ZHANG CONCEPT MAP REVIEW/SI SESSION
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
what are the organs in renal anatomy
kidney
ureter
bladder
urethra
urine flow for renal anatomy
collecting ducts
minor calices
major calices
renal pelvis
ureter
bladder
urethra
what is the blood flow in renal anatomy
renal artery
segmental
interlobar
arcuate
interlobular
afferent arterioles
glomerular capillaries
efferent arterioles
basic histological and functional unit for renal is what
nephron
what are the functions in renal
glomerular filtration
tubular reabsorption
aldosterone regulated sodium reabsorption in collecting duct
arginine vasopressin regulates water reabsorption in the collecting duct
tubular secretion active secretion from the peritubular capillaries into the renal tubules hydrogen ions, potassium in the distal tubule
fluid flow of renal
bowman’s capsule
proximal convoluted tubule
loop of hence
distal convoluted tubule
collecting ducts
normal values of GFR for men
127
normal value of GFR in women
118
best index in renal is what
GFR
regulation of GFR by vessel tone is what
angiotensin ll
PGE2/PGI
constrict efferent
increases GFR
is what class?
angiotensin ll
dilate afferent
increase GFR
what class?
PGE2/PGI
Cl < GFR
molecule that is what ?
reabsorbed
Cl > GFR
molecule that is what?
secreted
water
small molecules
proteins
are in what category
glomerular filtration
in proteins what is not permeable ?
<5kDa
>60kDa
>60kDa
normal serum concentration range for potassium is what
3.5-5 mEq/L
intracellular potassium concentration is usually aprox what
150 mEq/L
what is responsible for the compartmentalization in potassium
Na+-K+-ATPase
what are primary causes of hypokalemia
loop and thiazide diuretic administration
excessive loss of potassium rich GI fluid as a result of diarrhea and/or vomiting
what are the drug induced hypokalemia
beta2 agonists
insulin overdose
high dose of penicillin
what are the primary causes of hyperkalemia
increase potassium intake
decrease potassium excretion
tubular unresponsiveness to aldosterone
redistribution of potassium into the extracellular space
what are the drug induced hyperkalemia
ACE-l
ARBs
direct renin inhibitors
potassium spring diuretics
NSAIDs
beta blockers
hypomagnesemia contributes to the development of what
hypokalemia
it is imperative to correct the hypomagnesemia before the hypokalemia (t/f)
true
alkalosis leads to what type of K
hypokalemia
acidosis leads to what type of K
hyperkalemia
when aldosterone is activated what happens to K
hypokalemia
when aldosterone is inhibited what happens to K
hyperkalemia
what are the drugs in aldosterone activation
loops and thiazide
what are the drugs in aldosterone inhibition
ACE
ARB
direct renin inhibitors
potassium sparing diuretics
NSAIDs
what happens to K when there is Na+-K+-ATPase activation
hypokalemia
what happens to K when there is Na+-K+-ATPase inhibition
hyperkalemia
hyperphosphatemia & hypocalcemia
secretion of PTH
PTH decreases phosphorus absorption and increase calcium reabsorption
PTH also increases calcium mobilization from bone
FGF-23 production in bone
resetting of calcium and phosphorus homeostasis with elevated PTH level
pathophysiology of CKD-MBD
what happens to PTH in vitamin D therapies
decrease PTH synthesis
calcitriol has more risk of what
hypercalcemia and hyperphosphatemia
paricalcitol and doxercalciferol has less risk of what
hypercalcemia and hyperphosphatemia
what does phosphate binders do to the phosphorus
lowers phosphorus absorption in GI
hypercalcemia and calcification is disadvantage of what
calcium containing binders
lower LDL & increases HDL is advantage of what
sevelamer
for patients with ESRD and hypercalcemia is advantage of what
lanthanum carbonate
CNS toxicity worsening
anemia
disadvantages of what
almuinum containing binders
what stage of CKD is >90
stage 1
what stage of CKD is 60-89
stage 2
what stage of CKD is 30-59
stage 3
what stage of CKD is 15-29
stage 4
what stage of CKD is <15
stage 5
loss of nephron mass
remaining nephrons hypertrophy
intraglomerular hypertension
proteinuria
damage of kidney tubular cells
progressive reduction in GFR
order for what
pathophysiology of CKD
what are the etiology of CKD
susceptibility factor
initiation factor
progression factor
what are the factors in initiation factor of CKD
diabetes
hypertension
glomerulonephritis
what are the factors in progression factor of CKD
smoking
obesity
what are the preferred agents in CKD
ACE and ARBs
what class has no effect on bradykinin metabolism and are therefore more selective blockers of angiotensin effects than ACE
ARBs
ARBs also have the potential for more complete inhibition of angiotensin action compared with ACE inhibitor because there are enzymes other than ACE that are capable of generation angiotensin ll
true
What is less likely to cause cough than ACEs
ARBs
what balance determines the serum sodium concentration
water balance
what balance determines the volume status
sodium
hypertonic solution to the ECF does what to the volume
decrease in ICF (cell) volume
hypotonic solution to the ECF does what to the volume
increase in cell volume
hypertonic hyponatremia, the presence of excess, effective osmoses other than sodium in the ECF is what
glucose, glycine, sorbitol
in hypovolemic what drug causes hyponatremia
thiazide diuretics
diarrhea
in hypovolemic what causes hypernatremia
osmotic diuresis
in euvolemic what causes hyponatremia
SIADH
in euvolemic what causes hypernatremia
diabetes insipidus
in hypervolemic what causes hyponatremia
edema
in hypervolemic what causes hypernatremia
water weight, bloat (sodium overload)
in cortex how much percentage of renal blood flow goes to the cortex
90%
Which of the following best describes the chronological order of urine flow?
A. Renal artery → segmental → interlobar → arcuate → interlobular → afferent
arterioles → glomerular capillaries → efferent arterioles
B. Renal artery → segmental → interlobar → arcuate → interlobular → efferent
arterioles → glomerular capillaries → afferent arterioles
C. Collecting ducts → minor calyces → major calyces → renal pelvis → ureter →
bladder → urethra
D. Collecting ducts → minor calyces → major calyces → renal pelvis → bladder →
ureter → urethra
C
Which of the following best describes the chronological order of renal blood flow?
A. Renal artery → segmental → interlobar → arcuate → interlobular → afferent
arterioles → glomerular capillaries → efferent arterioles
B. Renal artery → segmental → interlobar → arcuate → interlobular → efferent
arterioles → glomerular capillaries → afferent arterioles
C. Collecting ducts → minor calyces → major calyces → renal pelvis → ureter →
bladder → urethra
D. Collecting ducts → minor calyces → major calyces → renal pelvis → bladder →
ureter → urethra
A
what is the functional unit of kidney
nephron
what are the major electrolytes that the kidney regulates
Potassium
sodium
chloride
list some endogenously produced waste materials
creatinine
urea
uric acid
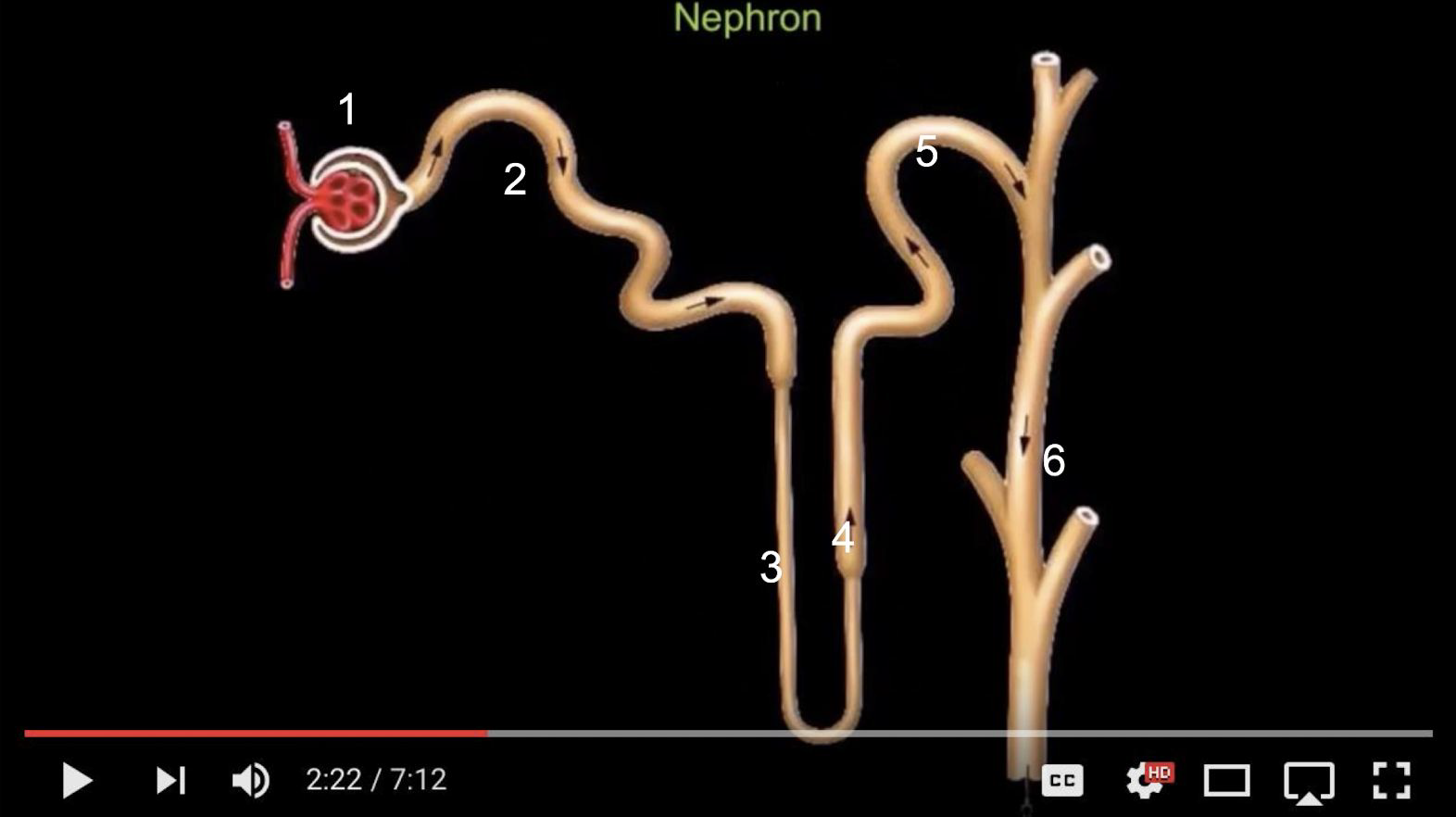
what is the fluid flow ?
1. Bowman’s capsule
2. Proximal convoluted tubule
3. Descending limb of the loop of Henle
4. Ascending limb of the loop of henle
5. Distal convoluted tubule
6. Collecting ducts
Which of the following are functions of the nephron? SATA
A. Glomerular filtration
B. Tubular secretion
C. Tubular reabsorption
D. Protein synthesis
E. Erythropoietin production
A, B, C
Where does glomerular filtration take place in the nephron?
A. Proximal convoluted tubule
B. Bowman’s capsule
C. Loop of Henle
D. Collecting duct
B
Which hormone increases sodium reabsorption in the collecting duct?
A. Vasopressin (ADH)
B. Aldosterone
C. Renin
D. Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
B
Which part of the nephron is impermeable to water? SATA
A. Descending limb of loop of Henle
B. Ascending limb of loop of Henle
C. Proximal tubule
D. Distal tubule
E. Collecting duct (with ADH present)
B,D
Which nerve carries parasympathetic innervation to the bladder?
A. Hypogastric
B. Pelvic
C. Pudendal
D. Vagus
B
Which receptor prevents bladder emptying by contracting the sphincter?
A. M3
B. β3
C. α1
D. M2
C
what nerve is sympathetic
hypogastric
what nerve is somatic
pudendal
Passive process where water and small molecules and ions (< _____ kDa)
diffuse across glomerular-capillary membrane into Bowman’s capsule then
enter the proximal tubule.
5-10
Can proteins be filtered?
no, most proteins are too large
Which of the following is the best index of kidney function?
A. Serum urea concentration
B. Serum creatinine alone
C. Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
D. Urine osmolality
C
Which factor increases GFR by constricting the efferent arteriole?
A. Angiotensin II
B. Prostaglandin E2
C. NSAIDs
D. ACE inhibitors
A
Creatinine clearance tends to ___________ GFR because creatinine undergoes
tubular secretion.
overestimate
creatinine is not only filtered at the glomerulus, but also secreted into
the tubules from the peritubular capillaries. (t/f)
true
Prostaglandin E2 dilates the ________ arteriole, while NSAIDs cause its constriction.
afferent
Rhabdomyolysis
Creatine supplements
High meat diet
increase or decrease SCr
increase
Amputation
Malnutrition
Muscle wasting
Medications
increase or decrease SCr
decrease SCr
what does increase SCr do to CrCl
underestimate
what does decrease SCr do to CrCl
overestimate
Loading doses are dependent on elimination
Maintenance doses are dependent on elimination
You must adjust the loading dose in patients with renal impairment
You must adjust the maintenance dose in patients with renal impairment
answer if each statements are true or false
false
true
false
true
Which of the following drugs require dose adjustment in patients with renal
impairment? SATA
A. Lovenox
B. Warfarin
C. Xarelto
D. Heparin
E. Fentanyl
F. Keppra
G. Morphine
H. Amikacin
A,C,F,G,H
● Enoxaparin, but not unfractionated heparin
● DOACs, but not warfarin
● Digoxin
● Opioids
(Fentanyl does not)
● Metoclopramide
● Lithium
● Vancomycin
● Aminoglycosides
drugs that has to be renally adjusted
Which medications are known to cause hypokalemia? (Select all that apply)
A. Beta2 agonists
B. Insulin overdose
C. Potassium-sparing diuretics
D. High-dose penicillins
E. ACE inhibitors
A, B, D
Hypokalemia due to gastrointestinal loss can occur through which of the following? (Select all that apply)
A. Vomiting
B. Constipation
C. Diarrhea
D. GI suctioning
A,C,D
Patient’s potassium level is 3.2 mEq/L and does not report muscle weakness or N/V
Patient’s potassium level is 2.6 mEq/L and does report muscle weakness of N/V
Patient potassium level is 3.6 mEq/L and reports feeling fatigued
Patient’s potassium level is 2.4 mEq/L and is currently intubated
no need for supplements
initial oral potassium
each more potassium food
initiate IV potassium supplements
Which of the following potassium supplement formulations is more likely to cause gastrointestinal upset and therefore should be taken with meals and a full glass of water?
A. Potassium chloride liquid
B. Wax-matrix extended-release tablets
C. Controlled-release microencapsulated tablets
D. Effervescent potassium tablets
B
A 67-year-old woman with diabetic nephropathy (CKD stage 5,not on dialysis yet) presents with weakness and nausea.
Labs:
Na⁺ = 140 mEq/L
K⁺ = 6.8 mEq/L
Mg²⁺ = 2.1 mg/dL
Ca²⁺ = 9.0 mg/dL
EKG: Peaked T waves, wide QRS
What is the first immediate intervention?
A. IV insulin with dextrose
B. IV calcium gluconate
C. Sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (Lokelma®)
D. Hemodialysis
B