Module 1.1: Relational Database Technology
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Prelim Topic
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Relational Database
It is a collection of relations or two-dimensional tables.
Allows tables to be related by means of a common field.
As few as two tables can be considered a relational database if they share a common field
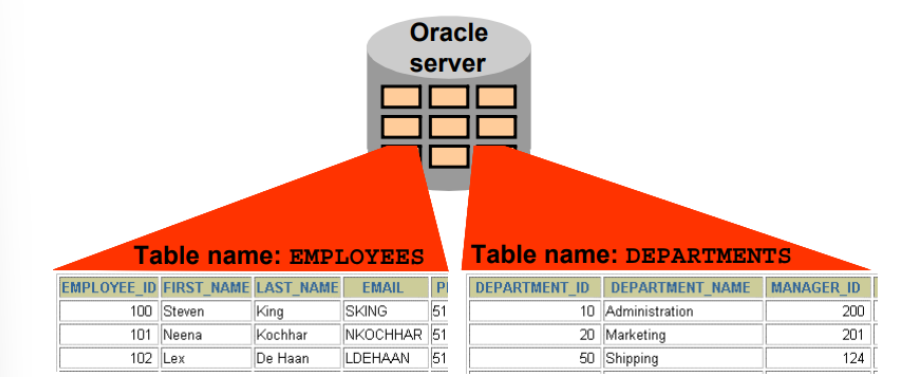
Table
(Key Terms)
Basic storage structure
Column
(Key Terms)
One kind of data in a table
Row
(Key Terms)
Data for one table instance
Field
(Key Terms)
The one value found at the intersection of a row and a column
Primary Key
(Key Terms)
Unique identifier for each row
Each row of data in a table is uniquely identified by this
Foreign Key
(Key Terms)
A column that refers to a primary-key column in another table
You can logically relate data from multiple tables using these
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
(Categories of SQL Statements)
These statements begin with SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, or MERGE and are used to modify the table data by entering new rows, changing existing rows, or removing existing rows.
Data Definition Language (DDL)
(Categories of SQL Statements)
These statements create, change, and remove data structures from the database.
The keywords CREATE, ALTER, DROP, RENAME, TRUNCATE, COMMENT.
Transaction Control Language (TCL)
(Categories of SQL Statements)
These statements are used to manage the changes made by DML statements.
Changes to the data are executed using COMMIT, ROLLBACK, and SAVEPOINT
_ changes can be grouped together into logical transactions
Data Control Language (DCL)
DCL keywords GRANT and REVOKE are used to give or remove access rights to the database and the structures within it