CEM 142 MSU Final Exam
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
189 Terms
Does aqueous sugar conduct electricity, why or why not
No, because there are no ions
Does aqueous NaCl conduct electricity?
Yes, because this is an ionic compound (metal/nonmetal)
What is the only IMF present in non polar molecules
London Dispersion Forces
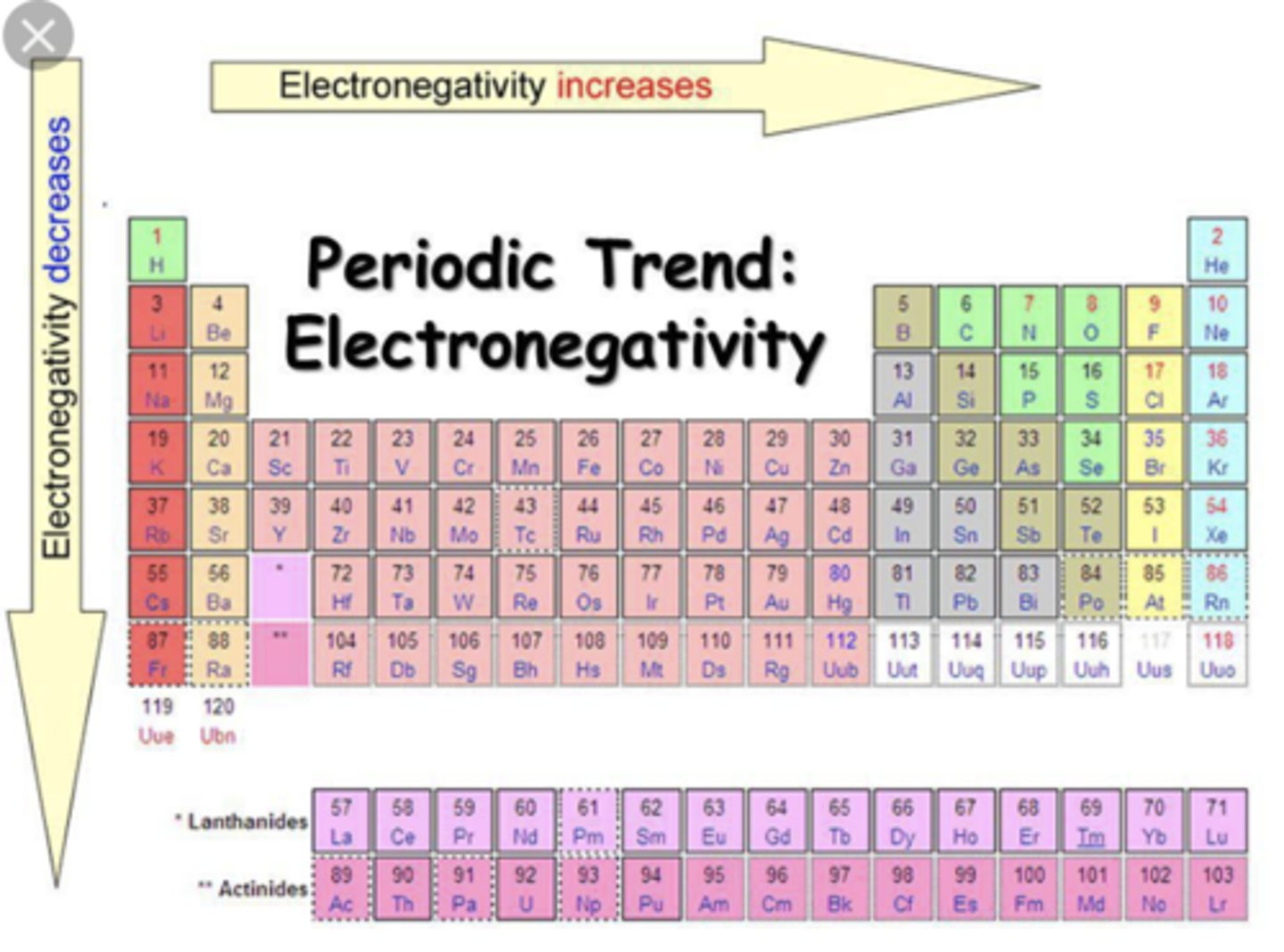
How does electronegativity change in the periodic table
Electronegativity increases from left to right (with the right being most electronegative), and increases from bottom to top (with top most electronegative)
What is present in ALL molecules
LDFs
What is Coulombs Law
unlike charges attract and like charges repel
What is an LDF
temporary fluctuating dipoles
What is the sign of an exothermic reaction
negative
Dipole dipole interactions are present...
only in polar substances
What is the sign of an endothermic reaction
positive
Explain hydrogen bonding and it's rules
Present between 2 molecules:
- the first must contain H covalently bonded to O, N, or F
- the second must have O, N, or F with a lone pair
Are bonds formed or broken during exothermic reactions
formed
If a hydrogen bond is present...
then so are LDFs and dipole dipole interactions
Is energy released or absorbed during exothermic reactions
released
How do you know which molecules has a higher boiling point when comparing 2 molecules
the molecule with stronger IMFs takes more force (energy) to break so it has a higher boiling point
Are bonds formed or broken in endothermic reactions
broken
The attraction between charges particles is caused by...
electronegativity
Is energy released or absorbed during endothermic reactions
absorbed
Does temperature increase or decrease during exothermic reactions
increase
(heat goes out of the system and the surroundings get hotter)
Does temperature increase or decrease during endothermic reactions
decrease
(heat goes into the system and the surroundings get colder)
When are IMFs present in water
solid and liquid phase
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed
What is a state function
depends only on the initial and final states, does not depends on the path taken
ex: the elevation of a camp site on a mountain is a state function because it is independent of that path taken to reach it
Enthalpy is a ______ function
state
What is the sign of enthalpy?
delta H
What is the sign of entropy?
delta S
What does it mean if delta S is negative
there is more order
What does it mean if delta S is positive
There is more disorder or chaos, more number of arrangements
The more possible arrangements, the _______ the probability of that state
higher
Systems are more likely to be in a ________ state
mixed
Why are systems more likely to be in a mixed state?
There are a great number of arrangements in this state, therefore entropy of the universe would be increasing
Why will energy always transfer from a hot block to a cold block
The energy will transfer from the hot block to the cold block until the two are at the same temperature because this allows for the greatest number of arrangements
In what phase is entropy (number of arrangements) the highest
gas
Explain the order of entropy from most to least
gas>liquid>solid
How can something be in a solid state if the entropy of the system decreases?
the entropy of the surroundings increases which means the total entropy of the universe is increasing
What is the delta S of the system if a cup of water is on a hot plate but the plate is below 273K?
The delta S of the system will be less than 0 because the number of arrangements decreases as the water freezes
What is the delta H of the previous system?
Heat is leaving the system since bonds are being formed, so the reaction is exothermic (-)
When 2 molecules are being compared, how do you tell which has the highest delta H of vaporization?
The one with the strongest IMFs because these require more energy to break
Delta S of the surroundings depends on what?
Temperature
If temperature is high, entropy change is...
low
If temperature is low, entropy change is...
high
What is the free energy equation?
deltaG= deltaH - (T)(deltaS)
Temperature is always _____ in the free energy equation
positive
Definition of a solution
homogenous mixture of 2 or more components
Definition of solute
thing being dissolved
Definition of solvent
Thing doing the dissolving
You make a solution of 100 grams of H2O and 5 grams of NaCl. What is the resulting mass?
Exactly 105 grams
You make a solution of 100mL of water and 5mL of ethanol. What is the resulting volume and why?
Between 100-105mL because volumes are not additive. Molecules can get closer together when they're mixed because the molecules can pack in tightly
How do you make a solution
Using a volumetric flask, add the solute to the flask and fill up the required volume with solvent, then read at the bottom of meniscus
What are the 7 strong acids
HCl, HNO3, H2SO4, HBr, HI, HCIO3, HCIO4
What are the 8 strong bases
LiOH, NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2, RbOH, Sr(OH)2, CsOH, Ba(OH)2
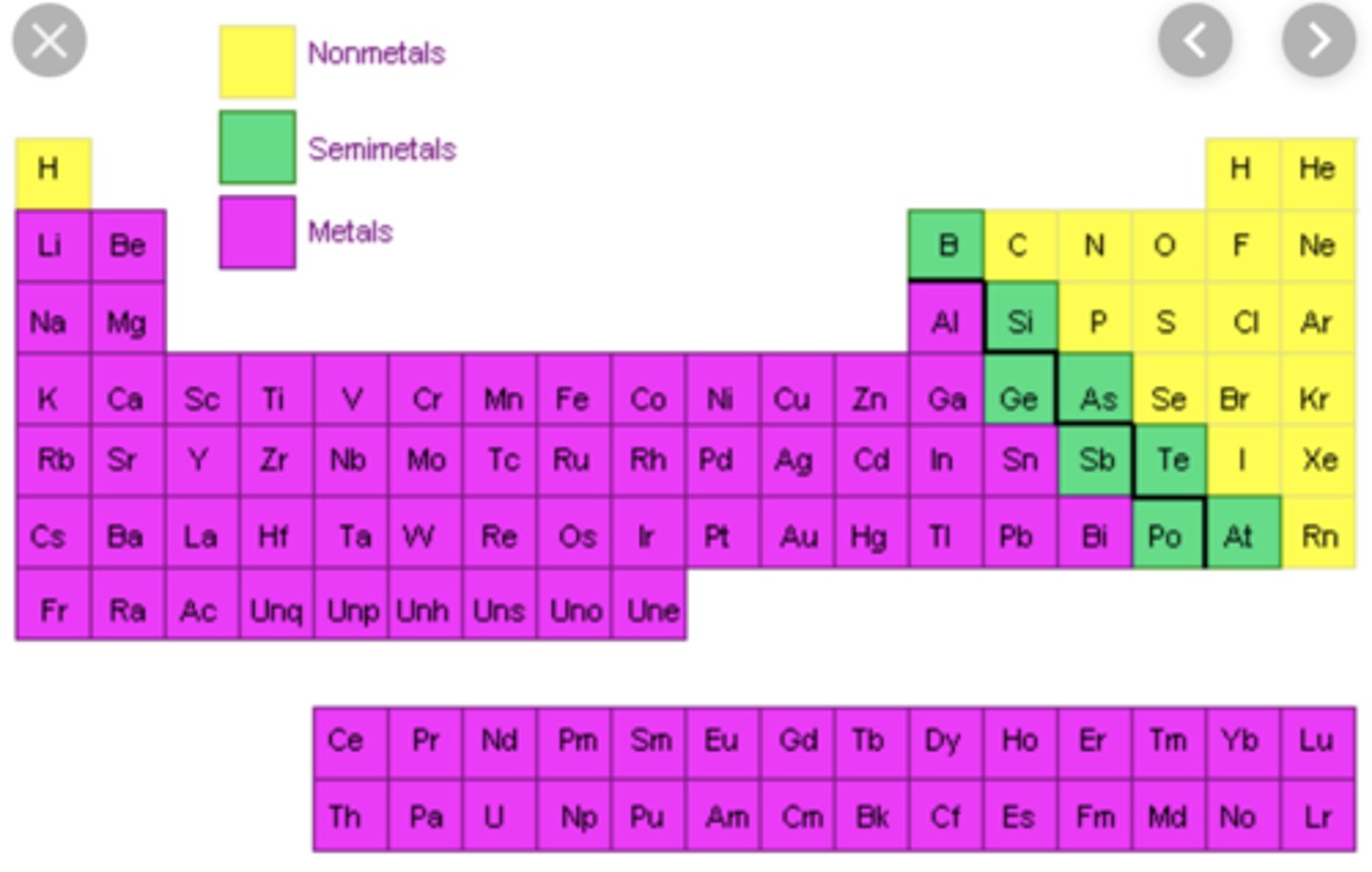
What are the metals and nonmetals
How do you tell if a molecule will dissociate into ions
If it's a metal paired with a nonmetal
Definition of immiscible
solute and solvent do not mix (like oil and water)
Definition of miscible
solute and solvent mix and form a solution; once mixed they do not unmix
Define saturated
no more solute will dissolve
Define unsaturated
if you add more solute it will dissolve
What is Molarity
mol/liter
What is percent mass?
same as parts per hundred
A 10% by mass solution has 10g of solute per 100 g solution
What is parts per millions (ppm)
1ppm solution has 1g of solute per 10^6 gram of solution
(same as 1ug microgram of solute per gram of solution)
What is parts per billion (ppb)
1ppb solution has 1g of solute per 10^9 gram of solution
(same as 1 nanogram ng solute per gram solution)
1 ppm =
1 mg/L
1 ppb=
1 ug/L
If you add water to a concentrated solution, does the concentration (amount of moles) change?
No, the amount of moles in the concentrated solution= the amount of moles in the dilute solution
What is the dilution formula
M1V1=M2V2
If interactions between particles in the solute are overcome, is this exothermic or endothermic
endothermic because bonds are being broken
If interactions between some particles in the solvent are overcome, is this exothermic or endothermic
endothermic because bonds are being broken
If interactions are formed between the solute and solvent, is this exothermic or endothermic
exothermic because bonds are being formed
The more CH groups a substance has...
the less soluble it is in water
What interactions exist within ionic compounds
ion-ion
Does delta G tell you anything about the temperature
No
When CaCl2 is added to water the temperature rises. What is the "system" in this scenario
the ions in solution and associated water molecules
When CaCl2 is added to water the temperature rises. What is the "surrounding" in this scenario
The non associated water molecules
If the temperature decreases during a reaction, what does this mean for the strength of bonds within the interaction and why?
This means that the solvent-solvent and solute-solute interactions are strongest. We can deduce this because if the temperature decreases, then the reaction is endothermic. This tells us that bonds are being broken, which tells us the breaking of the bonds is the strongest
If the temperature increases during a reaction, what does this mean fro the strength of bonds within the interaction and why?
This means that the solvent-solute interactions are strongest. We can deduce this because if the temperature increases, then the reaction is exothermic. This tells us that bonds are being formed, which tells us the forming of the bonds is the strongest
How do you find molarity from a given volume and mass?
Take the mass over the volume, (if the volume isn't in liters, convert it to liters), then multiply that by the molar mass to get the answer
If you're given the molarity, how do you find the concentration of one atom in the compound?
Take the molarity and multiply it by the individual moles given in the name of the compound (ex: CaCl2. The moles in Ca are 1 (because no number by it), and the moles in Cl2 are 2 (because 2 is by Cl2)

How do you find the total ion concentration?
Take the already calculated molarity, and multiply it by the amount of ions the molecule will split into over the total moles of the molecule (which will generally be 1)

Which thermodynamic factor is affected by temperature
delta S
Why don't oil and water mix?
The entropy of the system is higher in the unmixed state because non-polar molecules cause water molecules to cluster around them
What happens when a hydrocarbon enters water?
Water forms a cage (clathrate) around the hydrocarbon molecule
Definition of hydrophilic
water loving
Definition of hydrophobic
water fearing
Definition of amphipathic molecules
Have both polar and non polar parts
What happens when an amphipathic molecule enters water
the polar part interacts with water through H-bonds, and the non polar part causes the water to form a clathrate around it
What will amphipathic molecules do in water
form micelles
Definition of a micelle
organized clusters of amphipathic molecules
What part of the micelle is hydrophilic
The water loving head
What part of the micelle is hydrophobic
The water fearing tail
Solubility of gases ______ as temperature increases. Why?
Decreases; because the entropy of the gas would decrease as there would be fewer possible arrangements, so if T increases and delta S increases, delta G would become more positive
Definition of an alloy
mixture of metals
What are the two types of alloys?
substitute and interstitial
Define substitute alloy
if atoms are of a similar size, the solute atoms substitute for the solvent atoms
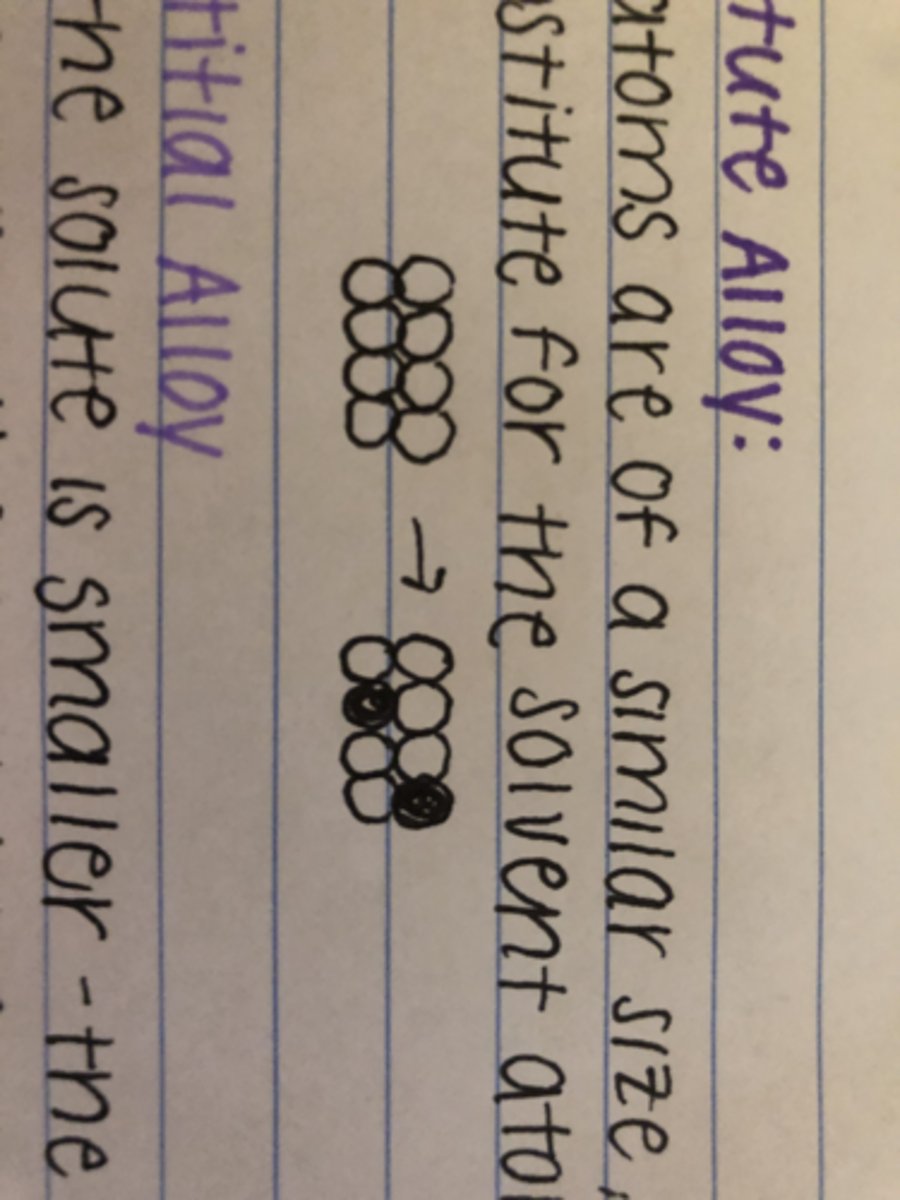
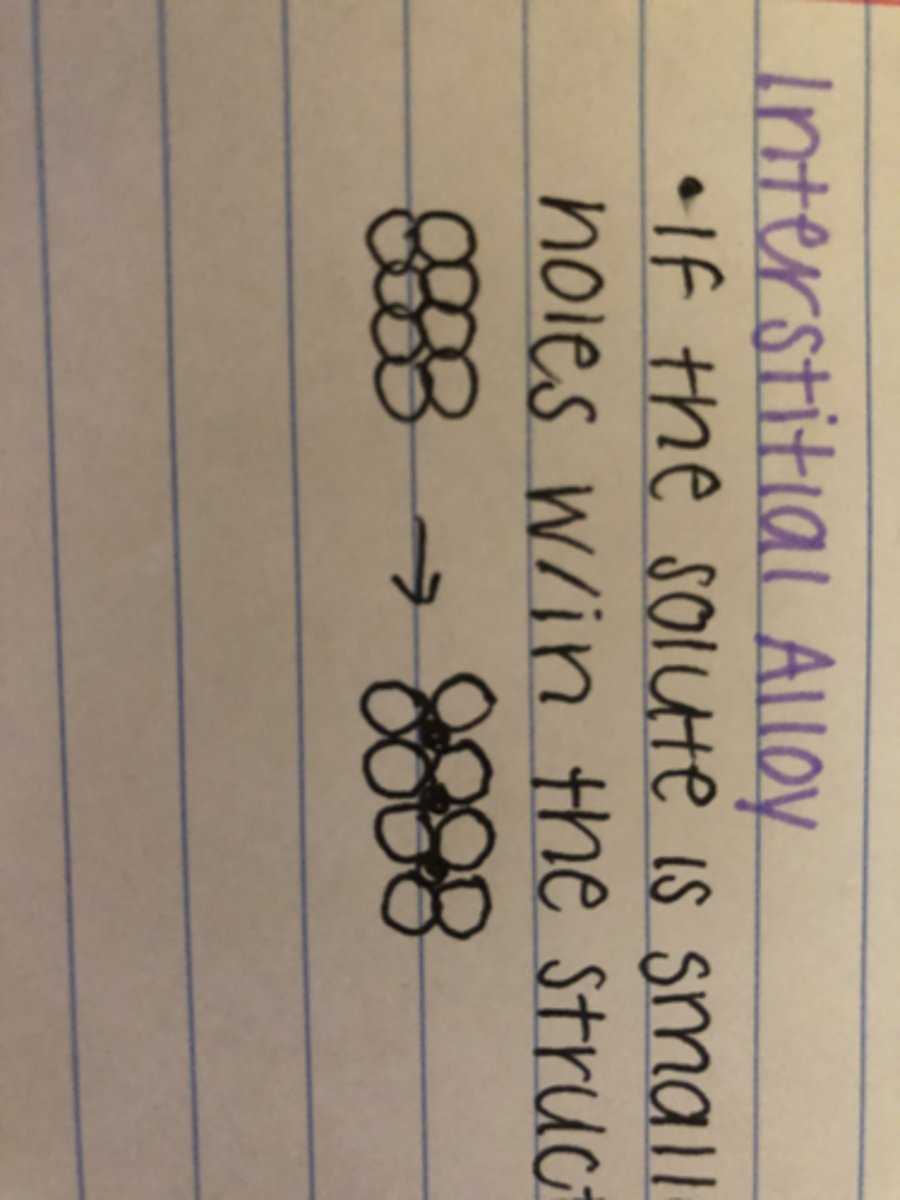
Define interstitial alloy
If the solute is smaller, the atoms can sit in holes within the structure
What is the Arrhenius Acid-Base model?
Says that an acid dissolves in water to always give H+, and a base dissolves in water to always give OH-. This model completely ignores the role of water and therefore isn't used that much
Does H+ exist in aqueous solution?
No, it's generally transferred to water which is why the Arrhenius Acid-Base model isn't a good representation
When given the equation HCl + NaOH <--> NaCl + H2O, what would be the detailed ionic equation?
H + Cl + Na+ OH <----> Na + Cl + H2O
When given the equation HCl + NaOH <--> NaCl + H2O, what would be the spectator ions?
Na+ and Cl-
Definition of spectator ions
species that don't change throughout the reaction are spectator ions
When given the equation HCl + NaOH <--> NaCl + H2O, what is the net ionic equation?
H + OH <----> H2O