Lecture Exam #4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/124
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
1
New cards
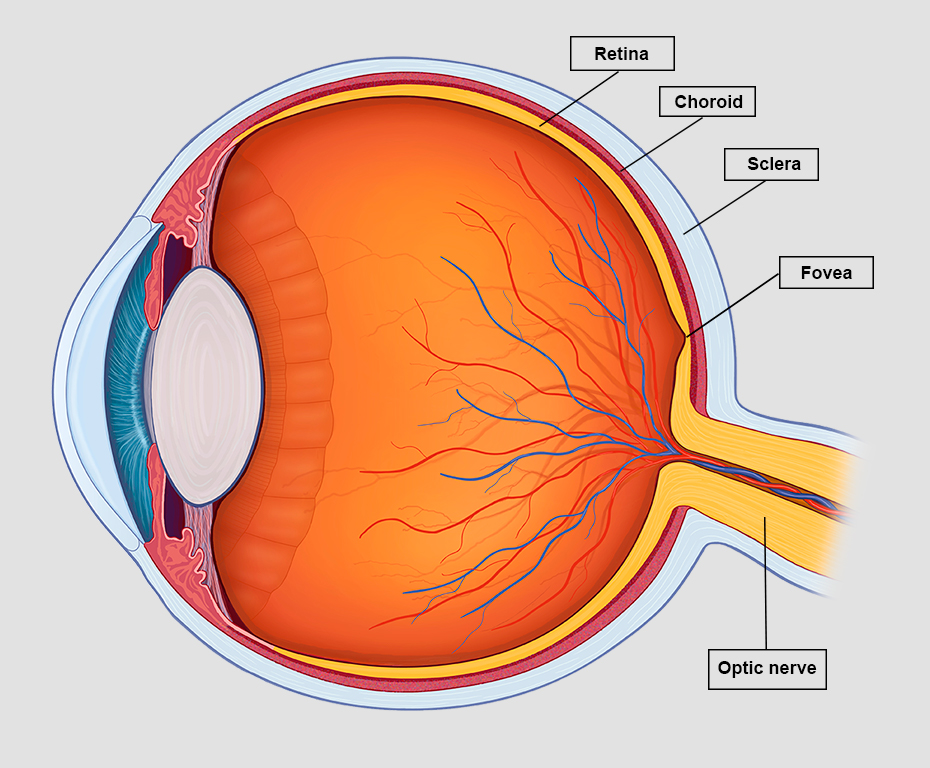
parts of the retina
macula, fovea, optic nerve, photoreceptors
2
New cards
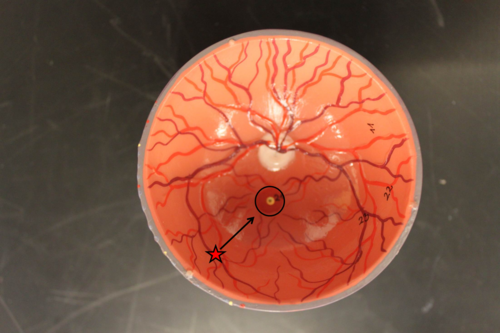
macula
Dark yellow-orange area with indistinct edges in the retina. It contains the fovea.
3
New cards
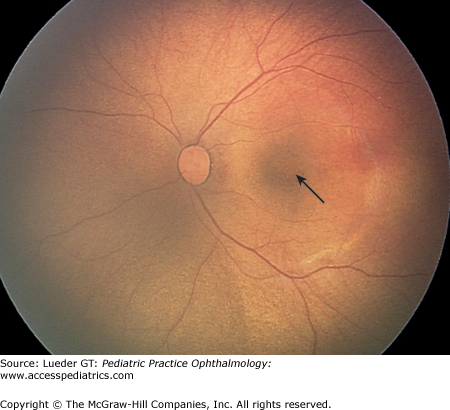
fovea
the center of the retina, where cones are densely packed
4
New cards
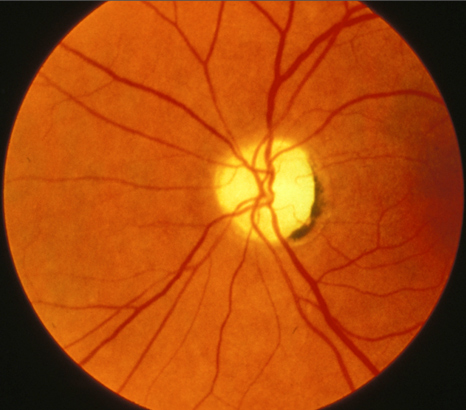
optic disc
Region at the back of the eye where the optic nerve meets the retina. It is the blind spot of the eye because it contains only nerve fibers, no rods or cones, and is thus insensitive to light.
5
New cards
rods and cones
photoreceptors in retina
6
New cards
parts of spinal cord
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral,
7
New cards
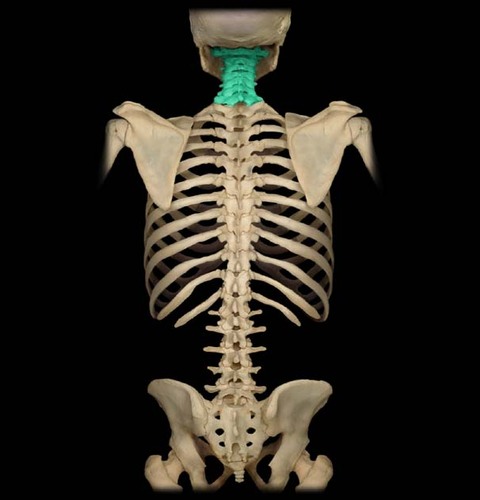
cervical
neck region
8
New cards
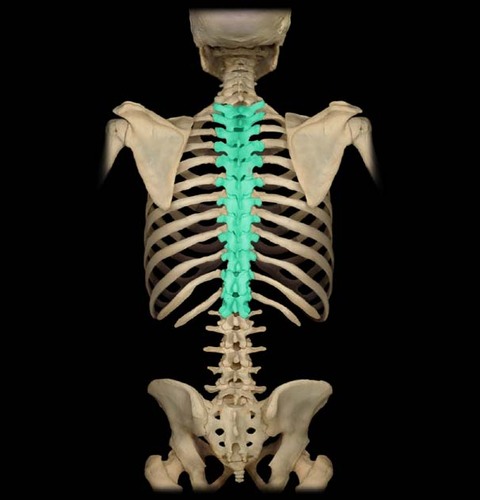
thoracic
chest region with ribs
9
New cards
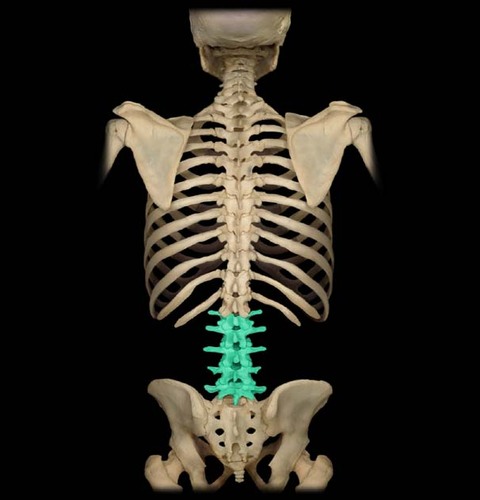
lumbar
lower back
10
New cards
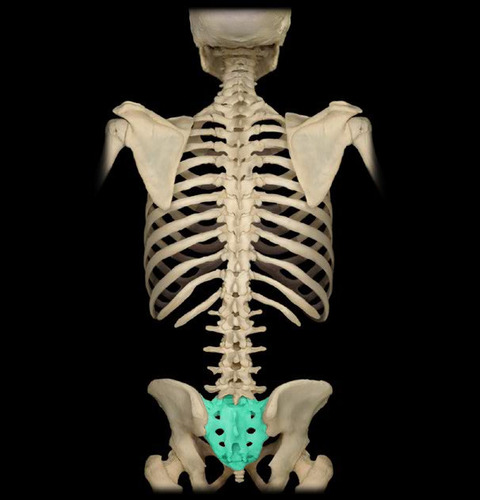
sacral
area between hips
11
New cards
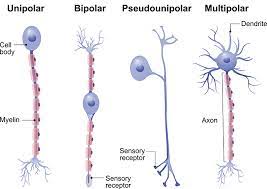
Structural classification of neurons
multipolar, bipolar, unipolar, anaxonic
12
New cards
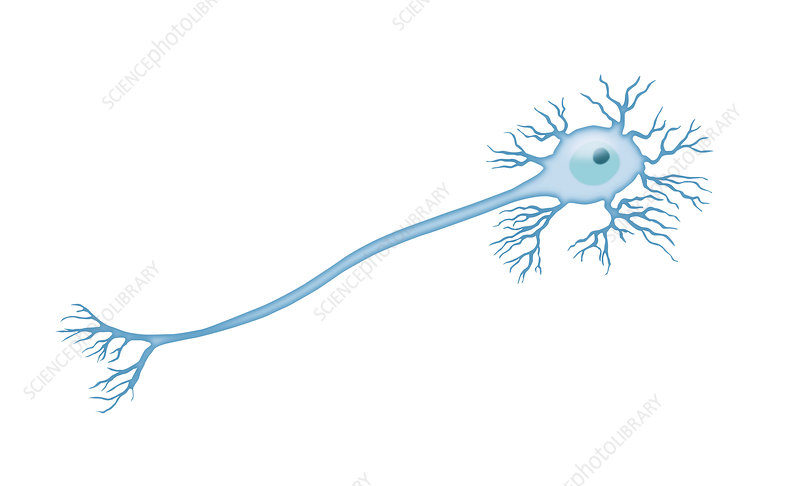
multipolar neurons
many dendrites, one axon (most common type)
13
New cards
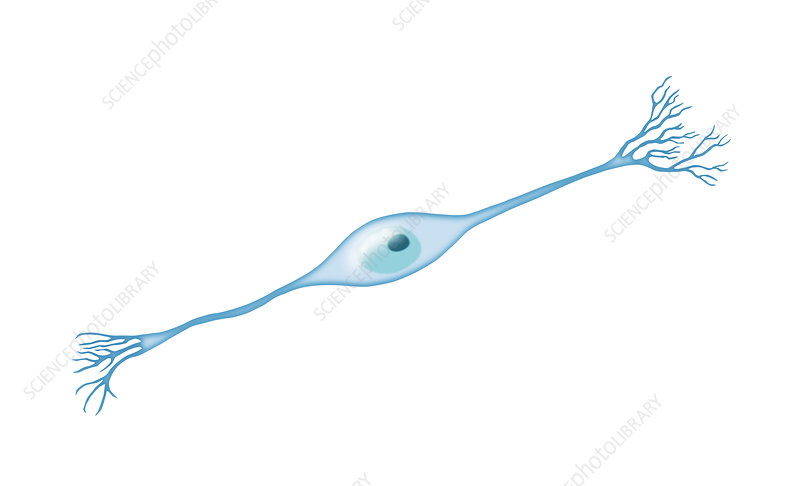
Bipolar Neurons
one dendrite and one axon
14
New cards
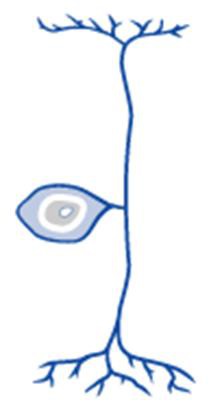
Unipolar neurons
one process extends from cell body
15
New cards
anaxonic neuron
have dendrites but no axons
16
New cards
Functional classifications of neurons
sensory, motor, interneurons
17
New cards
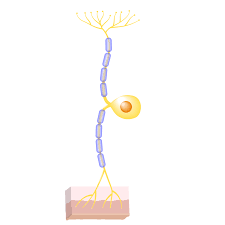
Sensory neurons
- Conduct input from somatic and visceral receptors to CNS
- Most are unipolar (a few bipolar)
- Most are unipolar (a few bipolar)
18
New cards
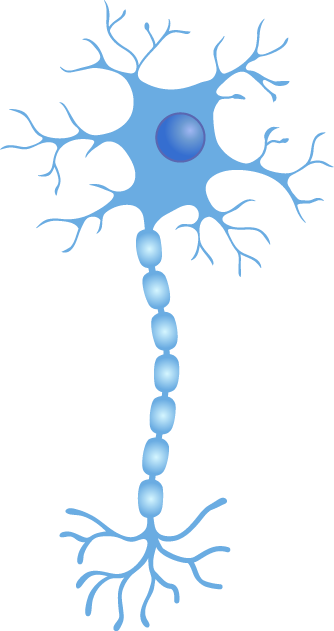
Motor neurons
- Conduct output from CNS to somatic and visceral effectors
- All are multipolar
- All are multipolar
19
New cards
interneurons
- Receive, process, and integrate information from many other neurons
- Generally are multipolar
- Generally are multipolar
20
New cards
different parts of a neuron
cell body (soma), dendrites, axon, cytoskeleton
21
New cards
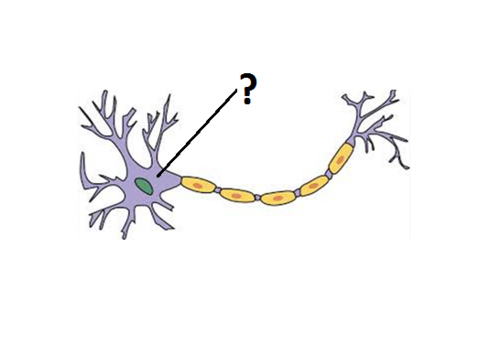
Cell body (soma)
contains nucleus
22
New cards
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
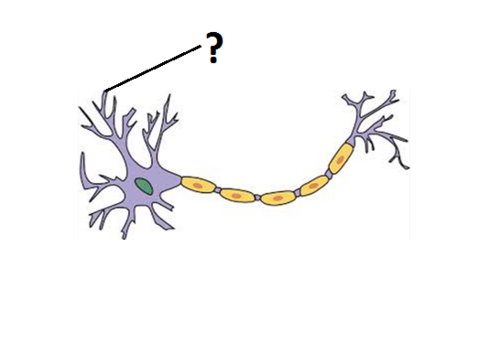
23
New cards
Axon
Long process emanating from cell body
- Makes contact with other neurons, muscle cells, or glands
- Makes contact with other neurons, muscle cells, or glands
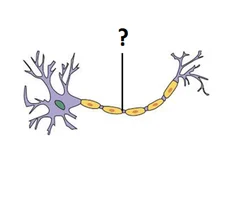
24
New cards
Cytoskeleton
Composed of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules
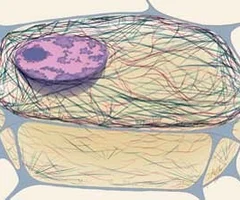
25
New cards
Types of glial cells in Central Nervous System:
astrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes
26
New cards
Astrocytes (star-shaped cells) (CNS)
- Help form blood-brain barrier
- regulate tissue fluid composition
- form structural support, assist neuronal development
- alter synaptic activity (add, eliminate, influence)
- Occupy the space of dying neurons
- regulate tissue fluid composition
- form structural support, assist neuronal development
- alter synaptic activity (add, eliminate, influence)
- Occupy the space of dying neurons
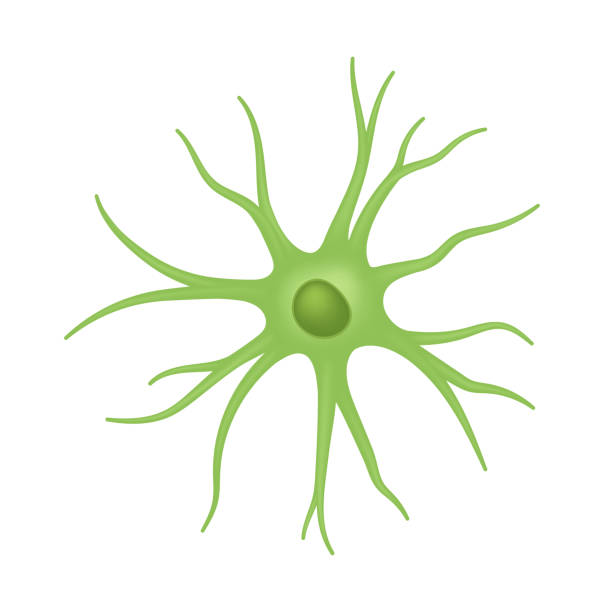
27
New cards
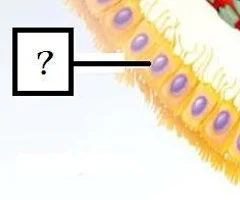
Ependymal cells (CNS)
- line cavities in brain and spinal cord
- part of choroid plexus which produces cerebrospinal
- part of choroid plexus which produces cerebrospinal
28
New cards
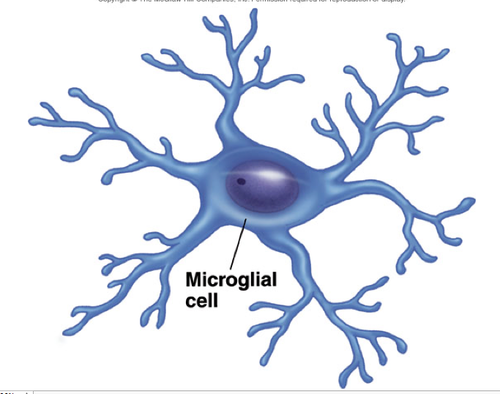
Microglia (CNS)
- Small cells that wander central nervous system and replicate in infection
- engulf infectious agents and remove debris
- engulf infectious agents and remove debris
29
New cards
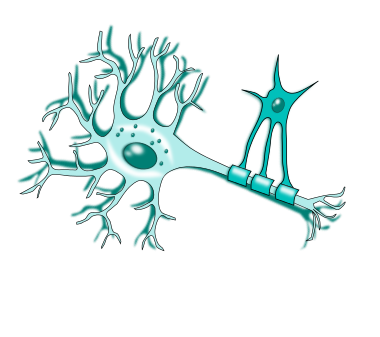
Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
Extensions wrap around axons of neurons forming myelin sheath
30
New cards
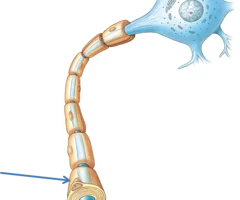
Glial Cells of the Peripheral Nervous System
satellite cells and neurolemmocytes cells (schwann)
31
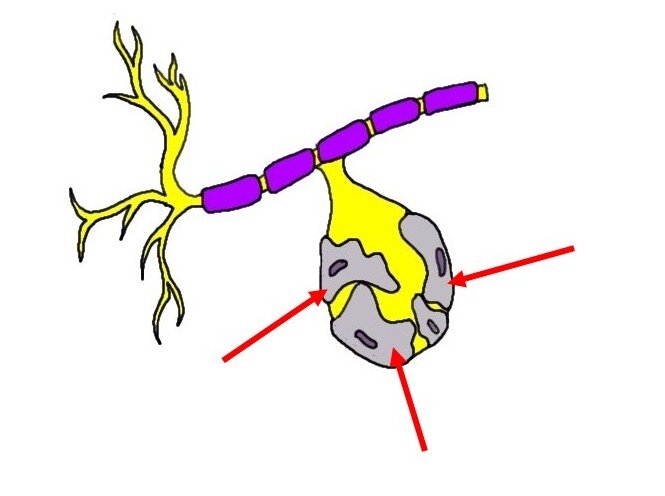
New cards
Satellite Cells (PNS)
Electrically insulate and regulate the exchange of nutrients and wastes
32
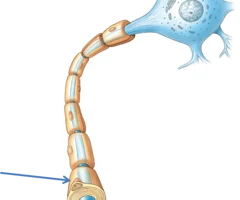
New cards
Neurolemmocytes (Schwann cells) (PNS)
allows for faster action potential propagation
33
New cards
Lobes of the brain
frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, insula
34
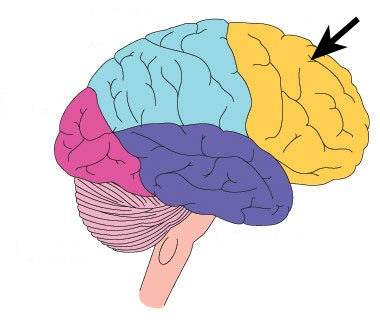
New cards
frontal lobe function
Motor control, concentration, verbal communication, decision making, planning, personality
35
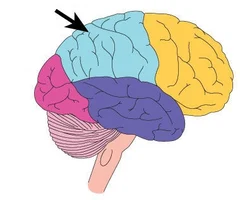
New cards
parietal lobe function
sensory (sensation)
36
New cards
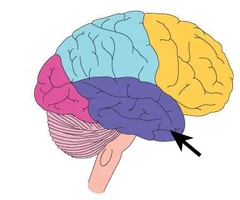
temporal lobe function
hearing and smell
37
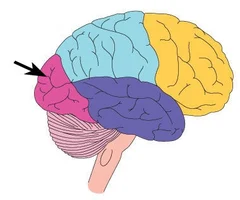
New cards
occipital lobe
vision and visual memories
38
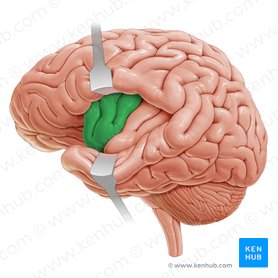
New cards
Insula
memory and sense of taste
39
New cards
parts of diencephalon
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
40
New cards
Epithalamus function
pineal gland: secretes melatonin and helps regulate day-night cycles
Habenular Nuclei: Help relay signals from limbic system to midbrain, Involved in visceral and emotional responses to odors
Habenular Nuclei: Help relay signals from limbic system to midbrain, Involved in visceral and emotional responses to odors
41
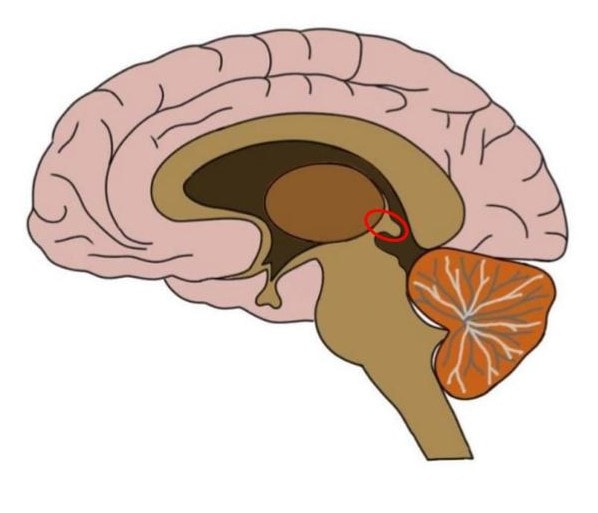
New cards
pineal gland
secretes melatonin
42
New cards
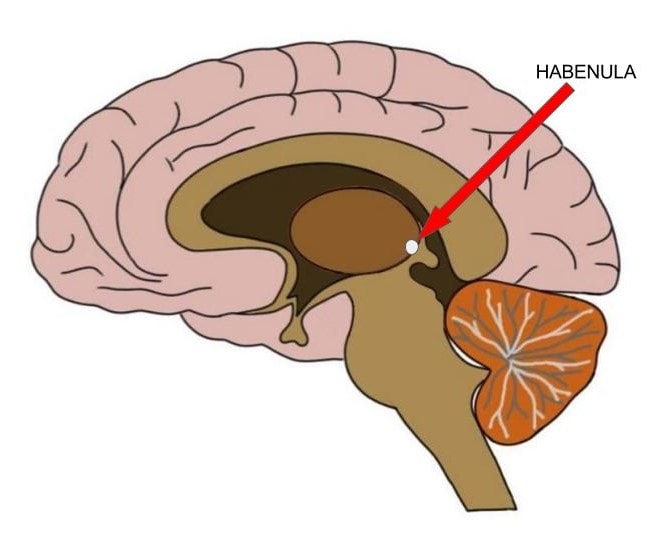
Habenular Nuclei function
Help relay signals from limbic system to midbrain, Involved in visceral and emotional responses to odors
43
New cards
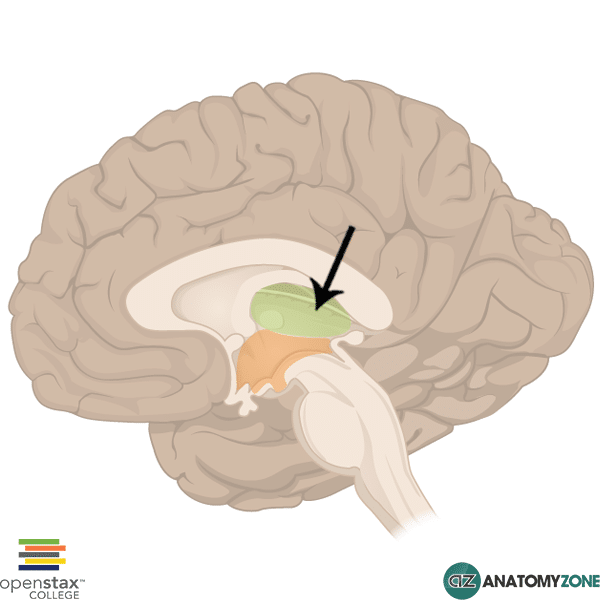
thalamus
Receives signals from all conscious senses except olfaction
44
New cards
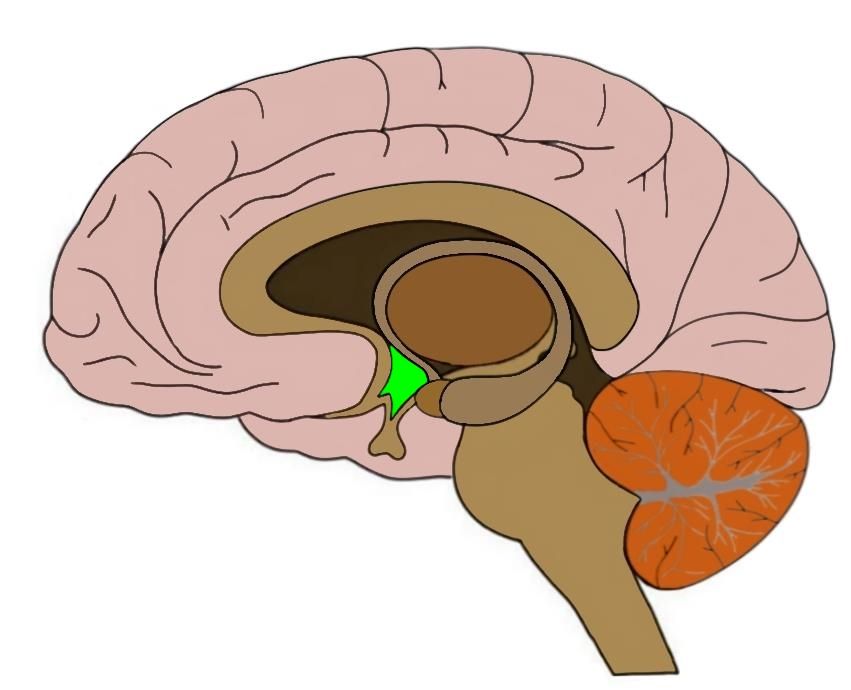
Hypothalamus
Control of autonomic nervous system, Control of endocrine system, Regulation of body temperature, Food and Water intake, Sleep-wake rhythms, Emotional behavior
45
New cards
Sclera
white of the eye

46
New cards
iris
Colored part of the eye
47
New cards
pupil
opening in the center of the iris (black part)
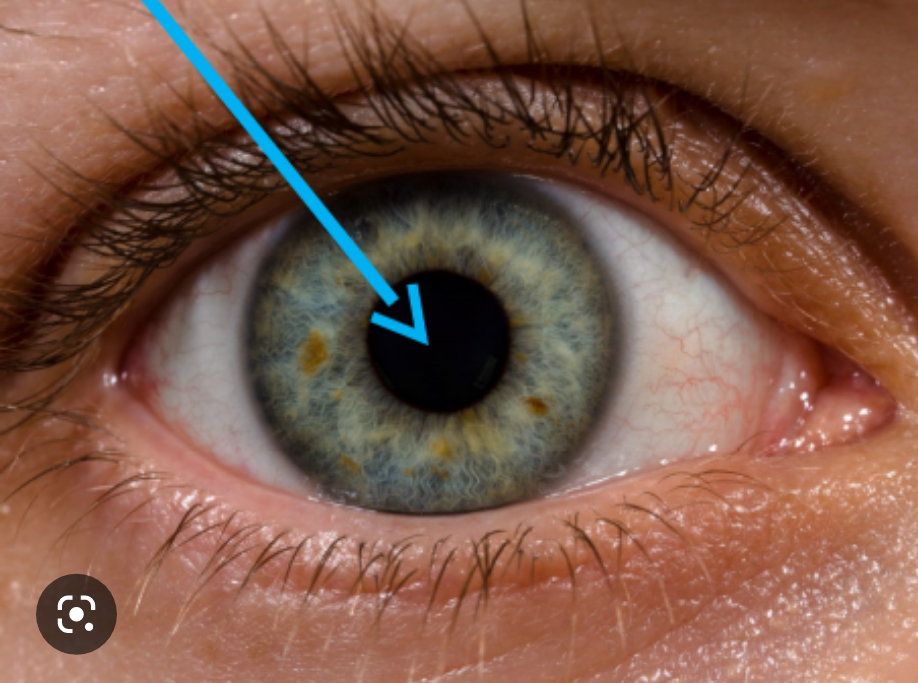
48
New cards
retina function
receive light that the lens has focused, convert the light into neural signals, and send these signals on to the brain for visual recognition
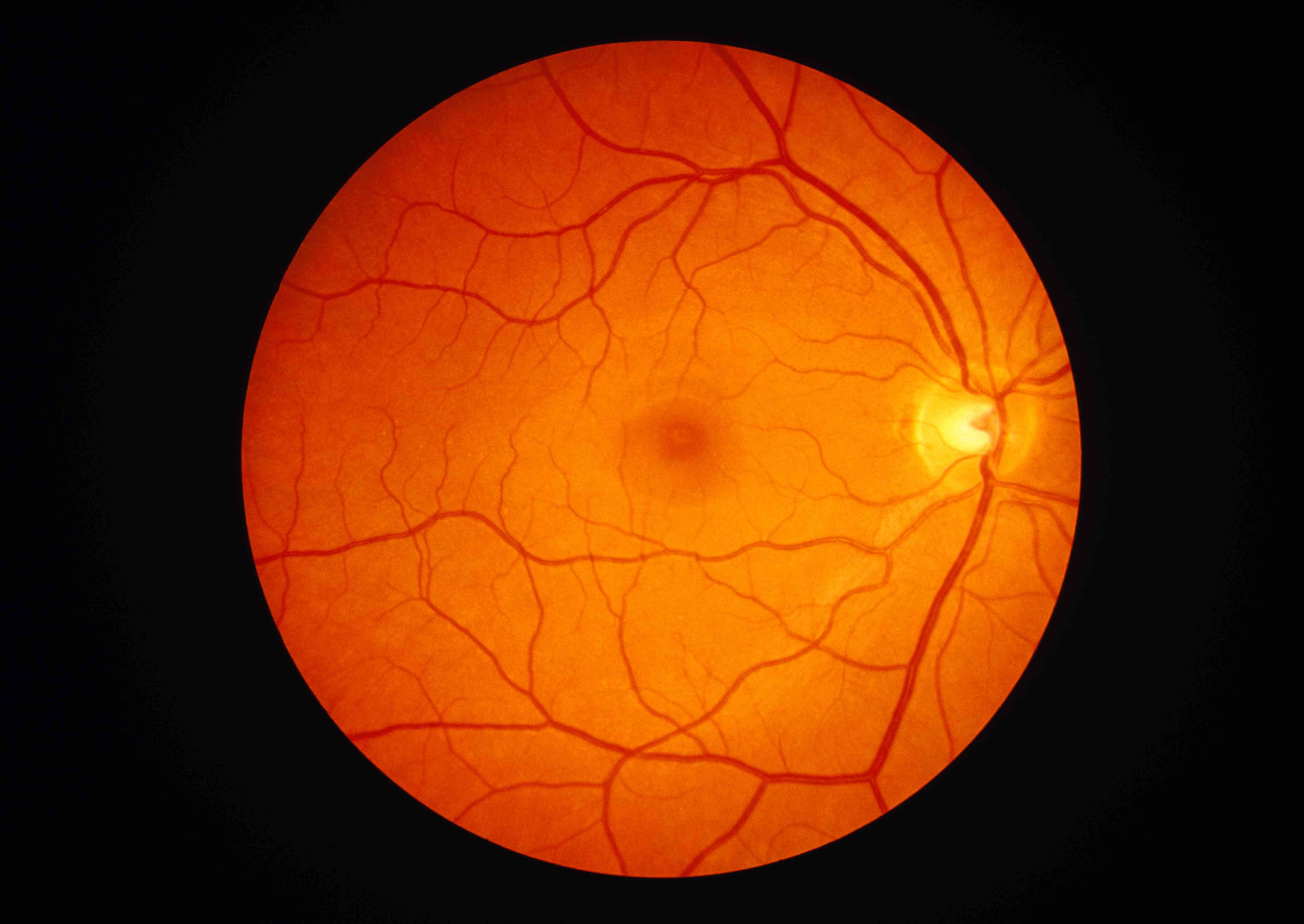
49
New cards
ciliary muscles function
Changes the shape of the lens to focus light into the retina
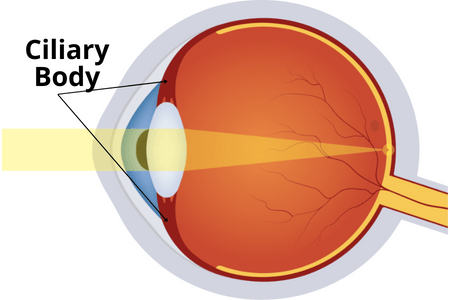
50
New cards
aqueous humor
fluid in front of the eye, found between the cornea and the lens
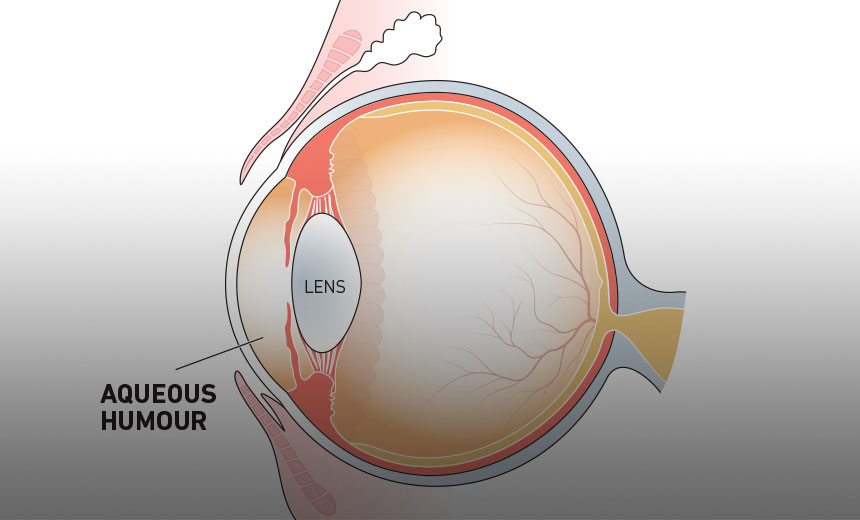
51
New cards
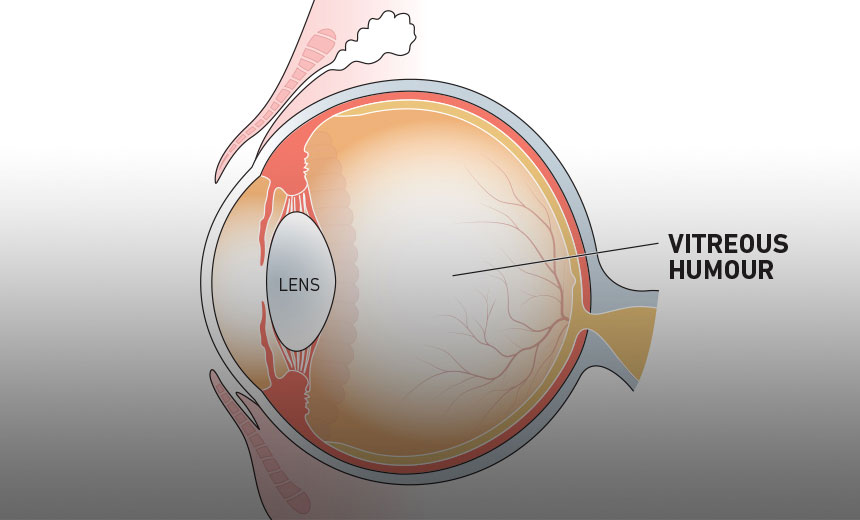
vitreous humor
jellylike substance found behind the lens in the posterior cavity of the eye that maintains its shape
52
New cards
sclera function
helps maintain your eyeball's shape and protects it from injury.
53
New cards
iris function
helps regulate the amount of light entering the eye.
54
New cards
pupil function
let's light into your eye as the muscles of your iris change its shape.
55
New cards
retina function
capture light that comes through the eye and change that light into an electrical signal that your brain interprets as an image.
56
New cards
optic nerve function
sends visual information from the retina to the vision centers of the brain.
57
New cards
ciliary muscle function
alters the shape of the lens with contraction and relaxation
58
New cards
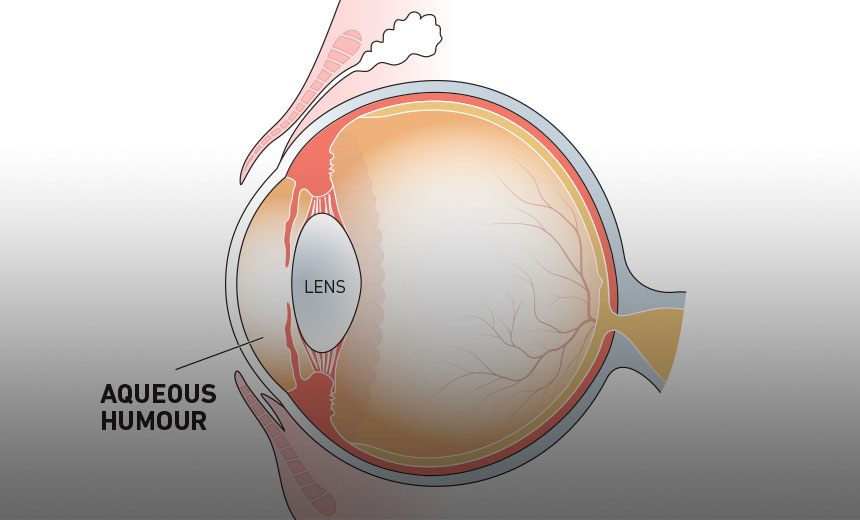
aqueous humor function
Helps the cornea keep its rounded shape, supplies nutrition to the eye
59
New cards
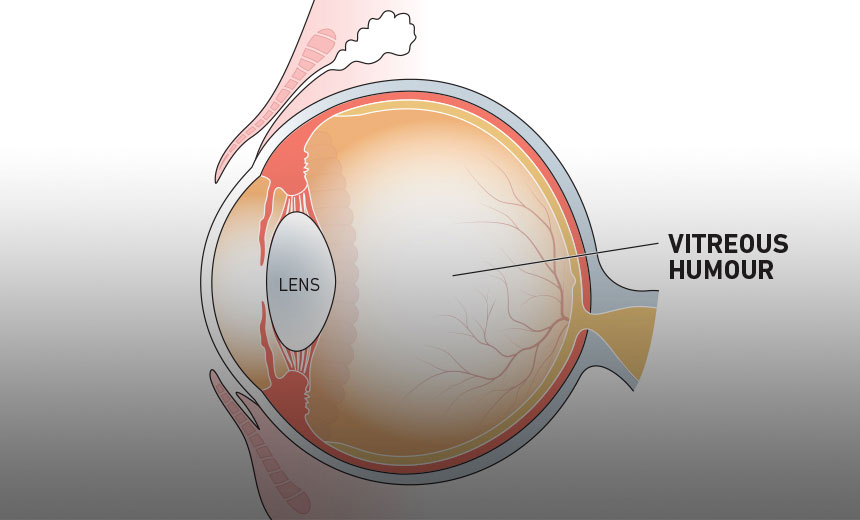
vitreous humor function
let's light pass through while helping eye keep its shape and absorb shock
60
New cards
components of a reflex arc
1. receptor
2. sensory neuron
3. integration center
4. motor neuron
5. effector
2. sensory neuron
3. integration center
4. motor neuron
5. effector
61
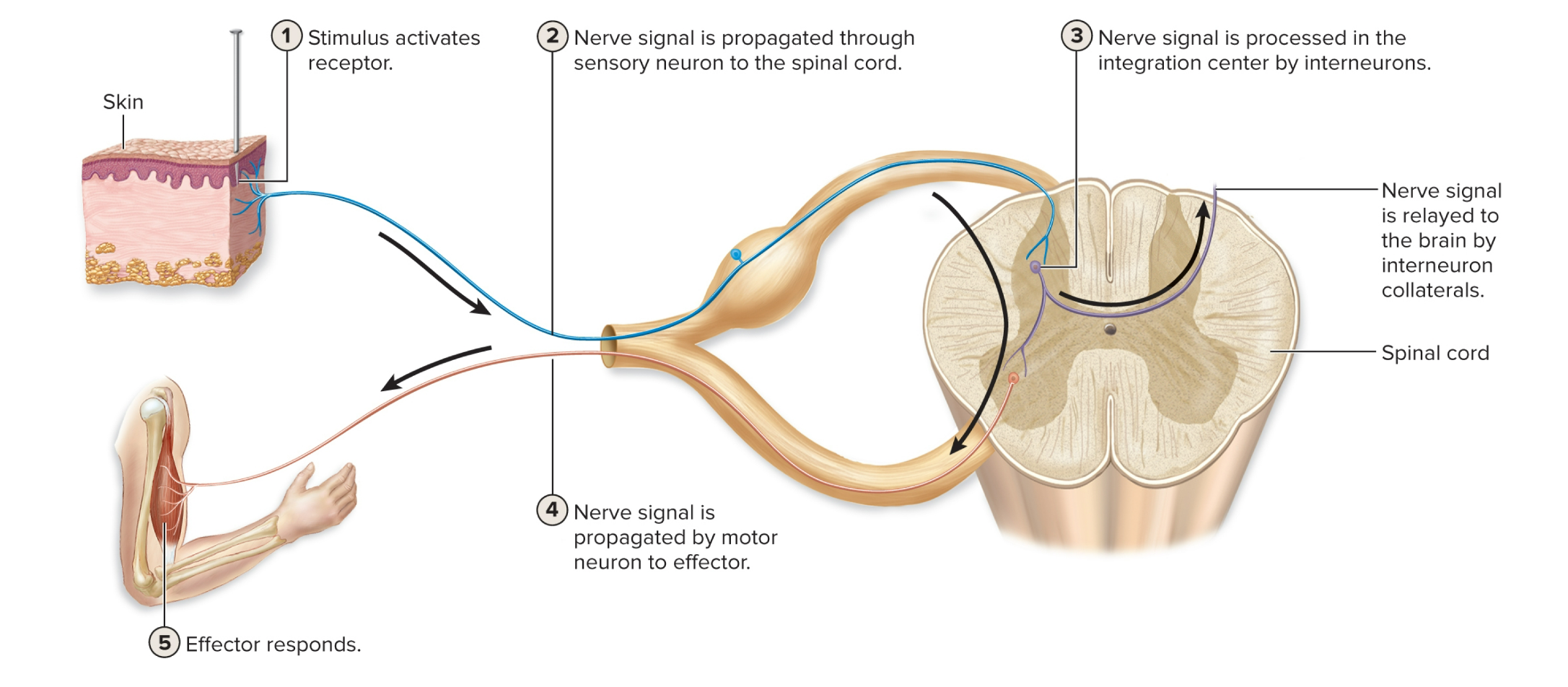
New cards
5 steps of reflex arc
1. stimulus activates receptor
2. Nerve signal is propagated through sensory neuron to the spinal cord
3. Nerve signal is processed in the integration center by interneurons
4. Nerve signal is propagated by motor neuron to effector
5. Effector responds
2. Nerve signal is propagated through sensory neuron to the spinal cord
3. Nerve signal is processed in the integration center by interneurons
4. Nerve signal is propagated by motor neuron to effector
5. Effector responds
62
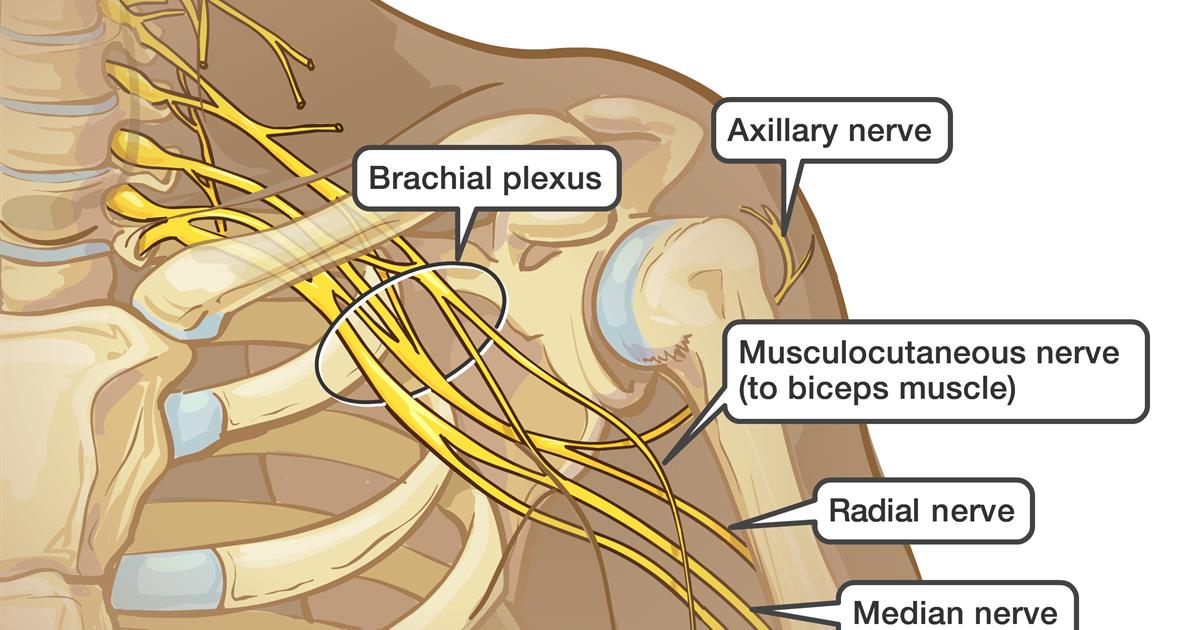
New cards
brachial plexus
network of interlacing nerves found in the upper arm area
63
New cards
brachial plexus nerves
axillary, musculocutaneous, median, ulnar, radial
64
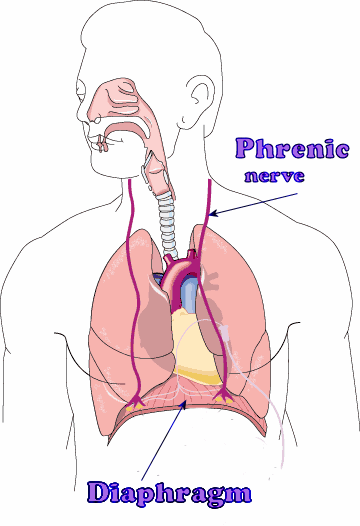
New cards
cervical plexuses
innervate the neck and sections of the head, chest, and shoulders and the diaphragm
65
New cards
cervical plexuses nerves
phrenic nerve
66
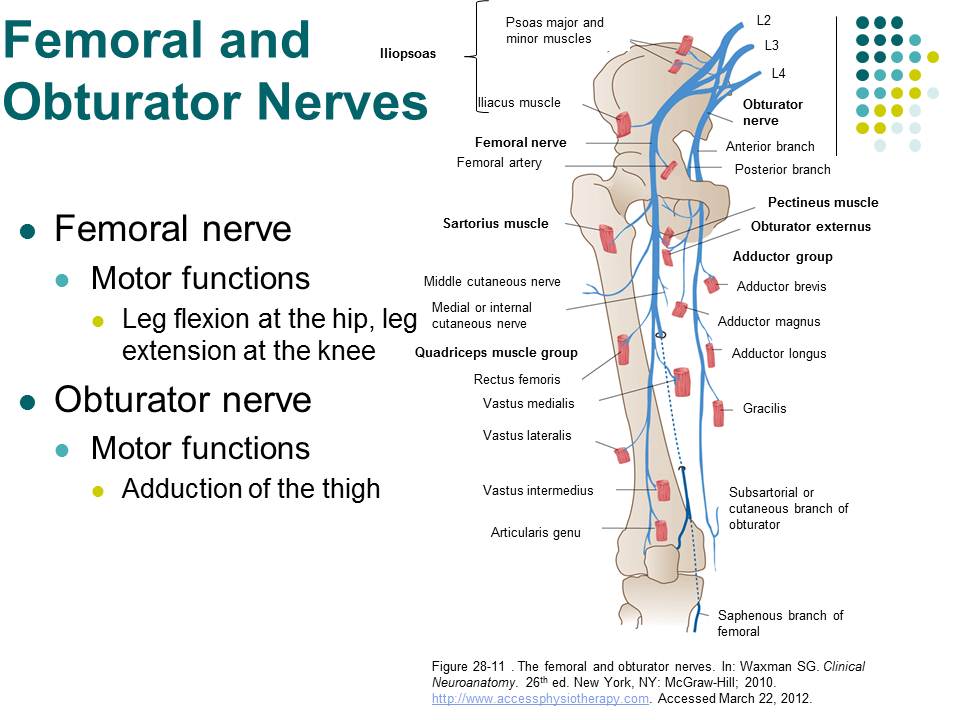
New cards
Lumbar plexuses nerves
femoral and obturator nerves
67
New cards
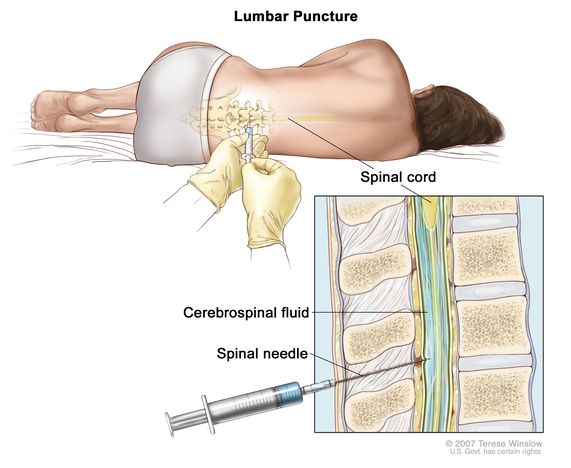
how to do a lumbar puncture/spinal tap
- Needle passes through Skin, back muscles, ligamentum flavum
- Lie on your side with your knees drawn up to your chest. Then a needle is inserted into your spinal canal — in your lower back — to collect cerebrospinal fluid for testing
- Lie on your side with your knees drawn up to your chest. Then a needle is inserted into your spinal canal — in your lower back — to collect cerebrospinal fluid for testing
68
New cards
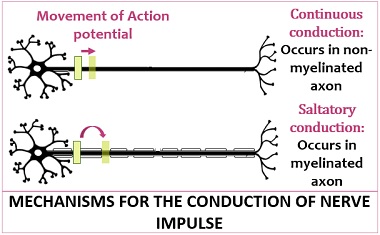
difference between saltatory and continuous nerve conduction.
Saltatory conduction is much faster than continuous conduction
and myelinated cells use less ATP to maintain resting membrane
potential
and myelinated cells use less ATP to maintain resting membrane
potential
69
New cards
continuous nerve conduction
unmyelinated axons where conduction is slower.
70
New cards
Saltatory nerve conduction
occurs on myelinated axons
71
New cards
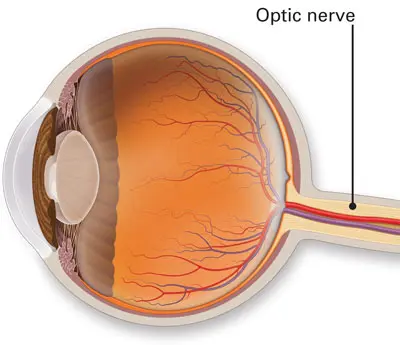
optic nerve
the nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
72
New cards
step 1 of reflex arc
1. stimulus activates receptor
73
New cards
step 2 of reflex arc
2. Nerve signal is propagated through sensory neuron to the spinal cord
74
New cards
step 3 of reflex arc
3. Nerve signal is processed in the integration center by interneurons
75
New cards
step 4 of reflex arc
4. Nerve signal is propagated by motor neuron to effector
76
New cards
step 5 of reflex arc
5. Effector responds
77
New cards
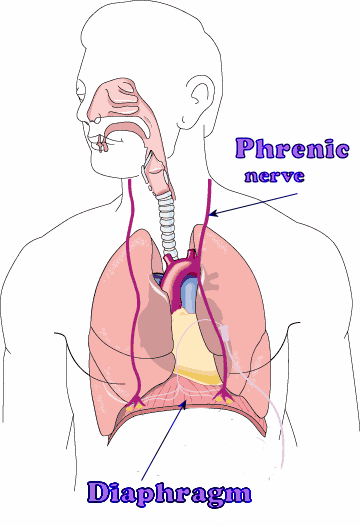
cervical plexuses
innervate the neck and sections of the head, chest, and shoulders and the diaphragm
78
New cards
cervical plexuses nerves
phrenic nerve
79
New cards
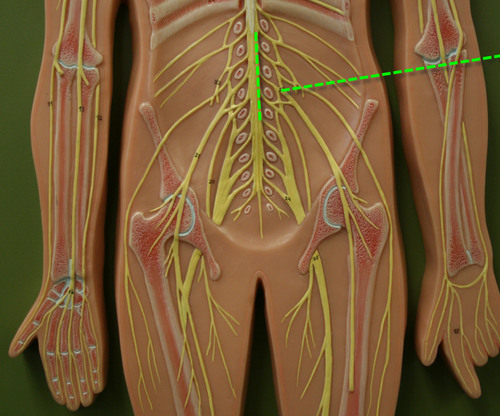
Lumbar plexuses
Innervates abdominal wall muscles, anterior and medial thigh
80
New cards
Lumbar plexuses nerves
femoral and obturator nerves
81
New cards
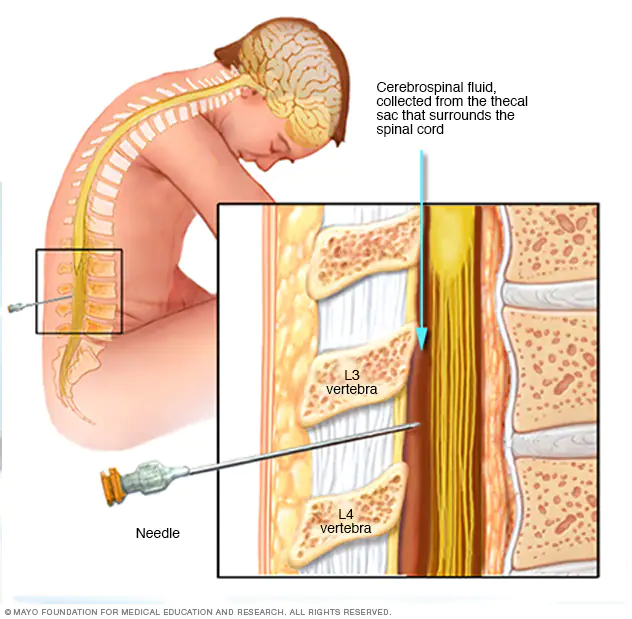
how to do a lumbar puncture/spinal tap
Needle passes through Skin, back muscles, ligamentum flavum
82
New cards
difference between saltatory and continuous nerve conduction
Saltatory conduction is much FASTER than continuous conduction
and myelinated cells use less ATP to maintain resting membrane
potential
and myelinated cells use less ATP to maintain resting membrane
potential
83
New cards
continuous nerve conduction
unmyelinated axons where conduction is slower.
84
New cards
Saltatory nerve conduction
occurs on myelinated axons
85
New cards
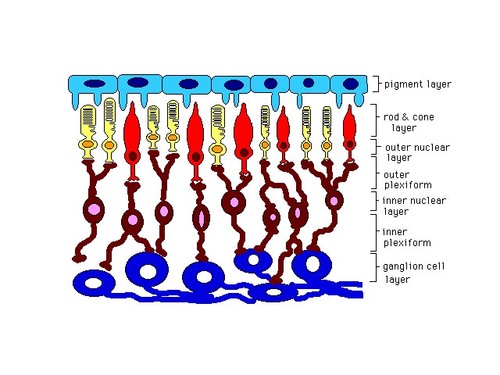
rods and cones
86
New cards
optic nerve
transmits electrical impulses from your eyes to your brain
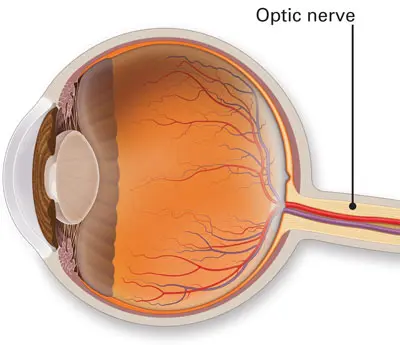
87
New cards
optic disk
Region at the back of the eye where the optic nerve meets the retina. It is the blind spot of the eye because it contains only nerve fibers, no rods or cones, and is thus insensitive to light.
88
New cards
eardrum
tightly stretched membrane located at the end of the ear canal that vibrates when struck by sound waves
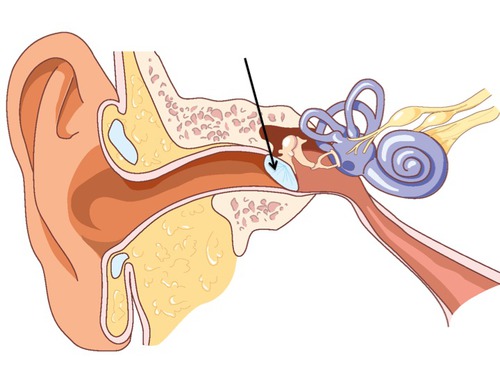
89
New cards
external auditory meatus
ear hole
90
New cards
ear canal
a tube running from the outer ear to the middle ear
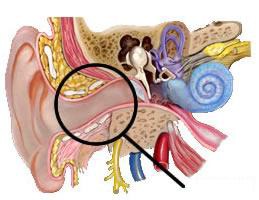
91
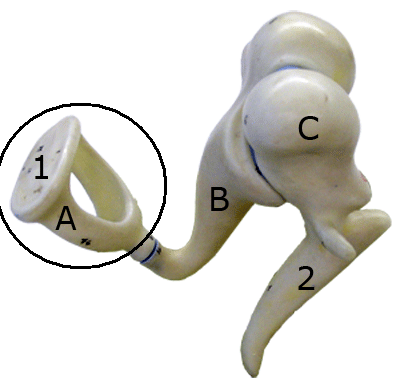
New cards
incus
a small hammer-shaped bone in the middle ear, transmitting vibrations between the malleus and stapes.
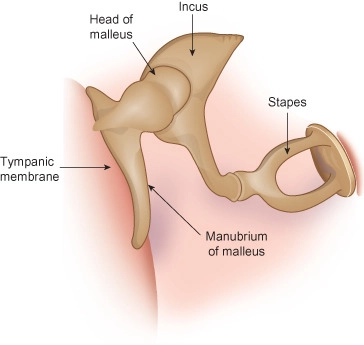
92
New cards
malleus
a small bone in the middle ear which transmits vibrations of the eardrum to the incus.
(thing in middle)
(thing in middle)
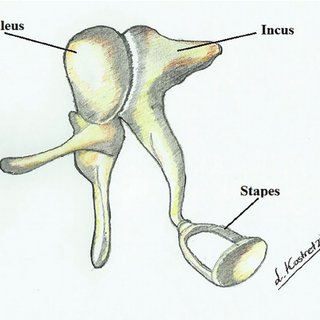
93
New cards
stapes
involved in the conduction of sound vibrations to the inner ear.
94
New cards
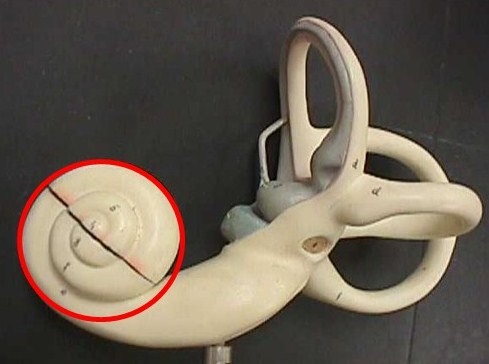
cochlea
snail-shaped structure of the inner ear that is filled with fluid
95
New cards
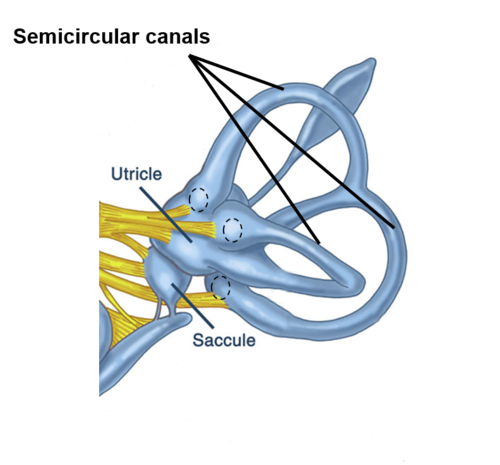
semicircular canals
Fluid filled canals in the inner ear responsible for our sense of balance.
96
New cards
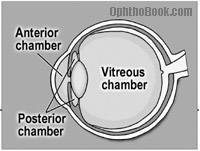
anterior chamber of eye
between cornea and iris
97
New cards
posterior chamber of eye
between iris and lens
98
New cards
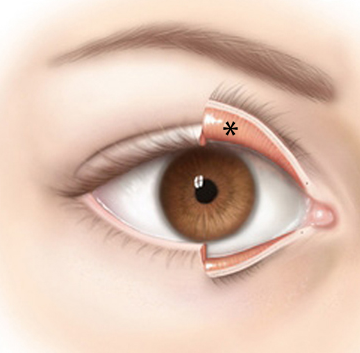
conjunctiva
Delicate membrane lining the eyelids and covering the eyeball
99
New cards
cornea
the transparent layer forming the front of the eye.
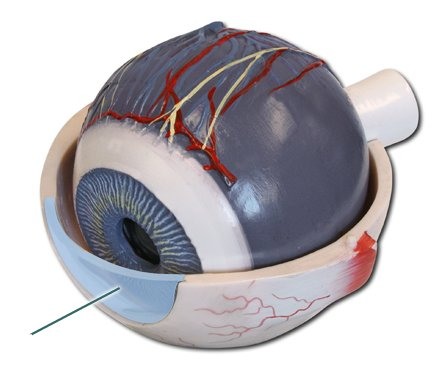
100
New cards
choroid
middle, vascular layer of the eye, between the retina and the sclera