W4:Topography
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
WATCH LECTURE RECORDING
Contents
Purpose and uses
Scales
Maps
Indices
Pachymetry
Meibomian gland evaluation
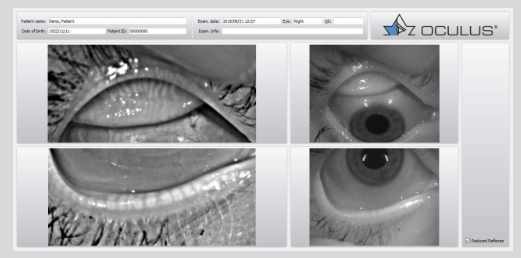
Uses instruments to accurately measure, assess and record the corneal curvature and regularity
Correctly interprets the information gathered
What are the purposes and clinical uses of corneal topography?
Study normal corneal topography
Study effects of disease
Pre- and post-surgical comparisons
Assess effects of contact lenses
Compare changes with refractive surgery
Document changes with orthokeratology
Aid design of customised contact lenses
Check whether the topographer measures anterior only or both anterior and posterior surfaces
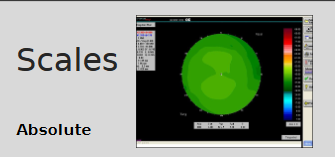
What are the features of absolute scales used in corneal topography?
Same colour assigned to a given dioptric interval
Compared with a computerised reference eye
Allows comparison between eyes
Useful for screening
Uses large step increments, so fine detail is lost
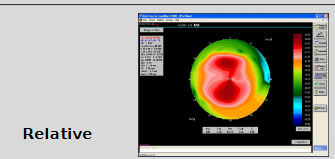
What are the features and limitations of relative scales in corneal topography?
Smaller dioptric range per colour than absolute scales
Colours of 2 diff maps cannot be compared directly
Provides a more detailed description
Removes smoothing effect
Cannot compare btwn eyes
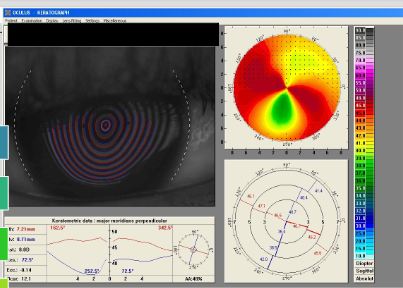
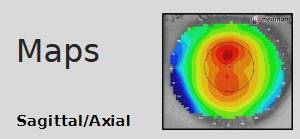
What does a sagittal (axial) corneal topography map measure?
Measures the curvature at a point on cornea in axial direction relative to the centre
Make the assumption that the centre of the radius of curvature is always on the central axis
Gives a global view of corneal curvature
Usually used in conjunction with an absolute scale
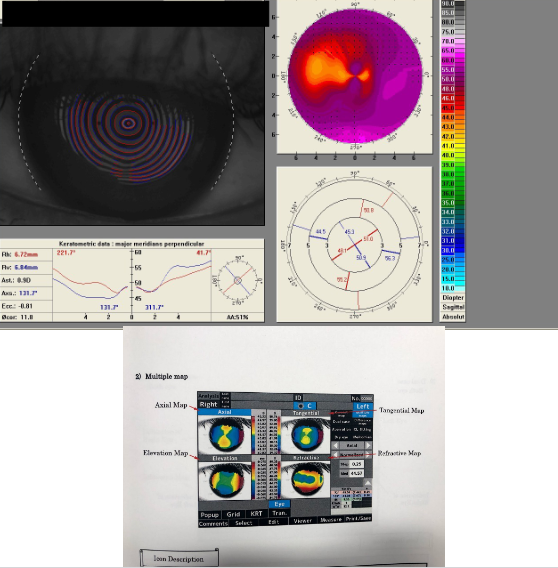
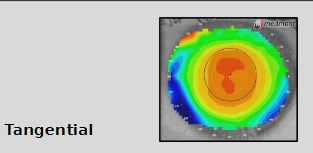
What does a tangential corneal topography map measure?
Measures curvature at a point on cornea in meridional direction relative to the other points on a particular ring
Does not assume:
eye is spherical
refracted rays converge to central point on visual axis: each data point is in relation to surrounding data points
where the centre of radius might be
Simply look at a certain part of the cornea + measure the radius of that point under 90◦ (as a tangent)of which the centre of radius could be anywhere
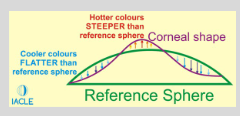
What does an elevation map show in corneal topography?
Shows the measured height from which the corneal curvature varies
from a computer generated reference sphere,
which best fits the measured corneal topography
How are steep and flat meridians represented on an elevation map?
Red dot:
steepest meridian, above
How many microns space between lens + corneal surface
Blue dot:
flattest meridian, below
How many microns needed between lens + corneal surface
What is the clinical use of elevation maps in contact lens practice?
Most useful in predicting fluorescein patterns w/ RGP lenses
What information is provided by a refractive map, and when is it useful?
Insight into:
∆s in refractive power across a pt’s cornea
the cornea’s contribution to the eye’s dioptric power
the magnitude of cylinder in an astigmatic eye
When is a refractive map useful?
When estimating values for LASIK refractive surgery
or selecting an IOL for cataract extraction
What are difference maps used for in corneal topography, and how are they interpreted?
Often used in orthokeratology fitting
Compare before and after lens fitting
Identify what has changed
Can be used pre- and post-surgery
Use only one eye in all comparisons
Blue indicates flattening
Red indicates steepening
Represented as A − B = C
What is an aberration map and who is it associated with?
Developed from work by Frits Zernike
Dutch physicist + Nobel Prize winner (1888–1966)
Uses a mathematical representation
Describes deviations of a real wavefront from an ideal wavefront
Expressed as a sum of polynomials
What factors influence correction of aberrations in the eye?
Spectacles correct lower-order aberrations
Tear film can mask corneal irregularities
Masking can improve higher-order aberrations caused by irregularities
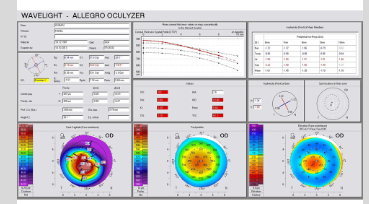
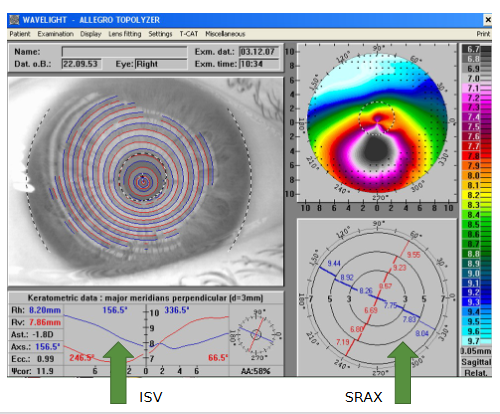
What does the Index of Surface Variance (ISV) measure?
Deviation of individual corneal radii from the mean value of a predetermined eye curvature
Displayed by two lines of the principal meridians on an x:y plotted graph
How is the Index of Surface Variance (ISV) interpreted clinically?
Elevated in all types of corneal surface irregularity
Normal + pathological
Examples incl:
Scars
Astigmatism
CL–induced deformities
Keratoconus
Red = pathological
Yellow = out of normal range
Which topography indices are used for keratoconus diagnosis with Orbscan and Atlas?
Irregularity Index (SRI)
Surface Asymmetry Index (SAI)
Which indices are used for keratoconus diagnosis with the Pentacam?
KC index (KI, CKI) on a 0–4 scale
Index of Surface Variance (ISV)
Asymmetry degree (IVA, IHA)
Index of Height Asymmetry (IHD)
Aberration coefficient (ABR > 1 = KC)
Pachymetry progression index
All based on number of standard deviations from the average
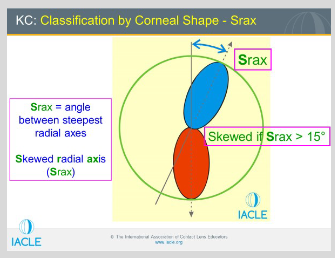
How is a skewed radial axis interpreted in corneal topography?
Difference in axis angle > 15° in one meridian = abnormal
Difference > 21° = diagnostic indicator for keratoconus
What comparisons are required when assessing a skewed radial axis map?
Compare ring pairs:
3 mm to 5 mm
5 mm to 7 mm
3 mm to 7 mm
Be critical of the map
Extrapolated data is not excluded
What factors can affect the analysed area and extrapolated data in ocular imaging?
Analysed area / extrapolated data / reflective device issues:
Lids
Blinking / ptosis
Nose
What reliability checks should be applied when interpreting ocular imaging results?
Use as much information as possible to identify an abnormality
Ensure the scan is centred
Use the right maps + scales together
How does imaging assist in contact lens design and fitting, and what is its limitation?
Helps predict pooling patterns
Does not account for lid involvement
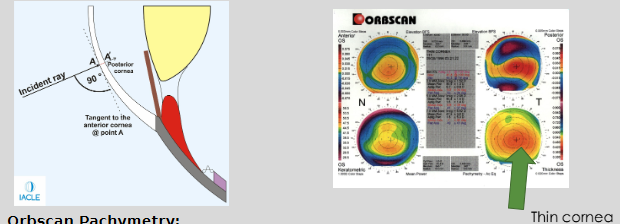
What are the key features of non-invasive pachymetry using Orbscan?
Non-invasive pachymetry method (Orbscan)
Measures CT perpendicular to the cornea
Ultrasonic pachymetry also measures perpendicularly
Orbscan thickness measurements are greater than manual ultrasonic pachymetry
7–10% thicker (≈ 30 μm)
Meibomian gland evaluation