Firearms and Toolmarks- Final Exam
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
What can function testing include?
Determining if the firearm is in mechanical operating condition
Testing firing
Determining if safety features are functioning properly
Testing scenarios for accidental discharge
Types of revolvers
Double-Action
Single-Action
Top-Break
Single-Action
Action requiring the manual cocking of the firing mechanism
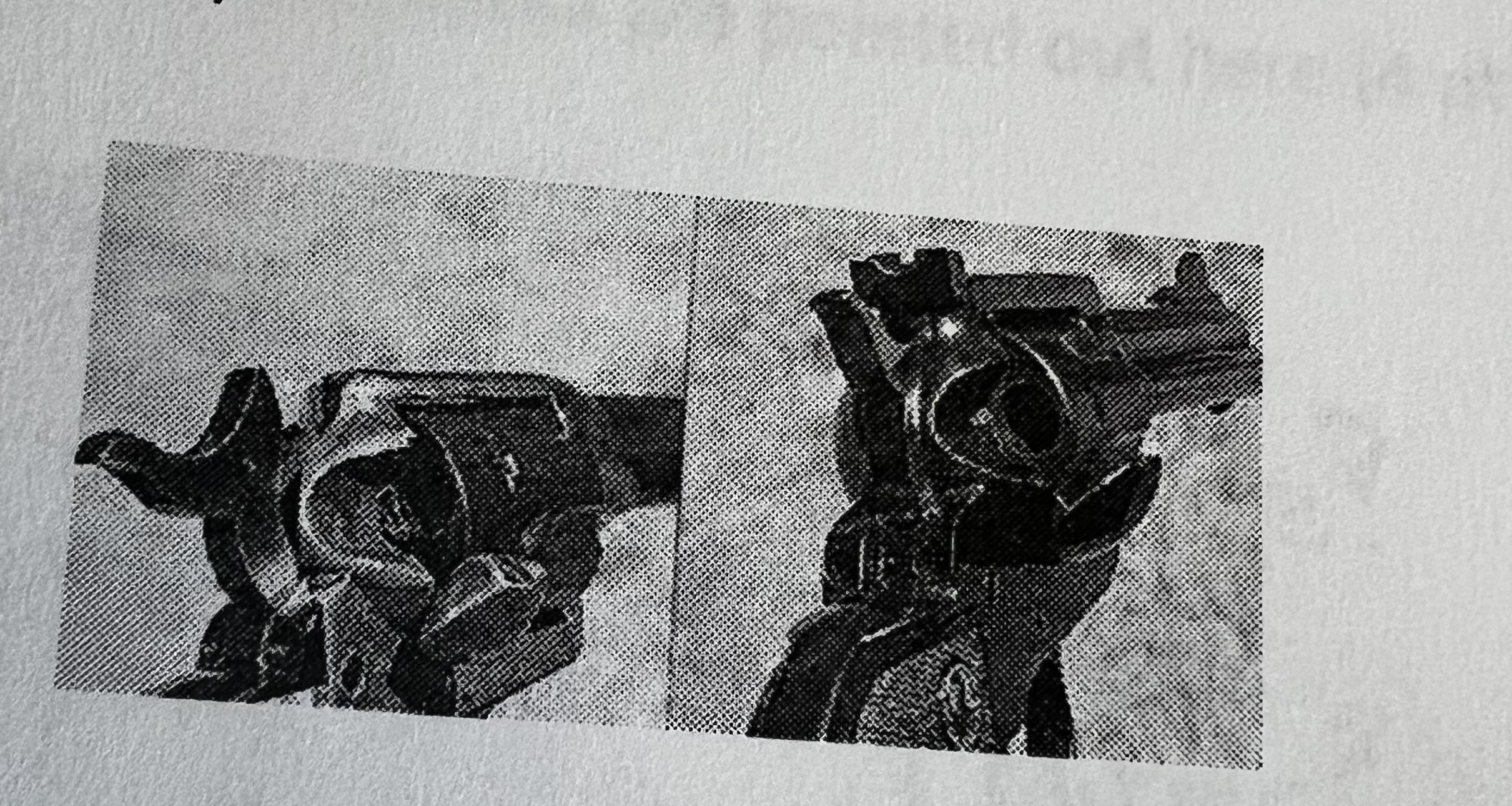

Double-Action
Action in which a single pull of the trigger cocks and releases the firing mechanism

Top-Break
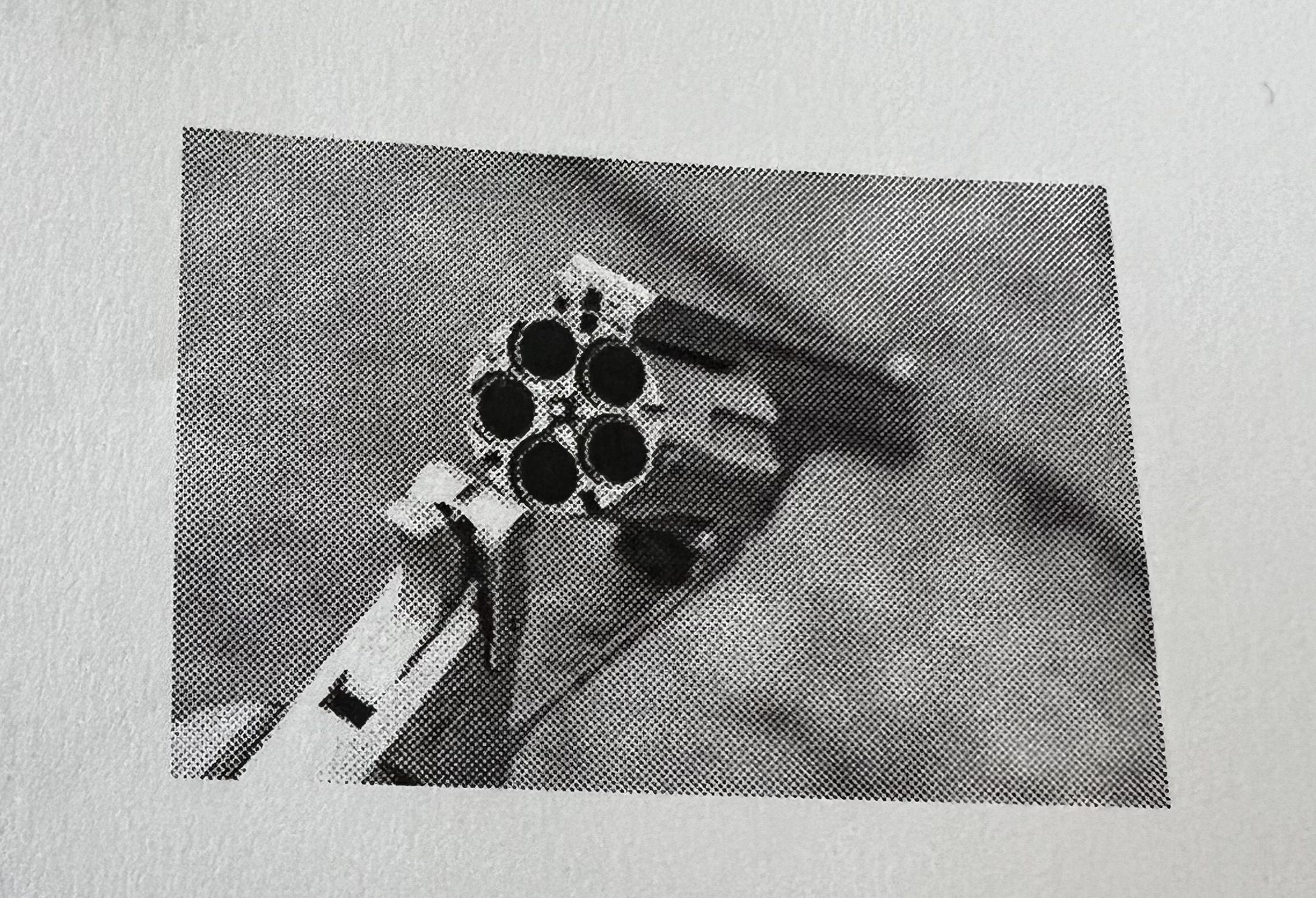
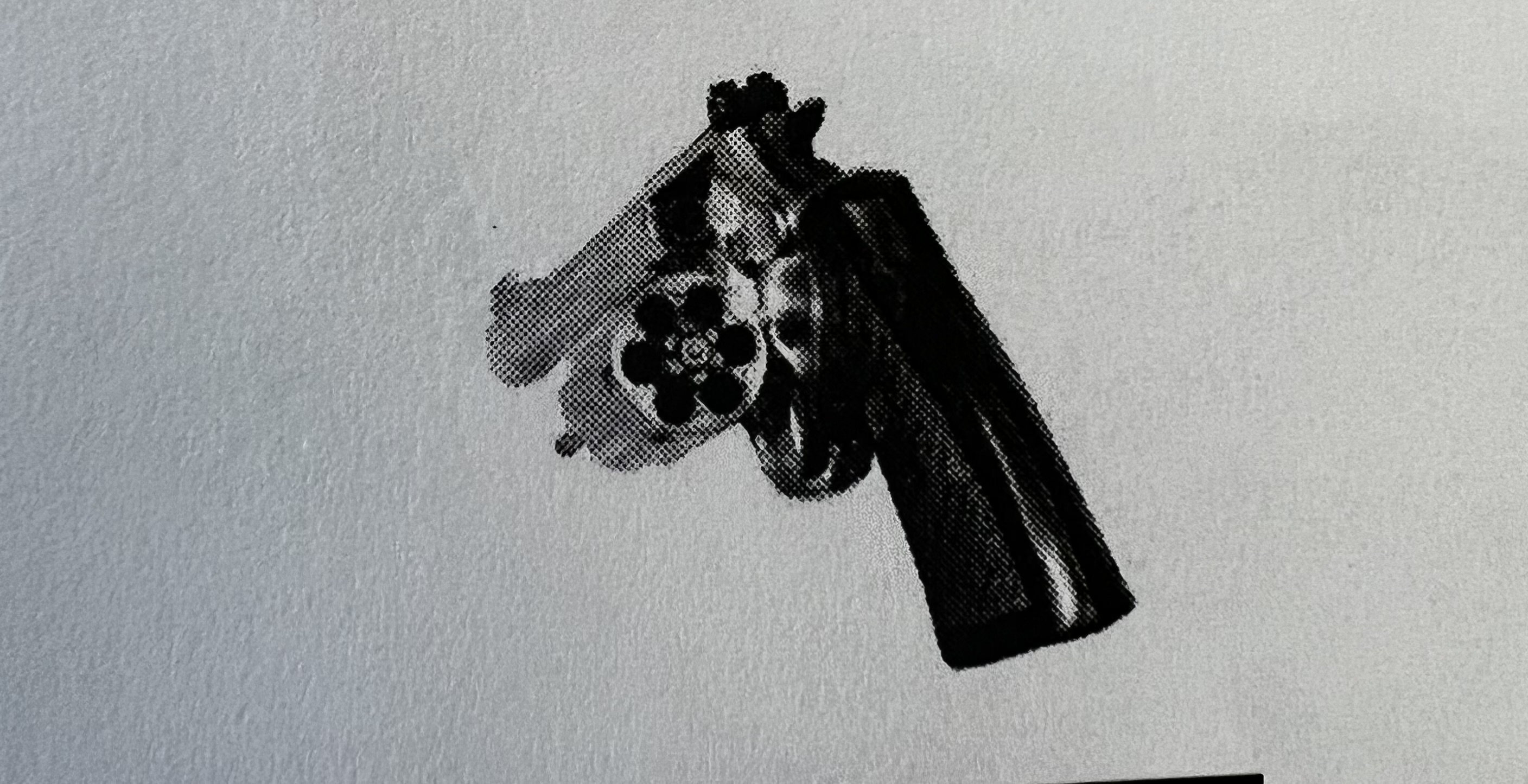
Two safeties that may be on a revolver
Hammer Block
Transfer Bar
Conventional
Rifling with sharp, defined edges between that land and groove

Polygonal
Rifling in which lands and grooves have a rounded profile
General Rifling Characteristics (GRC)
Number of lands and grooves
Width of lands and grooves
Direction of twist
Caliber
Hybrid
design that incorporates aspects of both single action and double action
Two types of firing mechanisms for pistols
Hammer Fired
Striker Fired
Blowback
mechanism has the barrel of the firearm fixed to the frame and the weight of the slide and tension on the recoil spring keeps the breech closed during firing
Recoil
mechanism is the barrel of the firearm no fixed to the frame and the slide and barrel travel/lock together for a portion of the recoil
Gas-operated
mechanism uses the propellant gases to unlock the breech and complete the cycle of extracting and ejecting
Three safeties that may be on a pistol
Key Lock
Disconnect
Manual grip safety
Accidental
discharge typically involves the discharge of a firearm without the trigger being pulled
Unintentional
discharge involved the trigger being pulled without the intent to fire
Semiautomatic
action in which each pull of the trigger results in a complete firing cycle
Automatic
firearm design that feeds cartridges, fires, extracts, and ejects cartridge cases as long as the trigger is fully depressed and there are cartridges in the feed system
Two types of rifles
Gas-operated
Lever action
Direct impingement
Gas is bled rearward to cycle the action in a rifle
Indirect impingement
Gas moves a piston, piston cycles the action in a rifle
Two common safety features on a rifle
cross bolt safety
disconnector
Military versions of the AR-type rifle may have a selector switch to choose between….
Semiautomatic
Automatic fire
Burst mode
Safe mode
AR-type rifles have what types of cartridges?
223 Remington/5.56 × 45 mm
AK-type and SKS-type rifles have what types of cartridges?
7.62 × 39 mm
Two types of shotguns
Slide-Action
Break open
Two common safety features on a shotgun
Trigger Safety
Lever Safety
True or False: 10 gauge has a smaller barrel diameter than 28 gauge
False
Choke
interior constriction at or near the muzzle end of a shotgun barrel bore to control shot dispersion
Rifles and Shotguns are….
Single Action
Breechface
area of a firearm that supports the head during firing
Firing pin aperture
opening in the firearm slide where the firing pin comes through
Shear
Types of marks produced when the firearm unlocks and scrapes the cartridge case across the surface of the breech face
Class Characteristics of Breechface Mark
Parallel
Circular
Arched
Granular
Cross-Hatched
Parallel Breechface Mark
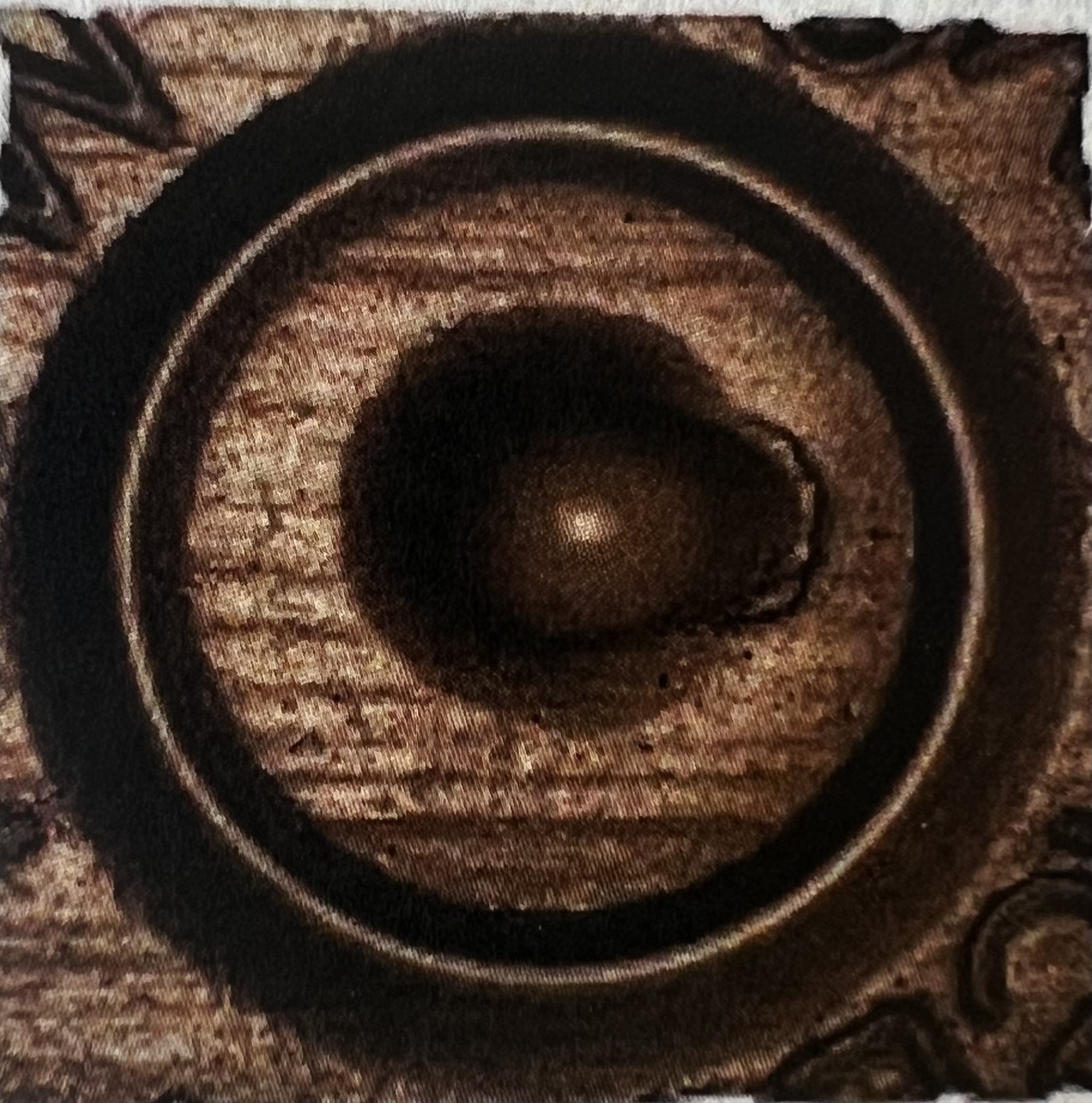

Circular Breechface Mark
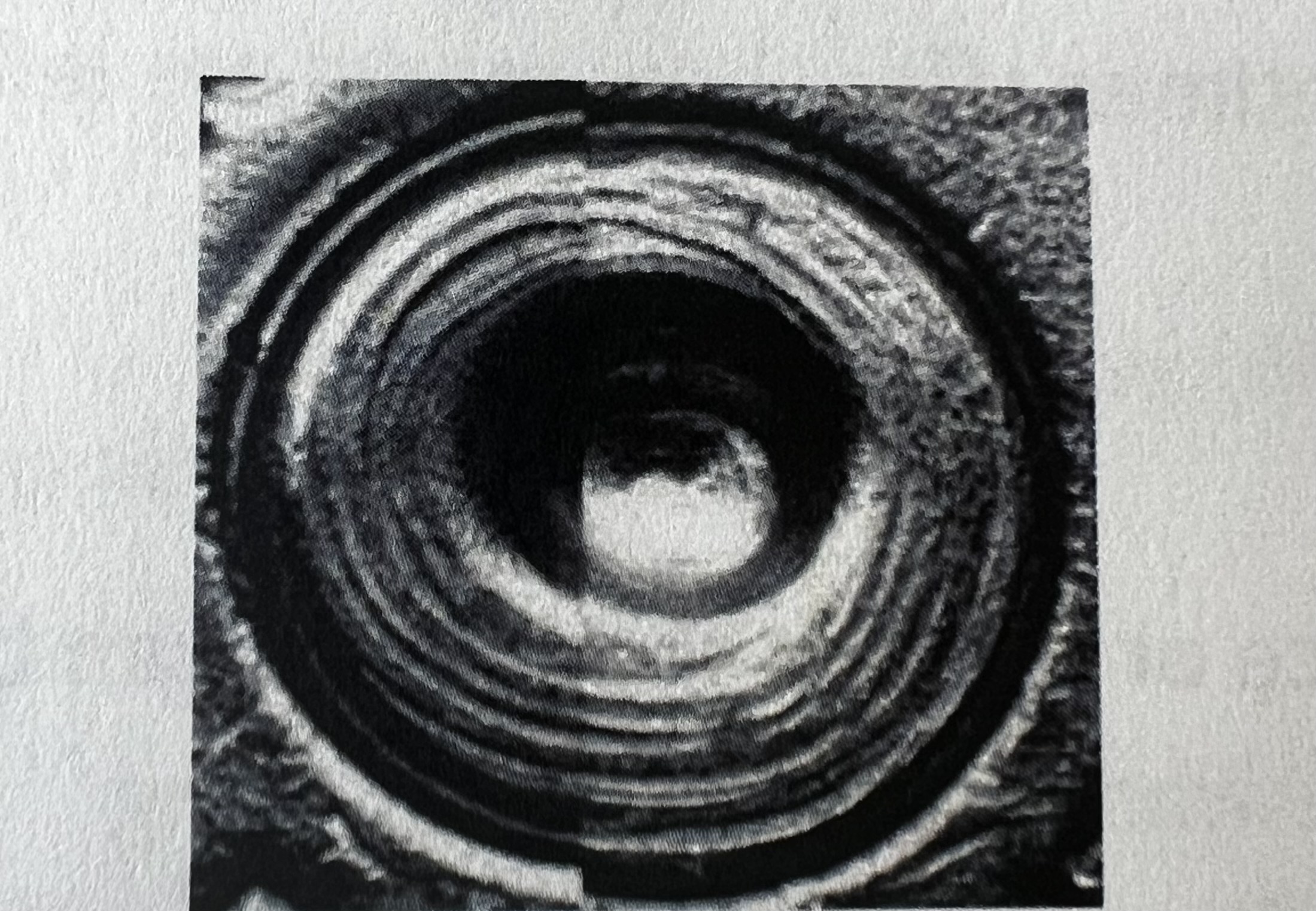
Arched Breechface Mark
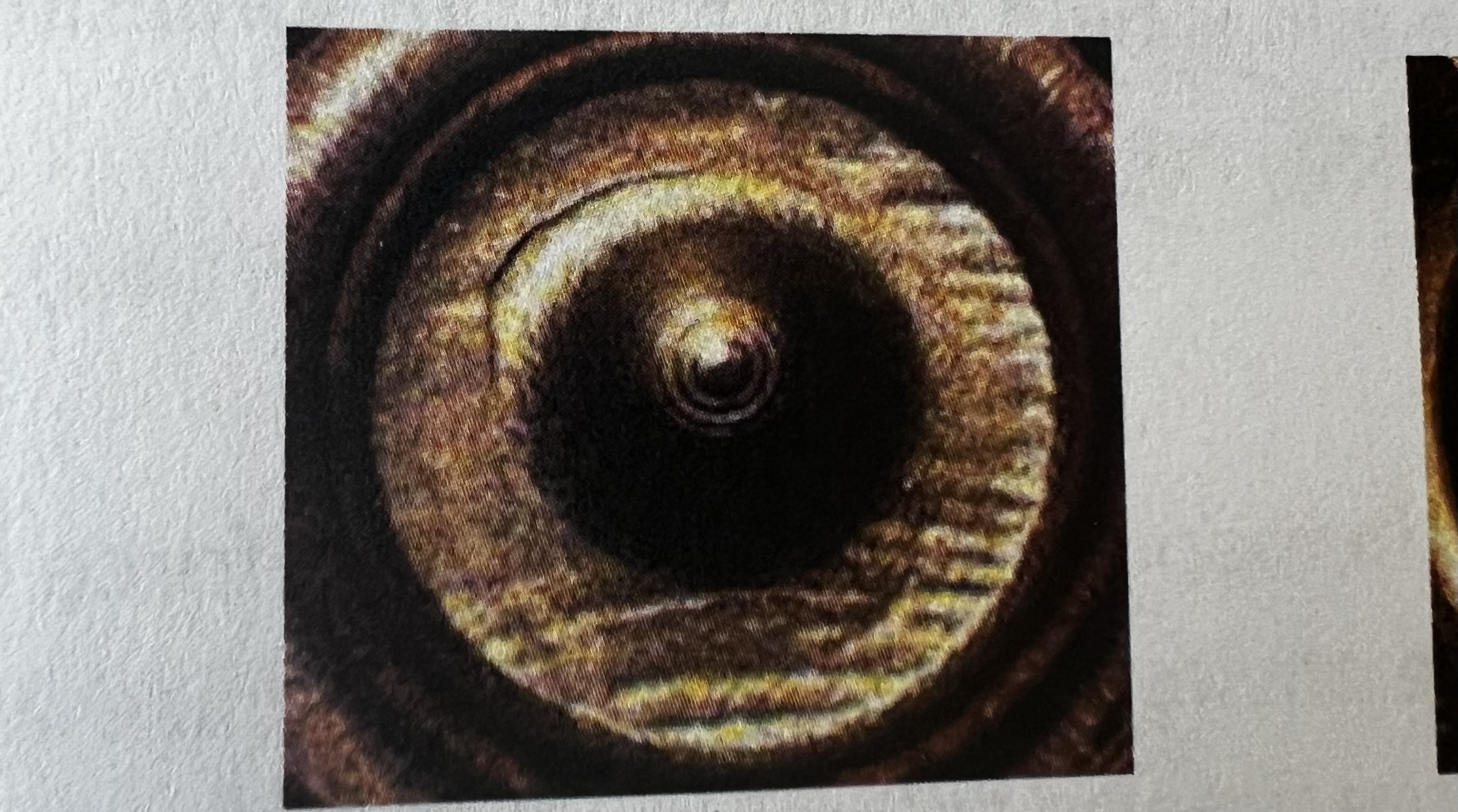

Granular Breechface Mark
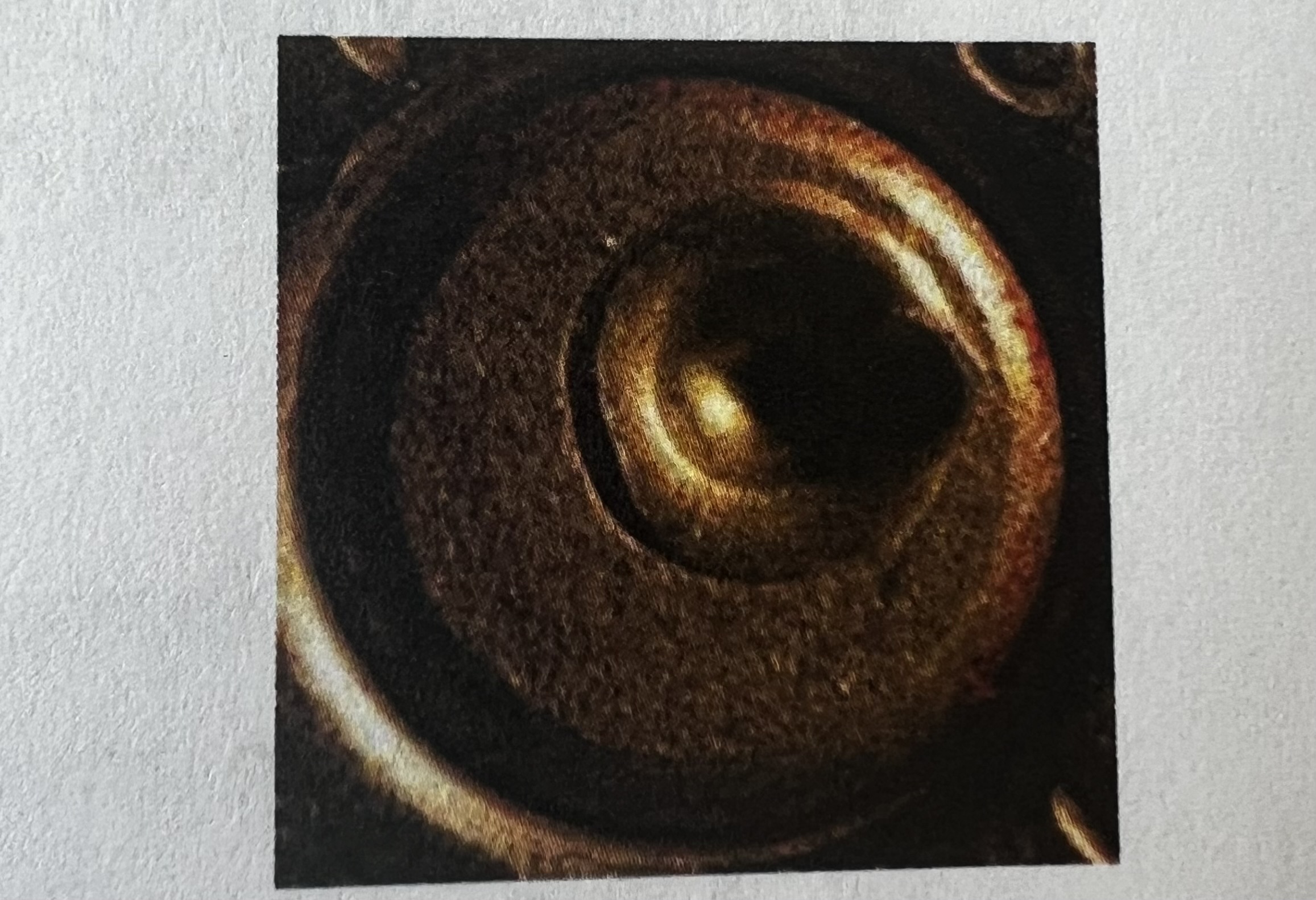
Hemispherical Firing Pin Mark
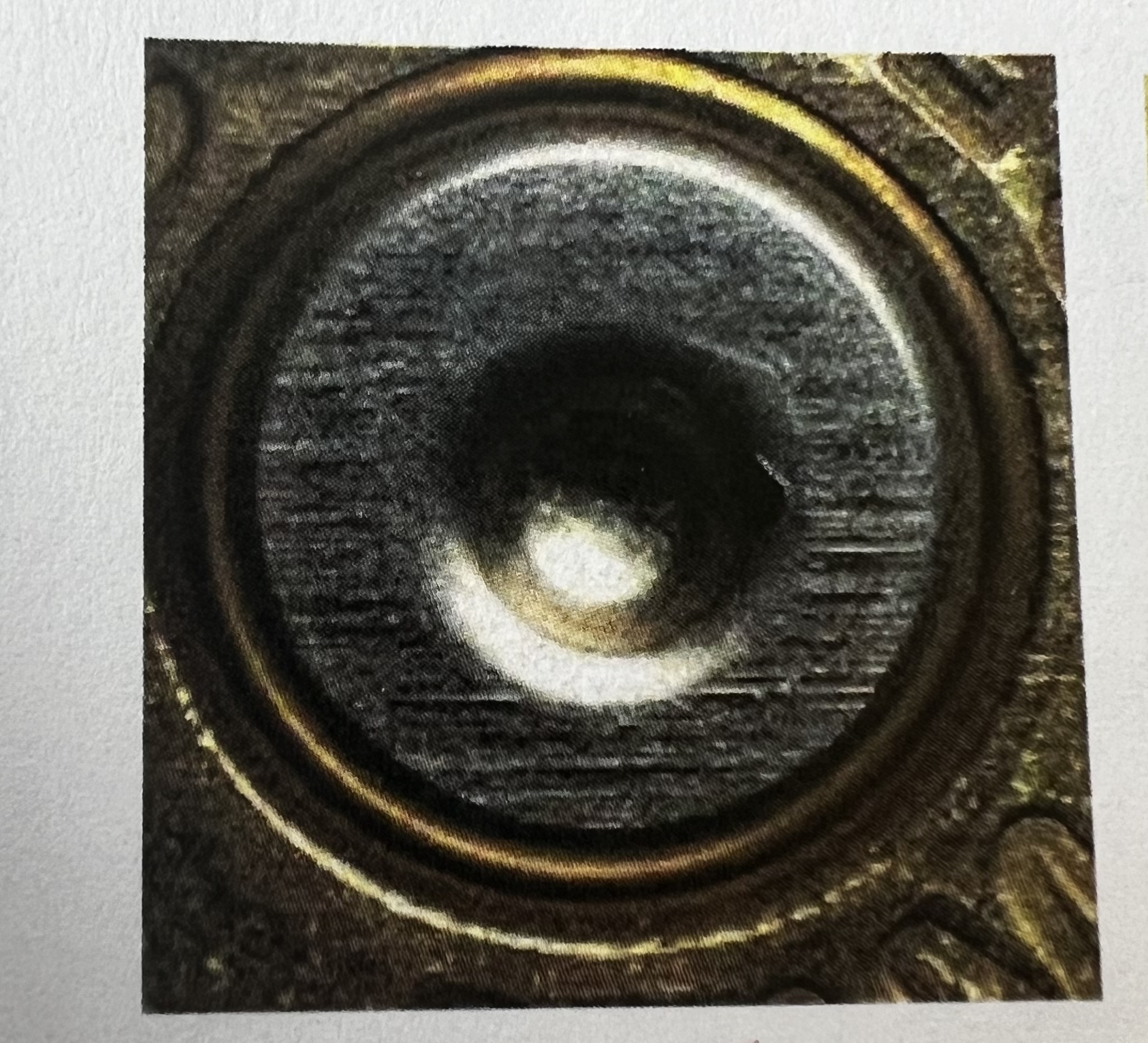

Rectangular Firing Pin Mark
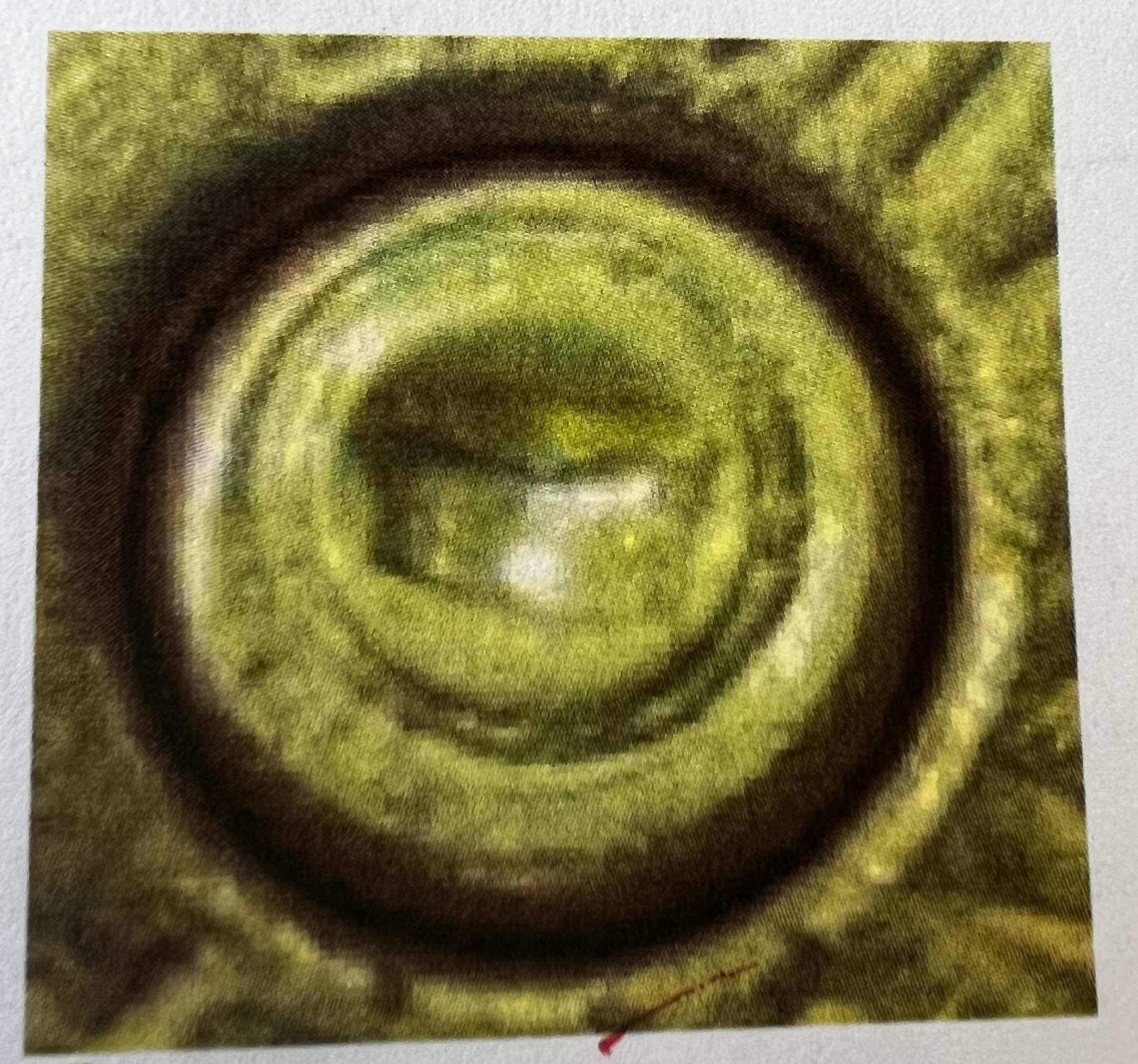
Elliptical Firing Pin Mark
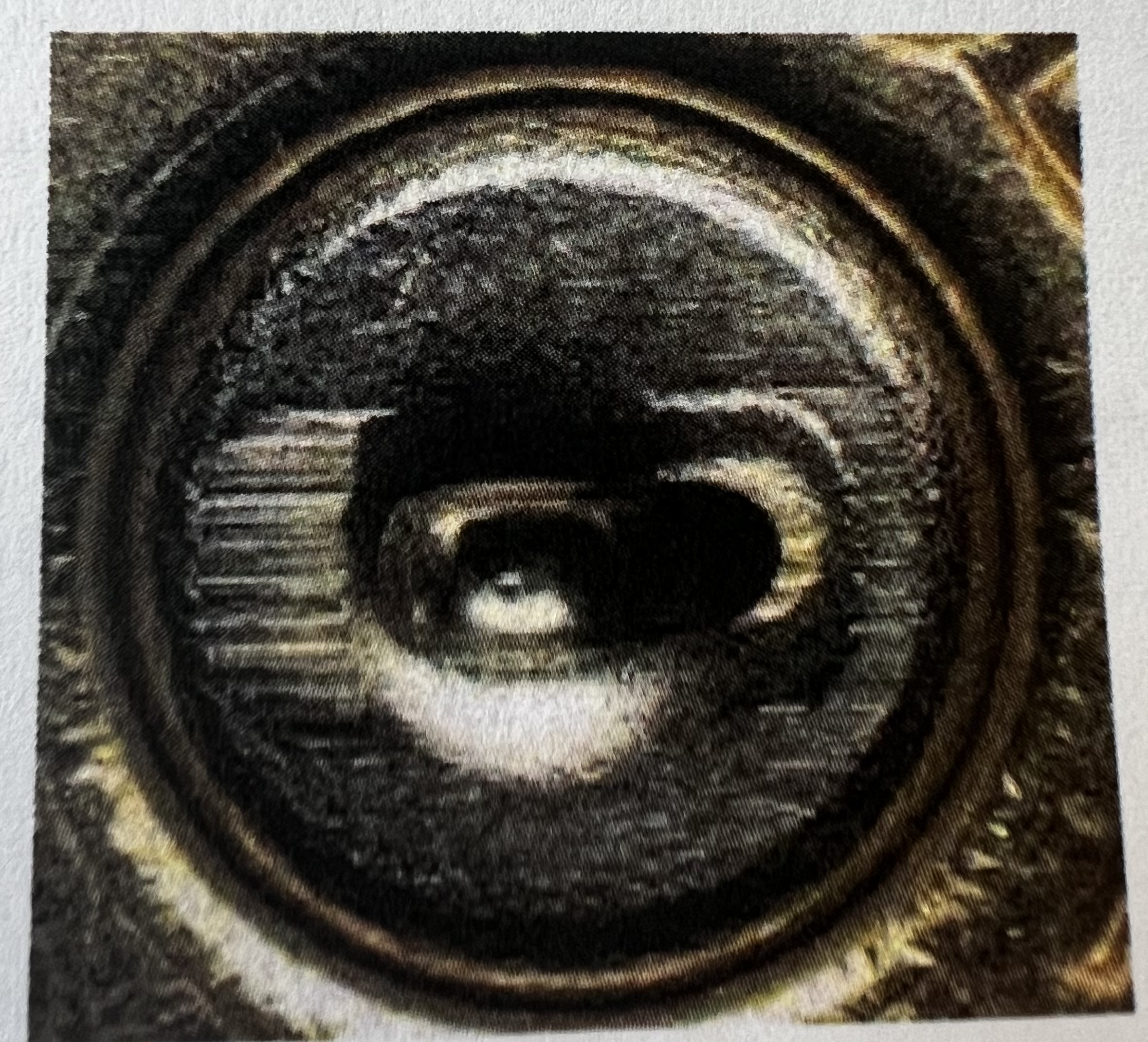
Circular Firing Pin Mark
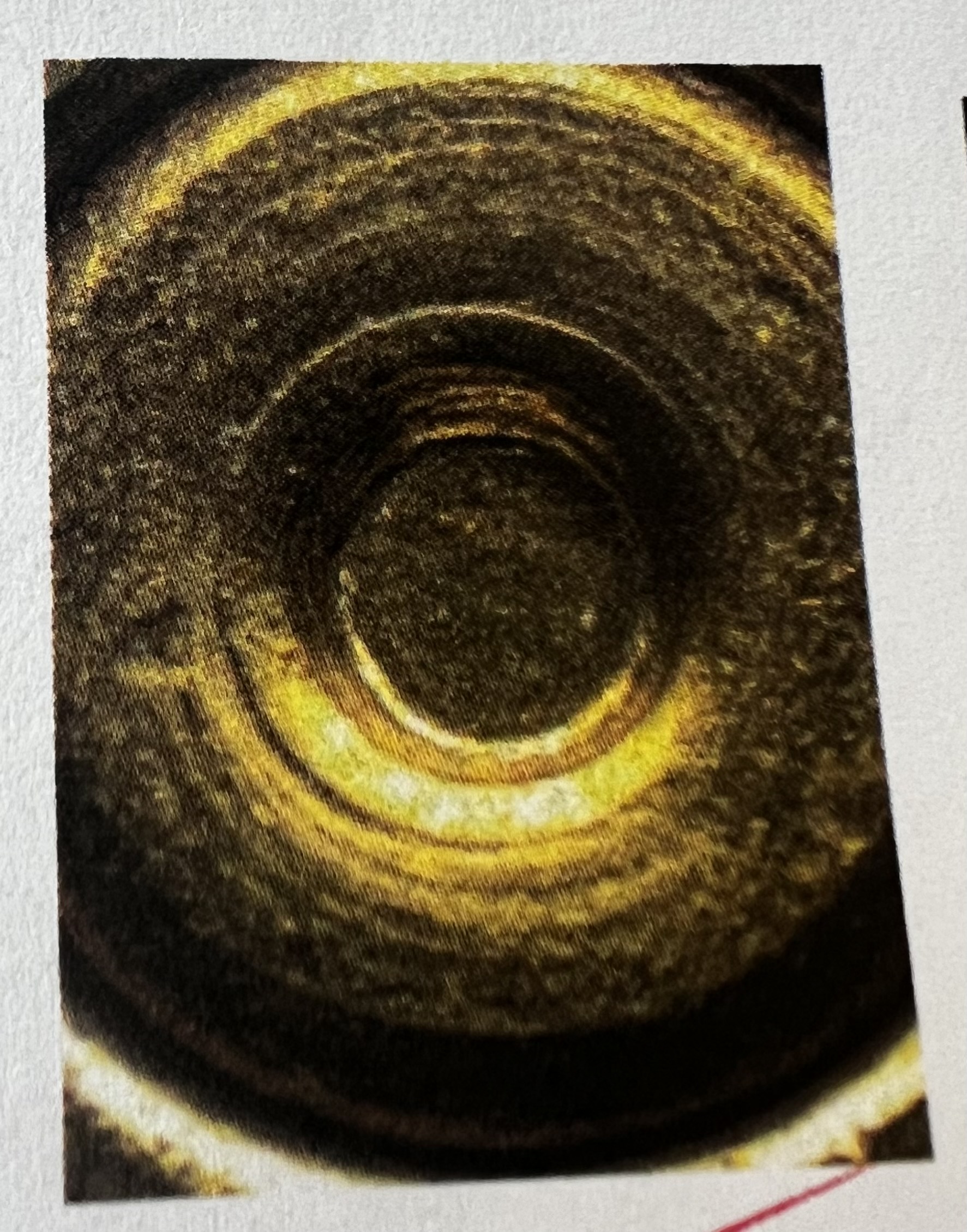
D-shaped Firing Pin Mark
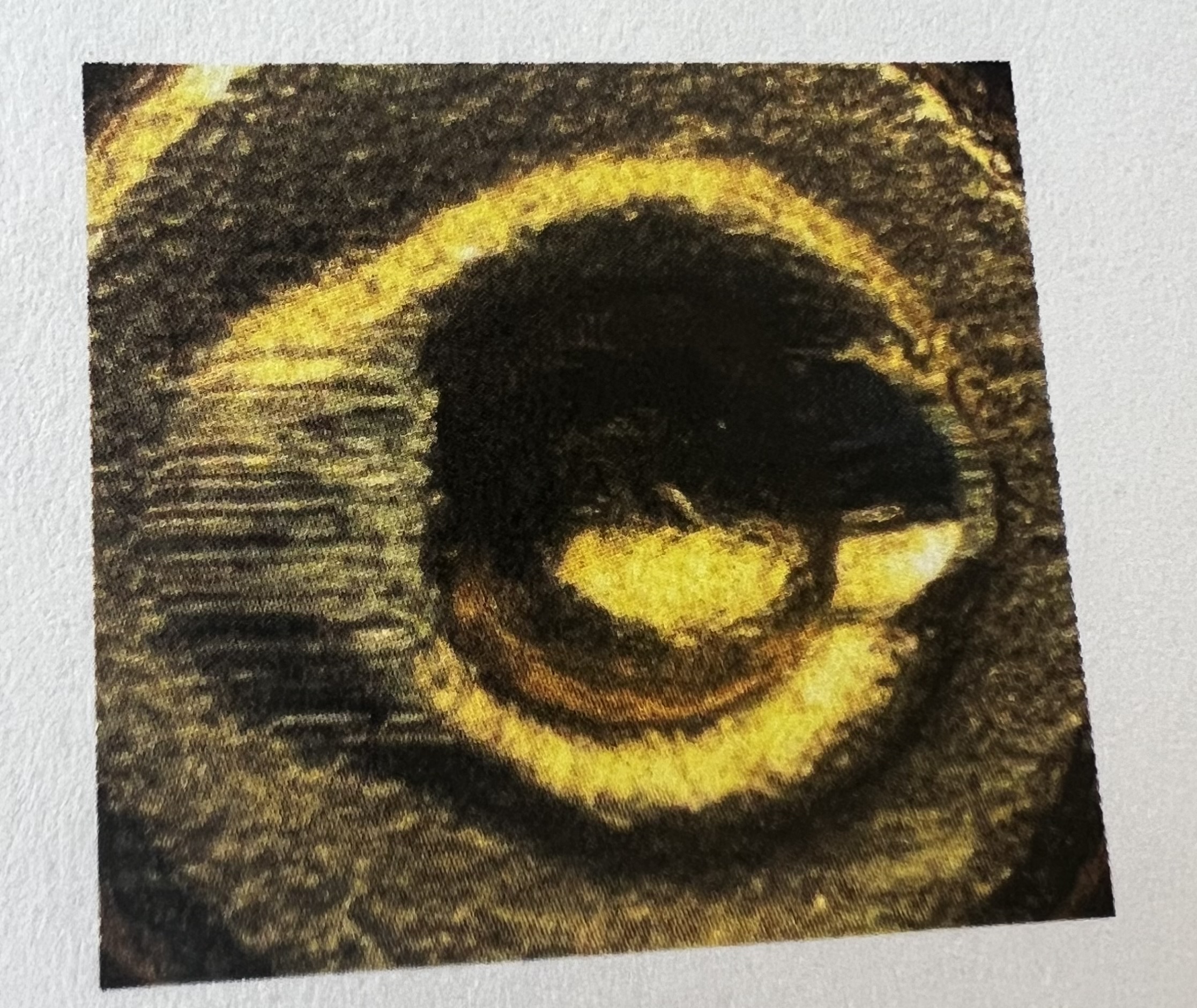
Two marks that can be created on a cartridge of a firearm without it being fired
Extractor
Ejector
Reproducibility
the appearance of the same marks in repeated test samples describes what concept?
What are some reasons that some features might not reproduce over all samples?
Different cartridge materials
Different projectile weights
True or False: NIBIN digitally captures images of cartridge cases, searches them against other images in the database, and automatically makes a match of the identified cartridge cases
False
True or False: The way a gun is held when fired can sometimes affect how marks are left behind on cartridge components
True
Variations in mark reproducibility from force or angle in the firearm can be attributed to this:
large firearm tolerances (loose fit of parts)
Distance Determination
the process of determining the distance from the firearm, usually the muzzle, to the target based on patterns of gunpowder or gunshot residues deposited upon that target
Gunshot residues can include these two things
Lead
Nitrate
Gunshot residues are expelled from what areas of the firearm
Muzzle
Ejection Port
Cylinder Gap
Breech
Modified Griess Test
Chemical Testing for nitrate compounds
Sodium Rhodizonate Test
Chemical Testing for lead residues
How firearms should be packaged
Unload → Ziptie → Proper seal w/ initials → immobilize item
True or False: For guns in water, submit the firearms fully submerged in the water it was found in
True
Describe how to package tools for examination in the firearms fully submerged in the water it was found in
protect the working surface → under proper seal → and immobilize
Tool
an object used to gain mechanical advantage
factors that affect the production of toolmarks
Direction
Force
Rate of Speed
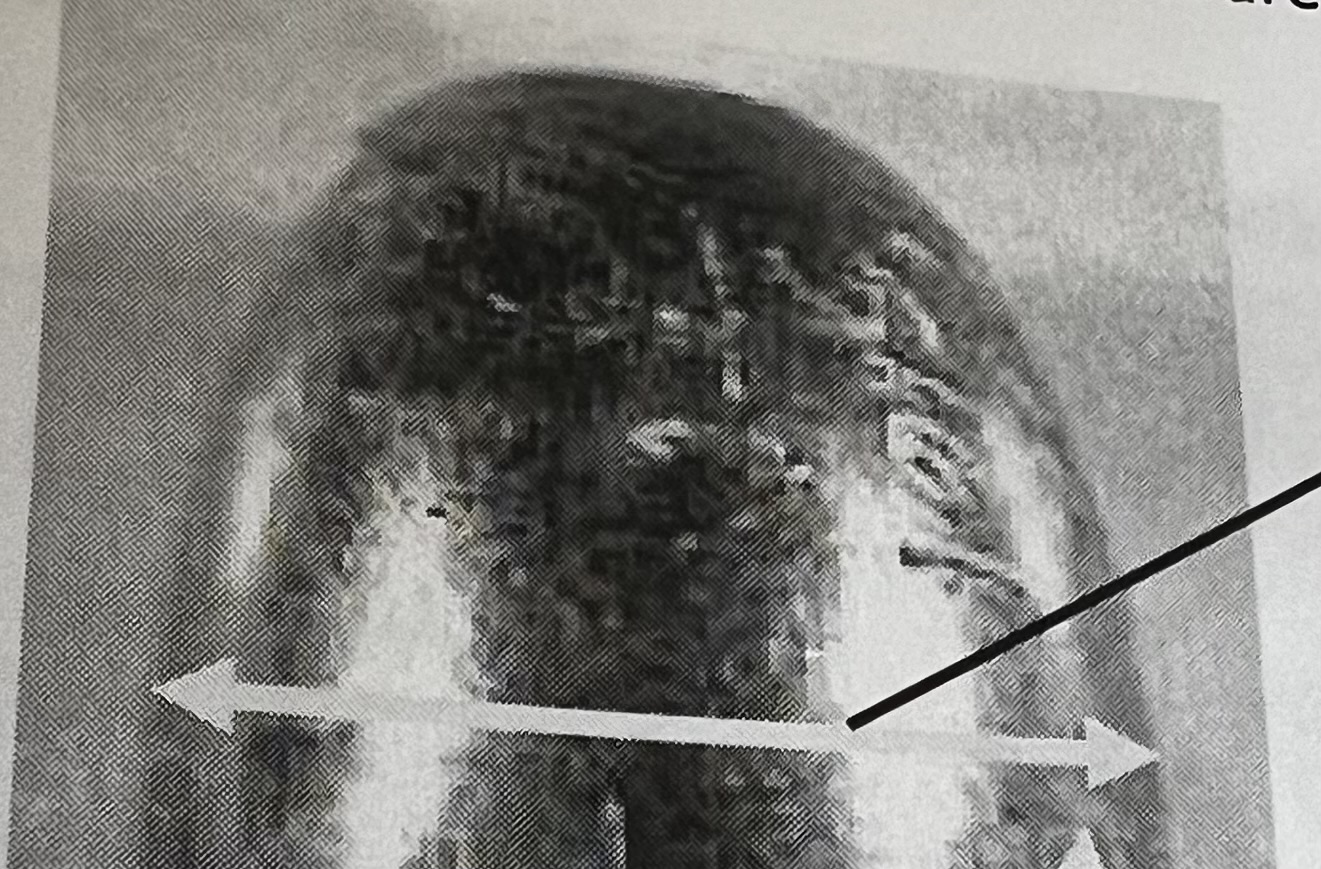
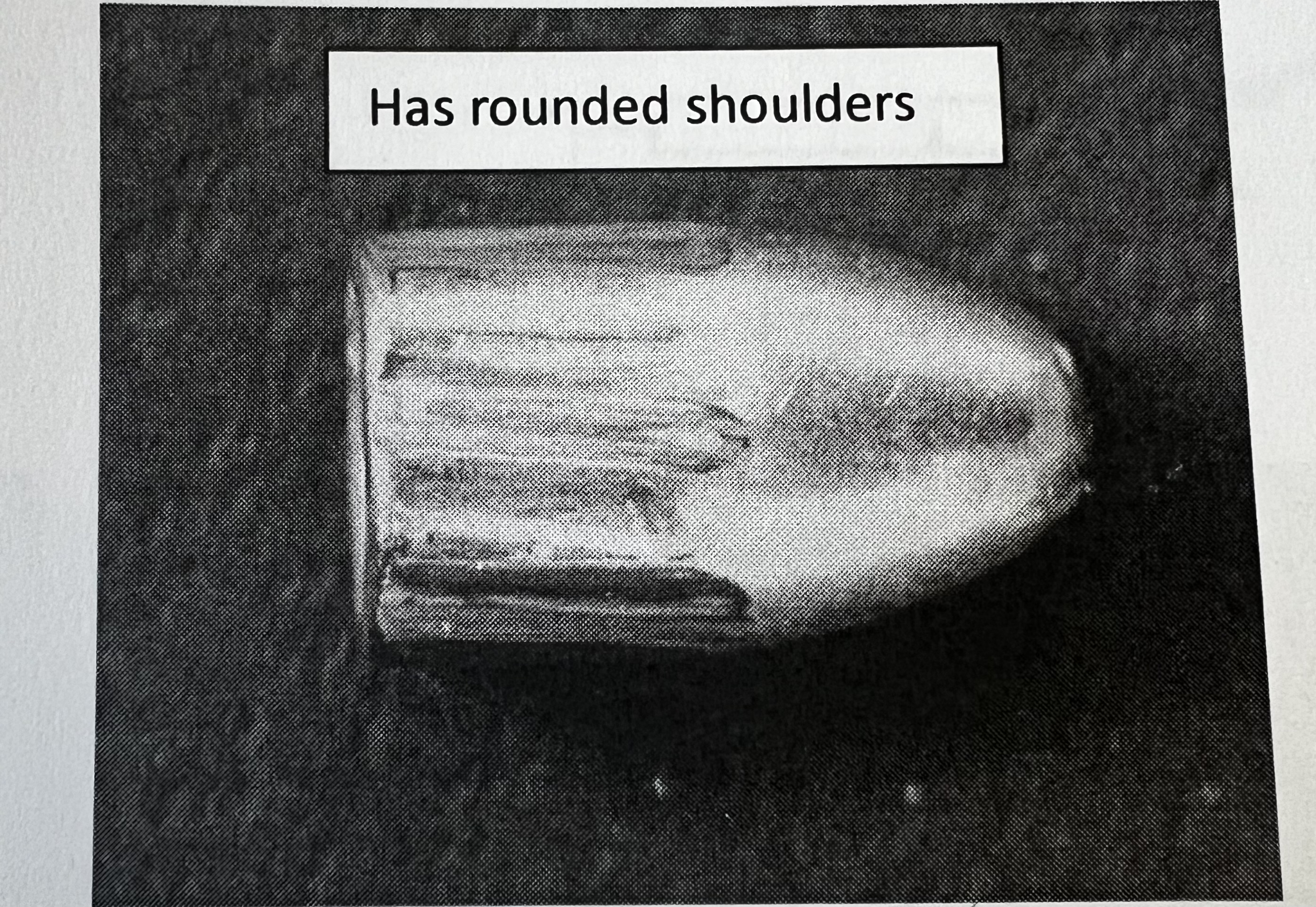
What general rifling characteristic is this?
Caliber
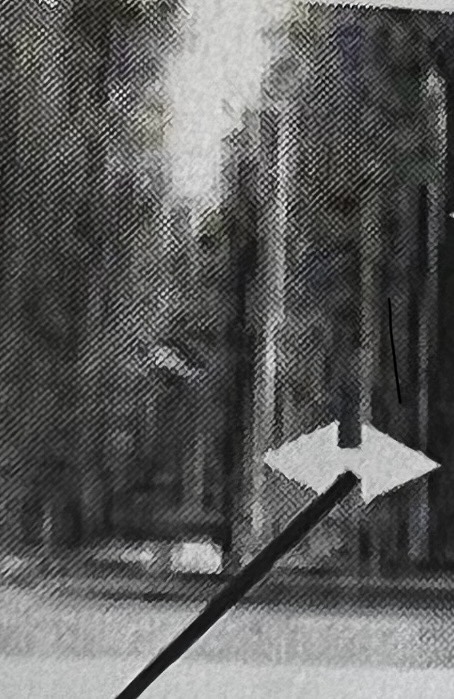

What general rifling characteristics is this?
Land
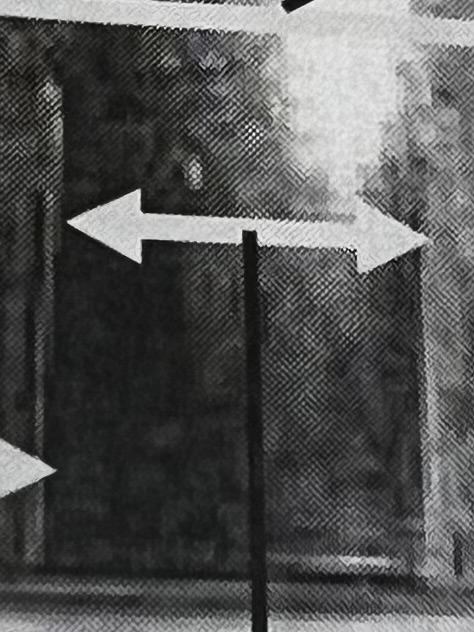

What general rifling characteristics is this?
Grooves
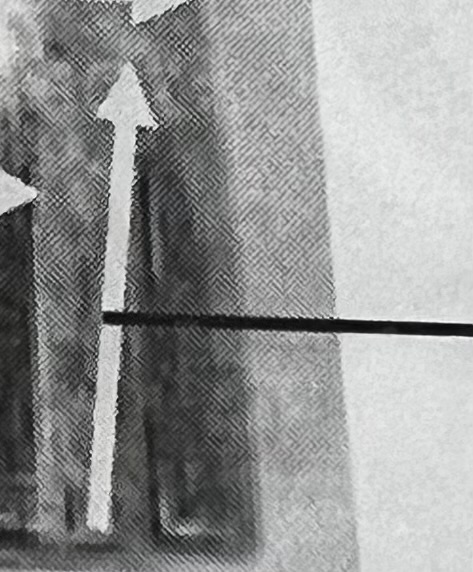
What general rifling characteristic is this?
Twist
two common causes of malfunctions
failure to load
failure to extract/eject
toolmark identification
the discipline of forensic science where the primary concern is to determine if a particular tools produced a tool mark
Tool
an object used to gain mechanical advantage, thought of as the harder of two objects
Subclass Characteristics
consistent among different items same tool in the same approximate state of wear
Striated Toolmark
tool is moved across the object (force and motion parallel to surface)
Impressed Toolmark
leaves an impression (force and motion perpendicular)
Microscopic Comparisons: Identification
Identified as produced by same tool
Microscopic Comparisons: Elimination
Eliminated by a particular tool
Eliminated by the same tool
Microscopic Comparisons: Inconclusive
not be identified or eliminated as having been produced by a particular tool
Microscopic Comparisons: Not suitable (unsuitable) for comparison
No microscopic markings present
Relative hardness between tool and surface too similar – marks not transferred from tool
Markings present are of poor quality and/or quantity
Tool may not produce suitable markings
Damaged after the mark was imparted (overlapping marks)
Blood and other body fluids can erode markings on metallic materials
Poor quality of a cast toolmark
Toolmark
Mark is produced when two objects come into forcible contact with one another- the softer surface receiving the mark
Tool Classification
Compression
Hammer
Punch
Stamp
Flat Action (Scraping)
Screwdriver
Chisel
Pry Bar
Slicing
Knife
Box Cutter
Axe
Gripping
Pipe Wrench
Groove and Joint Pliers
Pinching
Bolt Cutter
Diagonal Cutter
Shearing
Scissors
Tin Snips
Shears
Groove Joint Pliers
Gripping Tool
Class Characteristics include:
Jaw width
Jaw length
Teeth spacing
Jaw lip length
Number of teeth
Maximum opening
Improper Packaging
Plastic or paper bags
Unprotected edges
Preferred Packaging
Rigid boxes or container
Protect the edges and working surfaces of the tool
Consider trace evidence
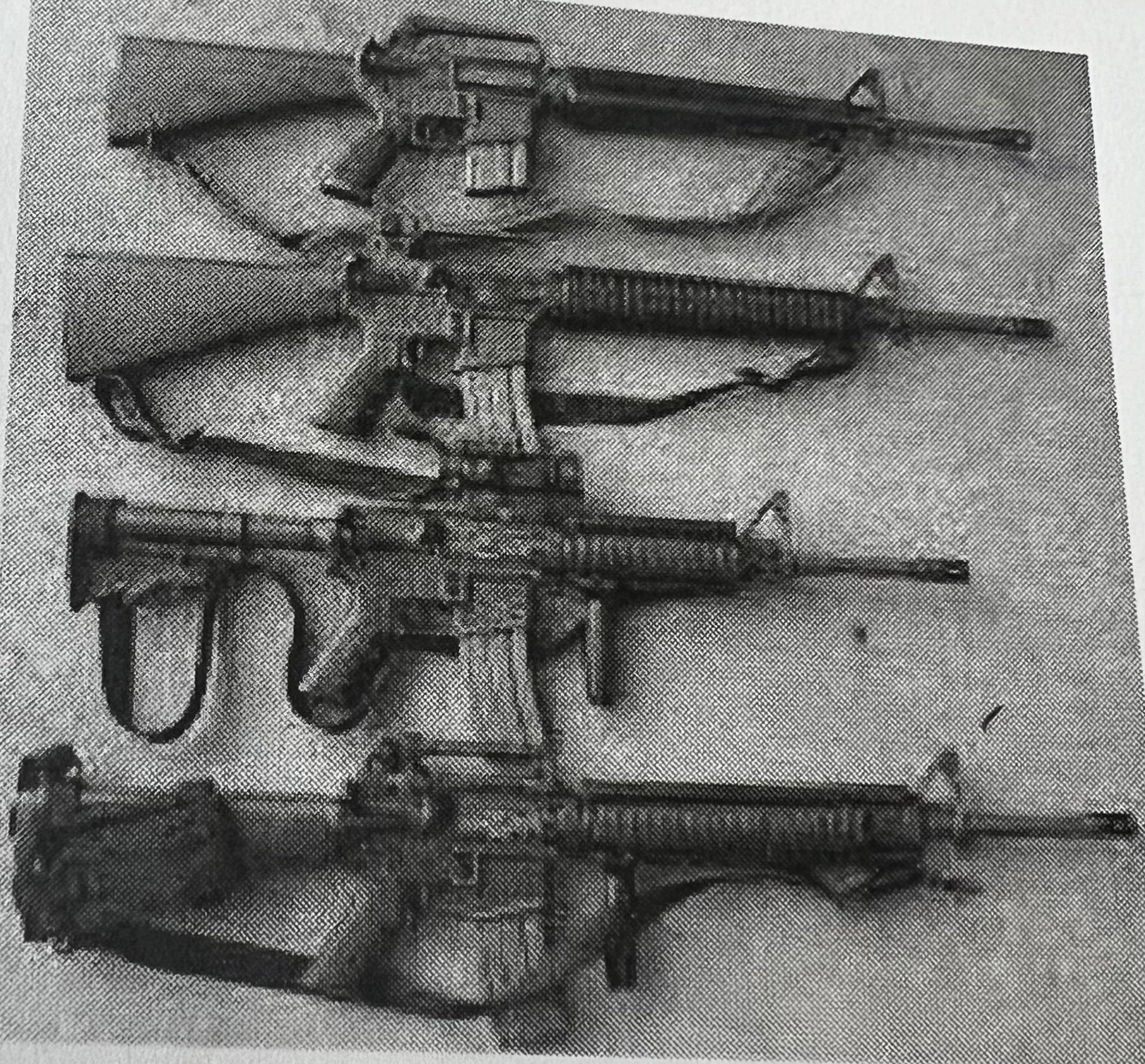
AR-type rifle

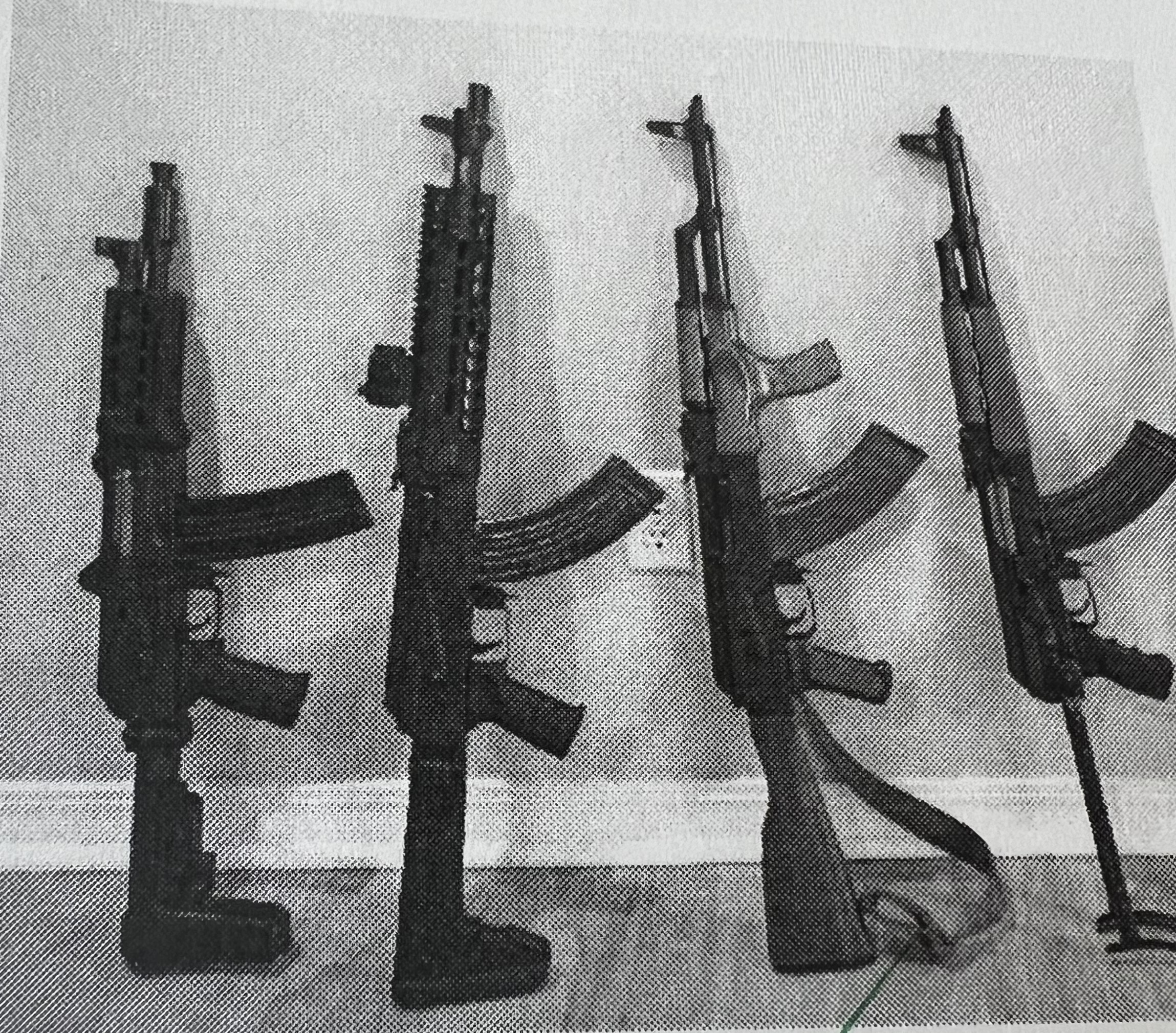
AK-type rifle

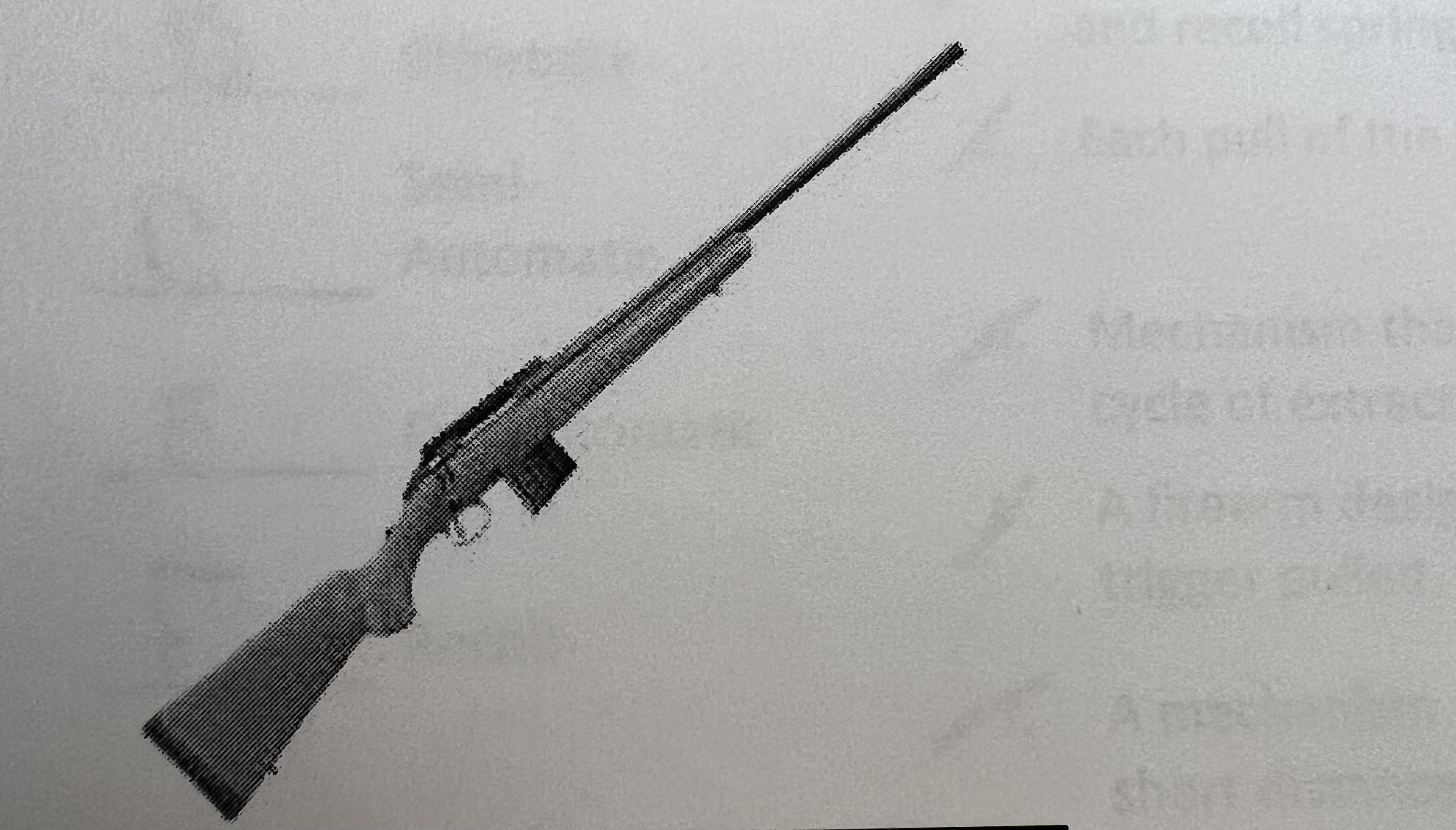
Bolt-Action or Slide-Action Rifle

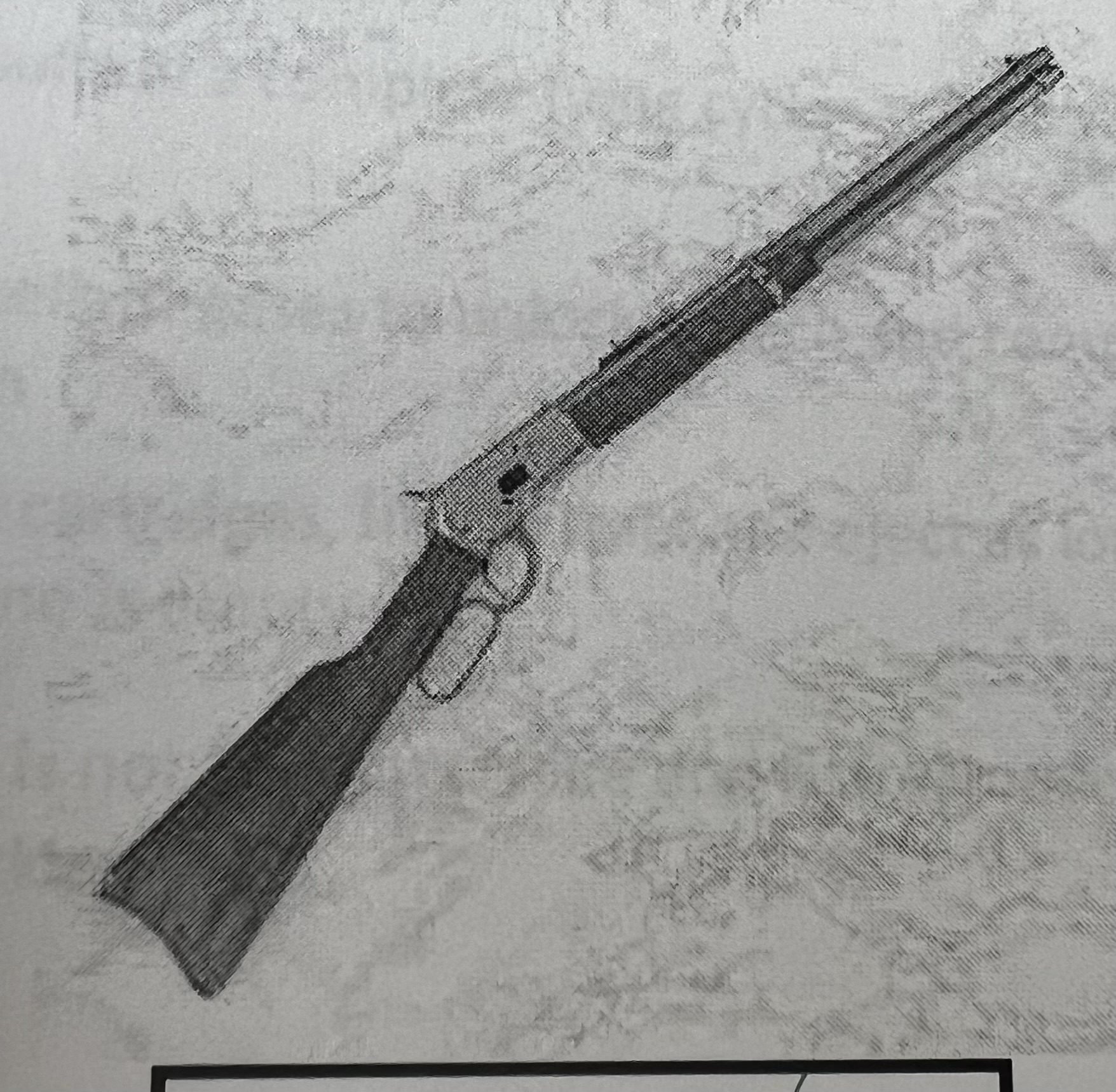
Lever-Action Rifle
