O2 Transport [1]
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
the process whereby gas molecules move from an area of high partial pressure to an area of low partial pressure.
diffusion
The relationship between Hb saturation and PO2 is not linear4 ; instead, it forms what curve
S-shaped curve
this part of the curve represents the normal operating range for arterial blood
upper flatter part
in this part of the curve, major changes in PaO2 have little effect on SaO2, indicating a strong affinity of Hb for O2.
flatter upper part
With a normal PaO2 of 100 mm Hg, SaO2 is approximately
97%
true or false: If a disease process results in a substantial reduction in PaO2 to 65 mm Hg, SaO2 would not drop as drastically and will be approximately 90% in the curve
true
in this drop of PO2, the curve steepens dramatically and the SaO2 drops significantly.
<60 mmHg
with PO2 less than 60 mm Hg, a small decrease in PO2 causes a large decrease in SaO2, indicating what affinity
less affinity
states that the total O2 uptake by the peripheral tissues is equal to the product of the blood flow to the peripheral tissues and the arterial-to-venous O2 content difference
fick equation
Fick’s equation
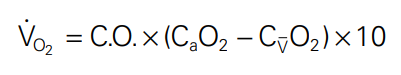
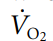
whole-body O2 consumption
CaO2
arterial O2 content

mixed venous O2 content
factors affecting O2 loading & unloading [3]
blood pH
body temperature
erythrocyte conc.
impact of changes in blood pH on Hb’s affinity for O2 is called
bohr effect
this Hb is less soluble than normal Hb, which causes it to become susceptible to polymerization and precipitation when deoxygenated.
sickle cell Hb
Certain events such as dehydration, hypoxia, and acidosis cause HbS to crystallize and the RBCs to become hardened and curved ; what Hb
sickle cell
this is an abnormal form of the molecule in which the iron in the heme-complex (Fe2+ ) loses an electron and is oxidized to its ferric state (Fe3+ ).
methemoglobin
In the ferric state, the iron ion cannot combine with O2. This is called
methemoglobinemia
this is the chemical combination of Hb with CO.
carboxyhemoglobin
The affinity of Hb for CO is more than how many times greater than it is for O2.
>200x
. The combination of CO with Hb shifts the HbO2 curve to?
left
Fick’s first law of diffusion law for determining the rate of gaseous diffusion across biologic membranes. [equation]

cross-sectional area available for diffusion
A
diffusion coefficient of the gas
D
thickness of the membrane
T
partial pressure gradient across the membrane
P1-P2
rewritten fick’s first law of diffusion
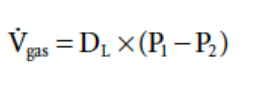
a measure of the proportion of available Hb that is carrying O2
saturation
this is computed as the ratio of HbO2 (content) to total Hb (capacity).
saturation
this Hb is for fetal life
fetal Hb
up to how long does fetal Hb exist
fetal life up to 1 yr
true or false: HbF has a greater affinity for O2 than normal adult Hb, manifested by a leftward shift of the HbO2 curve
true
what effect: Deoxygenation of the blood increases its ability to carry carbon dioxide
haldane
this is O2 delivery to tissues
DO2
O2 delivery to tissues formula
DO2 = CaO2 x CO
Expected PaO2 in older adults formula
100 - (0.323 x age in years)
this can still occur when the arterial O2 Content (CaO2) is normal but blood flow is reduced
hypoxia
this is Local Reductions in perfusion
ischemia
cyanide poisoning is under
dysoxia
in this, cellular uptake of O2 is decreased
cyanide poisoning
this disrupts the intracellular cytochrome oxidase system, preventing cellular use of O2
cyanide
A decrease in alveolar ventilation occurs when [3]
inadequate minute volume
increased dead space ventilation / min
V/Q imbalance