Structure and Function of Living Organisms
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What type of plants have only one cotyledon?
Monocotyledonous plants (e.g., grasses)
What type of plants have two cotyledons in their seeds?
Dicotyledonous plants (e.g., beans, peas)
What are the functions of roots in plants?
Roots provide physical support by anchoring the plant and absorbing water and minerals.
What role do the cell wall and vacuole play in plant support?
They create turgor pressure, helping the plant stay upright and preventing wilting.
What are the four main parts of a plant stem?
Epidermis, pith, cortex, and vascular bundles (xylem and phloem)
How do parenchyma and collenchyma cells provide support in plants?
Parenchyma cells exert pressure on collenchyma cells, providing flexible support.
What is the function of xylem in plants?
Xylem supports the plant's structure and transports water; it is made of dead cells with lignin.
What is a hydrostatic skeleton?
A soft skeleton supported by internal fluid pressure, found in many insect larvae, spiders, and worms.
What is an exoskeleton and its limitations?
A hard outer shell made of chitin that protects the internal organs; must be shed and replaced (ecdysis), leaving the animal vulnerable.
What are the two types of endoskeletons?
Cartilaginous endoskeleton (e.g., sharks) and bony endoskeleton (e.g., humans, most mammals).
Name the 4 classes of tissue
Muscle
Nerve
Epithelia
Connective
What is the medial plane?
Vertical plane that splits the body into equal halves
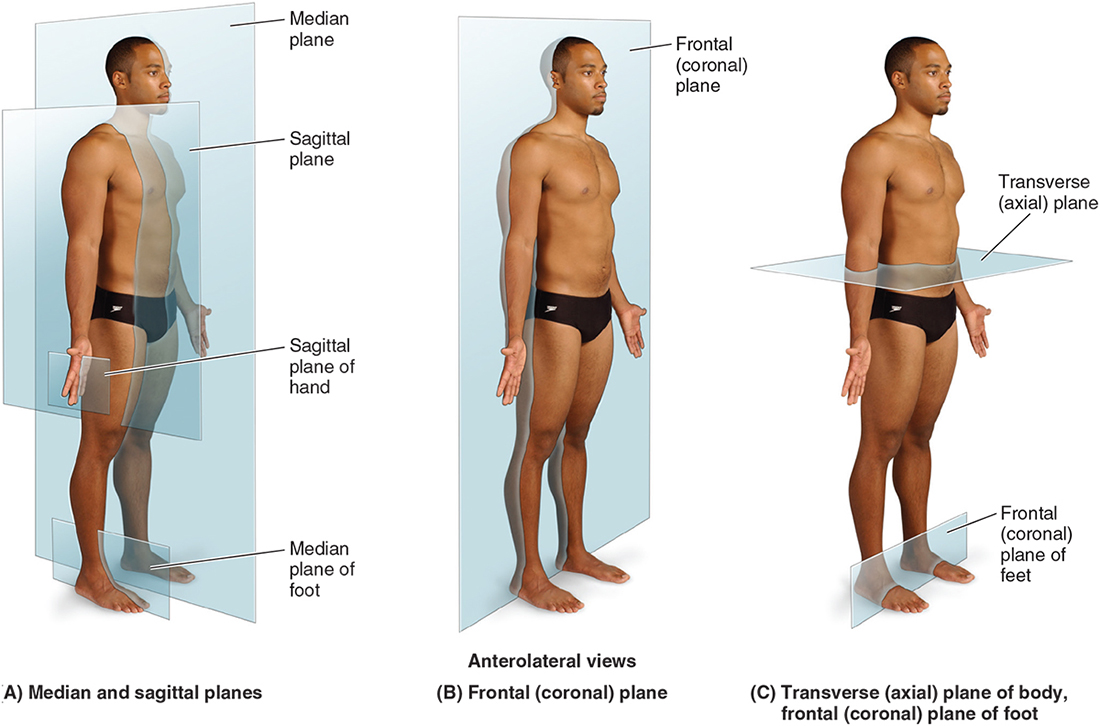
What is the frontal/coronal plane?
Plane that divides the front and back halves of the body
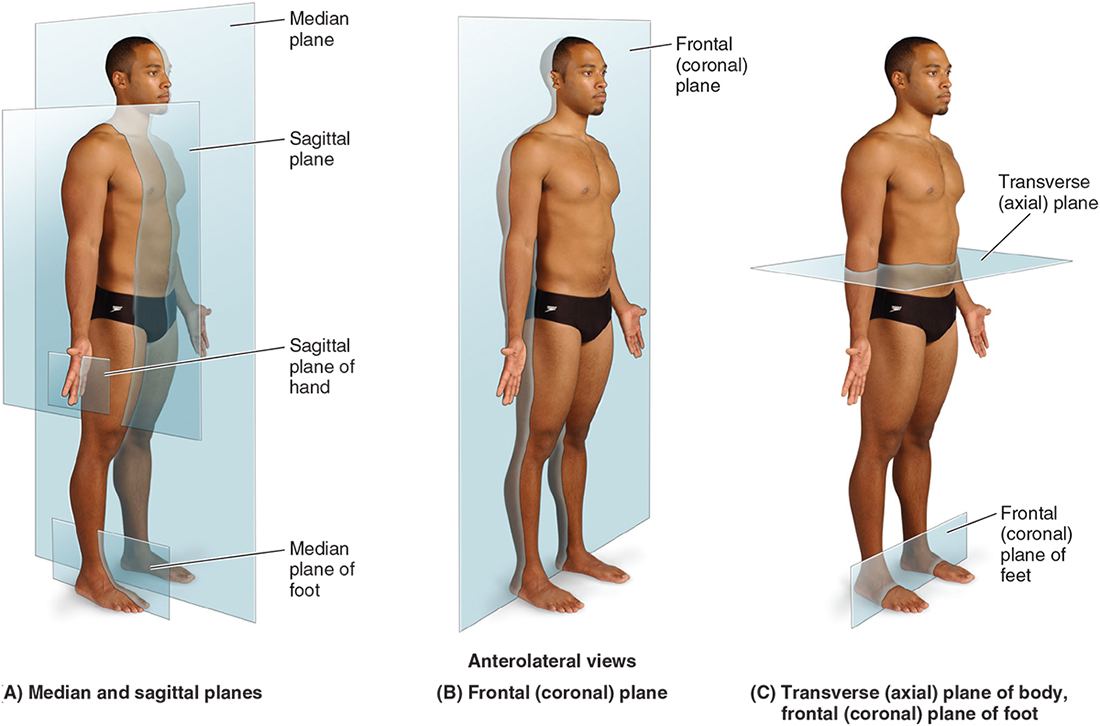
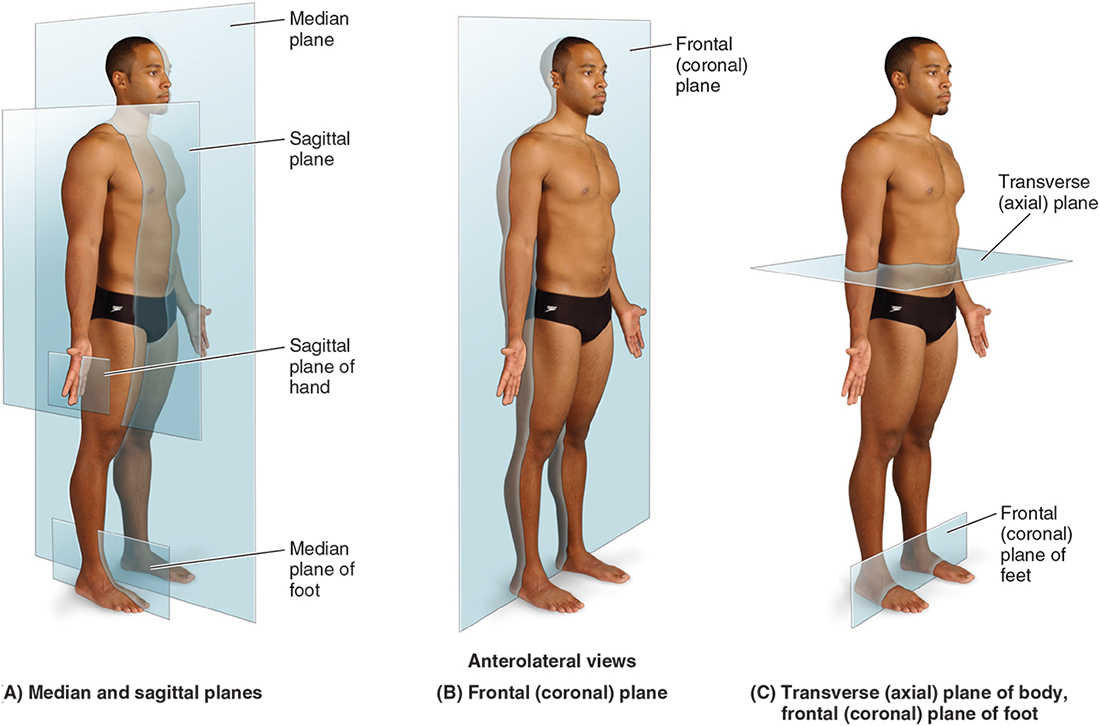
What is the transverse/axial plane?
Horizontal plane that splits body in upper and lower sections
Define superficial
Nearer the the surface (e.g muscles are superficial to bones)
Define intermediate
Something that is located between two structures (e.g the collarbone is intermediate between the shoulder and the breastbone)
Define deep
Further from the surface (e.g the humerus is deep to the arm muscles)
Define medial
Nearer to the medial plane (e.g the 5th digit is on the medial side of the hand)
Define lateral
Further from the medial plane (e.g the thumb is on the lateral side of the hand)
Define posterior
Nearer to the back (e.g the heel is posterior to the toes
Define inferior
Nearer to the feet (e.g the stomach is inferior to the heart)
Define anterior
Nearer to the front (e.g the toes are anterior to the ankle)
Define distal
Further from point of origin/limb (e.g the wrist is distal to the elbow)
Define proximal
Nearer to point of origin/limb (e.g the elbow is proximal to the wrist)
What are the types of bones?
Long
Short
Flat
Irregular
Sesamoid
Name the types of joints
Fibrous
Cartilaginous
Synovial
Functions of the skeletal system
Support
Movement
Protection
Mineral storage
Energy storage
Endocrine regulation
Blood cell formation