Exam 5 Med Surg
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Which behavior would the nurse include when teaching a family what to expect from a client who experienced a stroke on the left side of the brain?
Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct
Impaired judgment
Spatial-perceptual deficits
Slow performance and caution
Impaired speech/language aphasias
Tendency to deny or minimize problems
Awareness of deficits with depression and anxiety
Slow performance and caution
Impaired speech/language aphasias
Awareness of deficits with depression and anxiety
Left-side strokes result in slow performance and cautious behaviors, impaired speech and language aphasias, and awareness of deficits with resultant depression and anxiety. Right-sided strokes cause impaired judgment, spatial-perceptual deficits, and a tendency to deny or minimize problems.
Which assessment is the nurse’s priority before beginning an infusion of tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) to a client in the emergency department?
Vital signs
Electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring
Signs of bleeding
Level of chest pain
Signs of bleeding
Assessment for bleeding is a priority because it is a contraindication for administration of thrombolytic agents; administration in the presence of bleeding can cause life-threatening hemorrhage. All the other options are important, but none pose a life-threatening contraindication to tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA)administration.
Which assessment finding indicates that a client has had a stroke?
Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct.
Lopsided smile
Unilateral vision
Incoherent speech
Unable to raise right arm
Symptoms started 2 hours ago
All are correct.
The signs of a stroke follow the acronym FAST. The F stands for facial drooping (a lopsided smile); A for arm weakness (inability to raise the right arm); and S for speech difficulties (incoherent speech) The T stands for time, as the signs and symptoms need to be evaluated as soon as possible. Tissue plasminogen activator (TPA)can be administered to reestablish blood flow if treatment is initiated within 4½ hours of stroke onset. Unilateral vision loss can also signify stroke.
Which aspect would the nurse assess to determine whether intracranial pressure is increasing around the medulla?
Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct.
Taste
Breathing
Heart rate
Fluid balance
Voluntary movement
Breathing
Heart rate
The medulla, part of the brainstem just above the foramen magnum, is concerned with vital functions such as breathing and heart rate. The parietal cerebral lobe is concerned with taste sensations. The medulla is not concerned with fluid balance. Osmoreceptors of the hypothalamus cause increased or decreased antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion, depending on serum osmolarity. Voluntary movements are mediated through the somatomotor area of the cerebral cortex.
Which client would be at an increased risk for coronary artery disease (CAD)?
Client with total cholesterol 175 mg/dL and LDL cholesterol 80 mg/dL
Client with total cholesterol 190 mg/dL andHDL cholesterol 40 mg/dL
Client with total cholesterol 200 mg/dL and HDL cholesterol 45 mg/dL
Client with total cholesterol 250 mg/dL and LDL cholesterol 120 mg/dL
Client with total cholesterol 250 mg/dL and LDL cholesterol 120 mg/dL
Major risk factors for CAD include elevated serum lipid levels. A total cholesterol greater than 200 mg/dL, LDL cholesterol greater than 130 mg/dL, and HDL cholesterol less than 40 mg/dL increase a client’s risk for CAD. Therefore, the client with a total cholesterol of 250mg/dL is at an increased risk for CAD. Laboratory values of total cholesterol 175 mg/dL and LDL cholesterol 80mg/dL; total cholesterol 190 mg/dL and HDL cholesterol 40 mg/dL; and total cholesterol 200 mg/dL and HDL cholesterol 45 mg/dL are all within normal limits and do not indicate that the client is at increased risk for CAD.
Which topic is most important for the nurse to include when teaching about prevention of coronary artery disease (CAD) for a 50-year-old man who is 6 feet (183 cm) tall and weighs 293pounds (133 kg), smokes 1 pack a day of cigarettes, and has siblings with CAD?
Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct.
Age
Height
Weight
Tobacco use
Family history
Weight
Tobacco use
The focus of teaching about CAD prevention would be on modifiable risk factors such as weight and tobacco use. Although the incidence of CAD does increase with age, age is not a modifiable risk factor. Height affects body mass index but is not a modifiable risk factor for CAD. Family history of CAD does increase CAD risk but is not a modifiable risk factor.
Which assessment would the nurse exclude when dealing with a client who has receptive and expressive aphasia?
Ask the client to read simple sentences aloud.
Point to a familiar object and ask the client to name it.
Test the mental status by asking for feedback from the client.
Ask the client to respond to simple verbal commands such as "stand up."
Test the mental status by asking for feedback from the client.
Receptive and expressive aphasia are the two types of aphasia. A client with receptive aphasia is unable to understand written or verbal speech. A client with expressive aphasia understands written and verbal speech but cannot write or speak appropriately. A client with aphasia may not have the mental ability to give feedback; asking for feedback is ineffective. Asking the client to read simple sentences aloud is an effective way of dealing with this client. Pointing to a familiar object and asking the client to name it is also effective. A client with aphasia can understand simple verbal commands.
Which measure would the nurse take when administering enoxaparin subcutaneously?
Push over 2 minutes.
Administer in the abdomen.
Massage site after administration.
Remove air pocket from prepackaged syringe before administration.
Administer in the abdomen.
Enoxaparin specifically targets blood clots throughout the body and carries a lower risk of hemorrhage than that associated with the medications heparin and warfarin. Enoxaparin is administered once a day through a subcutaneous injection site around the naval. Enoxaparin should be injected into the fatty tissue only, which is why the abdomen is the recommended injection site. Avoid administering in a muscle. There are no recommendations to push this subcutaneous medication over 2 minutes. Rubbing the site is contraindicated, because it can cause bruising. Manufacturer recommendations indicate the air pocket from prepackaged syringes not be removed before administration.
Which agent will be used if an antidote is needed for a client taking warfarin?
Vitamin K
Fibrinogen
Prothrombin
Protamine sulfate
Vitamin K
Warfarin sodium inhibits vitamin K; therefore vitamin K is the antidote for warfarin sodium. Fibrinogen and prothrombin are blood-clotting factors, not the antidotes for warfarin sodium. Protamine sulfate is the antidote for heparin, not warfarin sodium.
Which rationale would the nurse include to address the client’s concern about why both warfarin and intravenous (IV) heparin are needed at the same time for a partial occlusion of the left common carotid artery?
This permits the administration of smaller doses of each medication.
Giving both medications allows clot dissolution while preventing new clot formation.
Heparin provides anticoagulant effects until warfarin reaches therapeutic levels.
Administration of heparin with warfarin provides immediate and maximum protection against clot formation.
Heparin provides anticoagulant effects until warfarin reaches therapeutic levels.
Warfarin is administered orally for 2 to 3 days to achieve the desired effect on the international normalized ratio(INR) level before heparin is discontinued. Because each medication affects a different part of the coagulation mechanism, dosages must be adjusted separately. These medications do not dissolve clots already present. That this approach immediately provides maximum protection against clot formation is not the reason for the administration of both medications; warfarin will not exert an immediate therapeutic effect.
Which laboratory value would the nurse use to determine whether a client is receiving a therapeutic dose of intravenous heparin?
International normalized ratio (INR) is between2 and 3
Prothrombin time (PT) is 2.5 times the control value
Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) is 70 seconds
Activated clotting time (ACT) is in the range of70 to 120 seconds
Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) is70 seconds
When a client is receiving intravenous heparin, the APTT should be 1.5 to 2 times the normal APTT of 40 seconds, or 60 to 80 seconds. INR and PT are used to evaluate therapeutic levels of warfarin. The ACT is not commonly used for monitoring of heparin, but ACT increases to a range of 150 to 200 seconds when heparin reaches therapeutic levels.
Which drug action will the nurse include when describing the purpose of heparin in a client who develops thrombophlebitis in the right calf and is prescribed bed rest and initiated on an intravenous (IV) infusion of heparin?
It prevents extension of the clot.
It reduces the size of the thrombus.
It dissolves the blood clot in the vein.
It facilitates absorption of red blood cells.
It prevents extension of the clot.
Heparin interferes with activation of prothrombin to thrombin and inhibits aggregation of platelets. Heparin does not reduce the size of a thrombus. Heparin does not dissolve blood clots in the veins. Heparin does not facilitate the absorption of red blood cells.
The nurse is planning care for an immobilized client who had a stroke with right-sided hemiparesis. Which activity would the nurse include in the plan of care?
Assess the client’s lung sounds daily.
Assist the client to perform range-of-motion(ROM) exercises every 1 to 2 hours.
Allow the client to sit upright in the chair for aslong as tolerated.
Have the unlicensed nursing personnelreposition the client every 4 hours.
Assist the client to perform range-of-motion(ROM) exercises every 1 to 2 hours.
Range-of-motion exercises should be performed often to prevent muscle atrophy and contractures. Assessing the client’s lung sounds every 8 hours is the minimum the nurse would assess lung sounds and it is important, but it is not a priority in planning care for immobilization. The client should not be allowed to sit in a chair for prolonged periods of time because of skin breakdown and venous return. The nursing assistant should be instructed to turn the client at least every 2hours.
Which behavior by a client who had a cerebrovascular accident (CVA) beginning to eat lunch indicates the client may be experiencing left hemianopsia?
The client asks to have food moved to the left side of the tray.
The client drops the coffee cup when trying to use the right hand.
The client ignores the food on the left side of the tray when eating.
The client reports not being able to use the right arm to help eat meals.
The client ignores the food on the left side of the tray when eating.
Clients with hemianopsia affecting the left fi eld of vision cannot see whatever is in the left fi eld of vision. Asking to have food moved to the left side of the tray may occur if the client has right hemianopsia and wishes to see better when eating. Dropping the coffee cup when trying to use the right hand may occur with right hemiparesis, not with hemianopsia. Reporting about not being able to use the right arm to help eat indicates hemiplegia, not hemianopsia.
Which information would the nurse include in the discharge teaching plan for a client who sustained a cerebrovascular accident (CVA) with residual hemiparesis and hemianopsia?
Necessity for bed rest at home
Use of oxygen (O 2) therapy at home
Significance of a safe environment
Need for decreased protein in the diet
Significance of a safe environment
Safety becomes a priority when the client has hemiparesis (paralysis on one side) and hemianopsia(abnormal visual fi eld). Although a balance between activity and rest is important, the client does not have to maintain bed rest. O2 generally is not necessary. All the basic nutrients should be included in the diet; there is no reason to reduce protein intake.
Which factor is the primary cause of aphasia and hemiparesis for a client who has had a subarachnoid hemorrhage?
Blood loss
Tissue death
Vascular spasms
Electrolyte imbalance
Vascular spasms
In an attempt to stop the bleeding, adjacent arteries constrict (vasospasm); this in turn contributes to the ischemia responsible for the neurological deficits. The volume of blood loss is not great enough to significantly alter the oxygen-carrying capability of the remaining blood supply. Although prolonged ischemia may cause necrosis, many of the manifestations of cerebral ischemia are reversed as pressure diminishes, and there may be no permanent damage. Severe electrolyte imbalance may cause generalized weakness; however, hemiparesis and aphasia are not the result of electrolyte loss.
Which information would the nurse include when explaining the cause of transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) to a client?
Genetic valvular heart disease
Atherosclerotic plaques within arteries
Developmental defects in arterial walls
Emboli ascending from the lower extremities
Atherosclerotic plaques within arteries
Atherosclerotic plaques within arteries progressively narrow the lumens of the carotid arteries, causing TIAs. Valvular defects usually cause cerebral emboli that result in a brain attack. Brain aneurysms are developmental defects that may rupture, resulting in a brain attack. Emboli arising from the lower extremities usually result in occlusions in the pulmonary vascular system, causing a pulmonary embolus.
Which therapeutic effect would the nurse expect to identify when mannitol is administered to a client?
Improved renal blood flow
Decreased intracranial pressure
Maintenance of circulatory volume
Prevention of the development of thrombi
Decreased intracranial pressure
As an osmotic diuretic, mannitol helps reduce cerebral edema. Although there may be a transient increase in blood volume as a result of an increased osmotic pressure, which increases renal perfusion, this is not the therapeutic effect. Prevention of the development of thrombi is not the reason for giving this medication.
Which clinical finding is consistent with an increase in intracranial pressure?
Thready, weak pulse
Narrowing pulse pressure
Regular, shallow breathing
Lowered level of consciousness
Lowered level of consciousness
Altered consciousness is the first sign of increased intracranial pressure. An increase in intracranial pressure causes impaired cerebral blood flow affecting the cells of the cerebral cortex, which results in a decreased level of consciousness. As the intracranial pressure increases, it places pressure on the thalamus, hypothalamus, pons, and medulla, resulting in a slow pulse. A widening pulse pressure occurs because of an increase in the systolic pressure. As the intracranial pressure increases, it places pressure on the thalamus, hypothalamus, pons, and medulla, resulting in irregular respirations that progress to deep, rapid breathing alternating with periods of apnea (Cheyne–Stokes respirations).
In which position would a nurse maintain a client who has experienced a sub arachnoid hemorrhage?
Supine
On the unaffected side
In bed with the head of the bed elevated
With sandbags on either side of the head
In bed with the head of the bed elevated
With the head of the bed elevated, the force of gravity helps prevent additional intracranial pressure (ICP),which will intensify the ischemic manifestations of hemorrhage. The supine position will not facilitate drainage of cerebral fluid; this position promotes accumulation of fluid, which increases ICP. Lying on the unaffected side will not facilitate drainage of cerebral fluid; this position promotes accumulation of fluid, which increases ICP. Vomiting can occur with increased ICP, and placing sandbags to immobilize the head can result in aspiration.
Which action would the nurse take for a clientwho underwent cerebral angiography?
Selectall that apply. One, some, or all responsesmay be correct.
Wipe off the gel applied before the test
Maintain pressure dressing for 2 hours
Remove the electrodes gently and thoroughly
Obtain vital signs and complete neurological checks
Check dressing for bleeding and swelling around the site
Maintain pressure dressing for 2 hours
Obtain vital signs and complete neurological checks
Check dressing for bleeding and swelling around the site
After cerebral angiography, the nurse would maintain a pressure dressing to the site for 2 hours and check the dressing for bleeding and swelling around the site. Vital signs and complete neurological signs are obtained after a client undergoes a cerebral angiogram. The gel is applied before sonography or an electroencephalogram(EEG). Electrodes are used in an EEG.
Which possible cause would the nurse suspect in a client with a head injury who has a fixed, dilated right pupil, responds only to painful stimuli, and exhibits flexion (decorticate)posturing?
Meningeal irritation
Subdural hemorrhage
Cerebral compression
Medullary compression
Cerebral compression
Cerebral compression affects pyramidal tracts, resulting in flexion (decorticate) rigidity and cranial nerve injury, which cause pupil dilation. Meningeal irritation will not produce postural or pupillary changes without cerebral compression. Collection of blood between the dura and arachnoid will not cause postural or pupillary changes without cerebral compression. Medullary compression results in alterations in vital signs.
A client has a brain attack (stroke) that involves the right cerebral cortex and cranial nerves. Which area of paralysis would the nurse expect to find upon assessment?
Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct.
Left leg
Left arm
Right leg
Right arm
Left side of face
Left leg
Left arm
Left side of face
Because nerves decussate (cross over), paralysis occurs on the side of the body opposite to the area of cerebral involvement. In this situation, the left leg and left arm would be affected. The face is innervated by the seventh cranial nerve, which comes in pairs (right and left) that do not decussate; therefore because injury is to the right cerebral cortex, the left seventh cranial nerve is damaged. This leads to paralysis of the left side of the face. The right leg and right arm will not be affected because the insult is to the right cerebral cortex, and nerve fibers decussate before reaching the periphery.
Which intervention is a priority when caring for a child who sustained a head injury 12hours earlier?
Assessing the level of consciousness every hour
Promoting rest by fostering a quiet environment
Asking about the circumstances that led to the injury
Administering the prescribed opioid for complaints of a headache
Assessing the level of consciousness every hour
Evidence of a subdural hemorrhage may take hours or days to develop; a diminishing level of consciousness is an early indication of neurological damage. Although the promotion of rest is important, early recognition of neurological damage is the priority. Taking a history at this time is not appropriate, nor is it a priority. Administering an opioid is contraindicated because it may mask the signs and symptoms of worsening neurological injury.
In which position should the nurse place a child who has undergone supratentorial craniotomy for evacuation of a subdural hematoma during the first 24 hours after surgery?
At a 45-degree angle
At a 90-degree angle
In the supine position
In the side-lying position
At a 45-degree angle
A potential problem after supratentorial surgery is increasing intracranial pressure; elevating the head of the bed facilitates cerebral drainage by way of gravity. Sitting upright is uncomfortable after surgery. Keeping the child flat in bed, either supine or side-lying, inhibits cerebral drainage and contributes to increasing intracranial pressure.
Which complication is a priority for the nurse to prevent for a client who has just returned to the nursing unit after coronary artery stenttng via access through the femoral artery?
Infection
Urinary retention
Hematoma formation
Orthostatic hypotension
Hematoma formation
Because blood in the femoral artery is at high pressure and the catheter used for stenting is large, there is ahigh risk for hemorrhage and hematoma formation at the site of the catheter insertion. Frequent monitoring of the insertion site and vital sign checks are used to detect bleeding rapidly so that a hematoma does not occur. Infection is possible after insertion of the catheter through the femoral artery but is not a common problem. Urinary retention and discomfort can occur because of the diuretic effect of the contrast dye used during cardiac catheterization and difficulty with voiding when clients are on bed rest post procedure, but it is nota life-threatening complication. Orthostatic hypotension can occur because of the effect of several hours of bedrest and the diuretic effect of the contrast dye used during cardiac catheterization, but it is not as life-threatening as hemorrhage and hematoma formation.
A client with a head injury has a computed tomography (CT) scan that shows a subdural hematoma. How would the nurse interpret this finding?
Blood within the brain tissue
Blood in the subarachnoid space
Blood between the dura and the skull
Blood between the dura mater and the arachnoid layer
Blood between the dura mater and the arachnoid layer
A subdural hematoma refers to blood between the dura mater and the arachnoid layer of the meninges. Blood within the brain tissue is an intracerebral hematoma. Blood in the subarachnoid space is below the arachnoid and is called a subarachnoid hematoma. Epidural hematoma refers to blood between the dura and the skull.
Which instructions about the use of nitroglycerin to prevent angina will the nurse provide to a client?
"At the point when pain first occurs, place two tablets under the tongue."
"Place one tablet under the tongue before activity, and swallow another if pain occurs."
"Before physical activity, place one tablet under the tongue, and repeat the dose in 5 minutes if pain occurs."
"Place one tablet under the tongue when pain occurs and use an additional tablet after the attack to prevent recurrence."
"Before physical activity, place one tablet under the tongue, and repeat the dose in 5 minutes if pain occurs."
Anginal pain, which can be anticipated during certain activities, may be prevented by dilating the coronary arteries immediately before engaging in the activity. Generally, one tablet is administered at a time; doubling the dosage may produce severe hypotension and headache. The sublingual form of nitroglycerin is absorbed directly through the mucous membranes and should not be swallowed. When the pain is relieved, rest generally will prevent its recurrence by reducing oxygen consumption of the myocardium.
Which priority nursing action would the nurse implement first when caring for a client receiving nitroglycerin for the treatment of angina?
Instruct the client to sit or stand slowly
Monitor the client’s urine output frequently
Advise the client to report when experiencing a headache
Instruct client to notify the health care provider if pain does not subside after 5 minutes
Instruct the client to sit or stand slowly
Nitroglycerin is a potent antihypertensive and antianginal medication. The nurse should instruct the client to sit and stand slowly after taking the medication to prevent orthostatic hypotension. After ensuring the client’s safety, the nurse should monitor the urine output. A headache is a common side effect of nitroglycerin. The client should have a tingling sensation after taking the nitroglycerin, which ensures that the medication is potent. Contacting the health care provider may be important if the pain does not subside after five minutes, but the client's immediate safety takes precedence.
A client is admitted to the intensive care unit with pulmonary edema. Which clinical finding would the nurse expect when performing the admission assessment?
Weak, rapid pulse
Decreased blood pressure
Radiating anterior chest pain
Crackles at bases of the lungs
Crackles at bases of the lungs
Crackles are the sound of air passing through fluid in the alveolar spaces; in pulmonary edema, fluid moves from the intravascular compartment into the alveoli. Hypervolemia leads to pulmonary edema. The pulse is bounding with hypervolemia. The blood pressure usually is increased with hypervolemia. Radiating anterior chest pain occurs with angina or a myocardial infarction.
Which description would the nurse expect the client to use to characterize the pain when admitted to the coronary care unit with a diagnosis of ST segment elevation myocardial infarction?
Severe, intense chest pain
Burning sensation of short duration
Sharp, stabbing chest pain with breathing
Squeezing chest pain, relieved by nitroglycerin
Severe, intense chest pain
Classic pain with myocardial infarction is described as intense and severe. It is continuous because it is caused by ongoing myocardial ischemia and injury. Burning pain is more consistent with gastric reflux of acid. Pain with myocardial infarction is not usually stabbing pain associated with breathing, which would be more typical of pericarditis or pleurisy. Pain that is relieved by nitroglycerin indicates angina rather than myocardial infarction.
Which assessment finding will the nurse expect when caring for a client with right ventricular failure?
Crackles throughout both lungs
Substernal chest pressure
Redness and swelling of a calf
Bilateral lower leg edema
Bilateral lower leg edema
Right ventricular heart failure causes increased pressure in the systemic venous system, which leads to a fluid shift into the interstitial spaces. Because of gravity, edema is seen initially in the lower extremities. Lung crackles are heard in left ventricular failure because of increased pressure in the pulmonary capillaries and movement of fluid into the alveoli. Substernal chest pressure is typical of angina or acute coronary syndrome. Unilateral redness and swelling are seen with venous thrombosis.
Which explanation would the nurse give about the purpose of the procedure when a client with angina is scheduled to have a cardiac catheterization?
To obtain the pressures in the heart chambers
To determine the existence of congenital heart disease
To visualize the disease process in the coronary arteries
To measure the oxygen content of various heart chambers
To visualize the disease process in the coronary arteries
Angina usually is caused by narrowing of the coronary arteries; the lumen of the arteries can be assessed by cardiac catheterization. Although pressures can be obtained, they are not the priority for this client; this assessment is appropriate for those with valvular disease. Determining the existence of congenital heart disease is appropriate for infants and young adults with cardiac birth defects. Measuring the oxygen content of various heart chambers is appropriate for infants and young children with suspected septal defects.
Which pain characteristic would the nurse expect to observe when a client is experiencing anginal pain?
Unchanged by rest
Precipitated by light activity
Described as a knifelike sharpness
Relieved by sublingual nitroglycerin
Relieved by sublingual nitroglycerin
Relief by sublingual nitroglycerin is a classic reaction because it causes vasodilation of peripheral veins and arteries, thereby decreasing oxygen demand by decreasing preload. To a lesser extent, sublingual nitroglycerin dilates coronary arteries, which increases oxygen to the myocardium, thereby decreasing pain. Immediate rest frequently relieves anginal pain. Angina usually is precipitated by exertion, emotion, or a heavy meal. Angina usually is described as tightness, indigestion, or heaviness.
Which finding about a client’s angina is most important for the nurse to communicate to the health care provider?
Causes mild perspiration
Occurs after moderate exercise
Continues after rest and nitroglycerin
Precipitates discomfort in the arms and jaw
Continues after rest and nitroglycerin
When neither rest nor nitroglycerin relieves the pain, the client may be experiencing acute coronary syndrome and need rapid diagnostic testing and actions to treat coronary occlusion. Mild perspiration may occur with angina, but it should resolve with nitroglycerin or rest. Angina that occurs after exercise is probably stable angina and may indicate a need to adjust antianginal medications, but it does not require immediate communication with the health care provider. Some clients may have angina that radiates to the arms and jaw. This will be reported to the health care provider, but it does not require any immediate change in the plan of care.
Which finding in a client with a diagnosis of stable angina is most important for the nurse to communicate to the health care provider?
Anginal symptoms are relieved by rest.
Discomfort is described as chest pressure.
Radiation of pain to the left arm and back occurs.
Angina episodes are occurring more frequently.
Angina episodes are occurring more frequently.
Increasing frequency of anginal episodes may indicate unstable angina and acute coronary syndrome, which requires urgent treatment because it is caused by prolonged myocardial ischemia. Because rest typically relieves stable angina, this finding does not need to be immediately communicated to the health care provider. Clients frequently describe angina as a feeling of chest pressure; this information does not indicate a need for rapid treatment. Radiation of pain to the arm or back frequently occurs with angina; this finding would not indicate a need for any change in the client’s treatment.
Which statement by the women indicates that the teaching has been effective after the nurse teaches a group of women about coronary artery disease (CAD) and myocardial infarction(MI)?
Unusual fatigue is a common symptom of CAD in women.
Women usually have a more rapid recovery than men after MI.
Cardiac surgery is generally more successful in women than men.
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels increase after menopause.
Unusual fatigue is a common symptom of CAD in women.
Studies indicate that women who have myocardial infarctions often experience unusual prodromal fatigue; also, during the prodromal period, women more commonly experience upper abdominal fullness instigated by exertion or emotional stress. Women report more disability than men after a cardiac event. Women have higher mortality and more complications than men after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Low-density lipoprotein levels increase after menopause, increasing CAD risk.
Which clinical condition is the result of changes in the integrity of arterial walls and small blood vessels?
Contusion
Thrombosis
Atherosclerosis
Tourniquet effect
Atherosclerosis
In atherosclerosis, there may be changes in the integrity of the walls of the arteries and smaller blood vessels. Direct manipulation of vessels or localized edema that impairs blood flow will lead to a contusion. Blood clotting that causes mechanical obstruction to blood flow indicates thrombosis. The tourniquet effect may be caused by the application of constricting devices, which may lead to impaired blood flow to areas below the site of constriction.
Which client in the emergency department would the nurse assess first?
Client with chest pressure and ST segment elevation on the electrocardiogram
Client who reports a sharp chest pain with deep inspiration for the past week
Client who has history of heart failure with ascites and bilateral 4+ ankle swelling
Client with palpitations and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation at a rate of 136 beats/minute
Client with chest pressure and ST segment elevation on the electrocardiogram
The client with chest pressure and ST segment elevation on the electrocardiogram will need emergency treatment for ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), including transport to the cardiac catheterization laboratory for percutaneous coronary intervention within 90 minutes, and should be seen first. The client with sharp pain with deep inspiration has symptoms consistent with pericarditis or pleural effusion and does need rapid assessment and treatment, but is not at risk for life-threatening complications. The client with heart failure and ascites and ankle swelling has symptoms of right ventricular failure that are not life-threatening. The client with palpitations and rapid atrial fibrillation will need assessment and evaluation, but the client experiencing myocardial infarction has amore life-threatening diagnosis.
Which information is most important to include when the nurse is teaching a client who has had an ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) about the purpose of salt restriction?
Low salt intake helps prevent ankle swelling.
Salt intake increases the work of the heart.
Decreasing salt intake will lower blood pressure.
Salt intake prevents diuretics from being effective.
Salt intake increases the work of the heart.
After STEMI, changes in cardiac contractility may lead to chronic heart failure; some of these changes can be prevented by decreasing cardiac work through lowering fluid retention. Although a high salt intake may lead to ankle edema, this is not the most important point to emphasize with this client. A decrease in salt intake will help lower blood pressure, but decreasing blood pressure is not the most important reason for salt restriction in this client. Many diuretics do work by increasing sodium excretion, but improving the effectiveness of diuretics is not the most relevant reason for low salt diet in this client.
Which finding in a client seen in the emergency department with chest pain is most
important to communicate to the health care provider?
Severe nausea and vomiting
Substernal pain level 9 (0 to 10 scale)
Blood glucose 230 mg/dL (12.78 mmol/L)
ST segment elevation on electrocardiogram
ST segment elevation on electrocardiogram
The client’s electrocardiogram indicates acute ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), which will require rapid treatment with thrombolytic medications or percutaneous intervention to achieve reperfusion. The nausea and vomiting may be caused by the STEMI or by the autonomic nervous system response to stress and should be treated as quickly as possible for client comfort; the highest priority is treatment of the coronary occlusion. Substernal pain should be treated with morphine sulfate, but a higher priority is action to treat the coronary occlusion. The blood glucose is elevated and the client may require treatment for diabetes, but this can be done after coronary reperfusion is achieved.
Which diagnostic test is most important for the nurse to obtain rapidly when caring for a client who has just arrived in the emergency department with possible acute coronary syndrome (ACS)?
Chest radiograph
Troponin T (cTnT)
Creatine kinase MB (CK-MB)
12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG)
12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG)
With acute coronary syndrome, ECG changes indicating myocardial injury and infarction occur within minutes. Because treatment for ACS usually involves actions to restore blood flow to the myocardium as rapidly as possible, it is essential that the ECG be done and evaluated immediately. The other tests are also appropriate but will be done after the ECG. Changes in the chest radiograph will occur if there is cardiac enlargement, pericardial effusion, or heart failure secondary to myocardial infarction. Troponin T will increase in an average of 4 to 6 hours with myocardial infarction. CK-MB starts to increase at about 6 hours after myocardial infarction.
Which laboratory value will be important for the nurse to monitor to determine whether a client with chest pain has acute coronary syndrome (ACS)?
Troponin T (cTnT)
C-reactive protein (CRP)
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
B-type natriuretic protein (BNP)
Troponin T (cTnT)
Cardiac troponins are released into circulation within hours after myocardial injury or infarction, and elevation in troponin levels helps determine that the client is experiencing ACS. The other three values will also be monitored but are not markers for ACS or acute myocardial infarction. C-reactive protein is a marker for inflammation and elevated levels can predict cardiac disease. Elevated LDL is a risk factor for atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease. Elevated BNP is diagnostic for heart failure.
Which component of the electrocardiogram would the nurse analyze to determine whether a client is experiencing acute coronary syndrome (ACS)?
P wave
PR interval
QRS complex
ST segment
ST segment
Elevation or depression of the ST segment is indicative of ACS because of changes in cardiac electrical activity that occur with ischemia and injury. P wave changes are not used to diagnose ACS. Changes in the PR interval are not diagnostic of ACS. Changes in the QRS complex do not occur with ACS.
Which finding in a client who had coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery 1 day previously is most important for the nurse to communicate to the health care provider?
Temperature of 102°F (38.9°C)
7/10 incisional pain (0 to 10 scale)
Sinus rhythm with PR interval of 0.22 seconds
120 mL of blood in the chest tube collection chamber
Temperature of 102°F (38.9°C)
Although mild temperature elevations are common after surgery due to the inflammatory response, a high temperature may indicate wound infection and a need for actions such as blood cultures and antibiotic administration. Incisional pain is common after cardiac surgery and would be addressed by the nurse with prescribed postoperative analgesics and actions such as repositioning the client. The client’s PR interval is mildly prolonged, but first-degree AV block does not affect cardiac output. A small amount of blood in the drainage device is common after cardiac or vascular surgery.
Which explanation would the nurse give to the spouse of a client who had coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery when asked why there is a dressing on the client's left leg?
"This is the access site for the heart-lung machine."
"A filter is inserted in the leg to prevent embolization."
"A vein in the leg was used to bypass the coronary artery."
"The arteries in the extremities are examined during surgery."
"A vein in the leg was used to bypass the coronary artery."
The response that a vein in the leg was used to bypass the coronary artery provides information and reduces anxiety. The nurse understands that the greater saphenous vein of the leg is used to bypass the diseased coronary artery. Cardiopulmonary bypass (extra corporeal circulation) is accomplished by placement of a cannula in the right atrium, vena cava, or femoral vein to withdraw blood from the body; blood is returned to the body via a cannula in the aorta or the femoral artery. A filter is not inserted in the leg to prevent embolization during a coronary artery bypass graft (CABG). The arteries in the extremities are not examined during a CABG.
Which finding in a client who has just arrived in the cardiac intensive care unit after having coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)requires the most rapid action by the nurse?
The serum potassium level is 3.1 mEq/L (3.1mmol/L).
The client is confused about the date and timeof day.
The client reports incisional pain at level 8 (0 to10 scale).
Chest tube collection chamber has 150 mL of bloody fluid.
The serum potassium level is 3.1 mEq/L (3.1mmol/L).
Hypokalemia is a common complication after CABG and immediate infusion of potassium to correct hypokalemia is needed to prevent postoperative dysrhythmias. Confusion in the immediate postoperative period is common after cardiopulmonary bypass and will be monitored by the nurse, but does not require any other action at this time. Incisional pain is common after CABG and the nurse will administer prescribed pain medications, but pain is not a life-threatening complication. Chest tube drainage of 100 to 200 mL is not unusual in the first hours after CABG; the nurse will monitor the chest tube drainage hourly, but no other action is needed.
When admitting a client with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) to the telemetry unit after cardiac catheterization and percutaneous intervention (PCI), which action would the nurse take first?
Attach the cardiac monitor.
Auscultate the heart sounds
Check the intravenous fluid rate.
Assess alertness and orientation.
Attach the cardiac monitor.
Because fatal dysrhythmias may occur in the first hours after myocardial infarction, cardiac monitoring is apriority. The nurse will also do auscultation of the heart, but changes in heart sounds are not expected with ACS and PCI. Checking the intravenous line for patency and correct infusion rate is also important, but would be done after establishing cardiac monitoring. Neurological status would be assessed, but changes in neurological status are not expected after PCI, which does not require general anesthesia.
Which finding would the nurse expect when caring for a client with right-sided heart failure?
Oliguria
Pallor
Cool extremities
Distended neck veins
Distended neck veins
Veins are distended because of the systemic venous pressure and congestion that are associated with right-sided heart failure. Oliguria is caused by decreased renal perfusion associated with left ventricular failure. Pallor is caused by decreased systemic perfusion secondary to left ventricular failure. Cool extremities area symptom of decreased systemic perfusion associated with left ventricular failure.
Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis
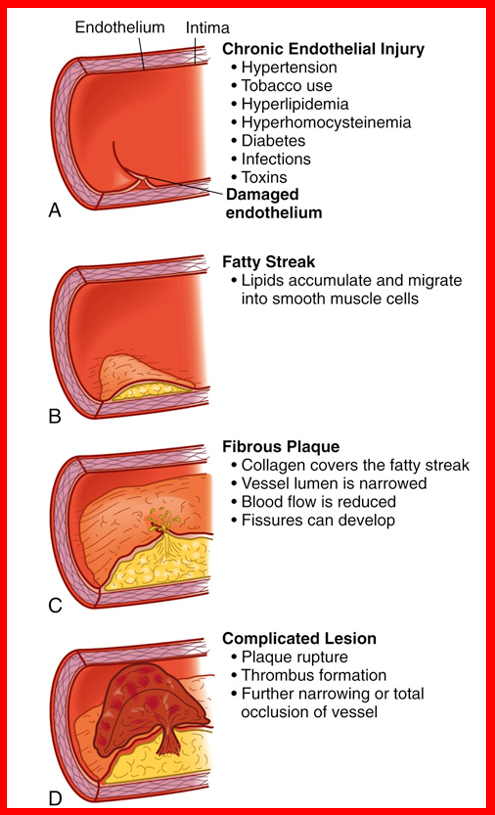
Earliest lesion; lipid filled smooth muscle cells, appears yellow
Fatty streak
Fatty Deposits that form in coronary arteries leading to CAD
Atheromas
High cholesterol
over 200 mg/dL
Stage 1 hypertension
130-139/80-89 mm Hg
Stage 2 hypertension
over 140/90 mm Hg
Modifiable risk factors for CAD
Hypertension
Tobacco use
Diabetes
Obesity
Cocaine and methamphetamine use
Total coronary occlusion: cellular response to O2 and glucose depravation
heart muscle hypoxic within 10 seconds
anaerobic metabolism, increased lactic acid
heart cells viable 20 mins; damage irreversible if no collateral circulation
if re-perfused, aerobic metabolism and contractility restored and cells impaired
Test to diagnose myocardial infarction. Differentiate between cardiac and non-cardiac causes of chest pain. Monitor the course of a heart attack. Normal is less than 4-6% normal concentration
CK-MB (Creatine Kinase-MB)
Chest pain from chronic stable angina, unstable Angina, or an MI - Acute Care

•Long sentences, made up words
•Have difficulty understanding speech
•Unaware of their spoken mistakes
Fluent – Wernicke’s – damage to either temporal lobe (left)
•Slow, short sentences (makes sense)
•Understands speech
•Aware of deficits, frustrated
Nonfluent – Broca’s – frontal lobe damage
Many patients worsen in the first 24-48 hours with _____stroke
Ischemic
How many hours of onset of clinical signs of ischemic stroke?
3 to 4 ½