lecture 5
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
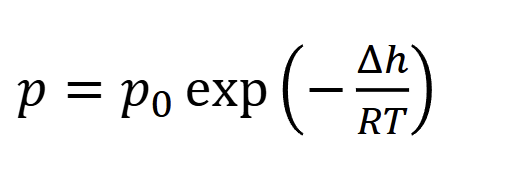
what do u assume
h is independent of temp
colligative properties
Change in other properties only dependent on number of solute
molecules → colligative properties
when are colligative properties valid
Only valid when concentration of solute is low enough to neglect
interactions between molecules
Examples of colligative properties
– Vapor pressure lowering
– Boiling point elevation
– Freezing point depression
– Osmotic pressure
Raoult’s law

does chemical potential water molecules in liquid phase decrease or increase when adding solute
Chemical potential of water molecules in liquid phase decreases
when we add solute
Water molecules now interact with solute particles too (e.g., via hydrogen bonding or ion-dipole interactions)
This makes water molecules less free to move or evaporate
👉 So their freedom goes down → chemical potential decreases
We now have 𝜇𝑤,𝑙𝑖𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑑 < 𝜇𝑤,𝑣𝑎𝑝𝑜𝑟
Henry’s Law what do u assume
assume gas dissolves liquid
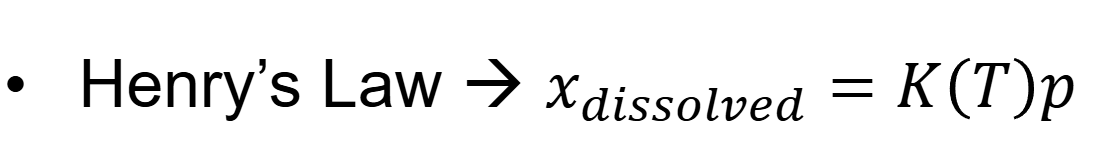
explain
Amount of dissolved gas increase or decrease with pressure
increase
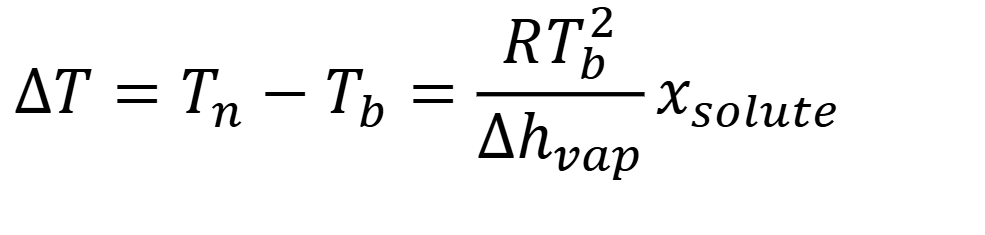
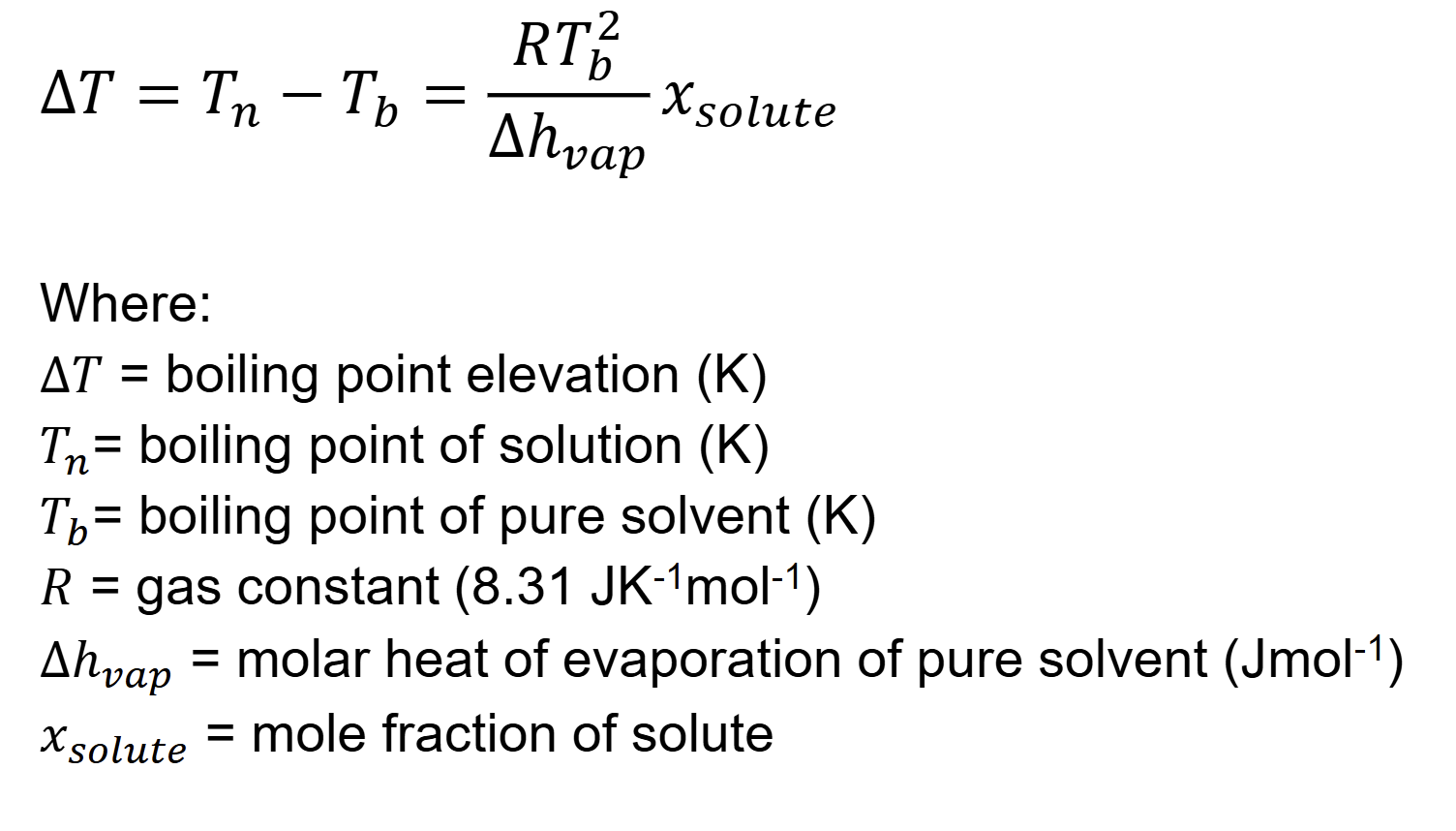
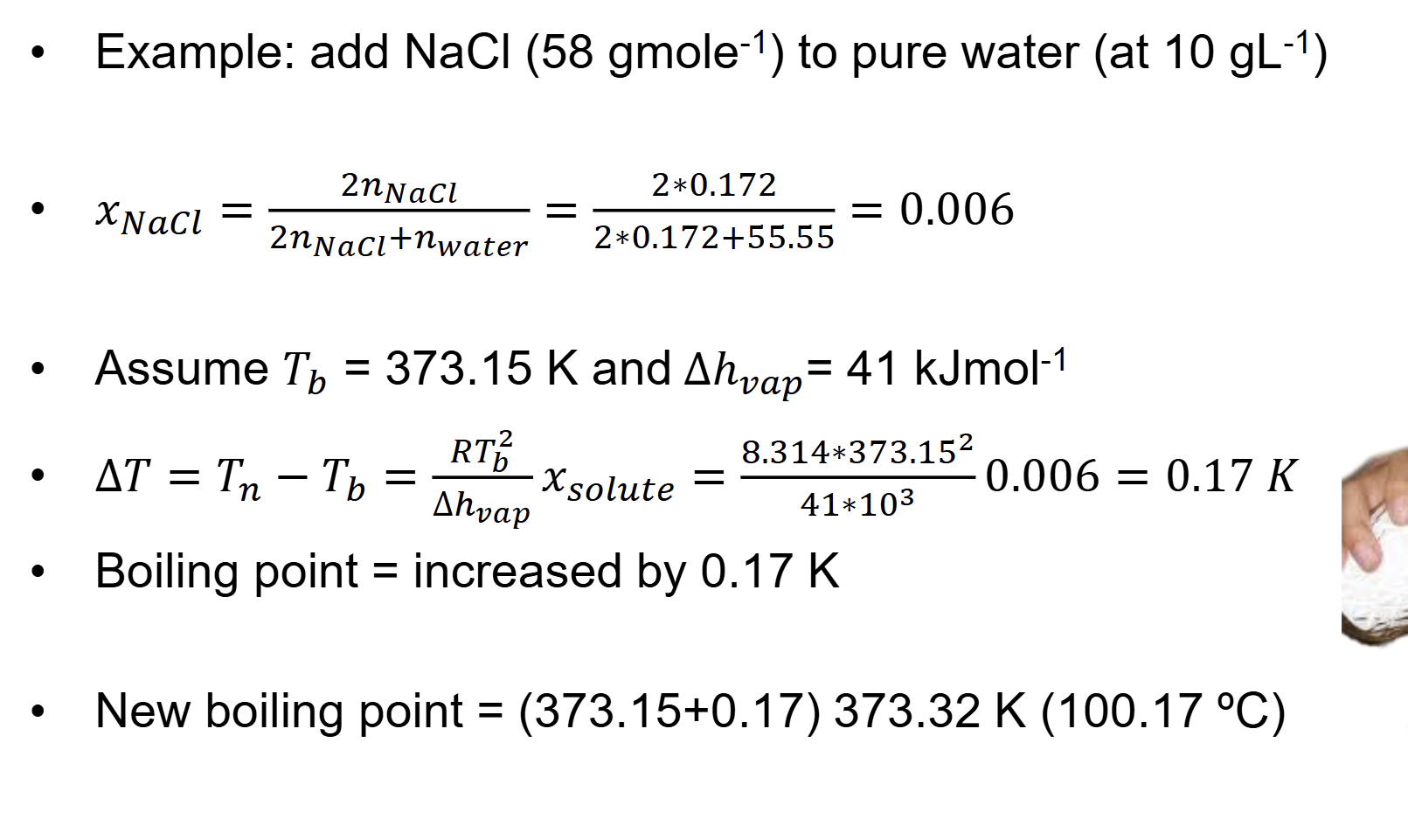
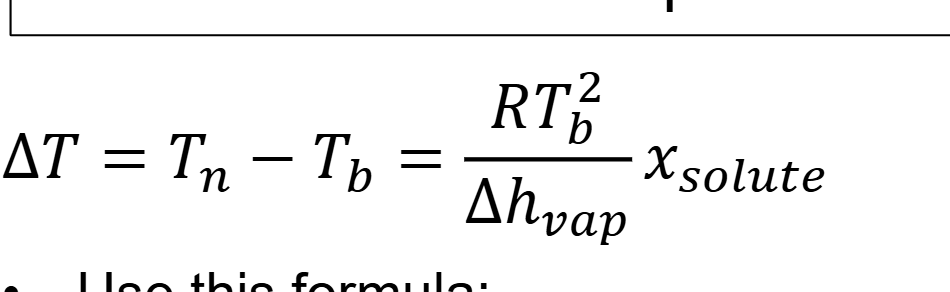
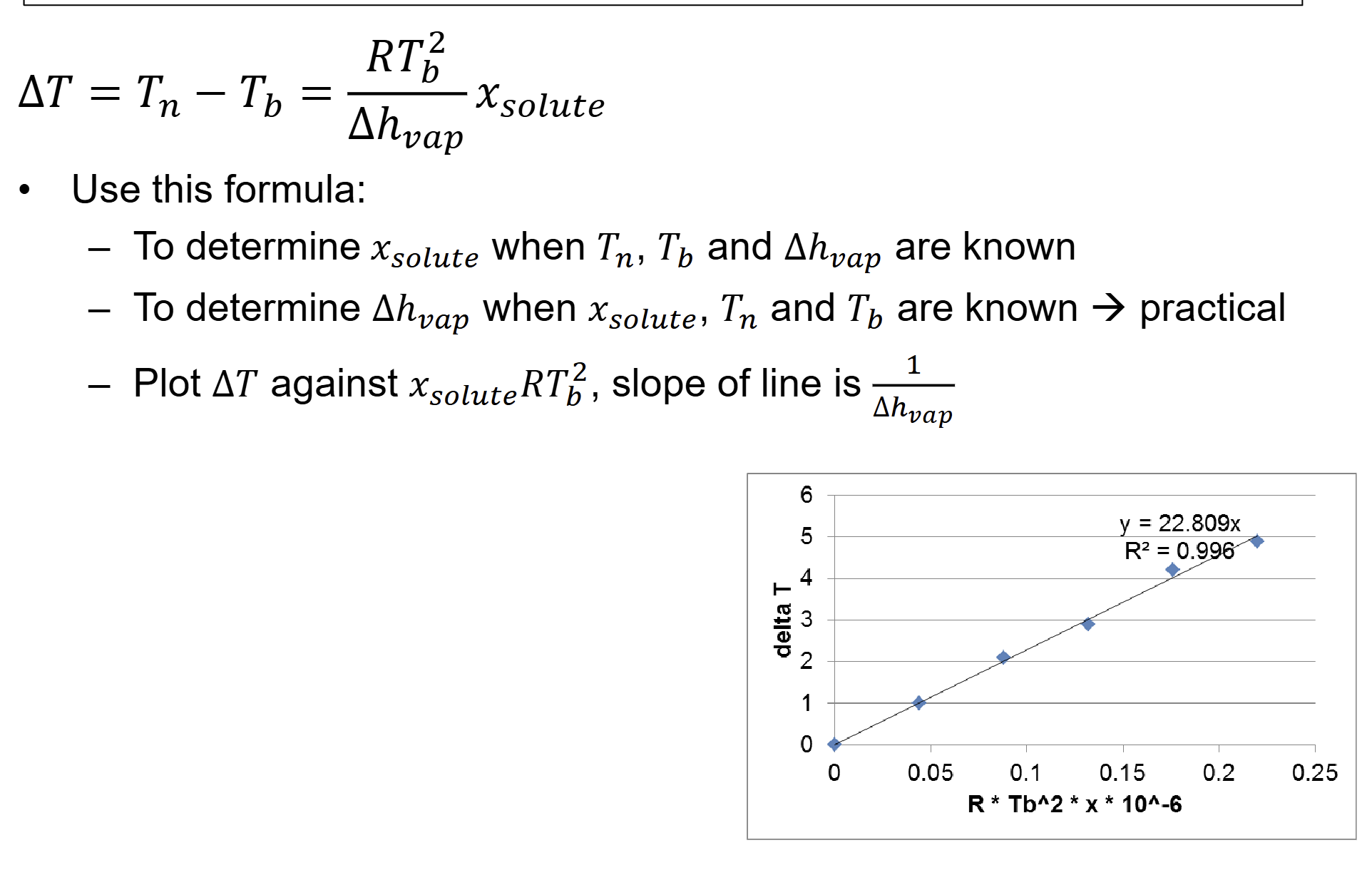
what is slope of line
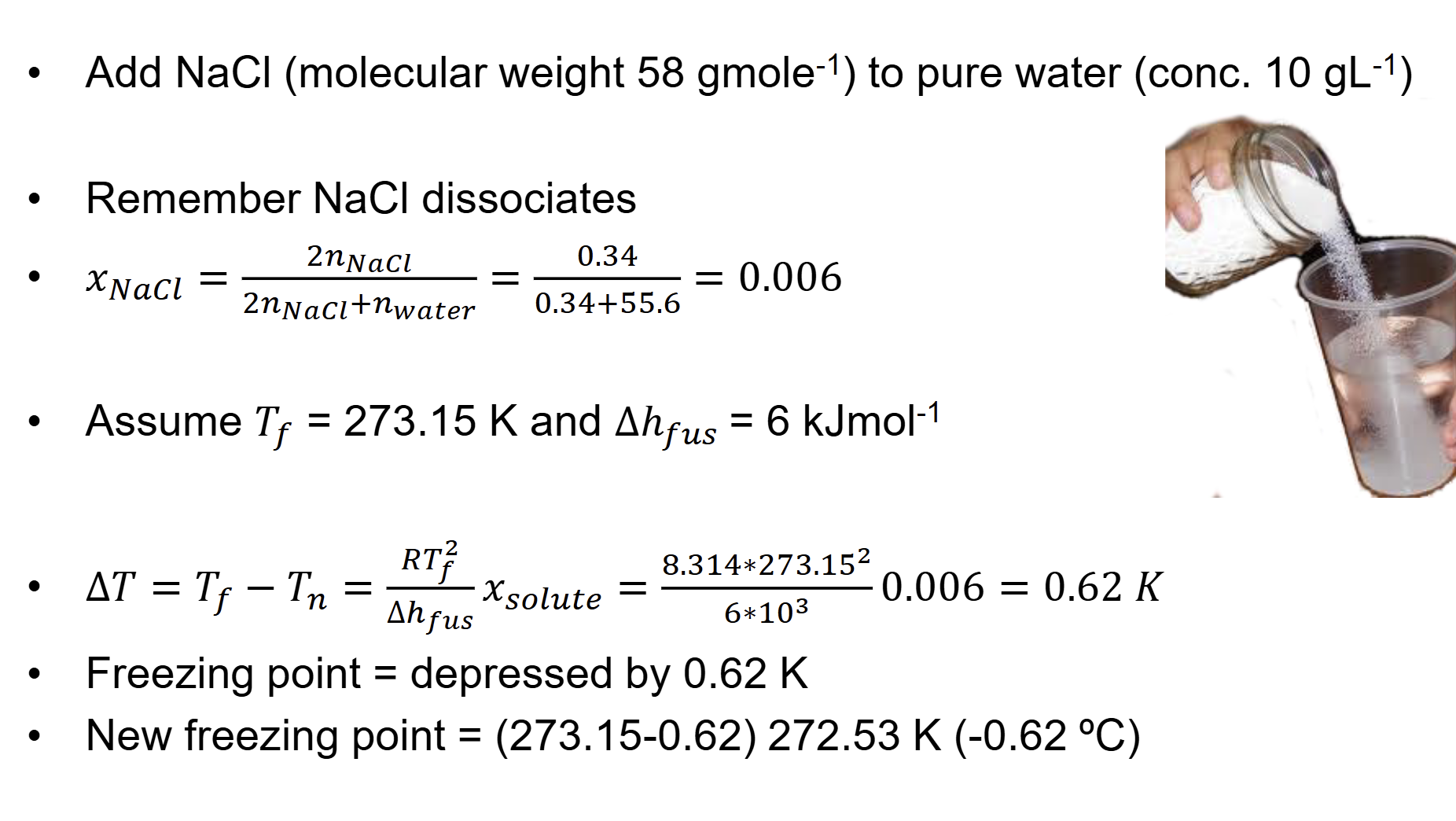
what happens when u add solute to liquid phase(freezing point depression)
Add solute to liquid phase
– Further decrease in freezing point
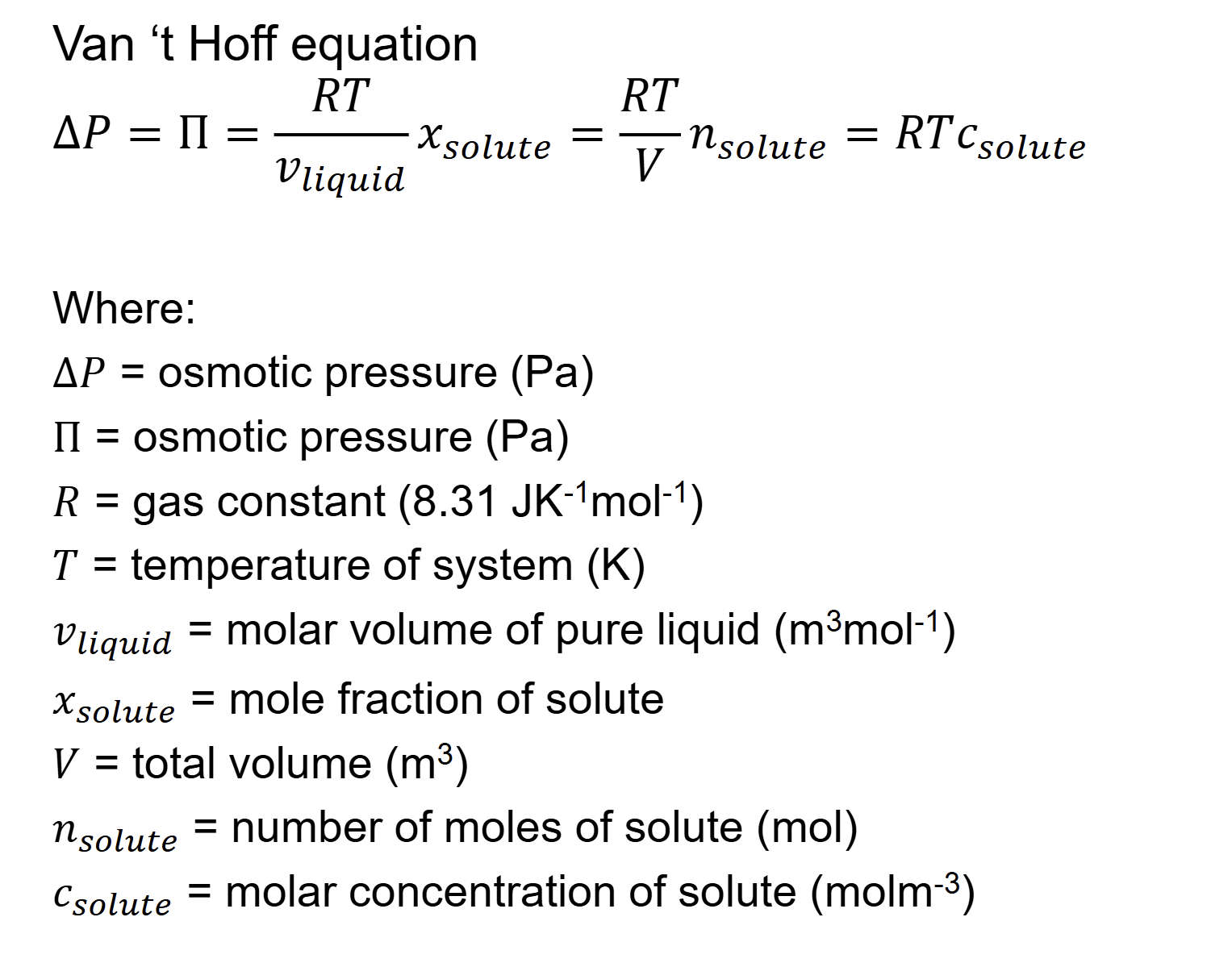
whats the principle of osmosis
semi-permeable membrane
pressure difference= osmotic pressure
what happens when adding solute osmosis
uw is lowered
when do u get eqm with osmosis
Process stops at fluid level where osmotic pressure is balanced by
hydrostatic pressure difference
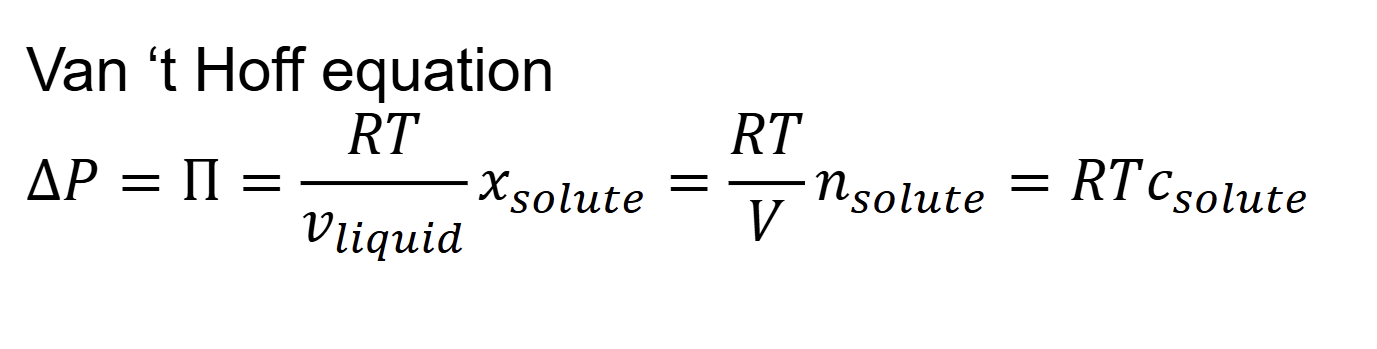
what happens with smaller molecules in osmosis, or more ions
smaller molecules=more moles= more particles
more ions=more particles=increase osmotic prressure
Does smaller molecules mean higher osmotic pressure?
On a weight basis small molecules are more effective than large
molecules, even more true when they dissociate
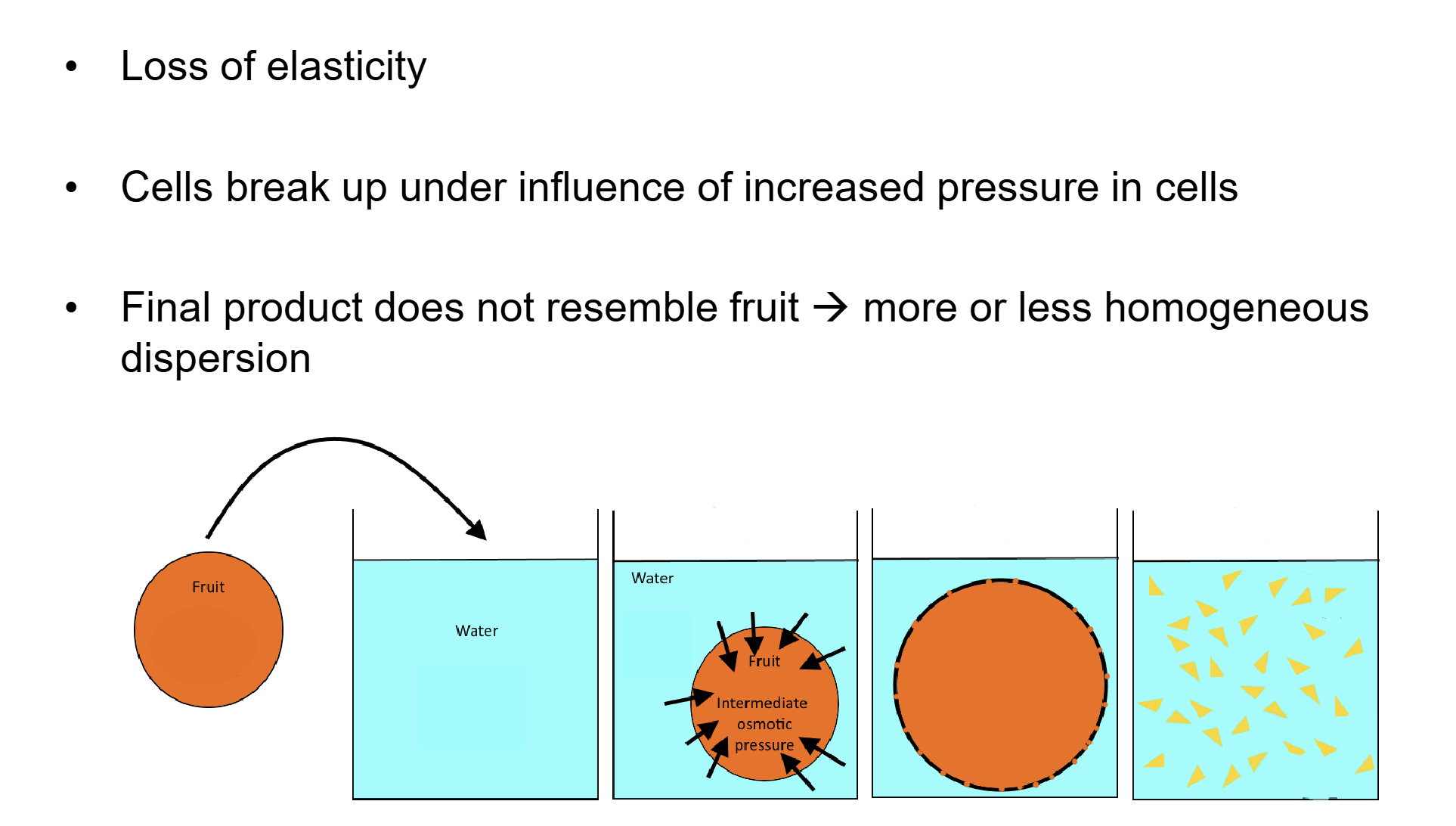
describe fruit cooking
Texture of fruit cooked in water vs. concentrated sugar solution
→ big difference
– Cook fruit in sugar solution → shrivels but stays intact
– Cook fruit in water → completely disintegrates
• Difference caused by water transport through osmosis
fluid for patient hydration has to be
Fluids for patient hydration need to be
isotonic
how would u desalt water
Process of osmosis reversed to de-salt seawater
• Apply external pressure → pure water is transported through semi-
permeable membrane leaving salt molecules behind
• Since osmosis is such a strong effect, reversed osmosis is
expensive
rank these :
freezing point depression
osmotic pressure
boiling point elevation
vapor pressure lowering
Osmotic pressure >> Vapor pressure lowering > Freezing
point depression > Boiling point elevation
Only Very Frosty Beverages
does osmotic pressure decrease or increase when dimers/trimers are formed
When proteins form dimers/trimers, the number of particles decreases (even though the total mass stays the same).
Fewer particles = lower osmotic pressure.