Cheat sheet 10: Biotechnology and Microscopy Concepts
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is the Cell Theory? (4)
• All living organisms are composed of one or more cells
• Cell is basic unit of structure, function, and organization
• All cells come from preexisting, living cells
• Cells carry hereditary information
What does the RNA World Hypothesis propose? (3)
• Self replicating RNA molecules were precursors to life
• RNA stores genetic information like DNA
• RNA can catalyze chemical reactions like enzymes
What is the Central Dogma of Biology?
The general flow of genetic information is from DNA to RNA to protein.
What does PCR do?
PCR creates a large amount of DNA by amplifying a DNA sample
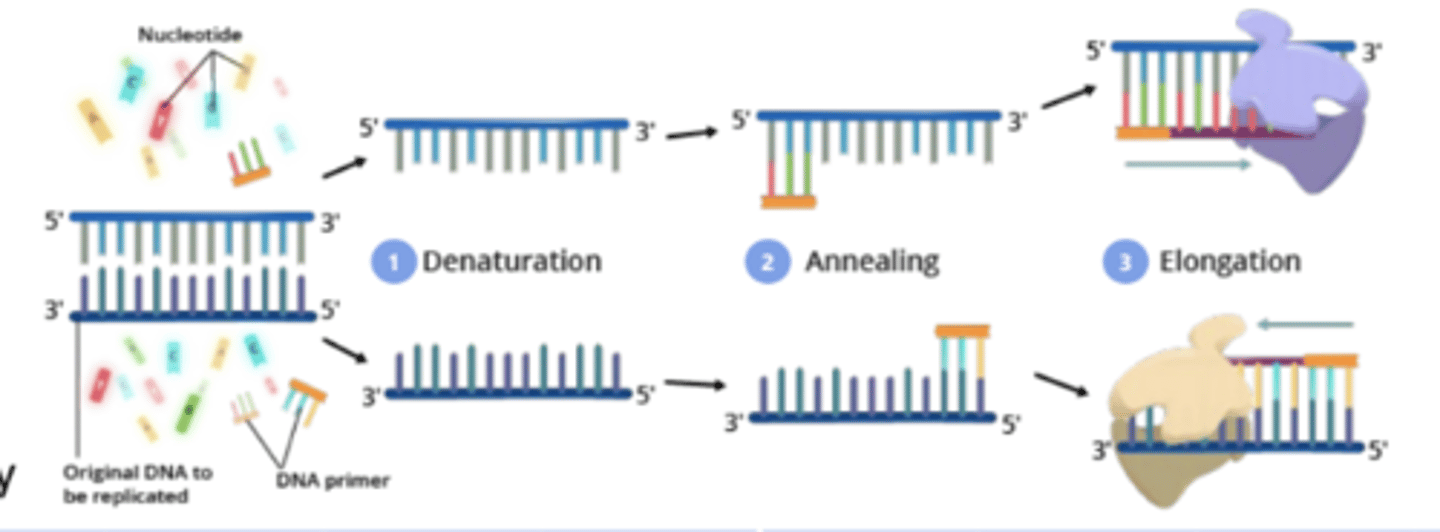
What are the steps involved in the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)?
1. Denaturation: High heat separates double-stranded DNA.
2. Annealing: Sample is cooled so primers attach to separated strands.
3. Elongation: Polymerase synthesizes new strands.
What is the purpose of a Light Microscope?
To use visible light to view a thin sample.
What is the function of a Scanning Electron Microscope?
To view the surface of 3D objects with high resolution.

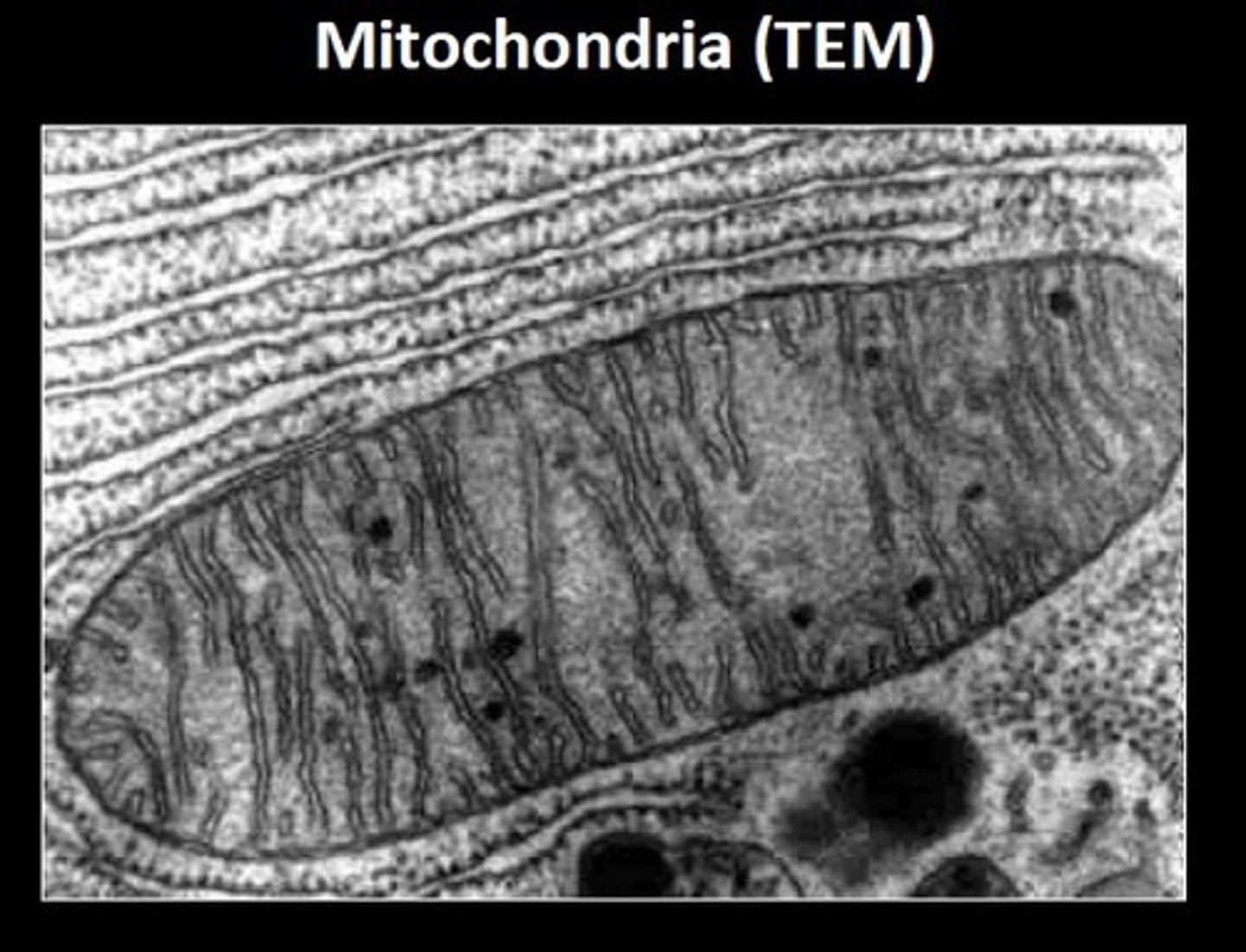
What is the use of a Transmission Electron Microscope?
To view thin cross sections and internal structures within samples at very high magnification.
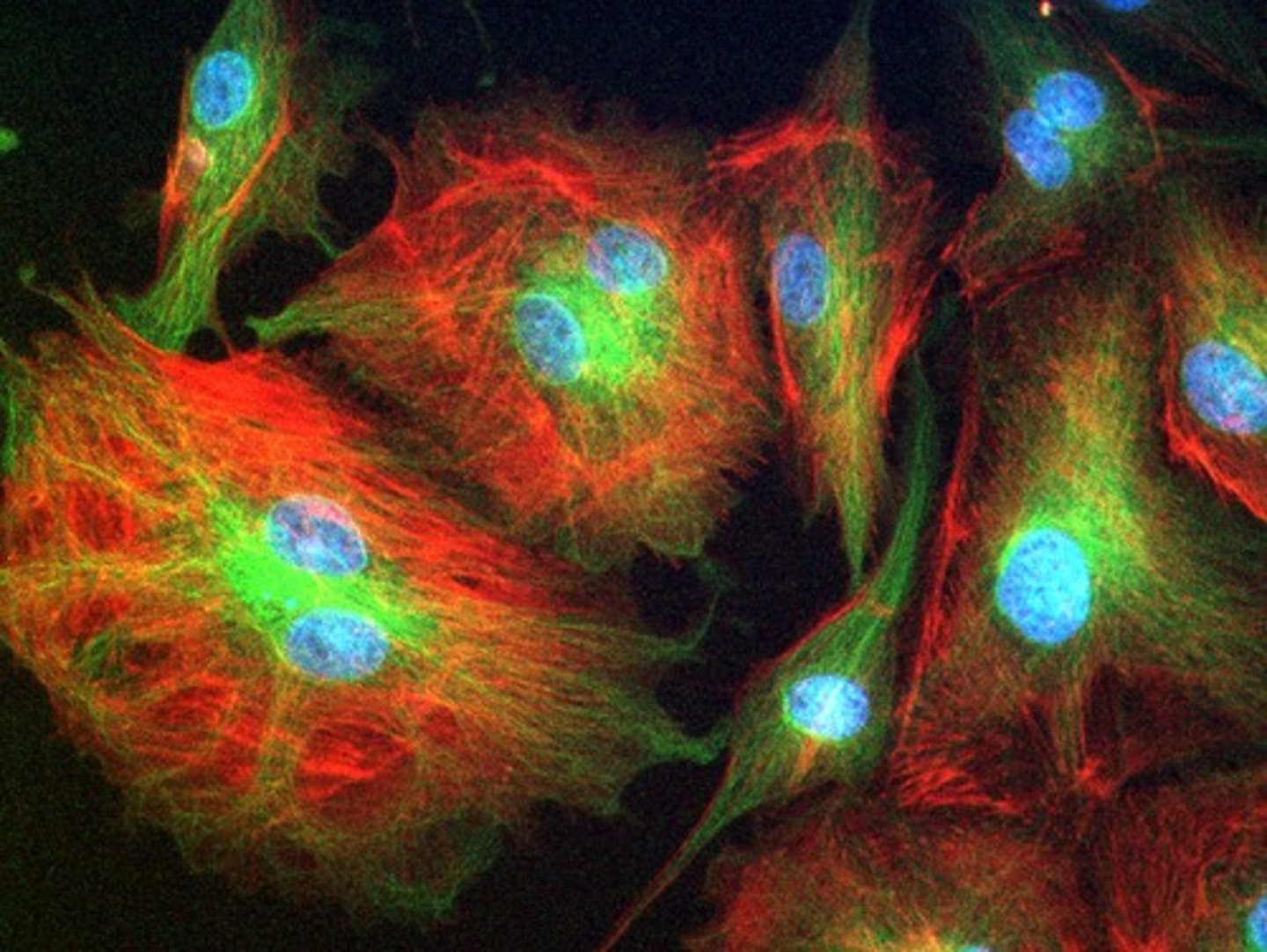
What is the Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope used for?
To observe specific parts of a cell using fluorescent tagging antibodies.
What is Centrifugation?
A technique to separate a liquified sample into its different components by spinning it rapidly.
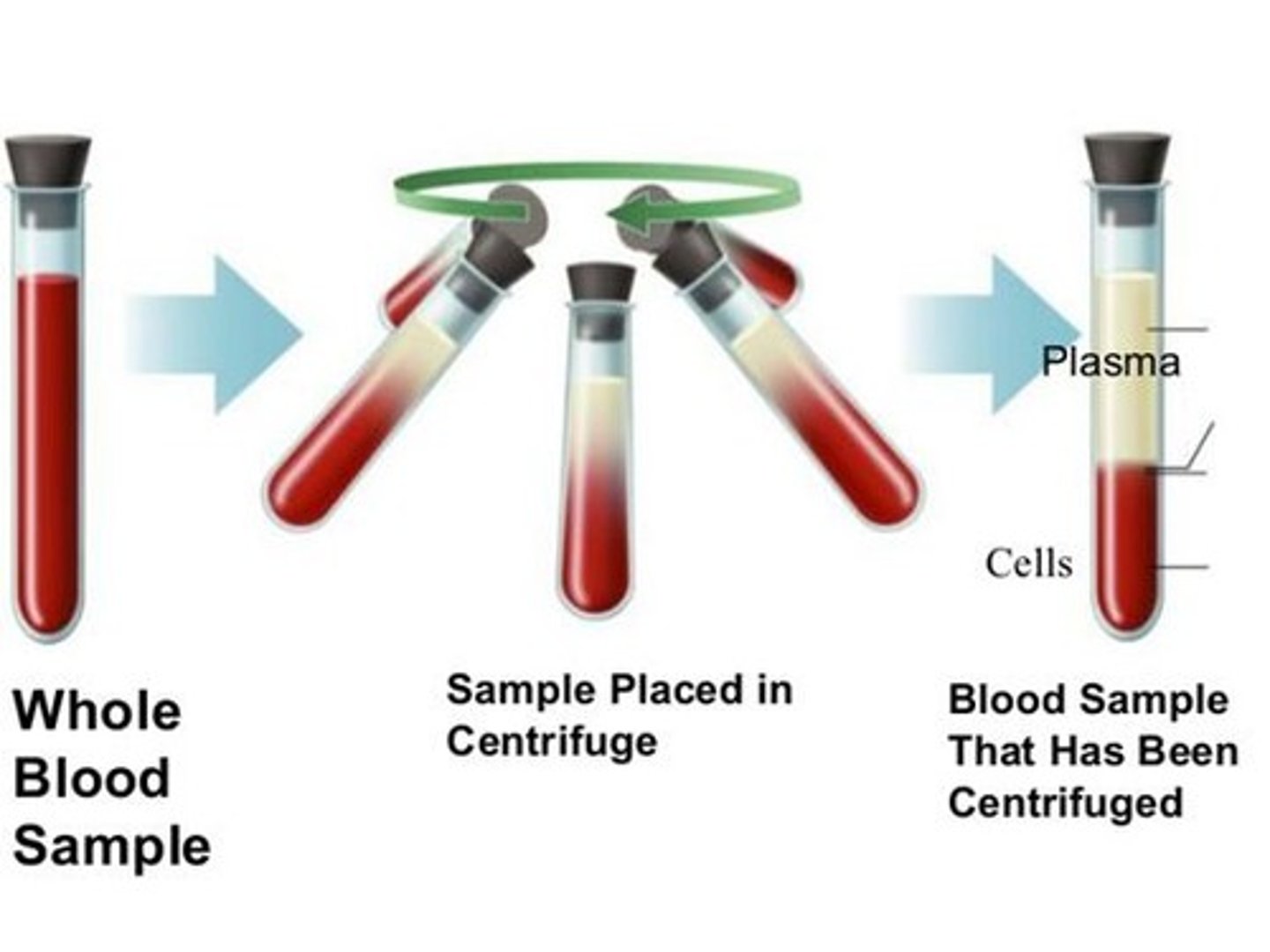
In centrifugation what separates first?
Largest/most dense separate first,
forming a pellet at bottom of
sample
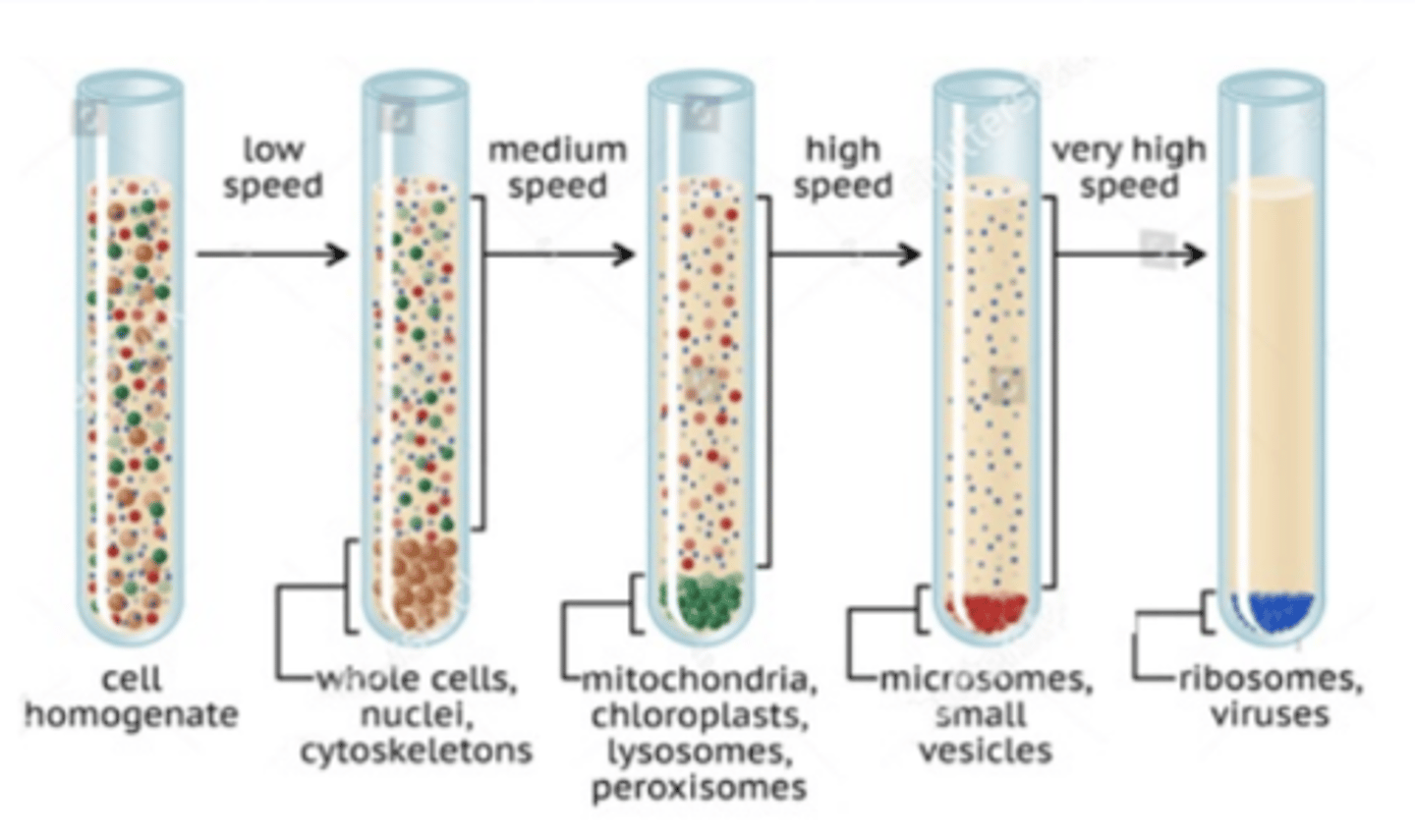
What is the cell fractionation in centrifugation? (largest to smallest)
1. Nuclei >
2.mitochondria/chloroplast >
3. ribosomes
What are the three types of Blotting techniques?
Southern (DNA), Northern (RNA), Western (Protein).
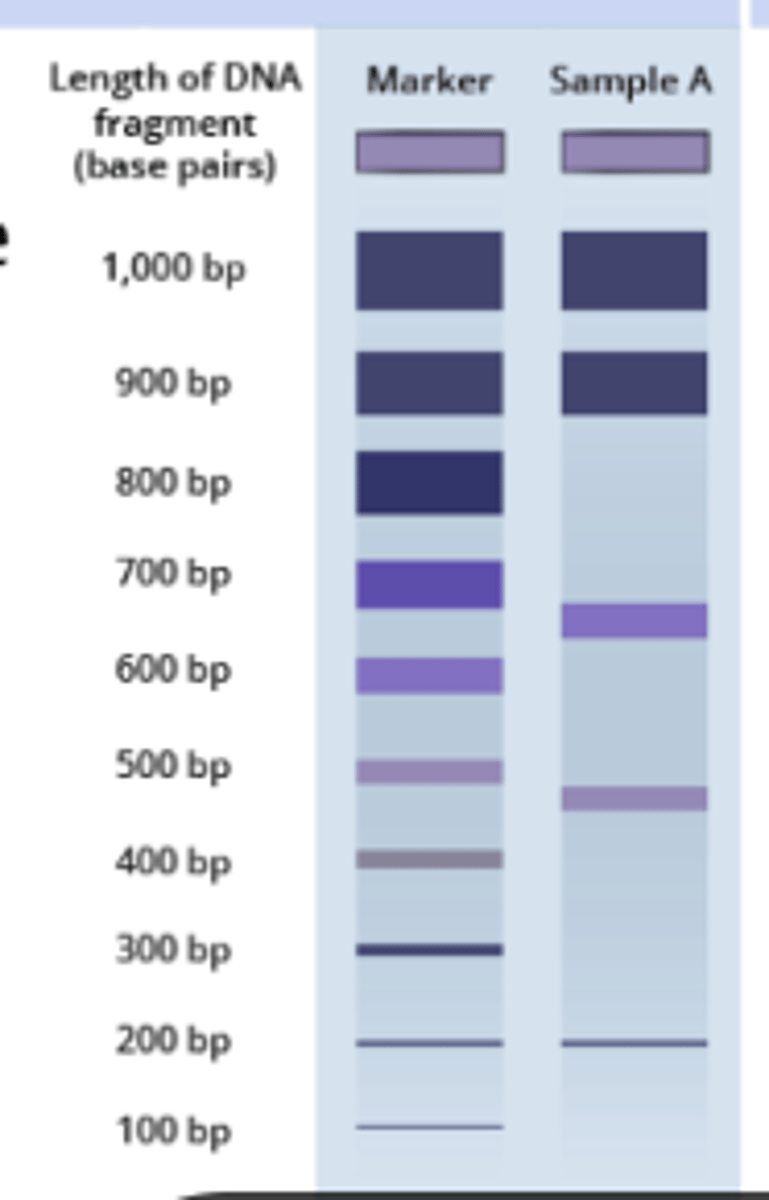
What is the purpose of Gel Electrophoresis?
To separate DNA molecules by size and charge; smaller molecules travel farther down the gel.
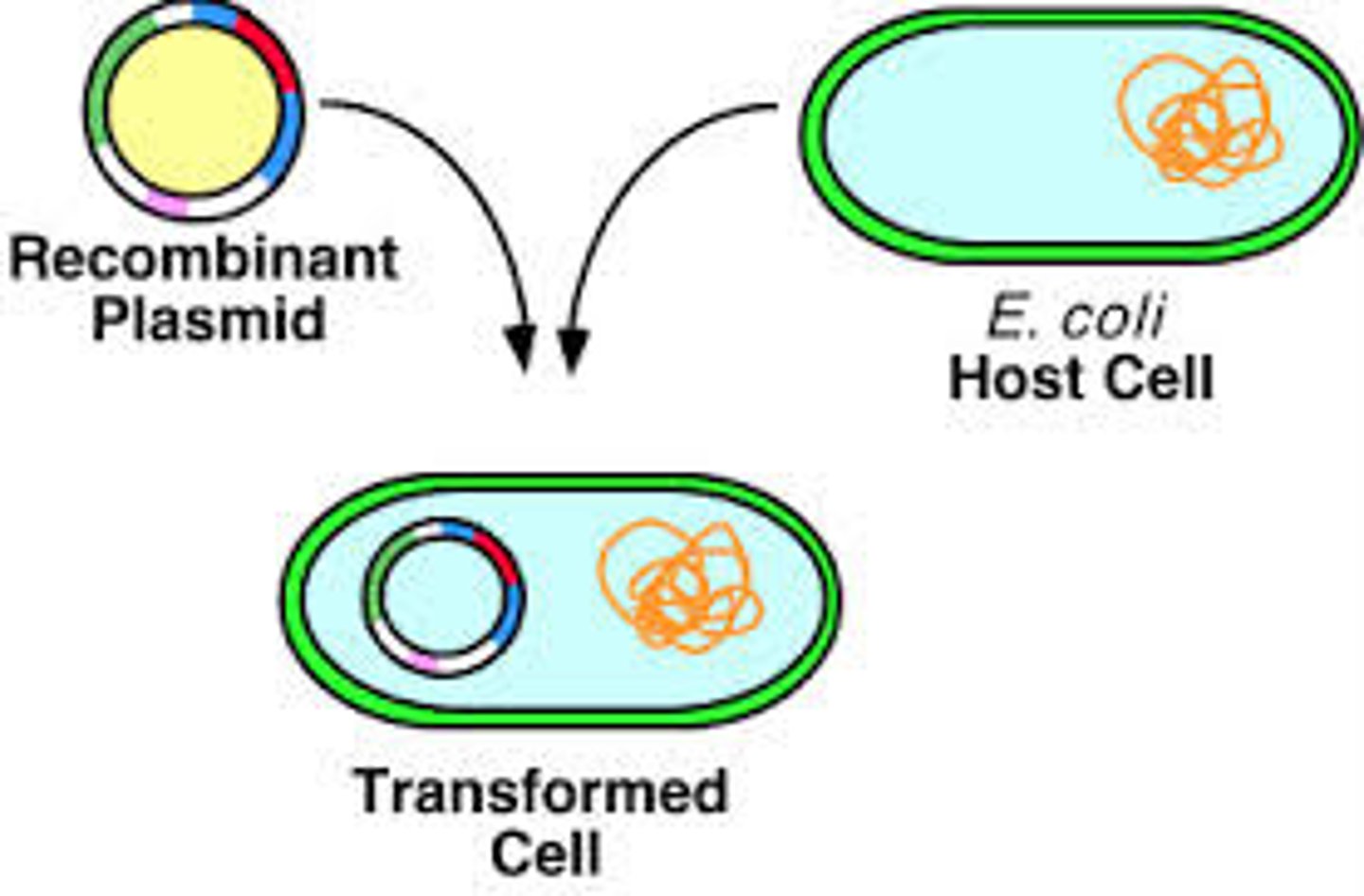
What is the process of creating Recombinant DNA?
1. Using restriction endonucleases (restriction enzymes) to cut
specific segments of DNA called restriction sites. These enzymes
create sticky ends, which allow new DNA pieces to bind
2. DNA ligase connects the different fragments together
3. A vector (vectors include plasmids and bacteriophages) can then be used to transfer foreign DNA into another
cell.
What is the role of DNA ligase in recombinant DNA technology?
To connect different DNA fragments together.
What is a vector in genetic engineering?
A vehicle used to transfer foreign DNA into another cell, examples include plasmids and bacteriophages.

What is the significance of antibiotic resistance in recombinant DNA technology?
It ensures that only bacteria containing the plasmid with the foreign DNA survive, allowing for selection of successful transformations.
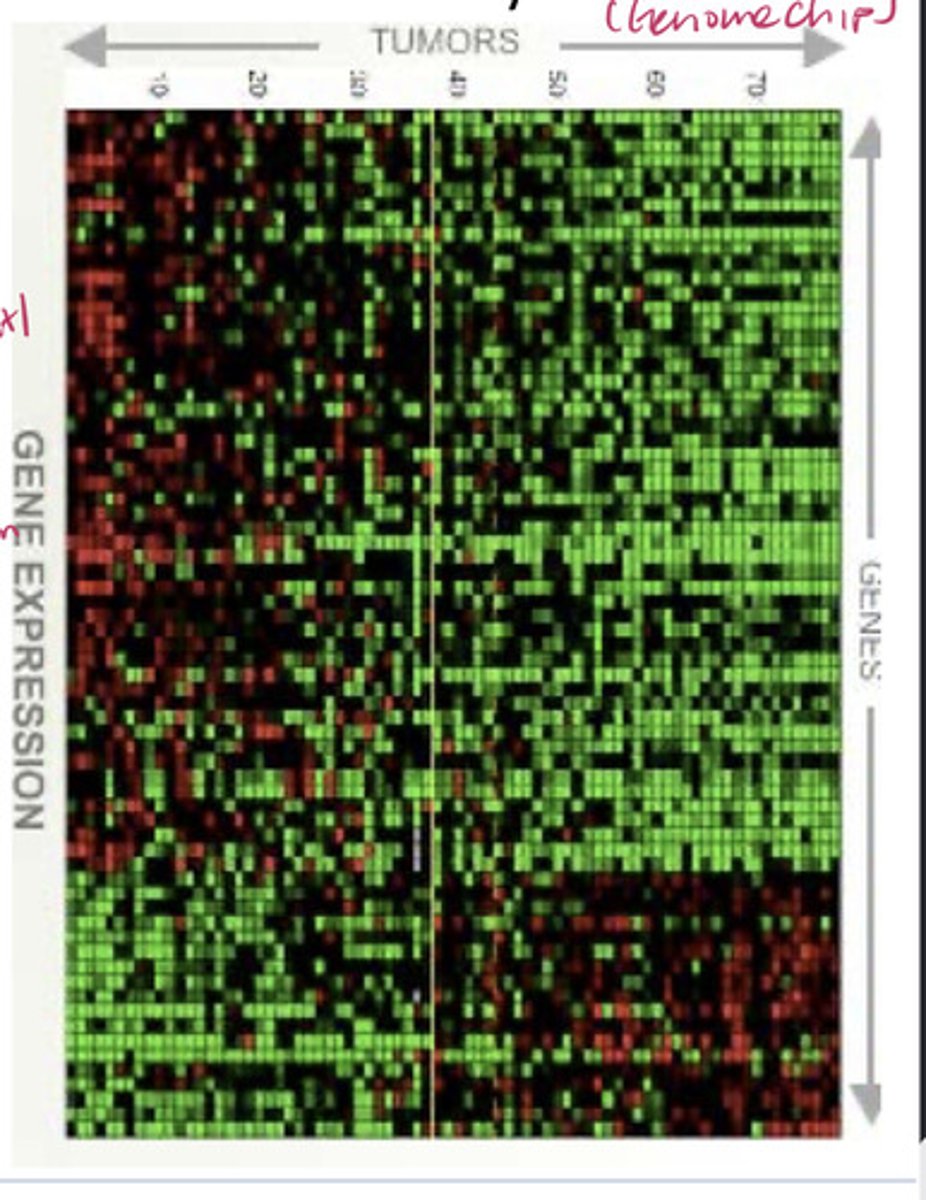
What is the purpose of Microarray Assays?
To monitor the expression of large groups of genes across a genome.
What is the function of Reverse Transcriptase?
• Used to synthesize DNA from an
RNA template
• In some lab procedures, it is used
to create complementary DNA
(cDNA) off an mRNA template.
cDNA lacks introns
• Naturally used by viruses
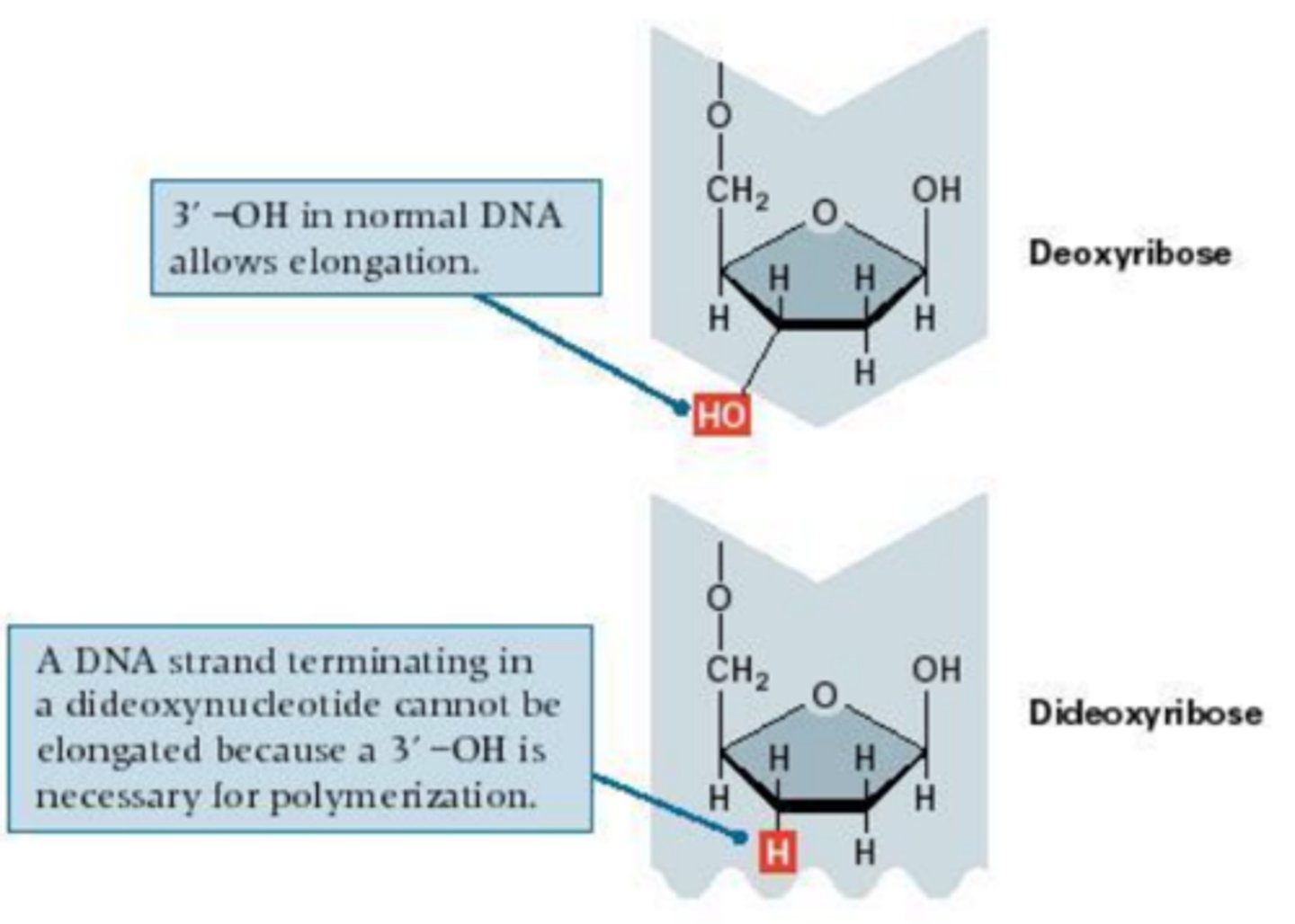
What is Dideoxy Chain Termination?
A method based on the principle that during DNA synthesis, the addition of a nucleotide requires a free OH group on the 3' carbon of the sugar of the last nucleotide of the growing DNA strand
What is Hybridization in the context of Blotting techniques?
When nucleic acids form complementary base pairs with nucleic acids of a different strand.
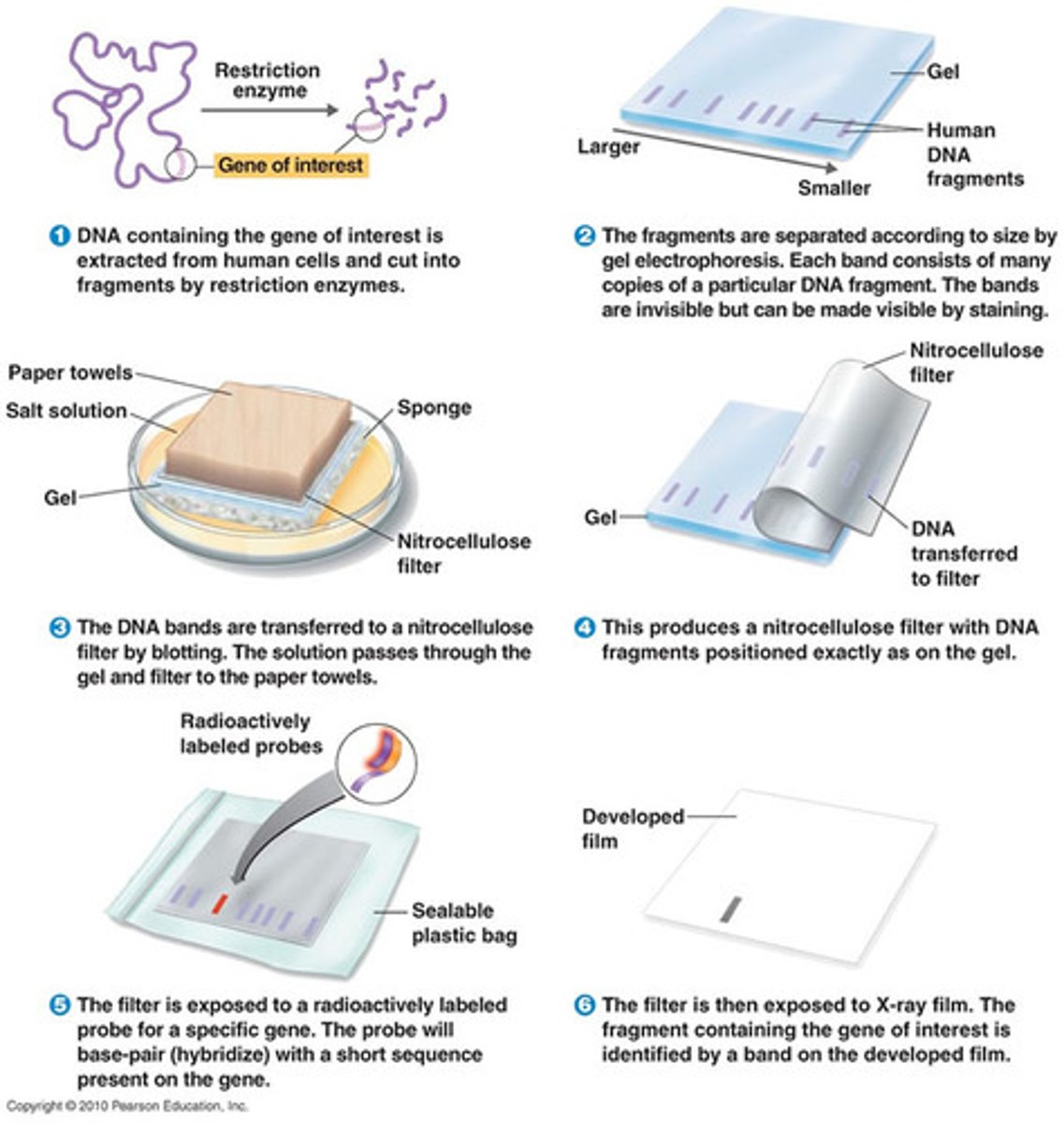
What is the purpose of Blotting techniques?
To identify specific fragments of DNA, RNA, or protein.
What is the significance of the PCR cycle repeating?
It increases the amount of DNA exponentially.
What is the role of restriction enzymes in recombinant DNA technology?
To cut DNA at specific sites, creating sticky ends for new DNA pieces to bind.
What is DNA sequencing used for?
Used to determine the sequence of
base pairs in a DNA or RNA molecule
