CPR
1/695
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
696 Terms
HTN in pregnancy
“New Moms Love Hugs”
Nifedipine
Methyldopa
Labetalol
Hydralazine
Tids
Native valve: viridans>enterococci>pyogenes
Prosthetic:
Acute: epi> aureus/epi
Chronic: epi > aureus > viridans
IV drug: aureus, Pseudomonas, viridans, candida
A1 VC, A2 VD
Shock:
PCWP low in hypovolemic, distributive, PE/pneumothorax
MS -hi PCWP > LVEDP, makes sense
Regurgs make PV loop blobs
Inc SV in regurgs
Dec SV in stenoses, mitral decreases EDV while aortic increases ESV
IV → RH IE → PE
Gallolyticus → AR
Distributive shock
pressors (VC), epi, NE. Not for others bcuz hypoperfusion
Ezetimibe
Inhibit chol absorb @ brush border. NPC1L1 transporter
Bempedoic Acid
Inhibit ATP citrate lyase → ↓Chol synth (combo w/ statins)
Bile Acid Resins
Chol → bile acids in liver → ↓LDL (combo w/ statins)
Cholestyramine
Colestipol
Colesevelam
PCSK9 Inhib
Monoclonal Ab prevent receptor degradation → ↑LDLR recycling → ↓LDL
Alirocumab
Inclisiran
Evolocumab
Fibrates
LOWER TG. Activate PPAR-alpha → upregulate LPL, ↑Liver FA ox
“Gem is not a gem” - do NOT combine w/ statins
Niacin
(B3, Nicotinic Acid)
Inhibit diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2.
Prostaglandins → flushing. Blunt w/ aspirin (inhibits prostagland).
Bile acid resins & statins overlap in what mech?
upregulate LDLR
VD (arterial)
Mech: ↓afterload → ↓BP
Adv: reflex tachy
- Hydralazine: lupus-like syndrome, fluid retention
- Minoxidil: opens K+ channels. Adv: hypertrichosis
Ca-Block Dihydropyridine
Mech: Greater effect on vessels. Coronary a VD = prevents vasospasm / ↓afterload → ↓O2 demand
Adv: edema, flushing, headache, constipation, gingival hyperplasia
Interactions: Inhibit action of simvastatin & digoxin
- Amlodipine
- Nifedipine: reflex tachy, hypotension, dizziness/transient headache, coronary steal
Ca-Block Non-Dihydropyridine
Mech: Greater effect on heart.
Adv: edema, constipation, bradycardia, AV block, gingival hyperplasia
Interactions: B-block
Contra: HFrEF!
- Verapamil
- Diltiazem
ACEi
Mech: No Ang II → ↑bradykinin → VD → ↓aldosterone (inhibit RAAS) → fluid offload. Reduce myocardial remodeling.
Adv: hyperkalemia, dry cough (bradykinin), high creatinine, angioedema
Interaction: NSAIDS
Contra: renal a stenosis
Lisinopril
Enalapril
Captopril
ARBs
Mech: Block Ang II → VD → ↓aldosterone → fluid offloading. No bradykinin impact = no cough.
Adv: hyperkalemia, mild creatinine
Contra: renal a stenosis
Valsartan
Losartan
Thiazide Diuretics
Mech: inhibit Na/Cl resorption in distal tubules → ↓venous return → ↓CO
Adv: “HyperGLUC” hyperGlycemia, dysLipidemia, gout (hyperUricemia), hyperCalcemia, hypokalemia (mm cramps, arrhythmia)
- Hydrochlorothiazide
- Chlorthalidone
Loops and thiazides both lead to gout, but…
Loops → hypocalcemia
Thiazide → hypercalcemia
Loop diuretics
Mech: Inhib Cl/Na/K symporter to offload Na/Cl → ↓CO, ↑TPR
Adv: hypokalemia, ototox, gout (hyperuricemia), alkalosis
Furosemide (Lasix)
K+ sparing Diuretics
Mech: Na/H2O excretion, block K excretion
Adv: Hyperkalemia, GI upset, acidosis
Aldosterone Antag / Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists:
Spironolactone - gynecomastia
Eplerenone
ENaC Inhib:
Directly block Na chann in collecting duct → Na offload
Adv: kidney stones
Amiloride
ACEs/ARBs
↓Afterload & Preload
Statin adverse effects
increased CK & myalgias, renal fail
How do B-blockers work?
↓afterload → ↓BP, HR, contract → ↓O2 demand
B1 block in kidneys → ↓renin release → ↓BP
Over time ↑CO → allowing heart to recover from sympathetic activation
Adv for all: “FED” Fatigue (exercise intolerance), ED, Depression. Other: bronchospasm, reflex tachy from stopping abruptly, masking hypoglycemia symptoms like tachycardia & tremors, NOT sweating (muscarinic).
Non-selective unique adv: hyperlipidemia (↓HDL, ↑triglycerides)
Contra: AV block, COPD/asthma (especially non-select)
B-Block Breakdown
Non-selective (B1&2): Prop, Tim
Adv: bronchospasm, hypotension, hyperlipidemia (↓HDL, ↑triglycerides)
Cardioselective (B1): Aten, Metop, Esm, Bisop
Adv: brady, AV block, fatigue
Nonselective w/ A1 Block (B1,B2, A1): Carvedilol, Labetalol
Partial VD effect from A1 antagonism
Adv: orthostatic hypo
Partial Agonists (B1, B2): Pindolol, Acebutolol
Less brady!
A1 Antag
Mech: VD smooth m → ↓Preload/Afterload → ↑CO
Adv: fainting
Prazosin
Terazosin
Direct Renin Inhib
Mech: ↓Ang I, II, aldosterone → ↓BP
Alsikiren
“karen cares for her kidneys!”
Adverse effects of nifedipine
Dihydropyridine Ca Block: edema, flushing, headache, constipation, gingival hyperplasia
Nifedipine-specific:
Reflex tachy
hypotension
dizziness/transient headache
coronary steal
Class I antihypertensives have an adverse rxn w/ which class?
Chloroquines!
Effect:
Mortality benefit in HFrEF
RAA antag (ACE, ARB, Nep)
B-block
MRA
SGLT2
Maximal med therapy w/ EF <35% → cardioverter defibrillator to prevent vent arrhythmias
Side effects ACE/ARNI/ARB
Angry (angioedema)
Hyper (hyperkalemia)
Hyppos (hypotension first dose)
Guffaw (GFR)
Terribly (teratogenic)
Two high intensity statins…..
Atorvastatin
Rosuvastatin
Atropine
chronotropy
Amiodarone effects
Bluegray color, angioedema
Isolated HTN in African American
Thiazide
Propranolol
SVT hyperthyroidism
Angina w/o troponin
vasospastic. Ca block
Digoxin
vagal tone
AV conduction
(PR interval)
slows in B-block & Ca-block
Statins and fibrates contraindicated due to
myoglobinuria
Acute Rheumatic Fever —> RHD —> mitral regurg (early) → mitral stenosis (severe)
Type II hypersensitivity rxn
Ab to bacterial M proteins
JONES
Joints (polyarthritis)
Carditis (valvulitis, myocarditis, pericarditis)
Nodules (subcu tendons/bones)
Erythema marginatum (rash on trunk)
Sydenham chorea (jerking)
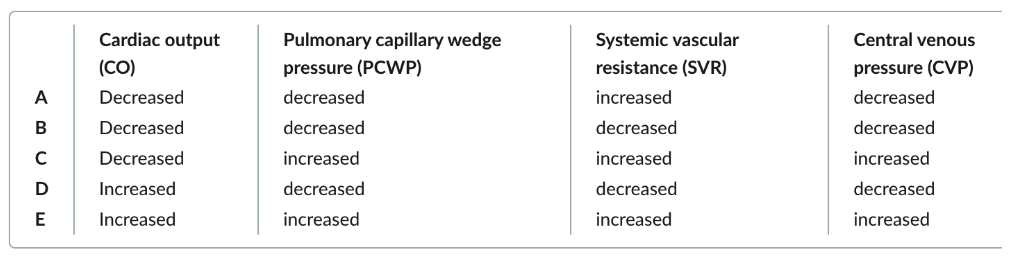
A: hypovolemic shock
B: late-stage septic shock
C: cardiogenic shock
D: distributive shock
Most important risk factor for aortic dissection
HTN
PDGF
intimal migration of smooth m
VD CHALK: CO2, H+, Adenosine, Lactate, K+
Prostacyclin
VC: thromboxane, endothelin
CK-MB best for acute recent/recurring MI <48hr
Trop elev in nstemi & stemi. 4 hr, rises for days
WPW = Bundle of Kent
Tall V in MR Wiggers
A before P, IIa before III (&apoE!) - “extravasation of lipoproteins” = achilles
MI progression
Coag necrose w/ dense neutrophilic infiltrate 1-3d - fibrinous pericarditis
Hyperemic gran tissu w/ macros 3-10d
Rupture happens late, 3-5d
Homocystinuria
downward subluxation + learning disability. Marfan upward w/ normal learning.
Abdominal aorta common site of endothel strain →
atherosclerotic plaques
Loops ↓CO, ↑TPR
Restrictive CM findings Congo, biatrial enlarge
Endothel cell dysfunc → LDL oxidation → foam cell (fatty streak)
subacute endocarditis: fibrin clot formation
ANP released from atria → cGMP → inhibit RAAS
BNP released from ventricles → cGMP → inhibit RAAS
Driving pressure for pulmonary circulation
diff btwn PA & LA (start to finish). MPAP - LAP
What part of myocyte AP does T wave (repolarization) occur?
phase 3 (rapid repolarization toward membrane pot)
PVR high in fetus
Low BP physiology effect
Low V → ↓ Kid perfusion (renin release) → Angiotensin I → Angiotensin II → VC
Atropine
blocks parasympathetics
Cardiac myocyte chng after blockage
cardiomyocyte will have increased excitability & expanded QRS complex (ischemia → less O2 → less ATP → less Na increase, shorter plateau
Look @ slope of phase 0 for conduction velocity. Fast = steeper slope.
Nodal cell phase 0 depolarization mainly triggered by opening of L-type Ca. Phase 4 gradual depolarization by funny chann
DADs provoked by
digitalis glycosides, ischemia, hypokalemia, catecholamine
Exercise pv loop: ↑ contractility = ↓ESV. ↑ venous return = ↑EDV. ↑ afterload = ↑Systolic P
Pressure increased upon birth
LAP
What part of the nodal AP does sympathetics and para alter?
Phase 4 funny channel slope to cause faster or slower depolarization
Non-infective endocarditis
procoagulant release
lymphocytes indicate a viral infection
neutrophils indicate a bacterial infection
A-hemolysis: green, partial RBC lysis
B-hemolysis: clear zone, complete lysis
Y-hemolysis: no lysis
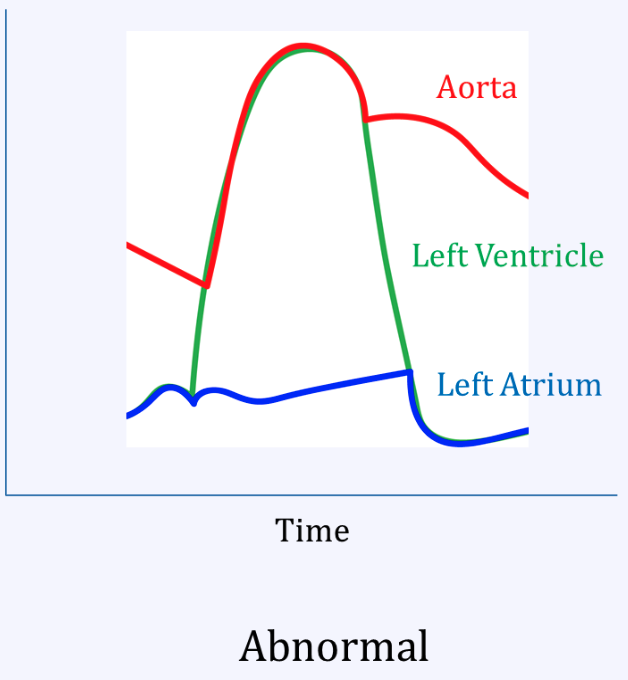
Aortic regurg
Mitral stenosis
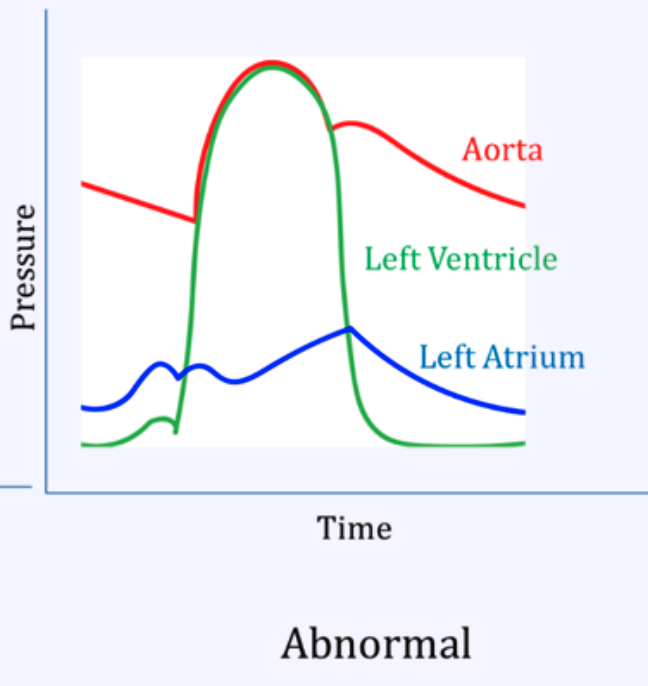
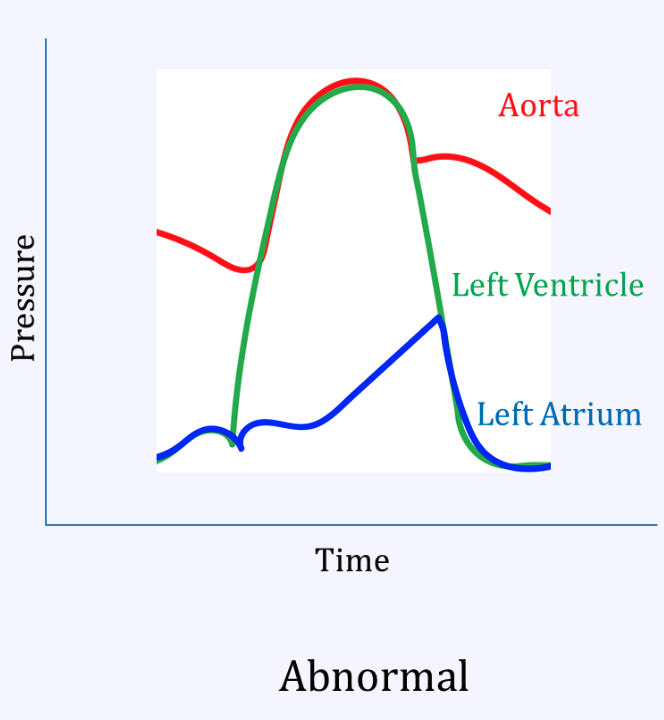
Mitral regurg
Aortic stenosis
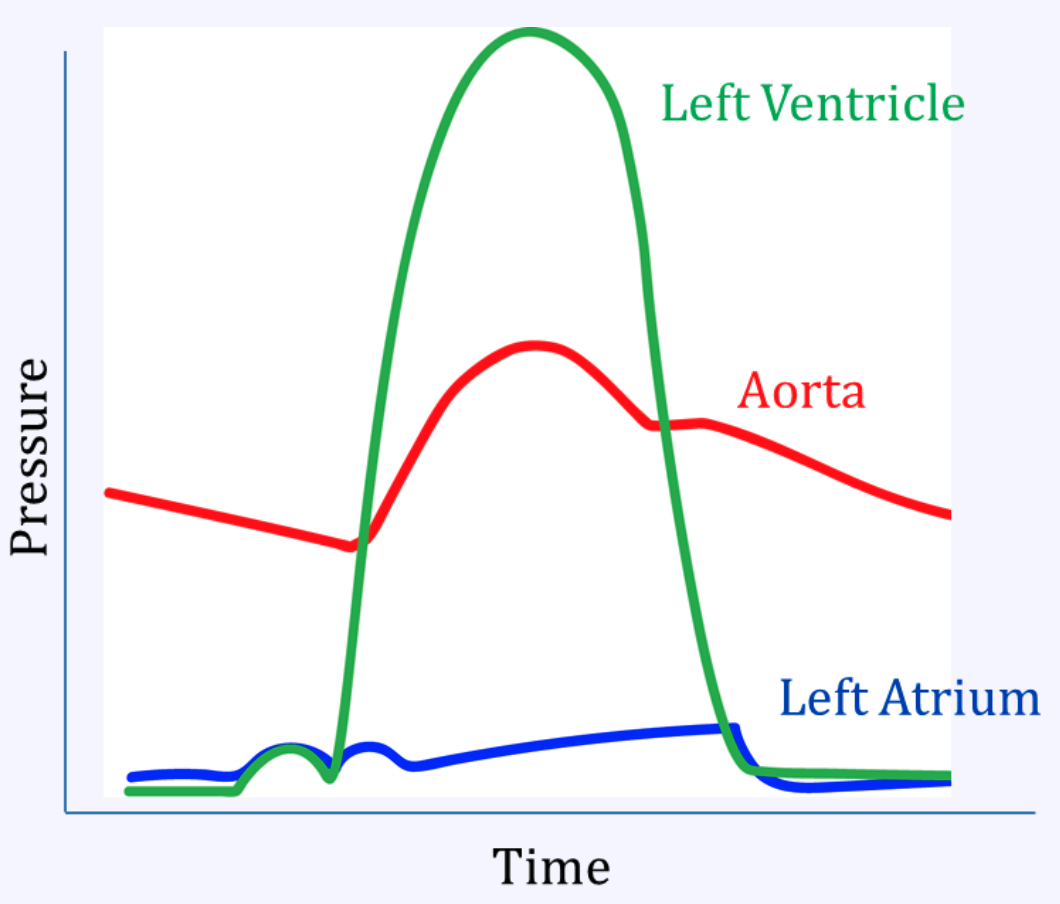
AV delay: 1st degree, Wenckebach, 3rd degree possible
His delay: Mobitz 2, 3rd degree possible
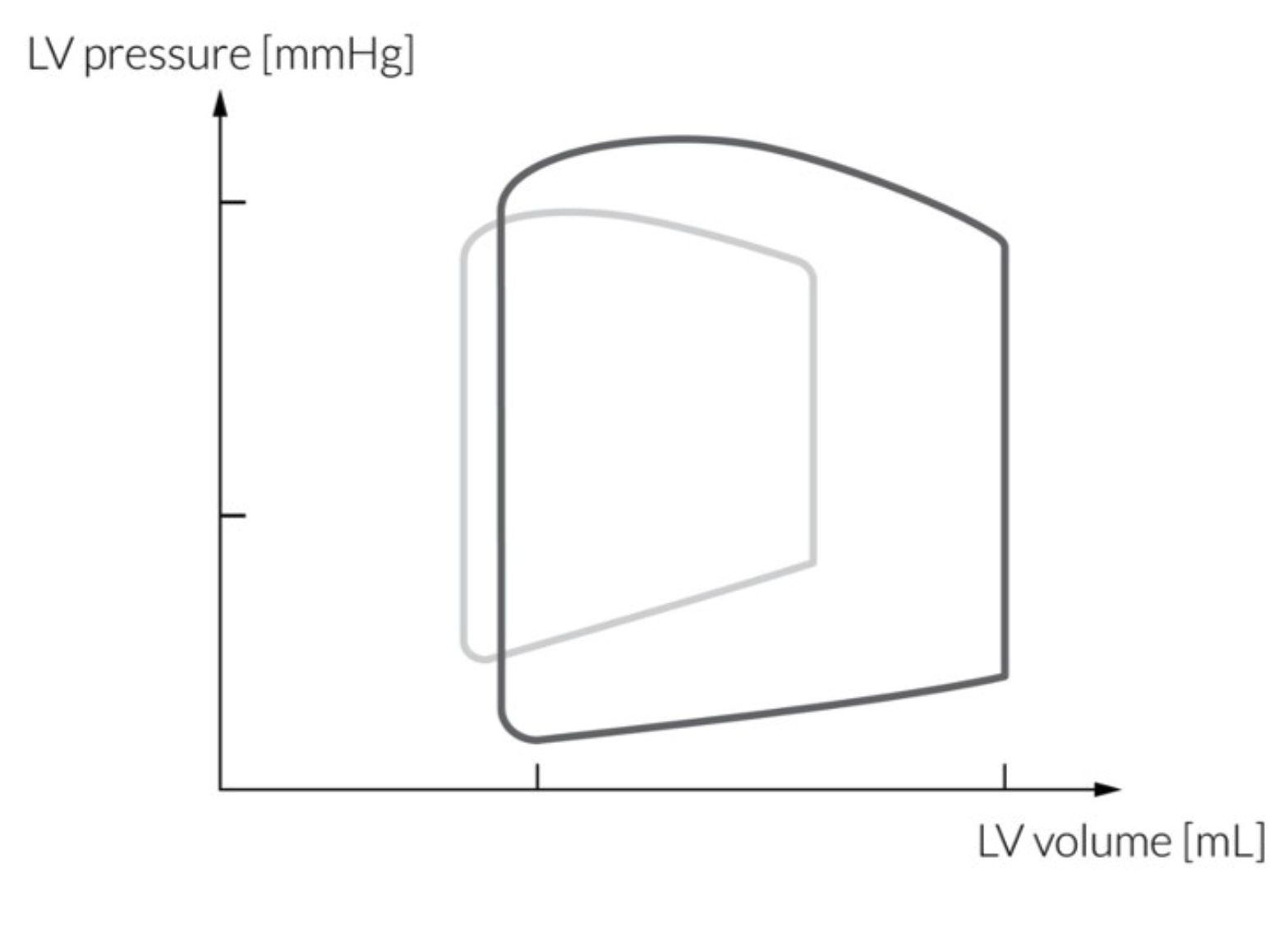
LV compliance decrease
RHC - vv
LHC - aa
HIS bundle = AV block
BBBs are just one side, not AV!
AV Blocks
Lyme disease, Borrelia burgdorferi can cause any of the following:
First Degree: PR > 0.2 (one large box)
Group beating diff from 3rd degree.
Second Degree:
Mobitz 1: “Long long PR drop, then you have a Wenckebach”
Mobitz 2: PR constant, random QRS drop
Third Degree (complete): P and QRS uncoordinated
Atria and vents beating rhythmically @ own paces
Side note:
First degree: R is far from P
Second degree: Some R’s don’t get through
Third degree (complete): The P’s and Q’s don’t agree
Extravasation of lipoproteins means
Achilles xanthomas
R dom: PDA off RCA
L dom: PDA off circumflex
Fenestrated cap in renal glomerulus
Sinusoidal cap in liver, spleen, marrow, lymph
DCM: TTN mutation. Balloon/banana appearing.
Cause: viral myocard
HCM:
ADom b-myosin
Restrictive CM:
“No restrictions in the Congo”
Bi-atrial enlarge & improper vent filling
dyspnea, edema, ascites, elev JVD
Takotsubo CM: Broken heart
stunned
Acute pericarditis: Fibrinous (triphasic friction rub), Hemorrhagic, Purulent (neutrophil bacterial or lymphocyte viral)
Chronic pericarditis: constrictive. Kussmaul, knock, PParadox on inspiration. Rapid y descent (Friedreich)
Subendocardial ischemia: non-totals
Hibernating: LV systolic dysfunc. Reversibly w/ revascularization.
Stunned: short-term ischemia.
Ischemic preconditioning: Brief episodes of ischemia prepare for prolonged episodes of ischemia.
Vent remod: weeks
Dressler syndrome
Type III.
Other MI comp:
Fibrinous pericard: 1-3w
Carcinoid HD: intestinal tumors secrete serotonin. Elev 24-urinary-5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid. RHF
Carcinoid syndrome: flushing, diarrhea, wheezing, intestinal tumors.
Atherosclerosis:
Causes AAA
Transmural inflamm w/ foam cells in tunica intima
Dissection:
HTN → intimal tear.
Cocaine, Marfan
Complication: tamponade
Myxomatous chng
Marfan-related Aortic Root Disease:
Cystic Medial Degeneration: mucopolysaccharide.
“Crescendo-decrescendo mid-systolic murmur” means….
Ejection. AS, PS, HOCM
R-sided valves: PT
R murmurs get louder on inspiration
Except: HCM (L-sided but louder w/ insp)
L-sided valves: AM
L murmurs get louder on exhalation
Except: HCM (L-sided but louder on inspiration)
AV valves: TM
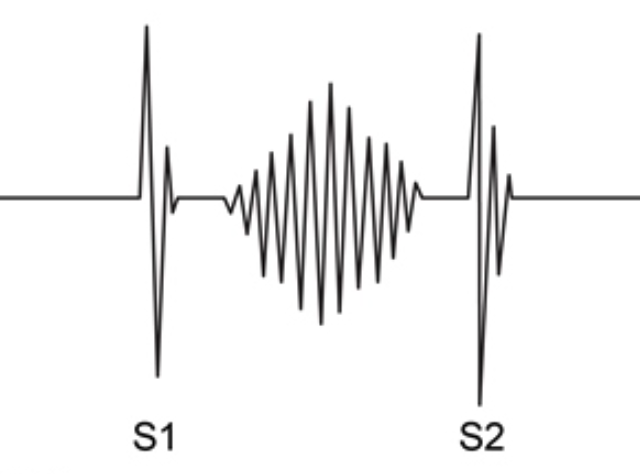
Close, beginning systole (S1)
Start of isovolumetric contraction
Aortic P lowest during this time
Semilunar valves: AP
Close @ end of systole (S2)
Start of isovolumetric relaxation
Systolic murmurs “AM PT”: aortic sten, mit regurg, pulm sten, tri regurg
Happen during ventricular contraction
Between S1 & S2
Diastolic murmurs “AM PT”: aortic regurg, mit sten, pulm regurg, tri sten
Happen during atrial contraction
Between S2 & S1
Ejection murmurs:
AS, PS, HOCM.
“Crescendo-decrescendo” mid-systolic.
↑afterload after & ↑EDP before affected valve due to valve obstruction during ejection
Holosystolic murmurs:
MR, TR, VSD.
Stenotic murmurs
↑P gradient across the valve to get blood across obstruction. ↑P before valve, ↓P after.
Mitral stenosis has opening snap… while mitral prolapse has
systolic click.
Mitral prolapse → regurg
HCM, endocarditis, RHD, congenital (Downs/cushion defect) → mitral regurg
Crescendo-decrescendo mid-systolic ejection.
AS, PS.
Early peaking murmur indicates early stenosis, late = severe
Ortner syndrome
Mitral stenosis → hoarseness from impingement of recurrent laryngeal n by enlarged LA → dysphagia
Kussmaul’s sign
increased JVP w/ inspiration
seen in constrictive pericarditis along w/ pericardial knock, PParadoxus (>10mmhg drop in systolic w/ insp), calcification
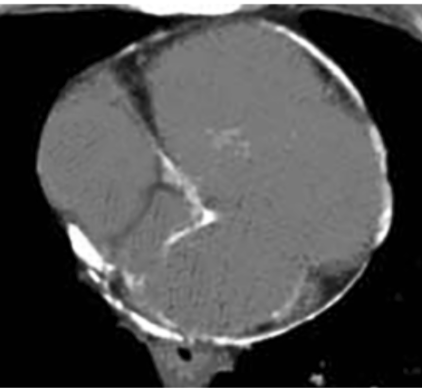
Tamponade
Beck triad: muffled sounds, hypotension, JVD
PParadox (>10mmHg systolic drop w/ insp)
Pulsus alternans (beat-to-beat variation in pulse amplitude (systolic BP)
Electric alternans: EKG conduction voltage R wave changes in R wave from sloshing
Equalization of pressures (four chambers become one)
Accentuated x descent (rapid drop in RAP)
Digoxin
Inhibits Na/K ATPase → indirectly limits Na/Ca exchange → contractility/+inotrope
Last resort refractory
Low K increases toxicity but it can lead to hyperkalemia
Do not use in AV block, brady, sick sinus, PVCs, WPW w/ Afib
What drug combo reduces mortality in African-American pts?
Hydralazine & Isosorbide dinitrate
PeRsistent/ “wide” S2 split:
Present throughout insp/exp, but wider during insp & narrower during exp
R-sided delay
Pulm HTN (“loud P2”), RBBB
Fixed S2 split:
ASD
Present throughout insp/exp
ParadoxicaL S2 split:
Only split in exp, normal insp
L-sided delay
LBBB
Pulmonic closes first
AS
*Cause of all splits is increased venous return*
Murmur grading

RUSB: AS
LUSB: Pulm, PDA
LSB (Erb’s): AR, HCM
LLSB: Tricusp
Apex: Mitral
PMI lateral shift = enlarged L heart
PMI epigastric/subxiphoid = enlarged R heart
AS & HOCM sound similar, both being ejection murmurs & all…
AS gets quieter w/ Valsalva while HOCM gets louder!
DeMusset’s sign
head bobbing. Seen in AR