Cog Neuro Exam 2
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
change blindness
time taken to detect change
inattentional blindness
failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere
attention is like a
spot light. may move from one location to another, may zoom in or out (fine vs coarse). doesn't/can't highlight everything
focus of attention doesn't necessarily mean
eye fixation
ex: highway hypnosis (eyes on road, but attention/focus not)
covert
moving attention by not the eyes/head
overt
moving attention as well as the eyes/head
Importance of cues
initially quicker response to cued location, but relationship flips after long delay
inhibition of return
a slowing of reaction time associated with going back to a previously attended location
endogenous
internally-guided attention, driven by goals/motivation, more top-down
ex: arrow points up in middle of screen, telling to shift attention up
exogenous
externally-guided attention, driven by sudden change in sensory input, bottom-up
ex: top cube flashes and captures attention
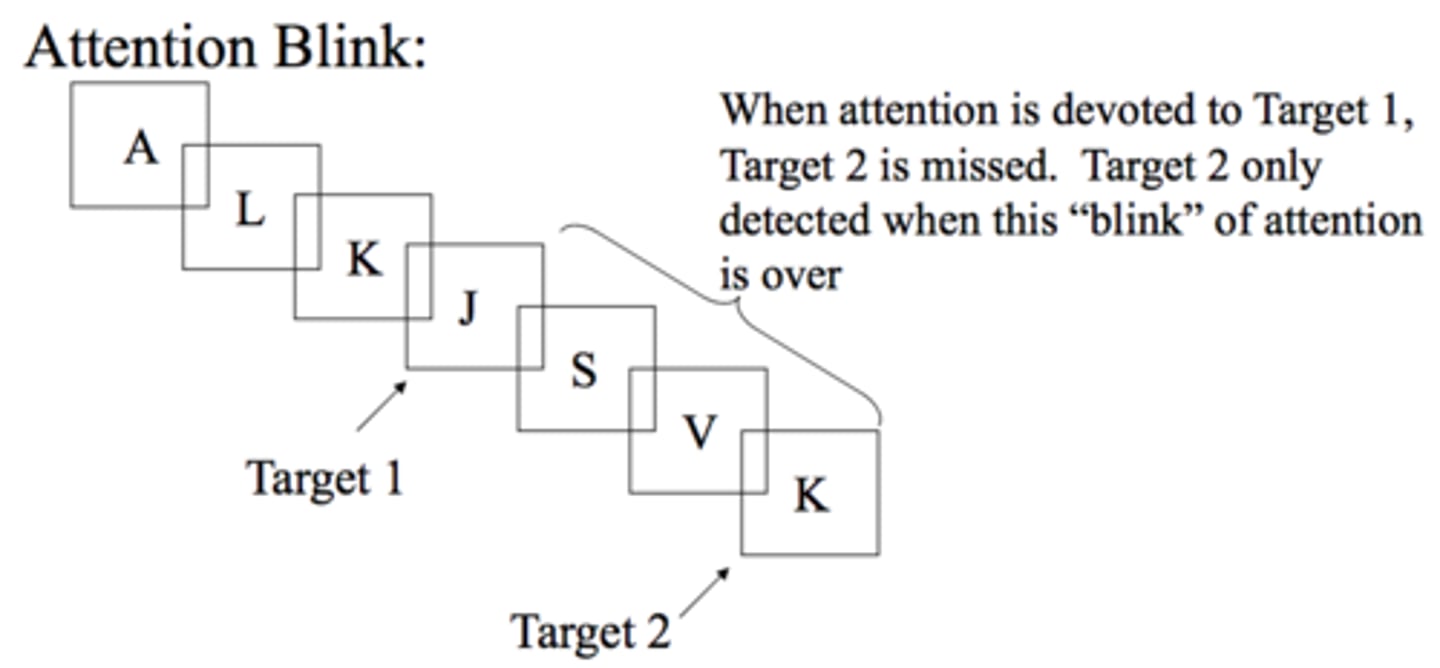
attentional blink
during a brief time after perceiving one stimulus, it is difficult to attend to something else
first target soaks up attentional resources, leading to subsequent inattentive period
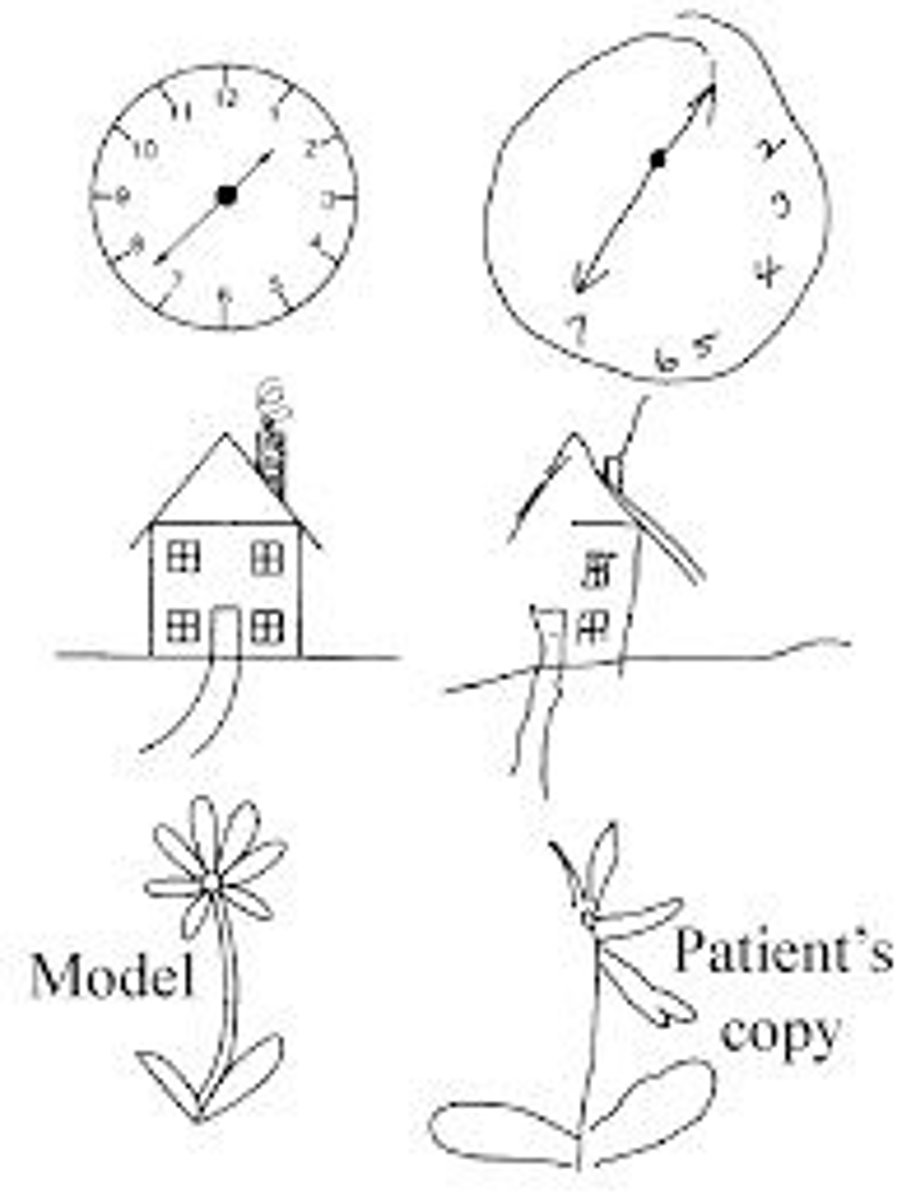
hemineglect
inability to perceive one side of the visual world, typically right-hemisphere damage, left side neglect. sensory cortex responds to the info! therefore must be something wrong with attention
neglect vs blindsight
neglect: not restricted to vision, can see in neglected area, egocentric
blindsight: visual only, can move eyes to blind region, retinocentric
what happens to neglected info?
ventral stream (what) process neglected objects
burning house experiment
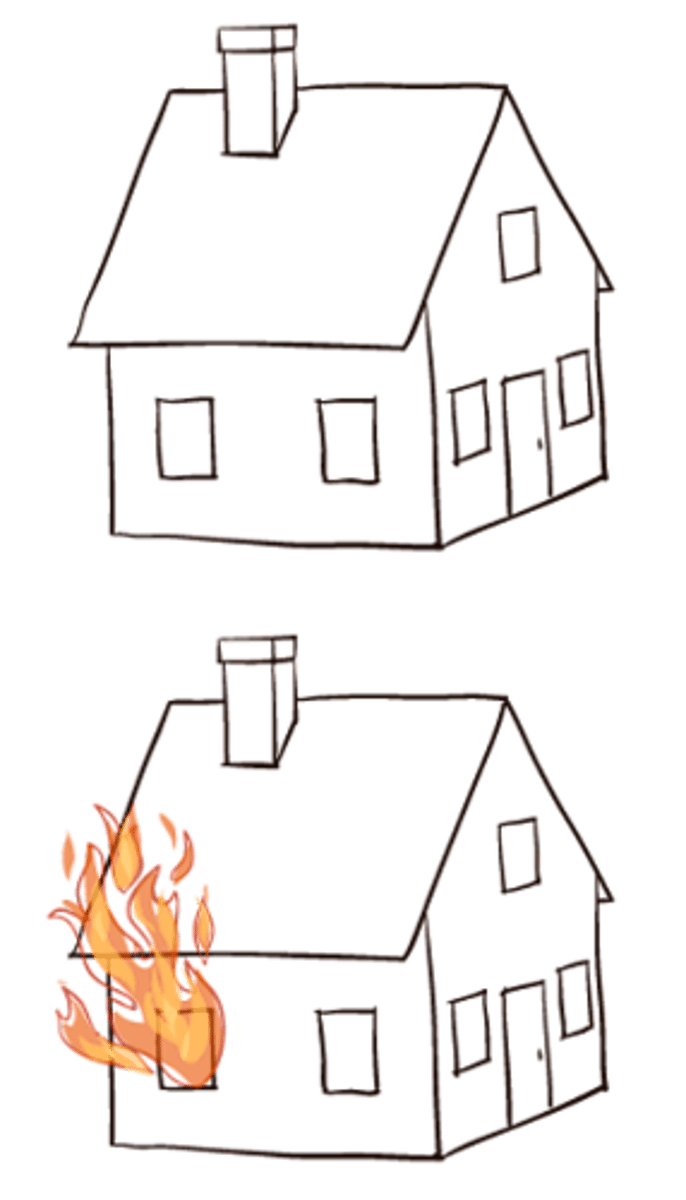

neglect is also about spatial reference frames
cannot detect differences on left side of an object even when falling into right side of space
spatial attention
lateral superior parietal areas (lateral = external)
nonspatial attention
lateral inferior temporal regions (lateral = external)
internally-guided spatial tasks
medial prefrontal and parietal areas (medial = internal)
attending to emotional states
medial prefrontal cortex and precuneus
bottom up
exogenous
top down
endogenous
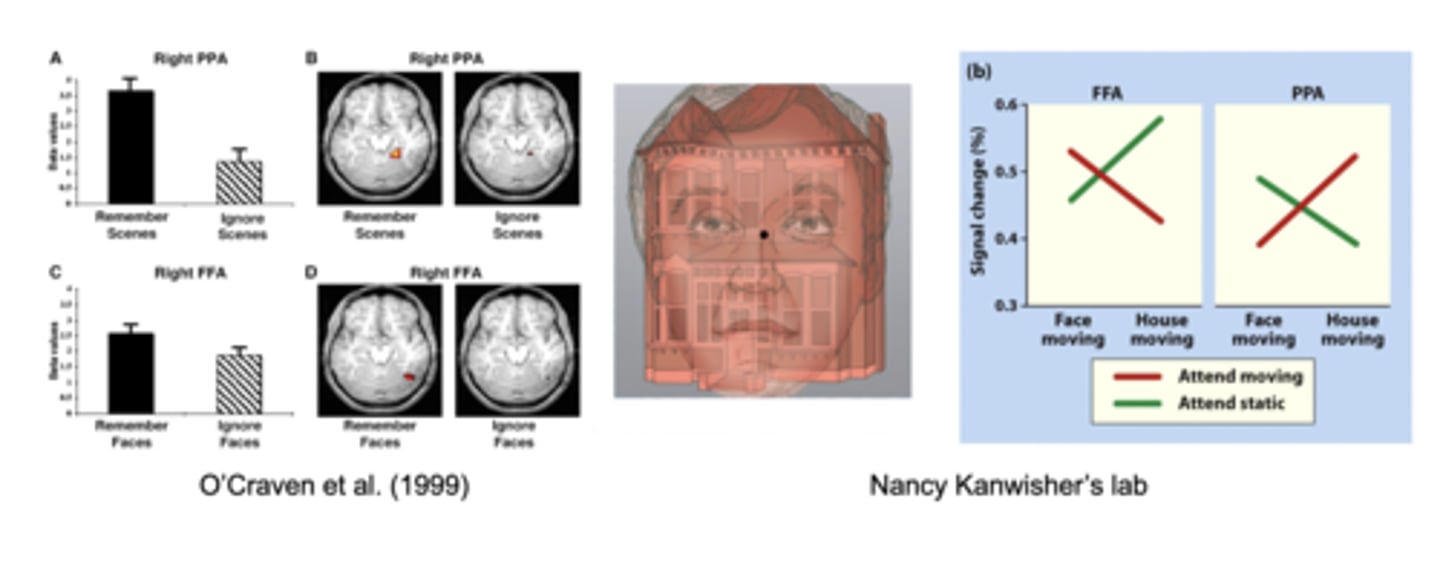
biased competition model in attention
bias towards house vs. face
frontal-parietal attention mechanism
dorsal route: goals + importance
ventral route: circuit breaker, interrupts ongoing activity to redirect attention to some important feature
Conscious awareness is a
hierarchical process from sensory to association cortex
Attention can be seen as
focusing or strengthening sensory activation and pushing it further up the hierarchy
activity in _____ is modulated by attention
V4
Attended has
increased spike rate
ignored stimuli has
decrease spike rate
signal-to-noise ratio
it becomes harder to detect a signal as background noise increases, filter out stuff you want and ignore what you don't want
Selecting and de-selecting stimuli
blue peaks at first because it takes time to process and then allocate attention
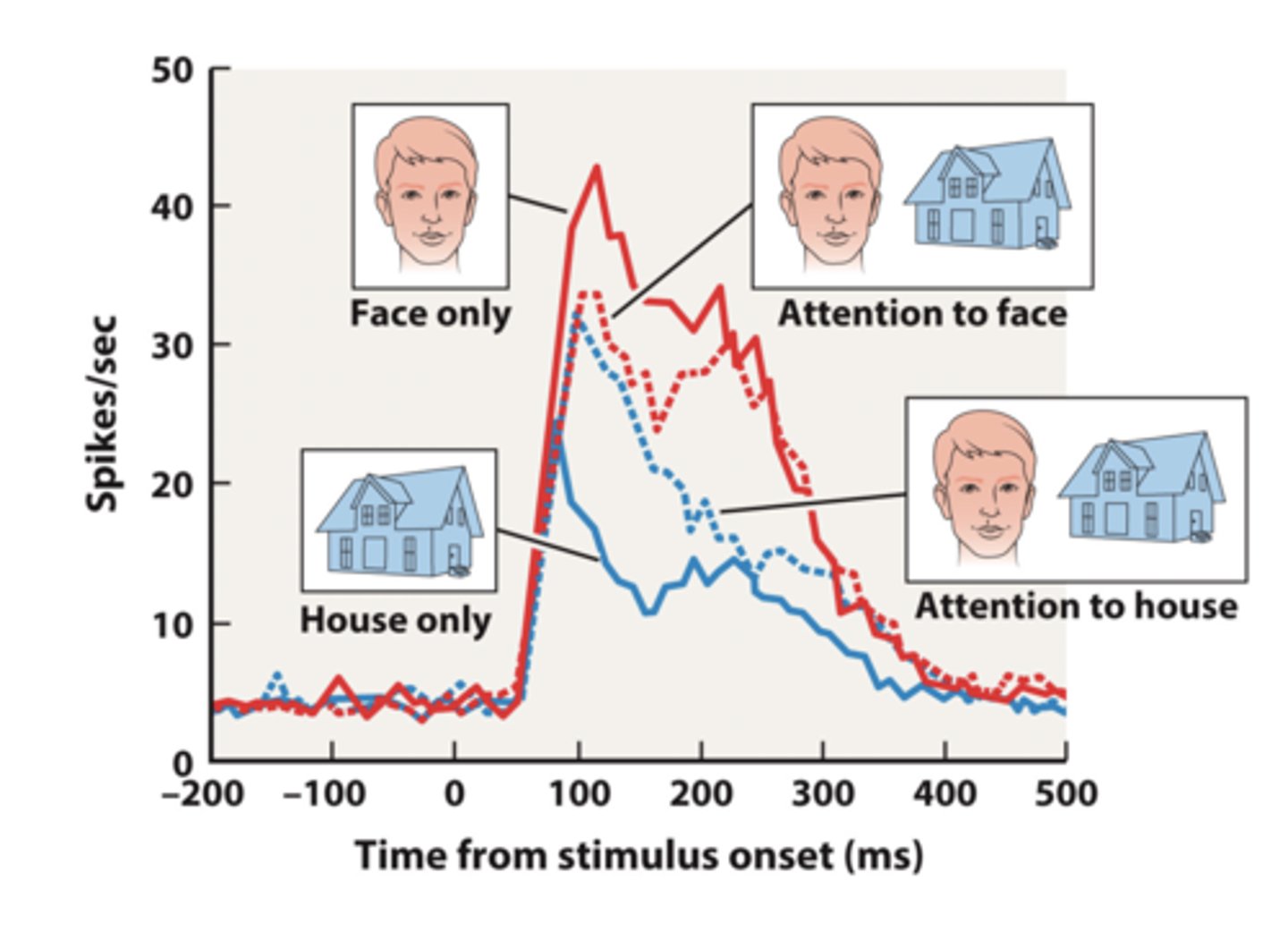
attending to a stimuli increases
change detection accuracy, decrease in noise correlation (population of neurons becomes more synched)
synchronization of neurons
varies widely across cognitive states (lots of spikes = awake, fewer spikes = REM sleep, spikes every now and then = anesthesia, slow long waves = coma)
subliminal messaging example
measure startle response during randomly selected images (negative, neutral, positive)
conditions of consciousness
sentience, awareness of external reality, internal experience, "self"
consciousness is...
constructive! interpret inputs, and experience of reality depends on interpretive framework of the brain
brain areas involved in consciousness
midbrain, reticular formation, and thalamus
reticular formation in consciousness
traffic lights, tells what signals to go and when and projects to thalamus
if you damage your reticular formation
you lose consciousness
sleep
a state of unconsciousness, body's innate circadian rhythm
cave study
light cues influence circadian rhythm, but natural rhythm is around 25 hrs
In deep sleep
The MF (logic /reasoning/planning) is isolated
in light sleep
there are higher synchrony between brain regions
dreams
spontaneous neural activity, brain loves patterns so it tries to create a story
nightmares are remembered because
they are salient
Sleep paralysis
affects REM sleep, body immobile, person partially conscious
lucid dreaming
becoming aware in dream and taking control
anesthesia
reversibly alters consciousness without long-term damage, reduce excitatory and enhave inhibitory signals
coma
deep, prolonged state of unconsciousness , no response, no sleep cycle, abnormal breathing
coma happens with
any damage to brainstem or major damage to the cortex
vegetative states
brainstem intact (breathing, sleep-wake), but no signs of perception, awareness, brain metabolism is permanently decreased
Vegatitive patient conscious?
sometimes. answer yes/no questions by imaging playing tennis (motor cortex) or walking through their house (where - pariental)
dualism
mind and body are totally separate
Functionalism
the brain's specialized processing units underlie different aspects of conscious experience; FFA perceives face; it is a big fragmented
Integrated information theory
informative and
combined info across the brain
• Informative: experience of "red" is not "green" or "blue"
• Integrated: you perceive a face not a combination of shapes/colors/textures
default mode network
a circuit of brain regions that is active during daydreaming/thinking, medial parietal area
animals conscious?
Humans seem particularly intelligent, but non-human
animals possess much of the same neural machinery
Examples of non-human consciousness
self-recognition in mirror, human words with semantic meanings (parrot), complex learning & self-awareness in
octopuses, neural responses in crow that correlate with subjective perception of stimuli
localizationism
every brain area is an island, ex: phrenology and FFA/PPA
types of localizationism
modularity: regional preferences, not hard-separated
domain-specificity: a region does only x, never y or z
globalism
brain works as a whole, modern ex: connectionism (info stored in weighted connections)
functional segregation
Different areas of the brain are specialised for different functions
Functional integration
Networks of interactions among specialized areas
fMRI activations in task
changes in BOLD signal, lots of noise in data, lots of spontaneous activity...
spontaneous BOLD activity
occurs during task and at rest (intrinsic brain activity), resting-state networks (correlation between spontaneous BOLD signals of brain regions known to be related)
functional connectivity
what parts of the brain talk to each other
clustering brain-wide correlations into networks
can be chunked into networks and stay intact across many different tasks
default mode network association
medial prefrontal and lateral parietal lobes, hippocampus and temporal lobe, and they are physically connected with white matter bundle
DMN deactivates when
doing certain high-effort tasks that prevent you from daydreaming
DMN grows
with age
dorsal network
top-down, endogenous, goal driven, IPS, SPL, FEF
Ventral network
temporo-parietal junction, IFG/MFG, bottom up, stimulus driven
frontoparietal control network
executive functioning, control actions/behaviors, in many mental illnesses (depression, OCD, bipolar, schizo)
memory includes
long-term and short-term
long-term memory includes
explicit and implicit
implicit memory
procedural memory, ride bike, tie shoes, etc.
Types of implicit memory
classical and operant conditioning
classical conditioning
conditioned stim (bell) and unconditioned stim (food) become paired to make unconditioned response
operant conditioning
behavior-outcome association. ex: reinforcement (food when go left), punishment ( shock when go left), changes for wanted outcomes
explicit memory
semantic and episodic
semantic memory
facts
episodic memory
event from your life
HM
removed hippocampus, no new memories
anterograde amnesia
can't form new memories
retrograde amnesia
can't retrieve old memories
temporally-graded (remember more the longer before incident, and less before incident)
amnesiacs have intact
STM (normal digit span), procedural memory, semantic memory... generally intact
weather prediction task
learn rules of a weather prediction game, can't remember what cards they've seen but get more correct with time
amnesiacs have difficulty
imagining future events, loss of episodic
amnesiacs almost always have
episodic memory deficits
What happens in amnesia (recap)?
stm - good
implicit/procedural - good
semantic - might be impaired
episodic - definitely impaired
Special role of hippocampus
overcoming interference, birds with overlapping features and penguin
hippocampus does
pattern separation and completion
pattern separation
taking similar inputs and splitting into distinct representations
pattern completion
taking similar inputs and generalizing to a shared representation
working memory
keeping info actively in mind and manipulating it
timescale: tens of seconds
manipulating information
central executive, prefrontal
ST stores
visuospatial sketchpad, episodic buffer, phonological loop, parietal and lateral temporal
LT stores
visual semantics, episodic LTM, language, hippocampus/MTL/anterior temporal
ways to measure WM
digit-span task (finding limit of number of digits you can remember)
WM has
limited capacity, differs person to person, 7 plus or minus 2
chunking
organizing items into familiar, manageable units that lets you get more in WM