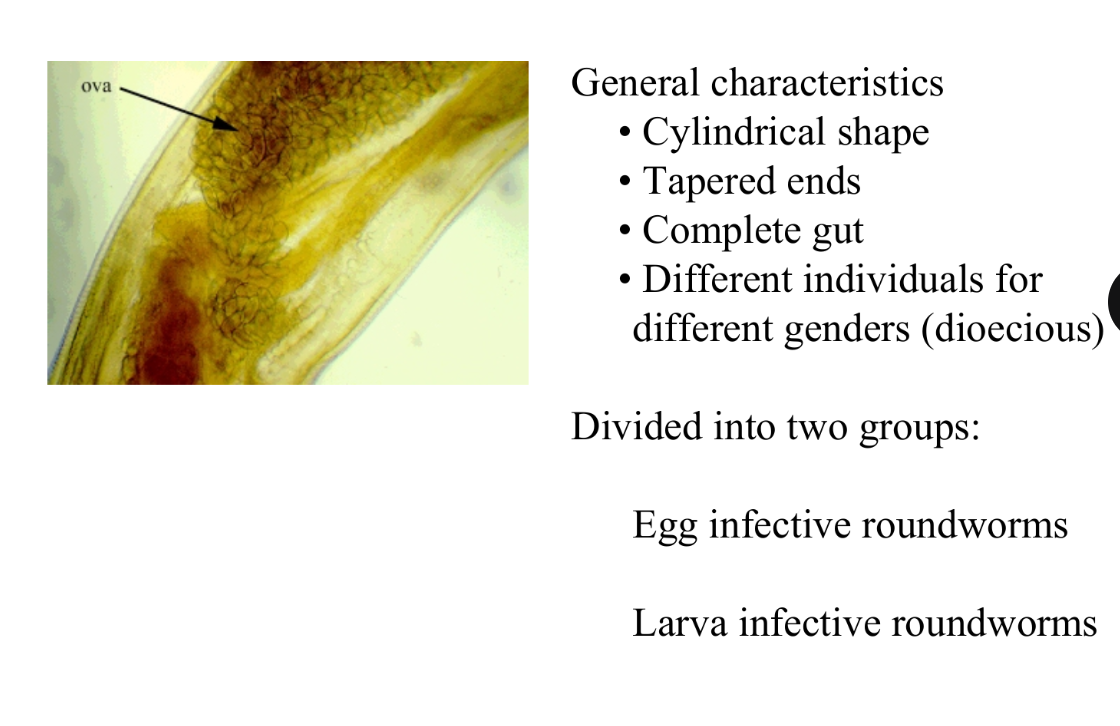
Roundworm Characteristics
Arthropods as Vectors (Kingdom, Phylum Class)
Arachnids: Ticks & Mites. 4x legs
Insects: Fleas, Lice, Flies, Mosquitoes, Kissing bugs. 3x legs
Ticks, Mites, Fleas & Lice (What do they feed on & symptoms)
Ticks
Epidermal parasites
Feed mainly on blood
May cause anaemia, dermatosis, paralysis, otoacariasis and
other infections (transmit viral, bacterial, protozoan and helminth pathogens)
Second only to mosquitoes in the number of diseases they transmit
Mites
Feed on skin debris or suck lymph
Some burrow into the skin, some live in hair follicles, and some in the ear canals
E.g. Scabies (burrows into skin and lays eggs- direct contact)
Fleas
Larvae are not parasitic but feed on debris associated mainly
with bedding
Adult stages are parasitic and feed on blood
Most fleas are not associated with humans but a few do feed
on humans
Plague is the most significant disease transmitted by fleas
Lice
Sucking and chewing varieties
Parasites that can also transmit disease
Most common among poor or overcrowded communities
Flies, Mosquitoes, Kissing bugs (What do they feed on & symptoms)
Flies
Among the most common insects
Those that transmit disease are generally bloodsuckers
Both adults and larvae may be parasitic
Cholera
E.g. Bot fly (Parasitic to mammals), intense pain.
Mosquitoes
Most important arthropod vector of disease
Carry some of the world’s most devastating diseases
Kissing bugs (Triatominae)
Feed on blood nocturnally near the mouth of their human hosts
while the host sleeps
Scabies