SAT Math: Triangles
1/9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Equilateral Triangle
All sides and angles are equal.
Isosceles Triangle
Two sides and two angles are equal.
Scalene Triangle
All sides and angles are different.
Acute Triangle
All angles are less than 90°
Right Triangle
One angle is 90°.
Obtuse Triangle
One angle is greater than 90°.
Triangle Inequality Theorem
Definition: The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third side.
Formulas:
( a + b > c )
( b + c > a )
( a + c > b )
Similar Triangles
Definition: Triangles are similar if their corresponding angles are equal and their corresponding sides are in proportion.
Key Ratios: In image
Tests for Similarity:
AA (Angle-Angle): If two angles of one triangle are equal to two angles of another triangle.
SSS (Side-Side-Side): If the sides of one triangle are proportional to the sides of another triangle.
SAS (Side-Angle-Side): If one angle and the sides including this angle are proportional.
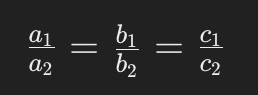
Congruent Triangles
Definition: Triangles are congruent if all corresponding sides and angles are equal.
Tests for Congruence:
SSS (Side-Side-Side): All three sides are equal.
SAS (Side-Angle-Side): Two sides and the included angle are equal.
ASA (Angle-Side-Angle): Two angles and the included side are equal.
AAS (Angle-Angle-Side): Two angles and a non-included side are equal.
HL (Hypotenuse-Leg): In right triangles, the hypotenuse and one leg are equal.
Key formulas:
