Evolution and Speciation
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is evolution
The cumulative change in heritable charactersitics of a popualtion
Explain the evidence for evolution by DNA or RNA base sequences. what does it show bascially
Comparing molecular seqeuences of DNA or RNA bases between 2 species shows how closely or distantly related the two species are.
the number of dfifferences can be used as a molecular clock to see when the two species diverged from a common ancestor.
How does selective breeding give evidence for evolutio
shows the accumulation of small changes inherited from generation to generation resulting in visible results
Whats a homologous structure and give an eg showcasing it
similar fundamental structures between species due to a common ancestor.
eg: pentadactyl limb with species having series of bones in 5 digits
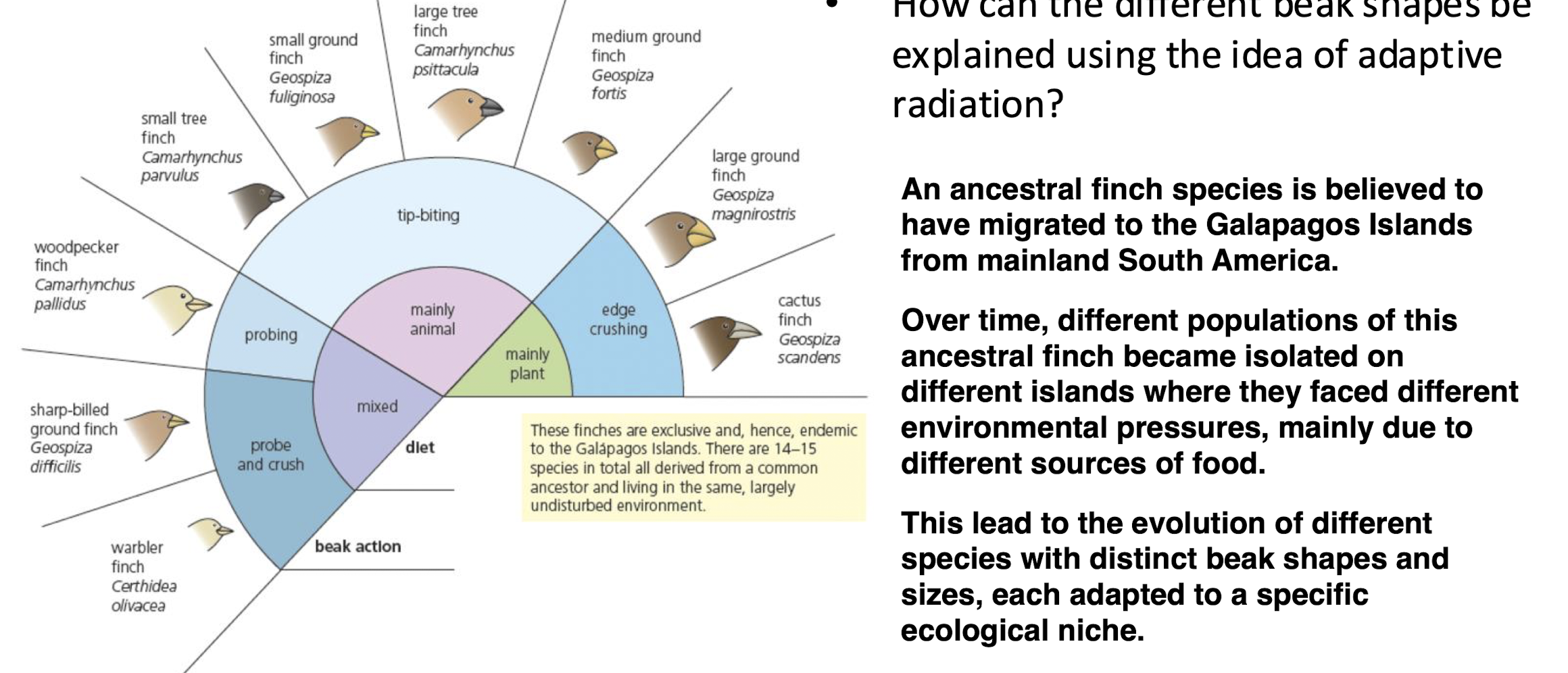
What is adaptive radiation? what kind of strucutre across species is produced as a result.
give an eg
evolutionary diversification of a species into new species with diverse morphological features in response to their environmental pressures.
homologous structure
What are analogous structures?
Structures in different species with same function but different form/shape as a result of convergent evolution.
Definition of species? What is needed for a new species to form i.e. speciation?
A group of organisms that can potentially interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
Reproductive isolation with genetic differences accumulating over time due to mutations, natural selection and genetic drift. When the differences prevent interbreeding, a new species is created.
What is geographic isolation? give an eg of speciation as a result of this and what the differences between species are.
barriers arise between populations restricting movement between them.
eg: chimpanzees and bonobos: river formed between them, separating them. this resulted in speciation of these two species with chimps being bigger, agressive and strong compared to bonobos.
What are the 3 types of reproductive isolation?
geographic: physical barrier
behavioral: different courtship patterns
temporal: different reproductive cycles
Whats allopatric and sympatric speciation?
Allopatric: geographic isolation physcially separating popualtions to cause speciation
Sympatric: divergence of a species within same location due to behavioral or temporal isolation.
what is pre-zygotic reproductive isolation? whats post-zygotic reproductive isolation?
mechanism that prevents fertilisation from occuring between species, thus stopping the formation of a zygote.
mechanism that occurs after fertilisation, leading to reduced function and viability of offspring. eg hybrids are infertile