AP Psych Unit 5 Part 2 Flashcards
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Based off Myers textbook (modules 37-41)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
What does it mean to be intelligent?
Many studies, intelligence is whatever intelligence tests measure, but in practice it can have a different meaning depending on the culture
How is intelligence defined?
The ability to learn, experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations
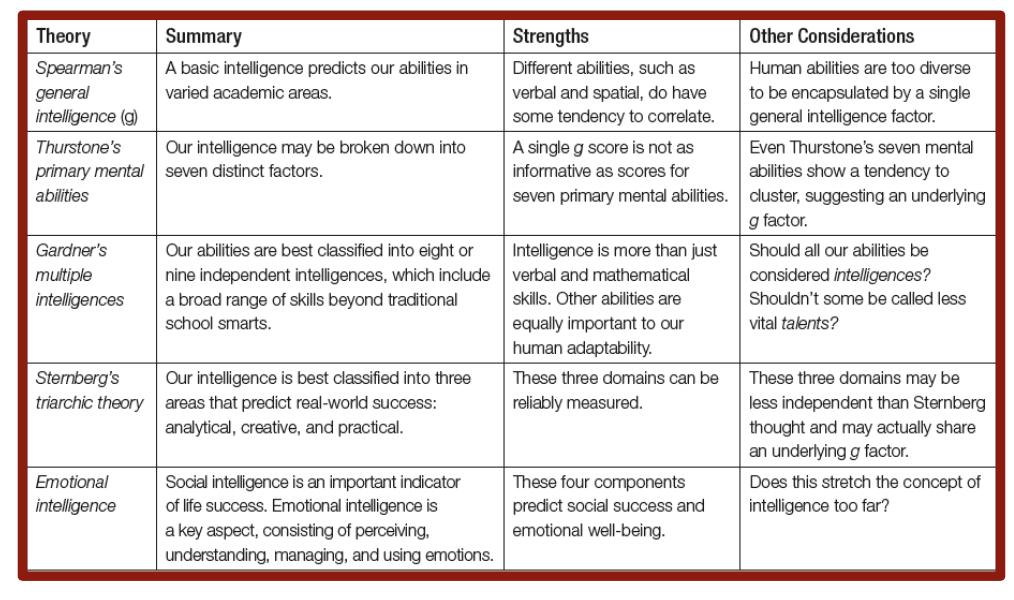
What is general intelligence (g)? Which psychologist made it?
Spearman; General intelligence or “g” underlies all mental abilities and is therefore measured by every task on an intelligence test
Belief that g is at heart of all behavior
What is special intelligence (s)? Which psychologist made it?
Spearman; Special, outstanding abilities or “s” — note generally “g” works as he found those who score in one area score high in another
What is factor analysis? Name an instance it was used.
Statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items (factors) on a test; used to identify different dimensions of performance that underlie a person’s total score
One instance used was by Spearman, utilized factor analysis to create his theory of “g” and “s”
What did Thurstone do? How did it differ from Spearman?
Thurstone gave a bunch of tests and found 7 clusters of primary mental abilities (word fluency, verbal comprehension, spatial ability, perceptual speed, numerical ability, inductive reasoning, and memory)
Differs from Spearman as Spearman holds the idea that a general mental capacity (g) can be expressed by a single intelligence score, whereas Thurstone advocated 7 varying clusters
How did Thurstones work support the existence of Spearman’s hypothesis?
Thurstone did not rank people on a single scale of general aptitude by when others studied this, they found that those who excelled in one of Thurstone’s clusters generally scores well in the others.
Essentially they found a correlation between scores, which supports the evidence of a “g” factor as it means there could be a common connection. Conversely, if Thurstone was 100% correct, there would likely be less correlation between cluster scores.
What is Gardner’s theory of multiple intelligences?
Gardner found 8 relatively independent intelligences including verbal and mathematical aptitudes assessed by standardized tests
Multiple intelligences refers to how intelligence takes many forms. One could be really good at architecture, or really good at poetry—just think it shows up in many ways.
Name and explain some of Gardner’s Multiple intelligences:
(possible answers) musical—ability to produce and understand pitch, tempo, and rhythm, visual spacial—ability to think in images and pictures, logical—mathematical—ability to think abstractly and see patterns in logic and math, body-kinesthetic—ability to control body movements and handle objects, interpersonal—ability to work well and understand others emotionally and socially, verbal—linguistic—ability to understand word meanings and sounds
What is savant syndrome?
A condition in which a person with otherwise limited mental ability has an exceptional specific skill—can score low on intelligence tests but have wild ability on other skills
What is different between Sternberg and Gardners theories?
Sternberg agreed with Gardner about there being more than traditional intelligence but believed in 3, as opposed to 8 or 9 intelligences
Analytical, creative, and practical intelligence
this is called Sternberg’s TRIARCHIC theory — try to associate the words triarchic and Sternberg
What is the analytical type of intelligence in Sternberg’s triarchic theory?
Academic problem solving intelligence is assessed by intelligence tests, which present well defined problems having a single right answer
What is the creative type of intelligence in Sternberg’s triarchic theory?
Creative intelligence is demonstrated by innovative smarts and the ability to adapt to new situations and generate novel ideas
What is the practical form of intelligence according to Sternberg’s triarchic theory?
Practical intelligence is required to perform everyday tasks that may be poorly defined and may have multiple solutions.
What is grit in psychology?
Passion and perseverance in the pursuit of long-term goals. Success is a combination of talent and GRIT!!!
What is emotional intelligence?
The ability to perceive, understand, manage, and use emotions—some have explored SOCIAL intelligence or the know how in understanding social situations is a critical part of emotional intelligence
What are the 4 abilities that underlie emotional intelligence?
Perceiving emotions, understanding emotions, managing emotions, and using emotions.
What is a trait of emotionally intelligent people?
Succeed better than those academically smarter and less emotionally intelligent, happier and healthier, and delay gratification for long-term rewards
Review the intelligence theories in the next slide:
AP Exam Tip:
be able to contrast the contributions of major theories (Spearman, Gardner, Sternberg)
What is an intelligence test?
method for assessing an individuals mental aptitudes and comparing them with those of others, using numerical scores. Either achievement which reflect what learned or aptitude which predict ability to learn new skill.
What is the difference between an achievement test and an aptitude test? (give examples)
Achievement reflects what’s learned: AP test
Aptitude reflects what can learn… aptitude: SAT/ACT
AP Exam Tip:
become familiar with key contributors in intelligence testing and be able to identify how they differ (Galton, Binet, Terman, Wechsler, and Stern)
What did Galton posit? What did he do?
Advocated those of high ability mate—eugenics. Methods to find intellectual strengths off of reaction time, sensory acuity, muscular power, and body proportions.
What were the results of Galton’s research?
Quest for simple intelligence measure failed, measurements did not correlate with intelligence.
Left phrase nature and nurture and belief in genius inheritance
How did Alfred Binet contribute to the field?
Commissioned by French gov to make testing that is fair and unbiased for schoolchildren
Who did Binet work with and what did they assume?
Simon; assumed that all children follow same intellectual development but some develop more rapidly
Goal of mental age, level of performance associated with certain age.
What is meant by mental age?
Mental age is the average mental capacity of someone that age
How Binet tested for mental age:
Binet and Simon theorized mental aptitude, like athletic aptitude is a general capacity that shows up in various ways
How were Binet’s tests modified by Terman?
Upper end to = teens → superior adults, used some of original items/added others, and made new age norms
Now called the Stanford Binet test, remember Stanford Binet is not made by Binet, but Terman
For Terman, intelligence tests revealed intelligence with which a person is born
What is the intelligence quotient and how is it derived? Who made it?
Stern made IQ, or intelligence quotient (mental age over chronological age times 100)
Average performance is a score of 100
Why did the Stanford Binet test fall out of fashion?
Worked well for children, not adults
How did the Army utilize intelligence tests?
Terman helped make Army Alpha and Beta for verbal and numerical abilities—indicated “inferiority” if not Anglo-Saxon in heritage
What did Galton do?
Introduced idea of measuring intellectual strengths
What did Binet and Simon do?
Came up with concept of mental age (score on the test, leads to formula)
What did Stern do?
came up with IQ formula
What did Terman do?
used the formula with Stanford-Binet test
What did Wechsler do?
Made WAIS, or Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale and made one for children and preschool children too
Why is the WAIS test superior to other tests?
Yields overall intelligence score but also individual scores for verbal comprehension, perceptual organization, working memory, and processing speed
Differences give insight into cognitive strengths and weaknesses
LOW on one but HIGH on others could mean a sort of impairment
What 3 criteria for an intelligence test?
(SRV) must be Standardized (meaningful to pretested sample), Reliable (consistent scores no matter who or when), and Valid (measures or predicts what is needed)
Characteristic of a normal curve distribution
Mean, median, and mode all at the center and same
Another characteristic of a normal curve
68% 1 standard deviation from mean, 95% 2 standard deviations and 99% 3 standard deviations
What does the test score indicate?
Both Stanford and Binet, indicates whether performance fell above or below the average
How is an intelligence score derived from the normal curve?
Higher than all but 2.5% means 130, lower than 97.5% is 70
How do the tests remain standardized?
To keep average near 100, Stanford Binet and Wechsler scales periodically restandardized
What is the Flynn effect? Why is it named after Flynn?
Phenomenon where intelligence test performance has improved—Flynn first calculated magnitude
What is reliability and how is it determined? What are the 3 ways?
Extent to which a test yields consistent results and can be assessed THREE DIFFERENT WAYS
Split half
Alternative form
Test-retest
What is the split half when determining reliability?
Scores on two halves of the test (even v odd) are compared
What is the alternative form when determining reliability?
Varying versions of the test are given and results are compared
What is the test-retest when determining reliability?
The same test is readministered and results are compared
How does correlation relate to reliability?
Higher correlation is higher reliability
What is validity?
The extent to which a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to
What is the difference between content validity and predictive validity?
Content validity is the extent to which a test samples the behavior that is of interest whereas predictive validity is success to which predicts behavior it is supposed to predict
What is content validity?
Extent to which a test samples behavior that is of interest
Road test has validity as it samples what a driver will routinely face
What is predictive validity?
Success in which it predicts a behavior
Academic aptitude tests can only predict success in certain ages
When can predictive validity yield little information?
When range is narrowed to an extent where one cannot see a trend; Trend must be significant
Limits of prediction:
As range of data under consideration narrows, predictive power diminishes
Why were intelligence tests first created?
Galton wanted those exceptional to mate, but could not construct a simple intelligence test
Binet used an environmental explanation of differences developed questions to find mental age and predict school system progress. Hoped test would improve education instead of limit opportunities
Terman modified Binets work and made Stanford Binet test
Sometimes used to document assumptions of superiority over other groups
Describe normal curve, explain standardization, reliability, and validity
Distribution usually around normal curve, with fewer at extremes
Standardization establishes basis for meaningful score comparisons
Reliability is extent to which yields consistent results (on two halves of test, or when retested)
Validity is if it measures what it is supposed to
Content validity is if it samples pertinent behavior
Predictive validity is if it predicts what is designed to predict
What is the long held belief about aging and intelligence?
WAIS created, Wechsler thought decline of mental ability with age is part of process as a whole
Does intelligence remain stable with age?
Yes! Scores even increased due to more experience with tests
Cross sectional research on aging:
Cross sectional shows decline with age, longitudinal shows stability and slight rise well into adulthood
What is the cross sectional research method?
Compares people of different ages at the same point in time
What are some considerations when conducting a cross sectional study?
Many variables are present in the same population that could impact the results
What is a longitudinal study?
Follow and retest same people over time
What are some considerations when conducting a longitudinal study?
Many variables could impact presence of members of sample population at various points in research
What is crystallized intelligence?
Crystallized intelligence is what is accumulated and what is verbal—skills that increase with age.
I.E. Ability to recount battles of WW2 needs CRYSTALLIZED INTELLIGENCE
What is fluid intelligence?
Ability to reason speedily and abstractly: decreases with age, especially during late adulthood
Ability to solve a logic puzzle needs fluid intelligence
How do aging adults both win and lose?
lose memory and processing speed (fluid intelligence) but gain vocab and knowledge (crystallized intelligence)
Fluid intelligence may decline, but older adults social reasoning skills increase, shown by ability to take multiple perspectives, appreciate knowledge limits, and offer helpful wisdom in conflict
Decisions less distorted by negative emotions
AP Exam Tip:
Many students confuse crystallized and fluid intelligence, remember to study these. Crystals grow larger over time, and so does our knowledge. Fluid evaporates over time and so does our abilities
How stable are intelligence scores over the lifetime?
Casual observation and intelligence tests before age 3 only modestly predict future aptitudes
By age 4, performance begins to predict adolescent and adult scores
By age 11, stability is impressive
What did Deary’s longitudinal study do?
Every child in Scotland took it: Essentially IQ score at 80 has a positive, moderate correlation to IQ score at 11
Those who score higher at an early age live longer (at least in women)
What is an intellectual disability?
Condition where you have limited mental ability: intelligence score below 70 or at 70 and difficulty adapting to demands a lot of life
What two criteria must be met to have an intellectual disability?
Low IQ test score: lowest 3%, 70 or below and difficulty adapting to independence, expressed in 3 areas: conceptual, social, and practical
What is Down Syndrome?
Condition of mild to severe intellectual disability and associated physical disorders, caused by extra copy of chromosome 21
Which chromosome copy is associated with Down Syndrome?
Chromosome 21, caused by an extra copy.
What is giftedness?
Children with high achievement in intellectual, creative, artistic, or leadership capacity in certain academic fields need services and activities not ordinarily provided by school to develop capabilities
What does the research show about success of gifted children?
1650 who had perfect math SAT at age 13 had 681 patents by the time they were 50
4% of those taking SAT had scored doctorates compared to 1%
What are the criticisms of gifted programs in public schools?
Segregate high scoring children in special classes with academic enrichment not available to peers.
Self-fulfilling prophecy, denying opportunities for enriched education widens gap between ability groups
How does aging affect crystallized and fluid intelligence?
Fluid intelligence declines in older adults and crystallized intelligence tends to increase
Define cross sectional and longitudinal studies and explain why important to know which method was used
Cross sectional compares people of different ages at the same point in time whereas longitudinal studies follow and retest same cohort
Cross sectional studies also compare people of different eras and life circumstances, providing excellent snapshot of particular point in time but longitudinal are better for tracing evolution of traits over longer time period
Describe stability of intelligence scores over life span:
Age 4, fluctuates somewhat but begin to predict well
By early adolescence, very stable and predictive
Discuss traits of low and high intelligence extrema
Below 70 = intellectual disability
Down syndrome: caused by extra copy of chromosome 21 is one known physical cause of intellectual disability
High score generally healthy and well adjusted, unusually successful academically. Sometimes track children and separate sometimes making self-fulfilling prophecies
Intelligence: nature or nurture
Most genetically similar people have most similar intelligence scores (1.00 is perfect correlation and zero is no correlation)
AP Exam Tip:
bar graph of intelligence score correlations is important to spend time on
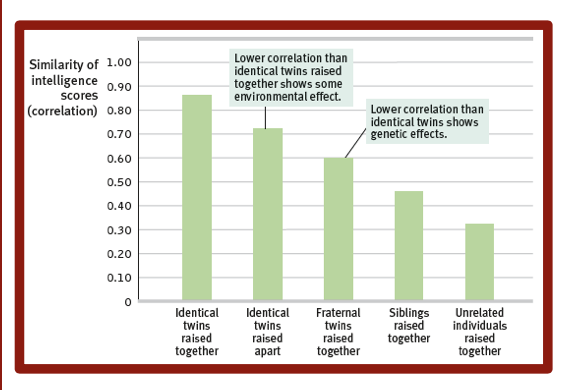
What does research show regarding genetics of intelligence?
Intelligence test scores of identical twins raised together are nearly as similar as those of same person taking test twice
Identical twins show substantial similarity in specific talents
Heredity accounts for more than half the variation in national math and science exam scores of British 16 year olds
Are there known genes for genius?
All gene variations only accounted for 2% of educational achievement differences
Follow up study predicted 9% variation in gene difference.
Moral of the story: not TOO influential
What does the research show regarding the environmental factors of intelligence?
Children adopted into wealthier families had IQ scores higher than non adopted biological siblings
Adoption enhances intelligence scores of mistreated or neglected children
Where environments vary widely, as they do among children of less-educated parents, environmental differences are more predictive of intelligence scores
What determines intelligence? Genes or environment?
In verbal ability, scores more biological than environmental
Do genetic influences become more apparent as we accumulate life experience?
Identical twin similarities continue or increase into their eighties
Adopted children’s intelligence scores resemble those of their biological parents more than their adoptive parents
heritability of general intelligence increases from about 30% in early childhood to well over 50% in adulthood
How does heredity differ from environment?
Heredity (nature) is genetic transfer of characteristics from parent or offspring
Environment (nurture) is every non-genetic influence, from prenatal nutrition to people and things around us
What is heritability?
Proportion of variation among individuals in a group that we can attribute to genes
May vary depending on range of populations and environments studied
What does intelligence is about 50% heritable mean and NOT mean?
means: genetic influence explains 50% of observed variation AMONG people
doesn’t mean: intelligence is 50% genetic
Heritability increases from
about 30% in early childhood to well over 50% in adulthood
What does it mean that intelligence may be polygenetic?
Intelligence involves many genes
What is the impact of neglect?
Delayed development, think Romanian orphans
Early environmental influences:
Schools that are title 1 have less qualified teachers and lower achievement scores
Impoverished peoples have other worries and lack the opportunity to consume cognitive bandwidth on education
How can early intervention impact intelligence?
Schooling is one intervention that pays intelligence score dividends
Schooling and intelligence interact
How does having a growth mindset influence intelligence? Who made the “growth mindset”
Dweck; intelligence is changeable and you need a growth mindset, focus on learning and growing. Fixed supports set, unchangeable intelligence level
Teaches brain is like a muscle
what does research show about a growth mindset?
Praise for effort and tackling challenged helps understand link between hard work and success
More resilient when others frustrate them
Superior achievements in fields from sports to science to music arise from combination of ability, opportunity, and disciplined effort